Clustering wireless sensor network malicious program propagation model based on evolution game
A wireless sensor and malicious program technology, applied in network topology, wireless communication, data exchange network, etc., can solve the problems of lack of reflection of time and space characteristics, no consideration of node differences, and inability to predict the distribution of malware propagation time, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0103] The present invention will be further described in detail below through the specific examples, the following examples are only descriptive, not restrictive, and cannot limit the protection scope of the present invention with this.
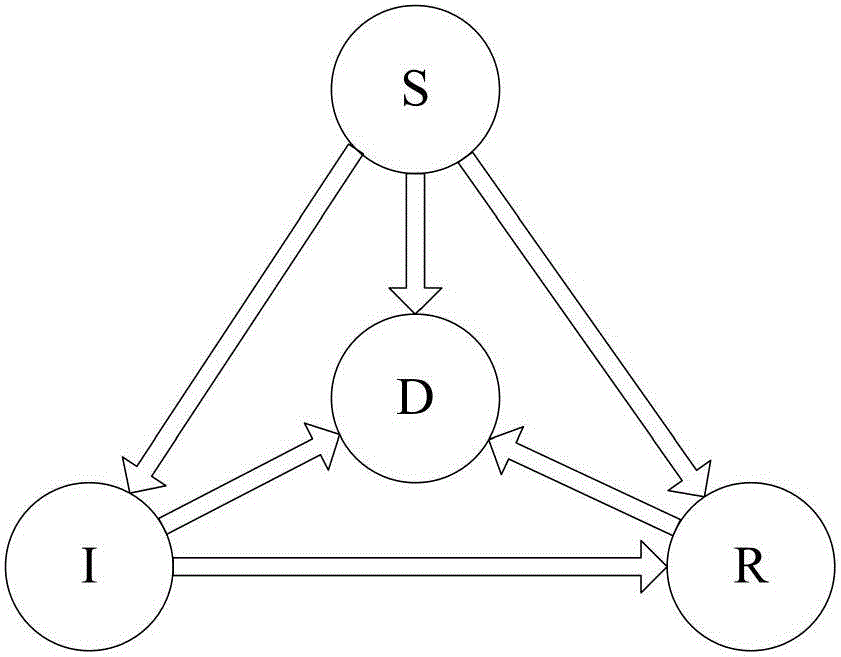
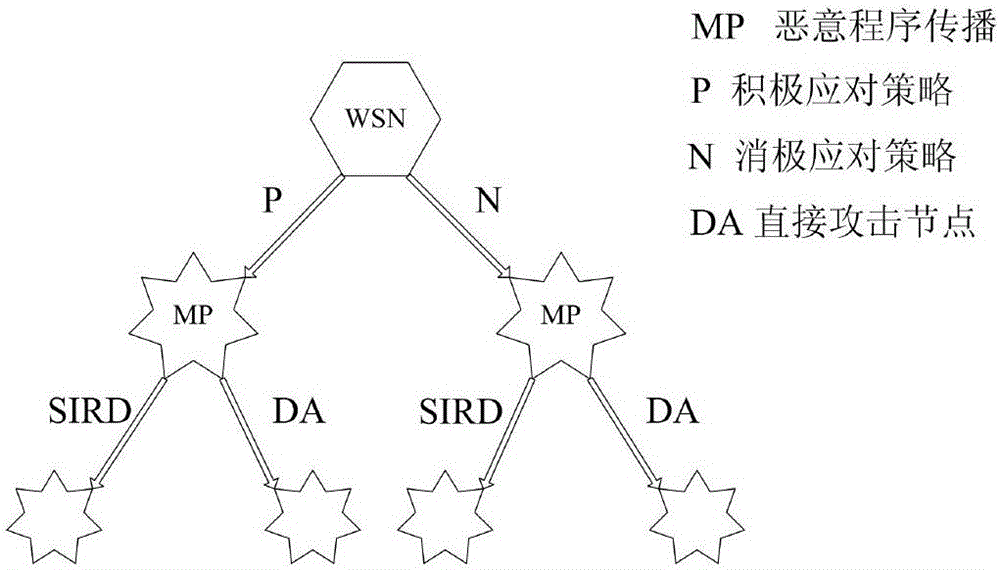
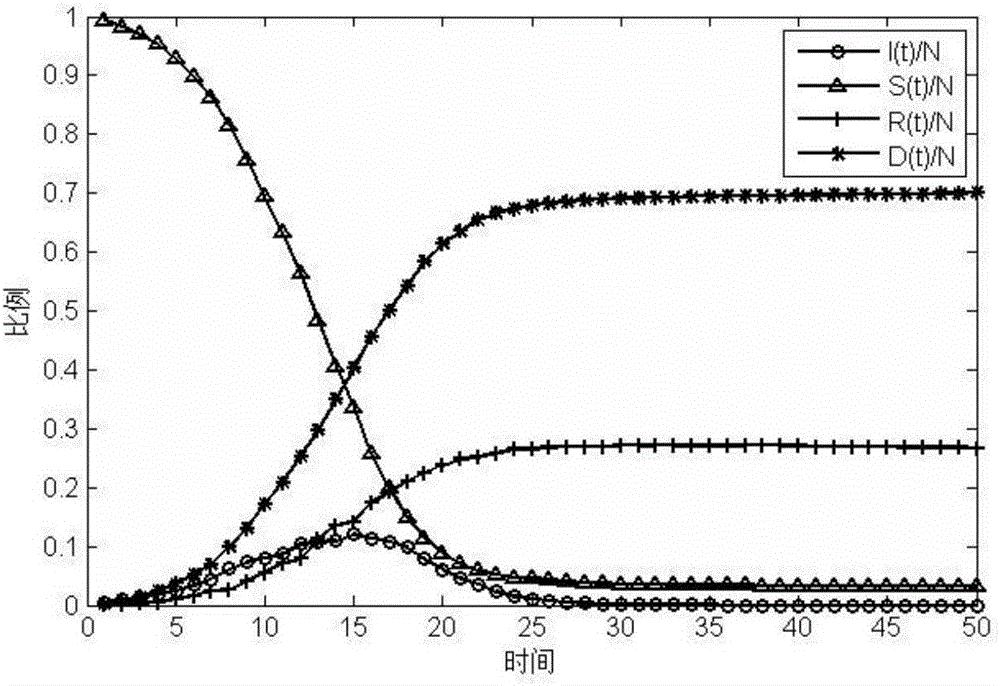
[0104] A clustered wireless sensor network malicious program propagation model based on evolutionary game, including three system models: a clustered wireless sensor network model, an improved two-dimensional cellular automaton malicious program propagation model, and a multi-person evolutionary game model. Clustered Wireless Sensor Network Model
[0105] The clustered wireless sensor network model contains n static sensor nodes, which are randomly and evenly distributed in the two-dimensional area with node density σ, and the maximum transmission distance of each sensor node is r. There are three types of nodes in this model: base station, cluster head node and terminal sensor node. The terminal sensor node is responsible for sensing and c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com