Novel high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel for non-magnetic drill collar and manufacturing method of novel high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel
A high-nitrogen austenite and non-magnetic drill collar technology, applied in the field of stainless steel materials, can solve the problems of deterioration of plasticity and toughness of stainless steel, and achieve excellent performance and excellent resistance to intergranular corrosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
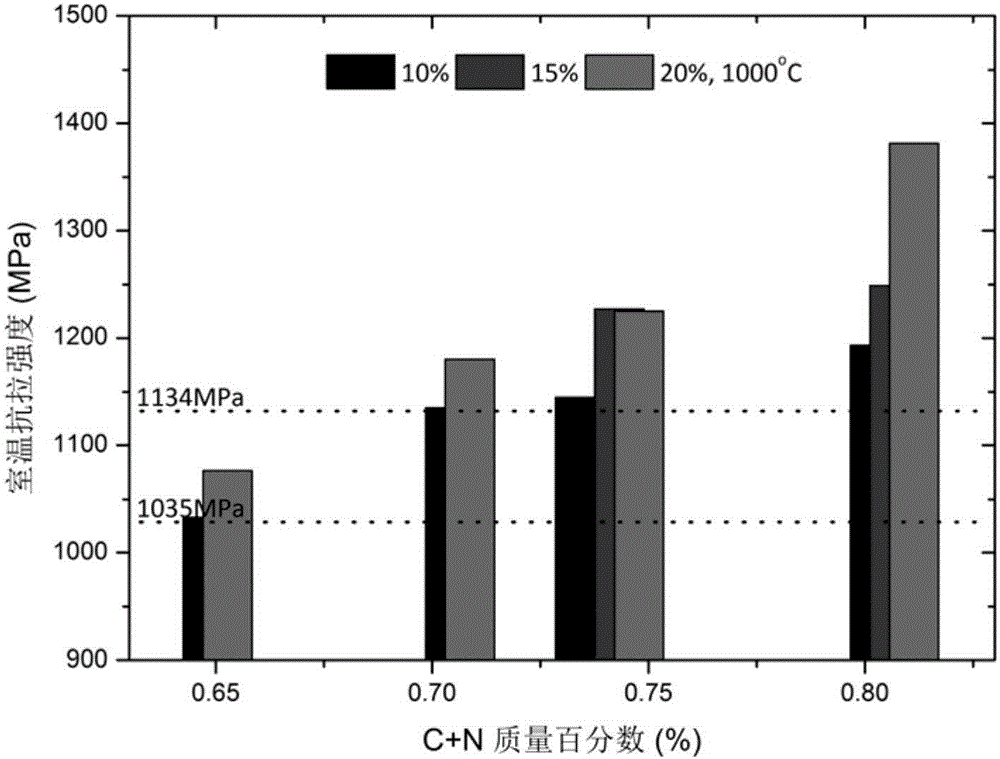
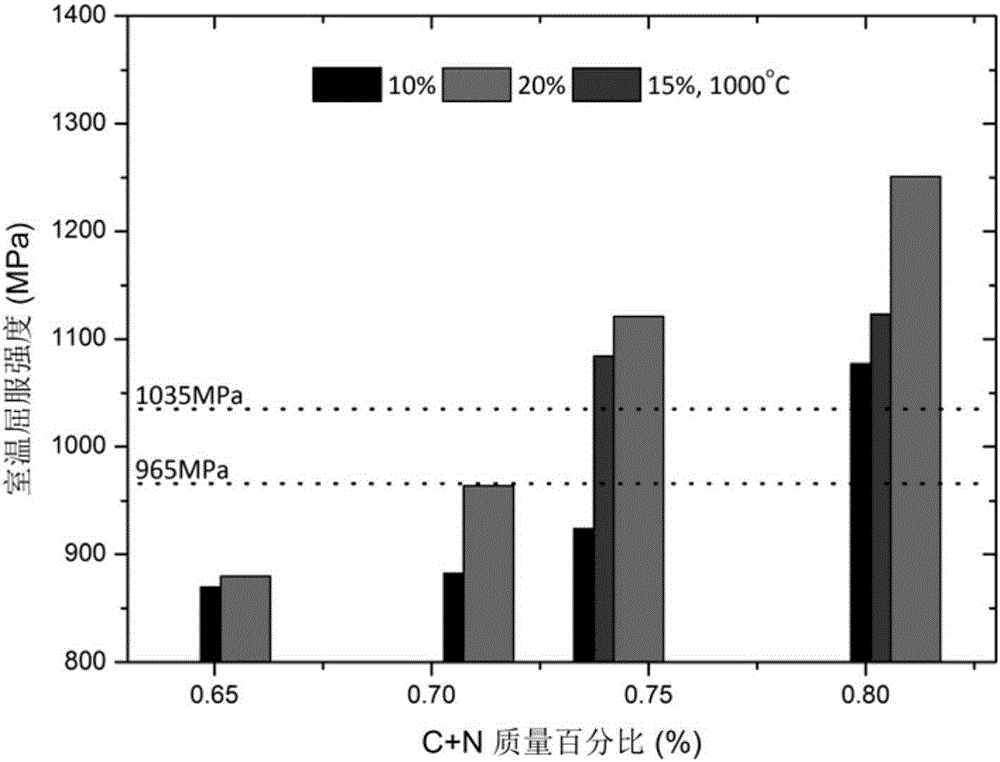
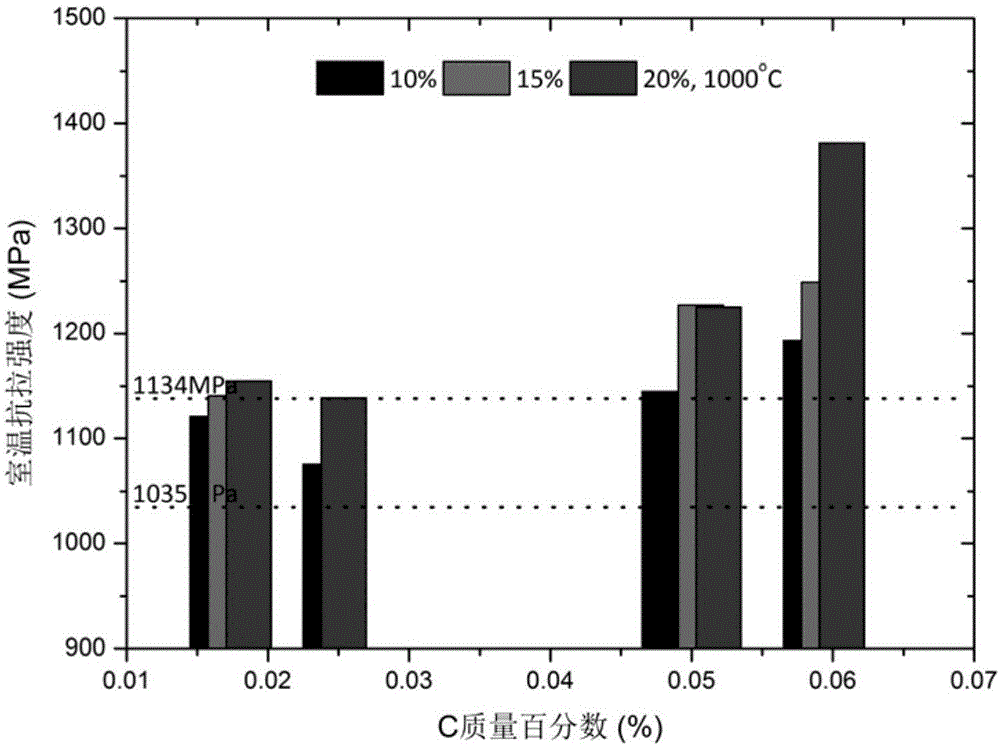
[0056] Example 1: Effects of C and N elements on the tensile properties at room temperature of a new type of high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel for non-magnetic drill collars
[0057] The tensile properties of the new high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel samples for non-magnetic drill collars with different C and N elements were tested according to the American Society for Testing and Materials standard ASTM-E8 at room temperature. The results show that when the final forging temperature is 1000℃, the room temperature tensile strength of the material ( figure 1 ) and yield strength ( figure 2 ) all increased with the increase of the sum of C element and N element content. In particular, when the total content of C and N elements is 0.72%, although the tensile strength can meet the material standard requirements (1035MPa), its room temperature yield strength cannot meet the standard requirements (965MPa). When the total content of C and N elements rises to 0.75%, i...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2: Influence of C and Cr elements on intergranular corrosion performance of new high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel for non-magnetic drill collars
[0060] The new high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel samples with different C and Cr contents for non-magnetic drill collars were tested for their intergranular corrosion performance according to the E method of the American Society for Testing and Materials standard ASTM-A262. In the test, all samples were tested in two states of wrought state (no solid solution) and sensitized state. The results show that all the samples in forged state (no solid solution) without sensitization treatment passed the test, but after the sensitization test, only some samples passed the test (Table 2). It can be seen from the Cr content of all samples that increasing the Cr content helps to improve the intergranular corrosion resistance of the material. This is mainly caused by the local diffusion of Cr element during the sen...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Embodiment 3: the impact of heating temperature on the generation of harmful precipitates
[0065] Cr carbides are one of the most harmful precipitates in high nitrogen austenitic stainless steels that have the greatest impact on hot working. A new type of high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel sample for non-magnetic drill collars was subjected to aging treatment at different temperatures and times to observe the precipitation of Cr carbides. The temperature of the aging treatment mainly revolves around the critical temperature range (920°C-980°C) of the thermal deformation process. After aging treatment for different times from 10min to 60min, the amount of carbide precipitation below 940°C is relatively large ( Figure 5-8 ), and when the aging temperature rises above 960 °C, the precipitation rate and total amount of carbides are greatly reduced. The results of the statistical distribution of precipitates show this trend more clearly ( Figure 9 ). Therefore, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com