Biocompatible built-in stent material
A technology of biocompatibility and prosthetic materials, applied in drug delivery, surgery, microcapsules, etc., can solve the problems of loss of EC function, vascular stenosis, and poor clinical effect of endothelial inoculation, so as to avoid restenosis and inhibit restenosis Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
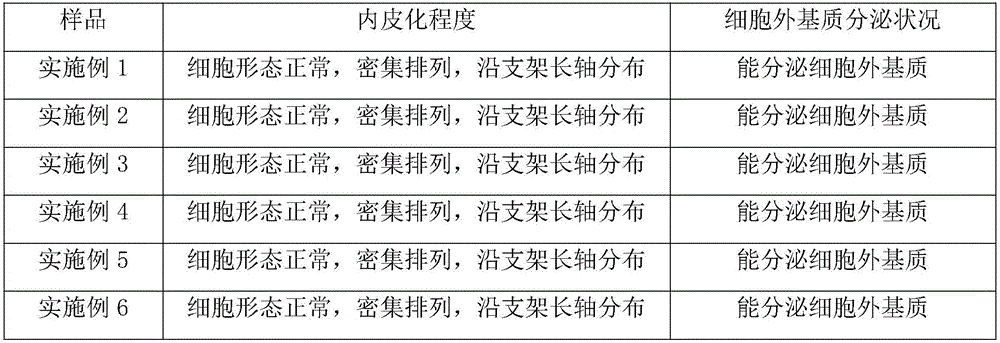
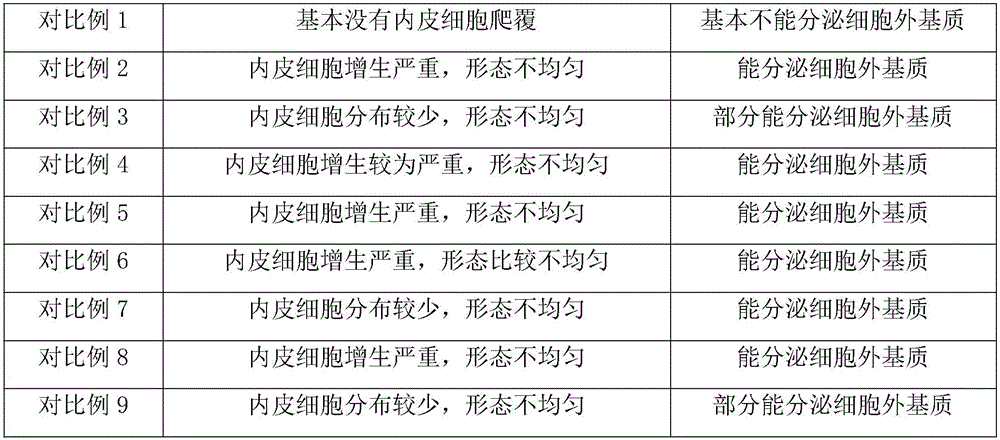
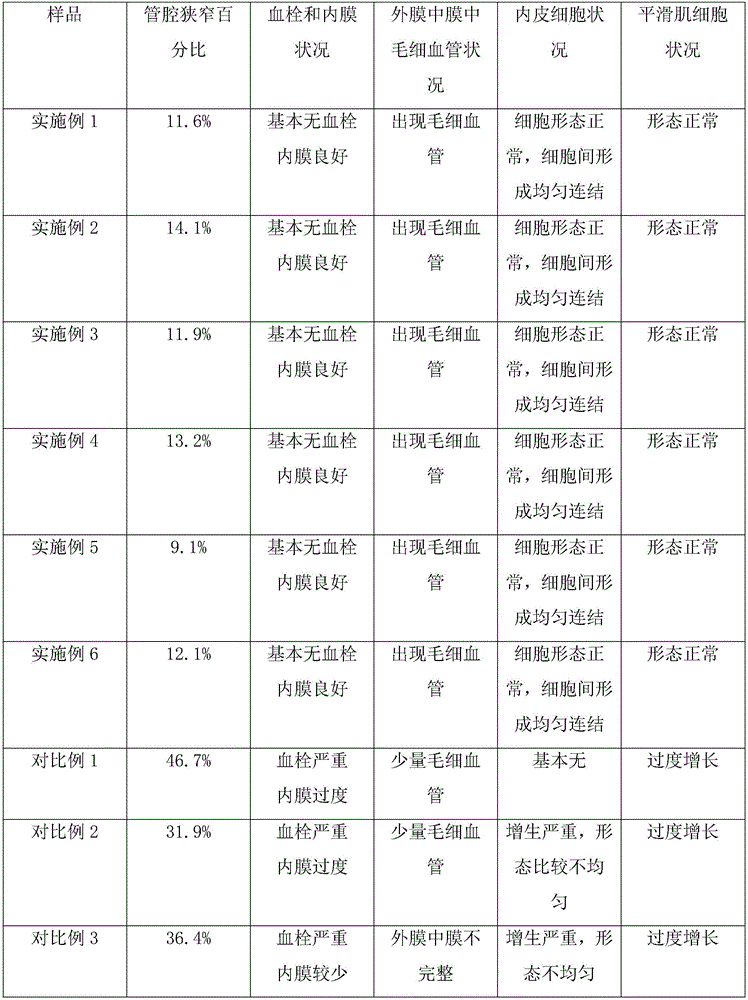
Embodiment 1
[0051] Preparation of prostheses (preferably endovascular stents) with microcavities and short peptide coatings
[0052] Step 1: Obtain the base material of the prosthesis, which can degrade the pure iron tubular material, and make it have holes connecting the inner and outer surfaces on the surface;
[0053] Step 2: Using laser engraving technology, a microcavity is obtained in the thickness direction of the above-mentioned hole that runs through the prosthesis; the microcavity has a hemispherical outline, the diameter of which is 30 μm, and the depth of the bottom is the diameter of the hole 1 / 3 of , and the total number of the microcavities is 30;
[0054] Step 3: Using conventional techniques, obtain a composition in the form of microcapsules, the composition comprising gelatin as a "shell", and histidine chelated iron as a "core", wherein the histidine chelated iron is in the composition The weight content of the gelatin is 0.5%, and the degradation cycle of the gelatin ...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Preparation of prostheses (preferably endovascular stents) with microcavities and short peptide coatings
[0060] The preparation process is the same as that in Example 1, except that: the matrix material used in step 1 is degradable polycaprolactone; in step 2, the diameter of the microcavity is 50 μm, and the depth dimension of the bottom is 1 / 4 of the diameter of the hole, The total number of microcavities is 40; in step 3, the shell is chitosan, the degradation period is about 1 week, the core is cysteine chelated iron, and the weight content of the core in the composition is 0.8%; The loading in step 4 was 8 μg.
Embodiment 3
[0062] Preparation of prostheses (preferably endovascular stents) with microcavities and short peptide coatings
[0063] The preparation process is the same as in Example 1, except that: the matrix material used in step 1 is degradable pure magnesium; the diameter of the microcavity in step 2 is 100 μm, the depth dimension of the bottom is 1 / 5 of the diameter of the hole, and the microcavity is 1 / 5 of the diameter of the hole. The total number is 60; in step 3, the shell is collagen, the degradation period is about 2 weeks, the core is cysteine chelated iron, and the weight content of the core in the composition is 1.5%; in step 4, the load is The amount is 10 μg; the sequences of the two short peptides in step 5 are the aforementioned sequence 3 and sequence 4, respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com