An anti-restenosis intraluminal stent material
An anti-restenosis and internal stent technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve the problems of vascular stenosis, poor clinical effect of endothelial inoculation, loss of EC function, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
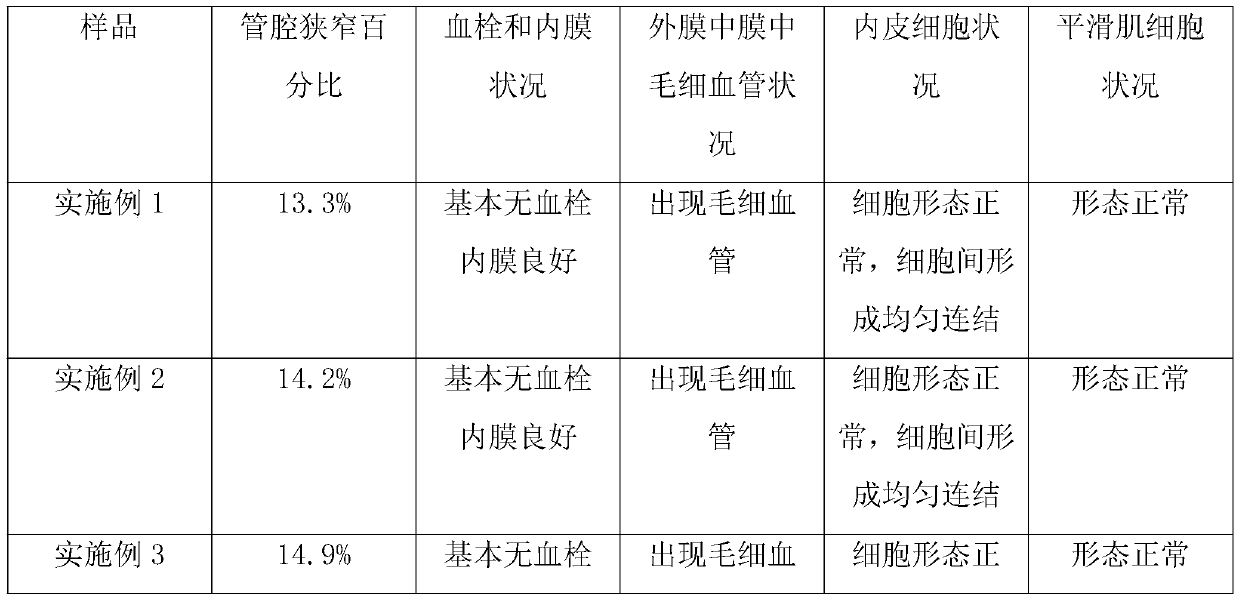
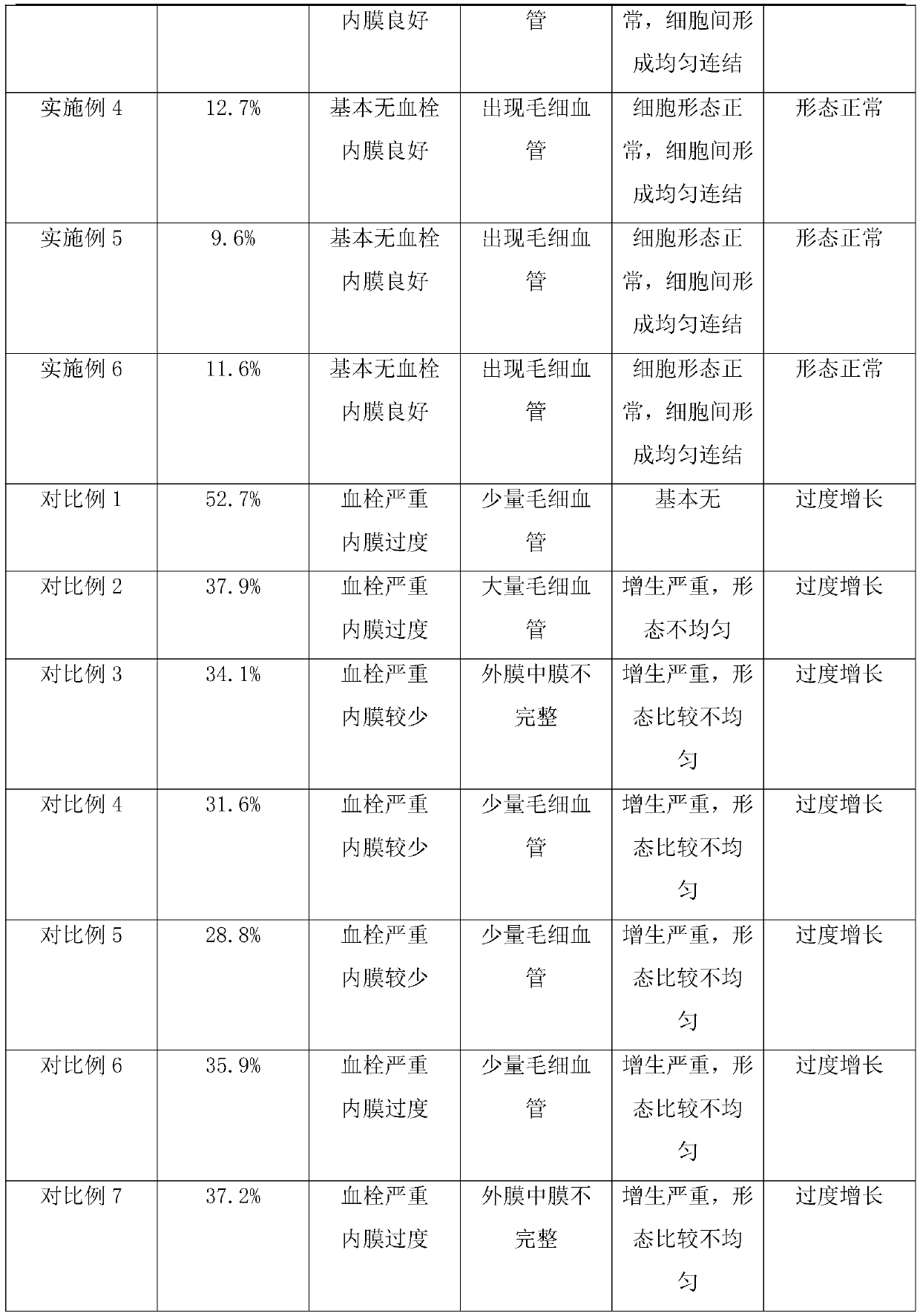
Embodiment 1
[0054] Preparation of Vascular Stents with Microgrooves and Short Peptide Coating
[0055] Step 1: Obtain the base material of the prosthesis, a tubular material that can degrade pure iron;
[0056] Step 2: Utilize laser engraving technology to obtain rectangular microgrooves in the direction parallel to the matrix axis on the outer surface of the matrix material; there are 8 microgrooves, and the ratio of the total opening area of the microgrooves to the total area of the outer surface of the matrix is 1 / 12. The depth dimension of the bottom is 1 / 5 of the thickness of the substrate;
[0057]Step 3: Utilize conventional technology, obtain degradable fibrous composition, described composition comprises chitosan fiber, and the histidine chelated iron loaded on described chitosan by spraying, wherein histidine chelated iron The weight content of iron in the composition is 0.6%, the degradation cycle of the chitosan fiber is about 1 month, and the degradable fibrous compos...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Preparation of Vascular Stents with Microgrooves and Short Peptide Coating
[0063] The preparation process is the same as in Example 1, the difference being that the base material used in step 1 is degradable polycaprolactone; in step 2, the microgrooves are 3 annular grooves along the perimeter of the substrate, and the total opening area of the microgrooves accounts for The ratio of the total area of the outer surface of the matrix is 1 / 15, and the depth dimension of the bottom is 1 / 3 of the thickness of the matrix; the fibers described in step 3 are collagen fibers, and the degradation cycle is about 40 days, and the chelated iron is Cysteine chelated iron, its weight content in the composition is 0.8%; the polymer in step 4 is polyvinyl alcohol, and its thickness is 1.5mm.
Embodiment 3
[0065] Preparation of Vascular Stents with Microgrooves and Short Peptide Coating
[0066] The preparation process is the same as in Example 1, the difference being that the matrix material used in step 1 is degradable poly(lactic acid-glycolic acid); in step 2, the microgrooves are 6 W-shaped grooves along the matrix axis, and the microgrooves The ratio of the total opening area to the total area of the outer surface of the substrate is 1 / 10, and the depth dimension of the bottom is 1 / 4 of the thickness of the substrate; the weight content of the histidine chelated iron in the composition in step 3 is 1%; the coating thickness in step 4 is 1.8mm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com