A one-step, seamless, non-homologous, multi-segment gene splicing transformation method and its kit
A gene splicing and genetic modification technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of DNA tail sequence modification, failure to realize standardization and reuse of DNA fragments, low efficiency, etc., and achieve the effect of high-efficiency transformation reaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] Example 1 Circular DNA Molecular Splicing
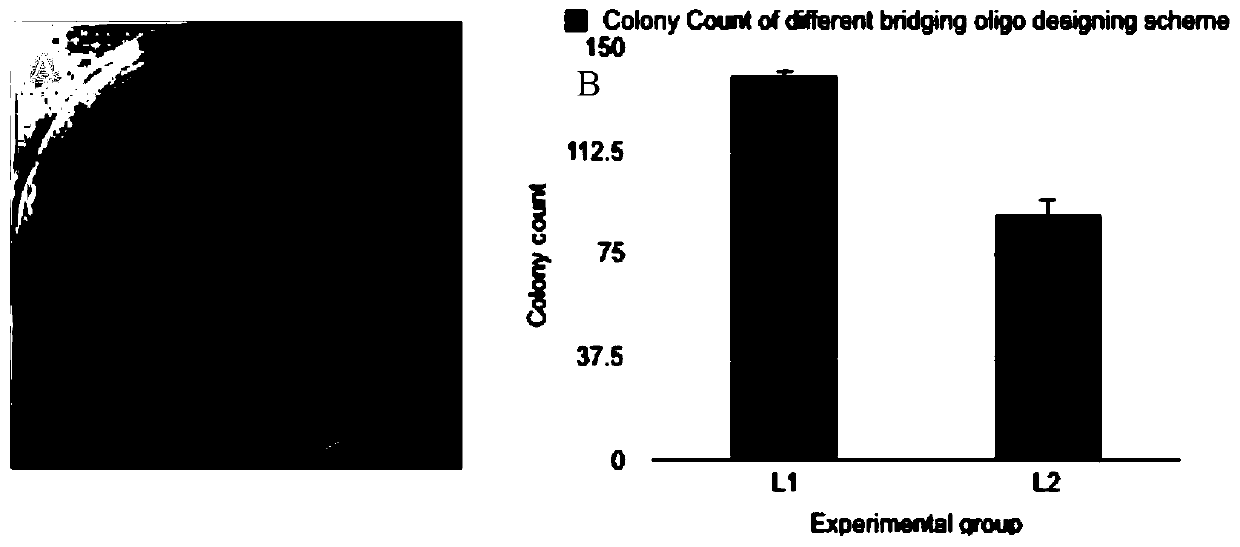
[0079] Table 5 shows the DNA sequences used and the corresponding fragment sizes. During the primer design process, the Tm values of all the half-bridge primers and the Tm values of the amplification primers were 60 degrees. The designed bridging primers were all in the range of 30-60bp in length. The sequences of the bridging primers and amplification primers used are shown in Table 6.
[0080] Table 5 Fragments used in circular DNA molecule splicing
[0081]
[0082] Table 6 The bridging primers and amplification primers used in the splicing of circular DNA molecules
[0083]
[0084]
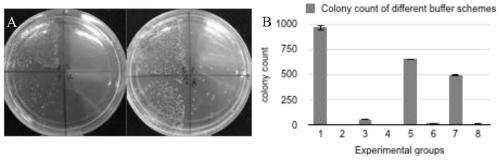
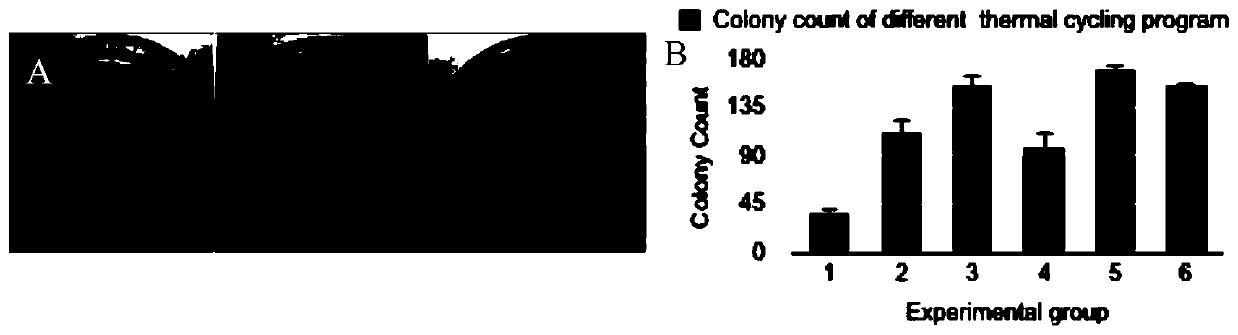
[0085] The specific components and concentrations used in the bridging method, the thermocycling program are listed in Table 7, and the buffer components are listed in Table 8. The bridging method completes the one-time splicing of 8 target fragments in one step, and at the same time obtains a high concentration of ligation pr...
Embodiment 2
[0094] Example 2 Linear DNA Molecular Splicing
[0095] Table 9 shows the DNA sequences used and the corresponding fragment sizes.
[0096] Table 9 Fragments used in linear DNA molecular splicing
[0097]
[0098] During the primer design process, the Tm values of all the half-bridge primers and the Tm values of the amplification primers were 60 degrees. The designed bridging primers were all in the range of 30-60bp in length. Both the bridging primer sequence and the amplification primer sequence used in the bridging method are listed in Table 10.
[0099] Table 10 Bridging primers and amplification primers used in linear DNA molecule splicing
[0100]
[0101]For conventional splicing of two fragments to form fusion fragments, fusion PCR is used in most cases. However, the fusion PCR method has low repeatability and poor stability. And for different DNA fragments, it is necessary to explore the parameters to obtain a better fusion reaction. However, if the br...
Embodiment 3
[0106] Example 3 One-step point mutation of plasmid DNA molecule
[0107] The plasmid DNA used is pZS-ssMBP-LKGFP (SEQ ID NO: 2), and the size of the plasmid is 5967bp. The resulting high-concentration mutated circular DNA ligation product can be directly used for transformation to obtain a large number of transformants.
[0108] The bridging primer sequences and amplification primer sequences used in the bridging method are listed in Table 11.
[0109] Table 11
[0110]
[0111] In principle, point mutations using the bridging method are equivalent to the last two steps in the full bridging method. The introduced amplification primers with mutations completely amplify the entire plasmid, and the linear amplification products complete the circularization reaction in the thermal cycle under the guidance of the bridging primers to obtain high-concentration target products.
[0112] For conventional point mutations, in most cases, fusion PCR reaction needs to be carried out...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com