Patents
Literature
54 results about "Gene splicing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gene splicing. A term used to refer to the process by which the DNA of an organism is cut and a gene, perhaps from another organism, is inserted. (See genetic engineering and recombinant DNA.) Gene splicing is often used in industry to allow single-celled organisms to produce useful products, such as human insulin.
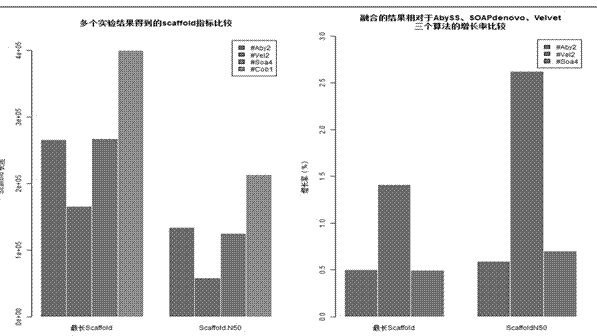
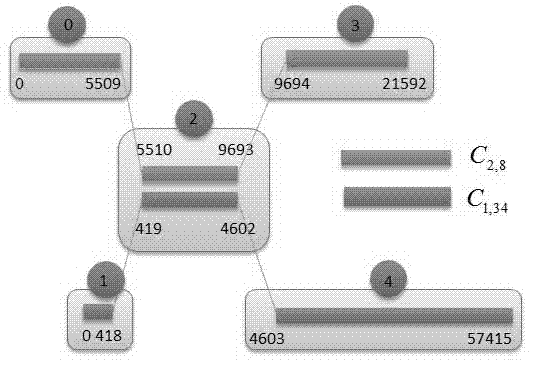
Parallel gene splicing algorithm based on cluster map structure
InactiveCN103761453ARealize the mergerLoad balancing distributionSpecial data processing applicationsGene splicingAlgorithm
The invention provides a parallel gene splicing algorithm based on a cluster map structure. According to the parallel gene splicing algorithm based on the cluster map structure, a long sequence (scaffold) obtained by the splicing of a plurality of other gene splicing algorithms and a short-read long gene sequence (read-pair) generated by a double-end sequencer are used as input, and complementary scaffold are spliced to be the longer sequence by building index, mapping read-pair and scaffold clusters, building cluster map, searching path and other steps. The two steps of building index and reading length mapping aim at obtaining correlations and matching degrees of long sequences scaffold obtained by different algorithms by reading length, and clustering according to the correlations and matching degrees; all scaffold in the cluster are complementary and are potential splicing sequences. At last the cluster map is built to solve the overall longest path of the map, and thus the spliced long gene sequence is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Recombinant protein for diagnosing bovine tuberculosis and application thereof
ActiveCN101684160AKeep natural activityGuaranteed spatial structureMicroorganism based processesFermentationGene splicingFusion gene
The invention discloses a recombinant protein for diagnosing bovine tuberculosis, which is obtained by a method comprising the following steps: extracting the genome DNA of mycobacterium tuberculosisvar. bovis as a template of a PCR reaction to amplify out CFP10 and ESAT6 genetic fragments; using a gene splicing technique to amplify out a target gene CFP10-ESAT6 fusion gene; cloning and transforming the target gene to obtain a recombinant fungus, and inducing and expressing the recombinant fungus according to a conventional method, and purifying an expression product to obtain the recombinantprotein. The recombinant protein and a diagnostic reagent provided by the invention are used for diagnosing the bovine tuberculosis to obtain the advantages of low cost, high speed, high sensitivityand specificity.
Owner:ZHAOQING DAHUANONG BIOLOGIC PHARMA
Hog cholera antibody ELISA diagnosis reagent kit
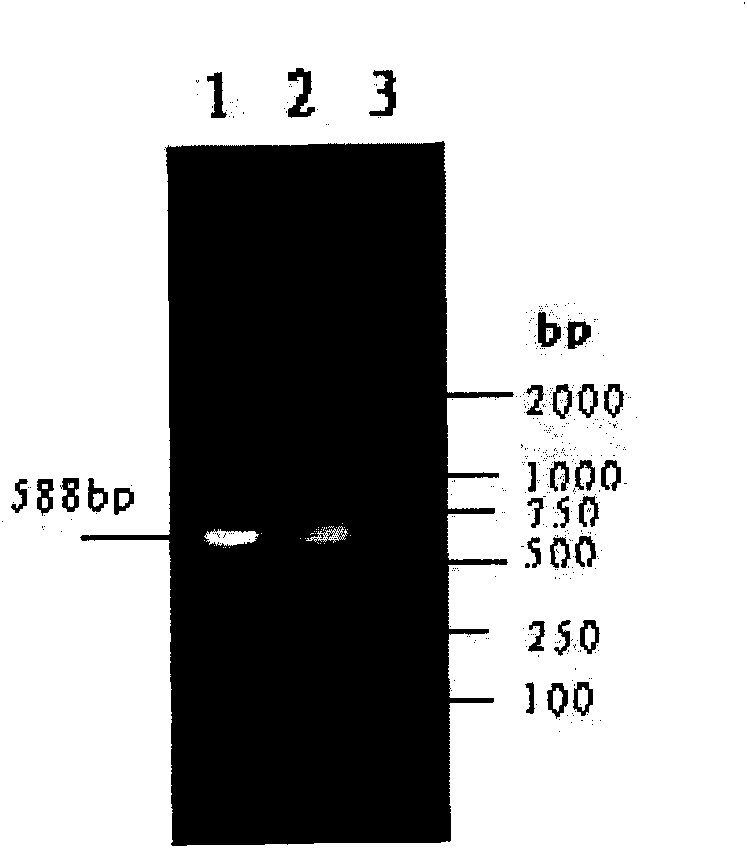
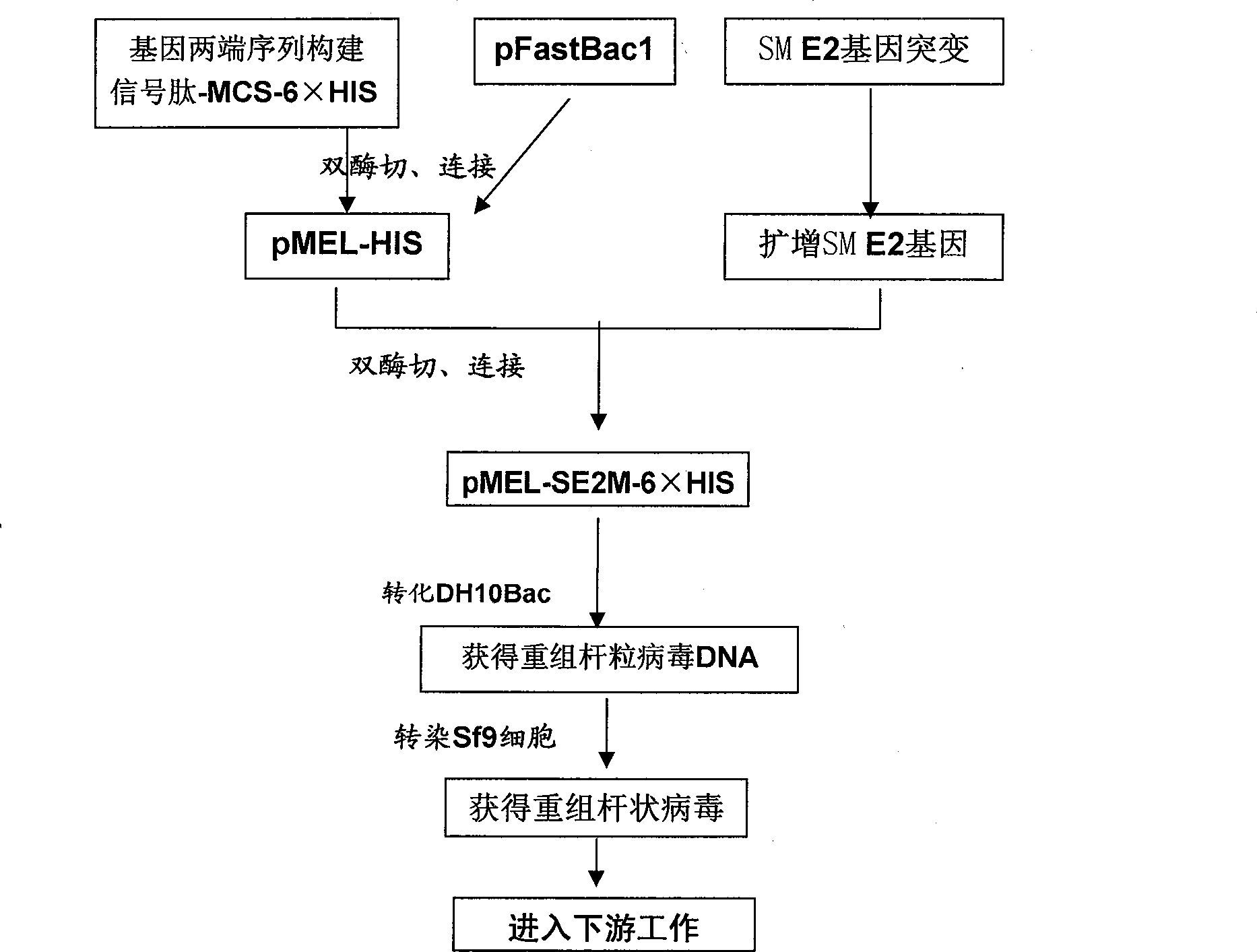
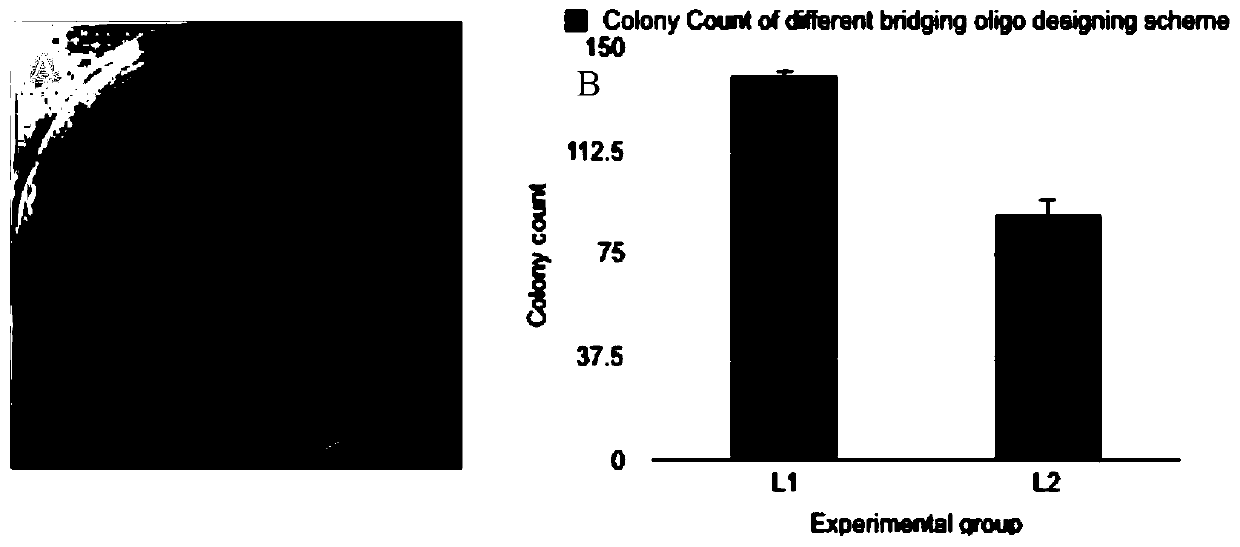
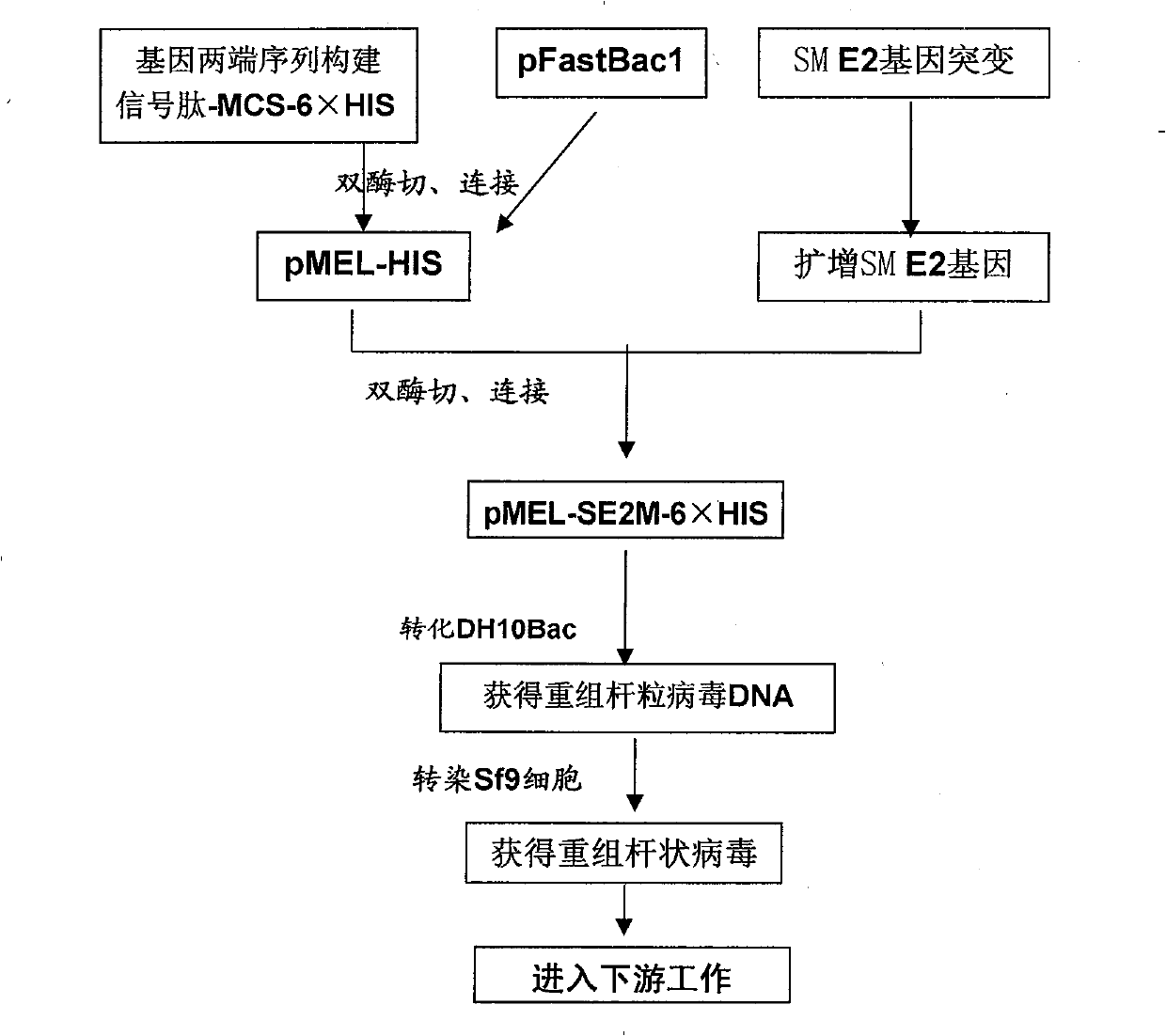
The invention relates to an ELISA diagnosis kit for swine fever virus. In the invention, by gene splicing technology, the swine fever virus E2 is jointed with secretion signal peptide sequence and purification label at two sides and is inserted into the autographa californica nucleopolyhedrosis virus expression vector so as to construct recombinant autographa californica nucleopolyhedrosis virus CGMCC No.2671 and to obtain coated ELISA swine fever virus Shimen Strain E2 gene soluble expression antigen. The kit of the invention is rapid, sensitive, and specific to the diagnosis and the immune evaluation of swine fever virus, and the diagnosis can be completed once within 2 hours.
Owner:CHINA INST OF VETERINARY DRUG CONTROL
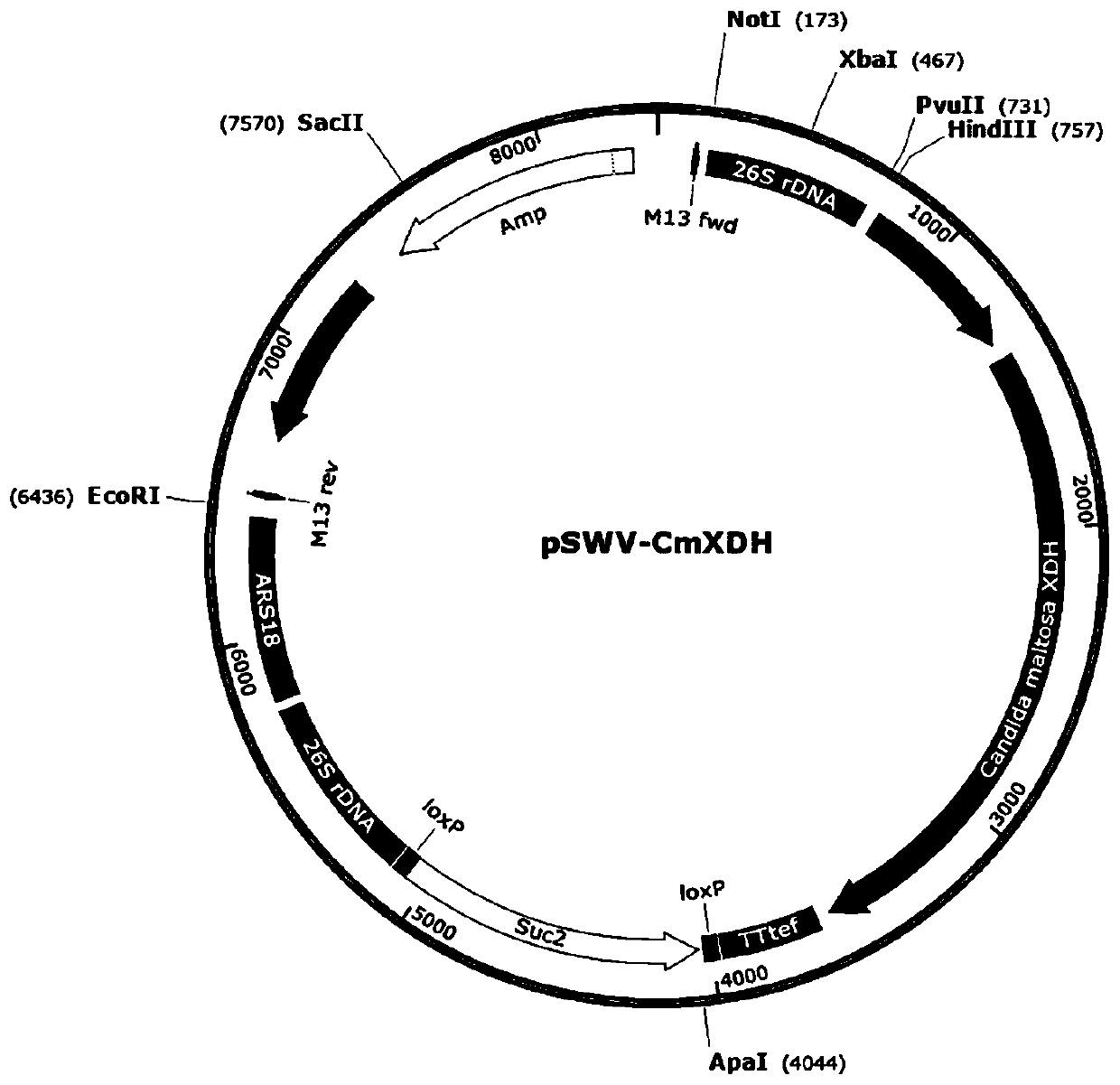
Construction method of recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica for synthesis of xylitol and strain thereof
The invention discloses a construction method of recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica for synthesis of xylitol and a strain thereof. Yarrowia lipolytica is used as a synthetic chassis. Through the improvement means of metabolic engineering, the yeast undergoes gene splicing, genes for synthesizing xylitol from glucose, fructose, glycerol and starch as carbon sources are introduced, and metabolic pathways of synthesis by-products are blocked, so that recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica can synthesize xylitol from glucose, fructose, glycerol and starch as carbon sources by fermentation, and an engineering strain for synthesizing xylitol from carbon sources such as glucose and the like is obtained. After fermentation, xylitol crystals are obtained by separation of a bacterial liquid, ion exchange of aclarified fermentation liquid, decolorization, concentration, crystallization and other processes. The construction method of the engineering yeast for synthesizing xylitol from carbon sources such as glucose and the Yarrowia lipolytica strain obtained by the method and for synthesizing xylitol from carbon sources such as glucose can simplify existing methods for chemically synthesizing xylitol and have better application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Lyase of self-cleaving escherichia coli, and applications thereof
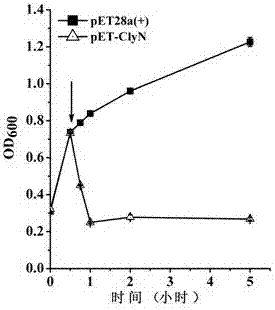
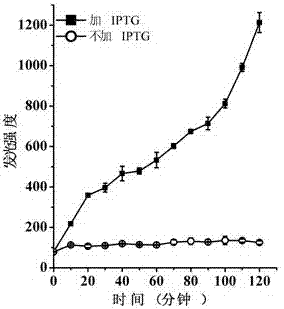
ActiveCN104762285AEfficient self-cleavageNo pollution in the processFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliHeterologous
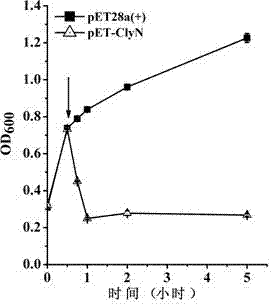
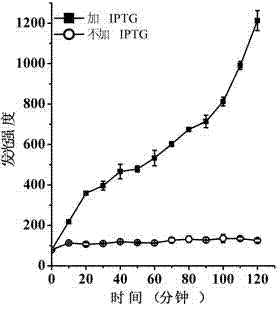
The invention discloses a lyase of self-cleaving escherichia coli, and applications thereof. A brandnew lyase ClyN is constructed by adopting gene splicing means, the lyase can result in the self-cleaving of the host escherichia coli after being expressed in the escherichia coli, to release intracellularly expressed ATP and protein. Recombinant ClyN expression plasmid can be duplicated in the escherichia coli BL21(DE3), and express for 15 min under the induction of IPTG to observe the obvious phenomenon of inducing the escherichia coli to self-cleave, and the induced cleaving efficiency achieves 99.8%. When the host bacteria express heterologous enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP), EGFP can be released in solution after escherichia coli is cleaved, and the release efficiency is 89% of direct ultrasonic breaking efficiency. Therefore, the ClyN can be used for extracting and release of heterologous protein after expression in the escherichia coli, thus having wide application prospects.
Owner:菲吉乐科股份有限公司
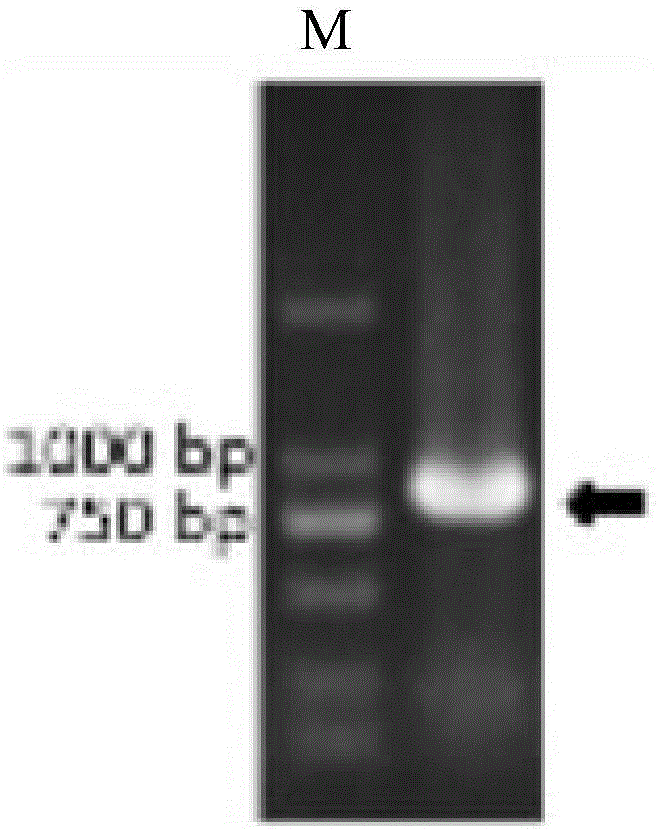
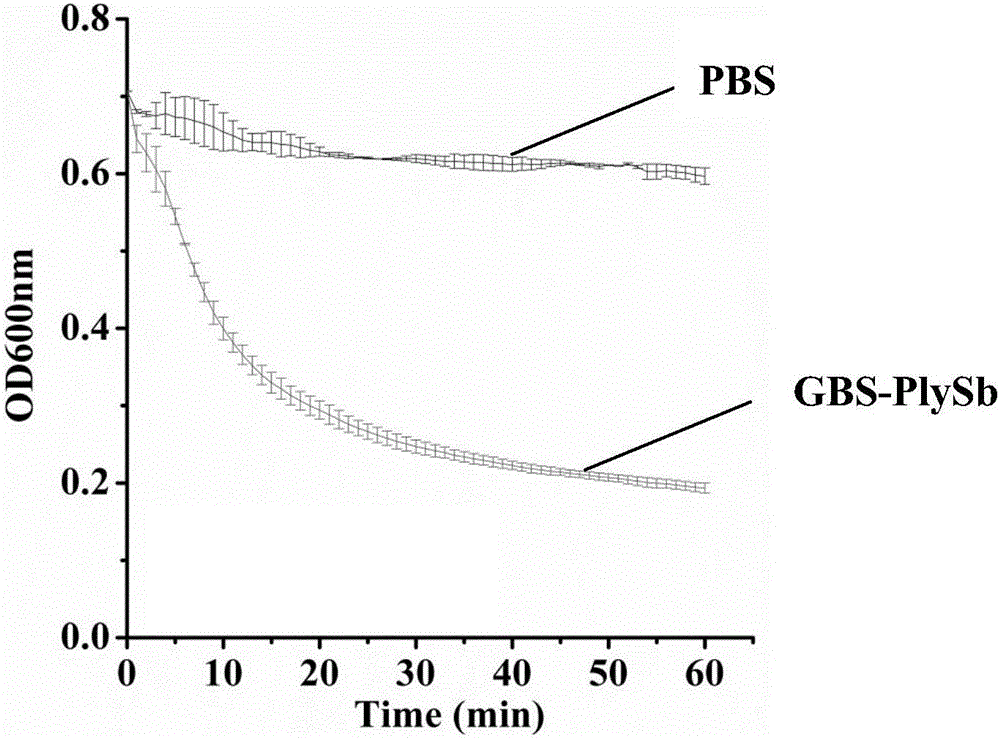
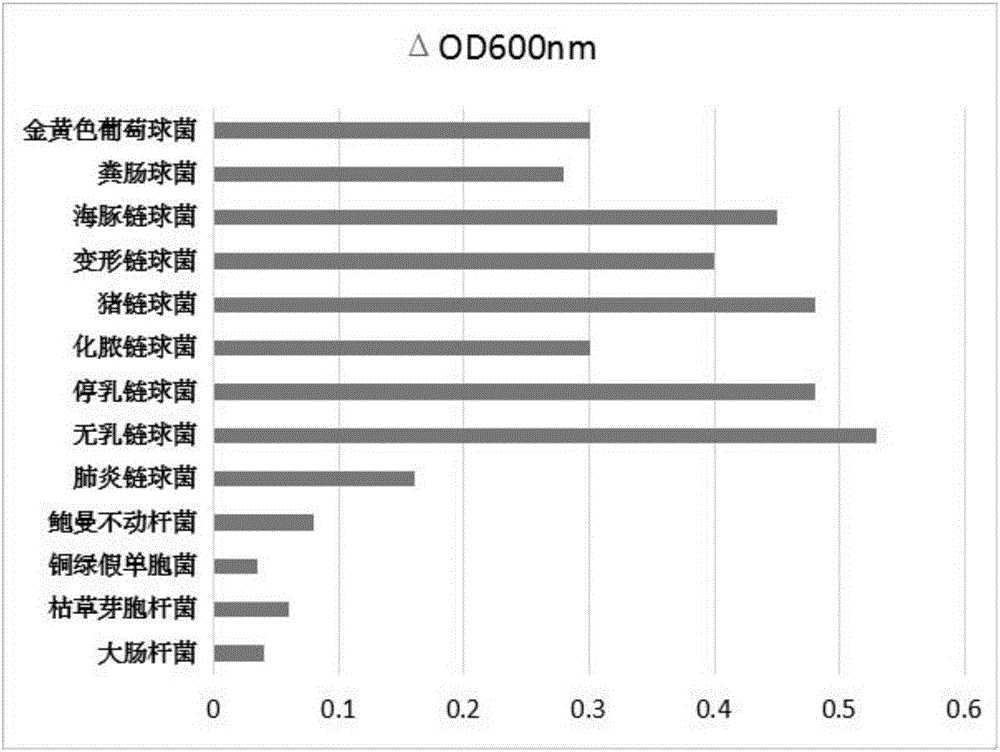
Novel broad-spectrum chimeric lysin BGS-PlySb and encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN107177580AImprove stabilityNo apparent cytotoxicityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliHigh concentration
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, in particular to novel broad-spectrum chimeric lysin BGS-PlySb and an encoding gene and application thereof. The novel broad-spectrum chimeric lysin BGS-PlySb has an amino acid sequence shown as in SEQ ID NO. 1; the encoding gene of the novel broad-spectrum chimeric lysin BGS-PlySb has a nucleotide sequence shown as in SEQ ID NO. 2. A novel chimeric lysin is constructed by means of gene splicing and is suitable for killing various species of Streptococcus and Staphylococcus, particularly various species of Enterococcus, and Staphylococcus aureus, as well as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus suis, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus iniae and other species; the novel broad-spectrum chimeric lysin BGS-PlySb has good stability and is insensitive to high-concentration NaCl, recombinant protein GBS-PlySb is well expressible in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), and a high dose of GBS-PlySb is free of significant cytotoxicity. Therefore, the novel broad-spectrum chimeric lysin BGS-PlySb is applicable independently to or as an additive to the control of various species of Streptococcus and the treatment of infections caused by these species, and has a promising application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
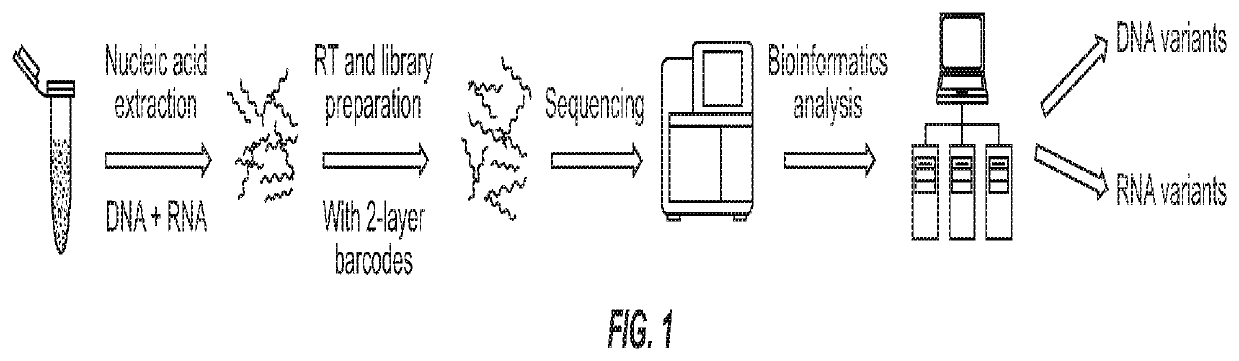
Systems and methods for combined detection of genetic alterations
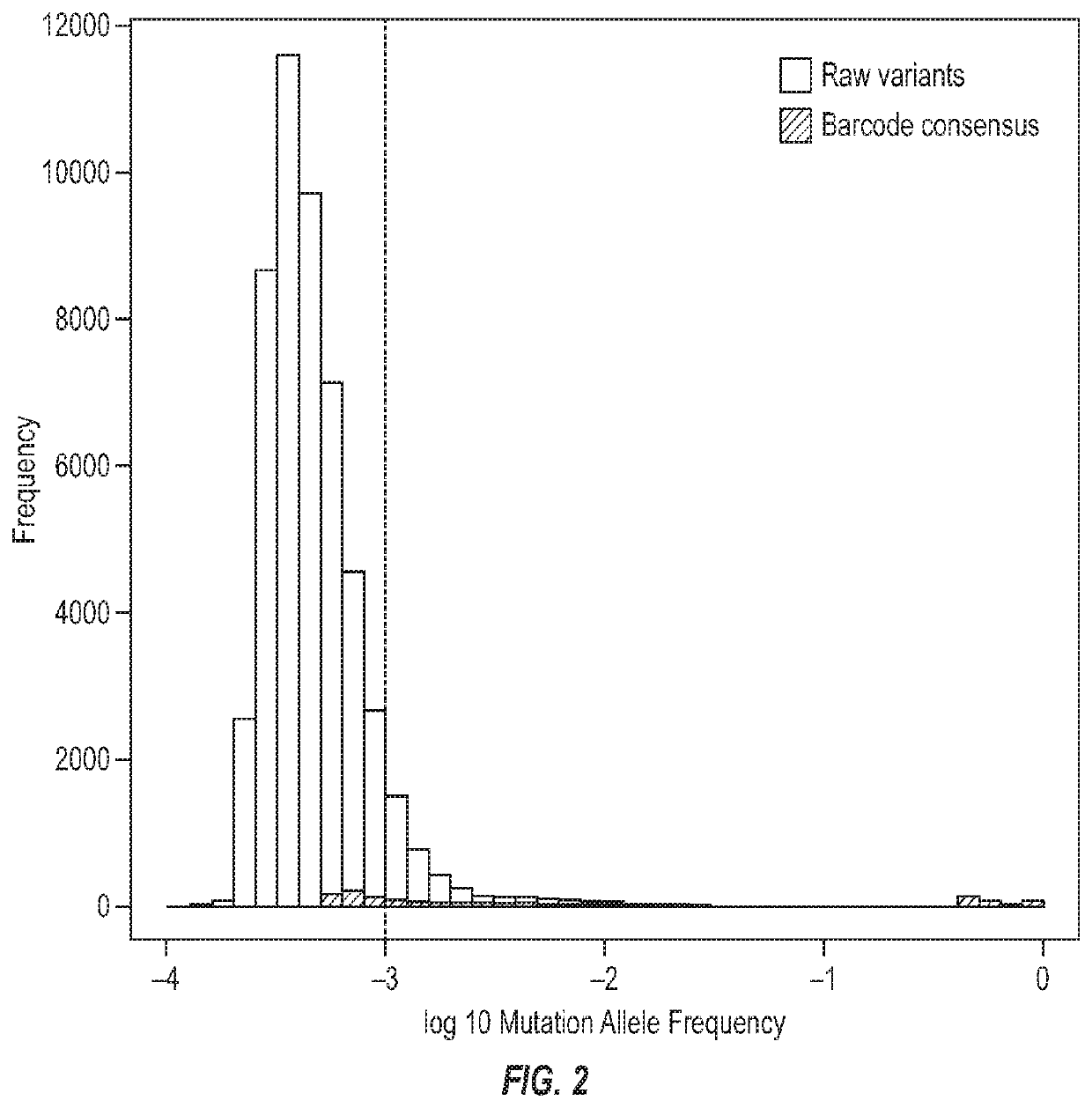
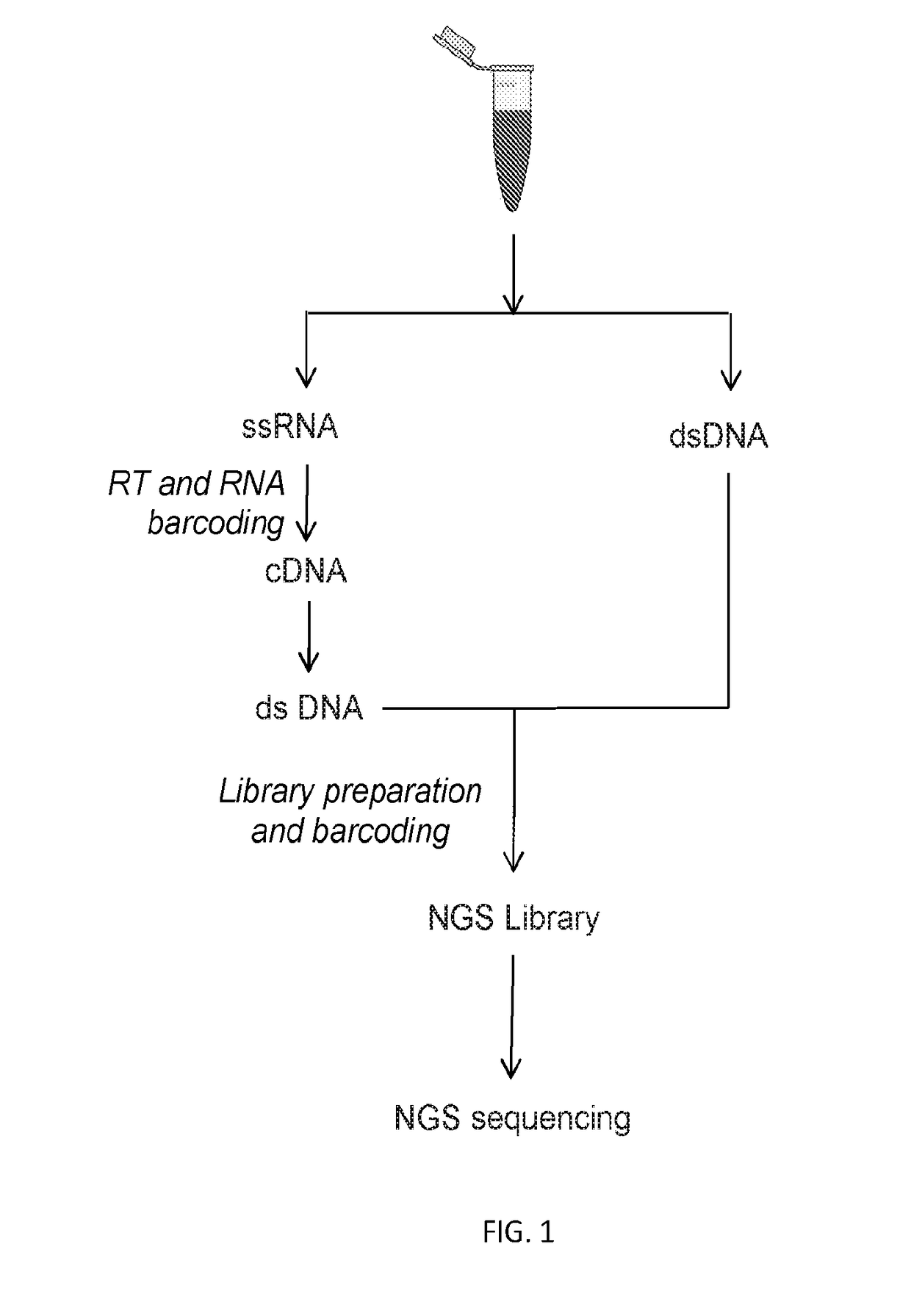
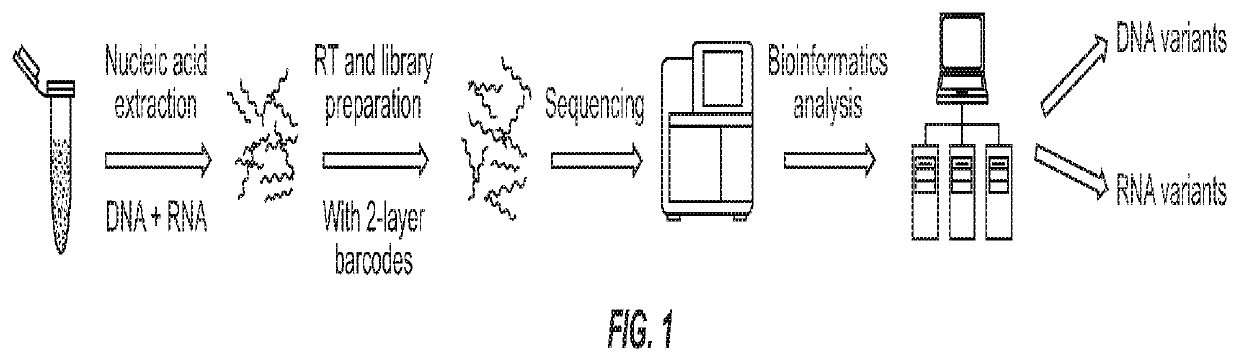
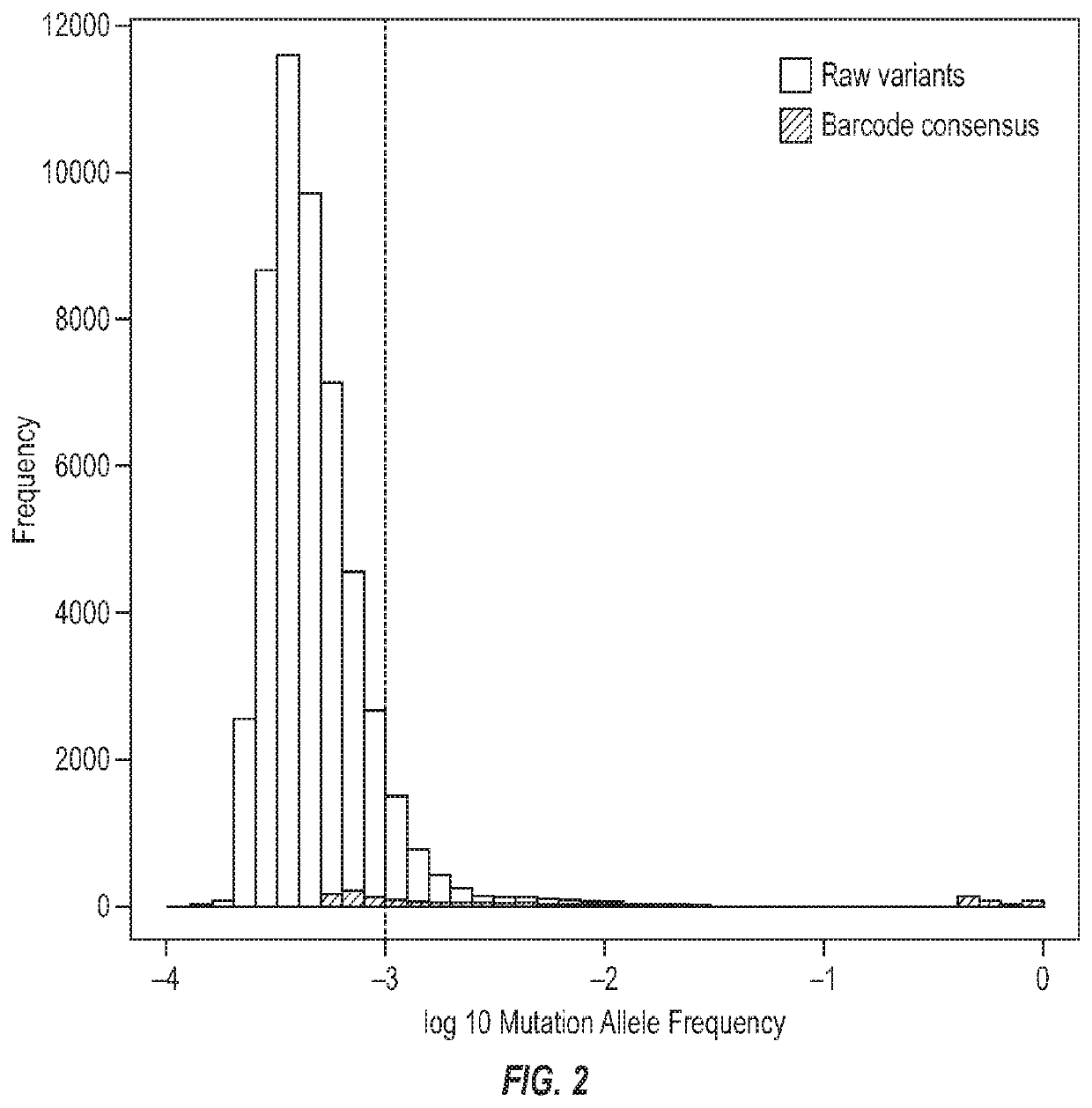
ActiveUS20200024644A1High barcode diversityAchieve quantificationNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGene splicingSolid tissue
Disclosed are systems and methods for simultaneous detection of DNA and RNA genetic alterations comprising gene splicing variants, mutations, indel, copy number changes, fusion and combination thereof, in a biofluid sample from the patient without physically separating RNA from DNA. The systems and methods are similarly applicable to the simultaneous detection of DNA and RNA genetic alterations in solid tissues comprising gene splicing variants, mutations, indel, copy number changes, fusion and combination thereof. The present method utilized a barcoding method for analysis. The streamlined methods improve the simplicity, quantification accuracy and detection sensitivity and specificity of non-invasive detections of biomarkers.
Owner:PREDICINE INC
Systems and methods for detecting genetic alterations
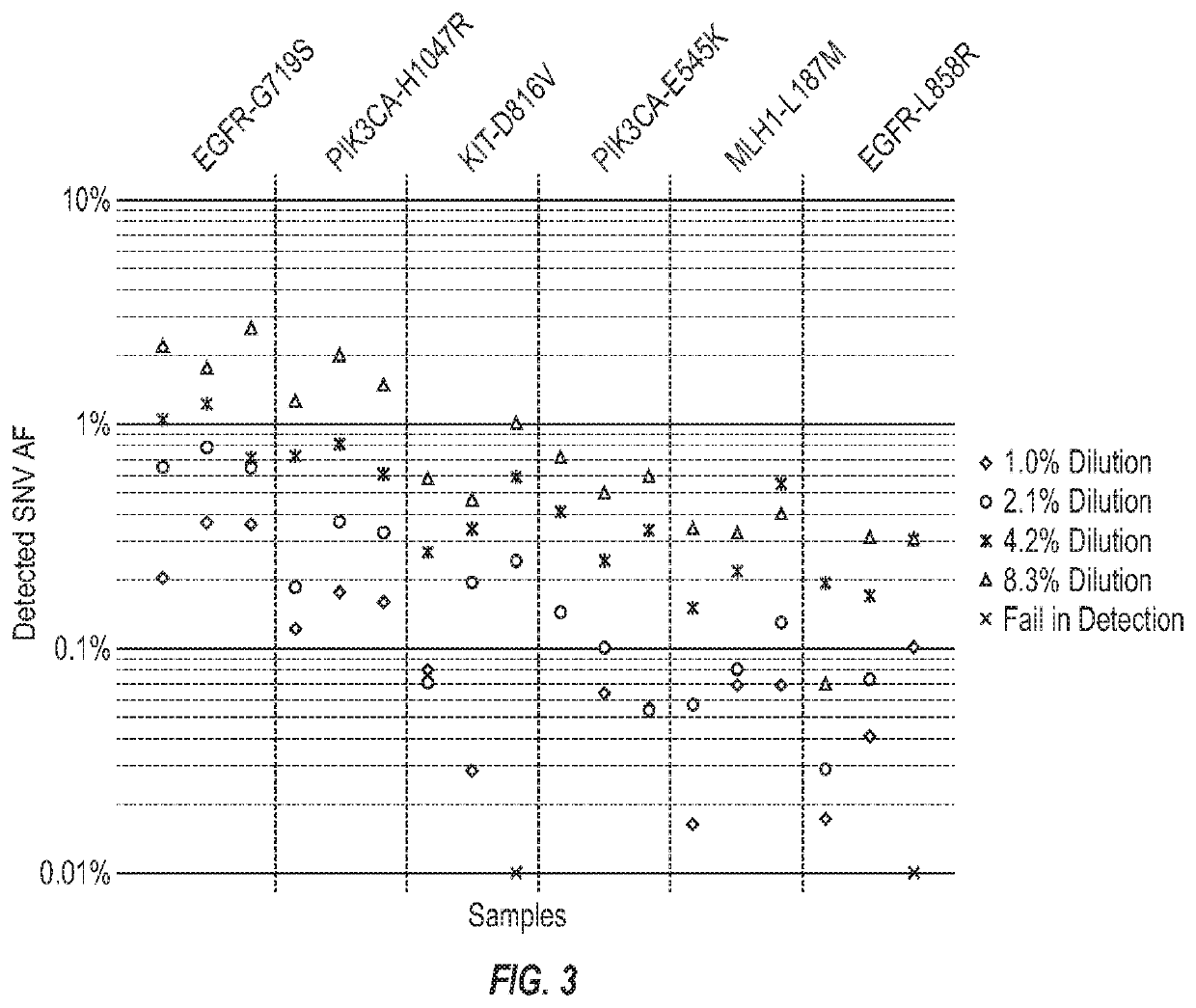
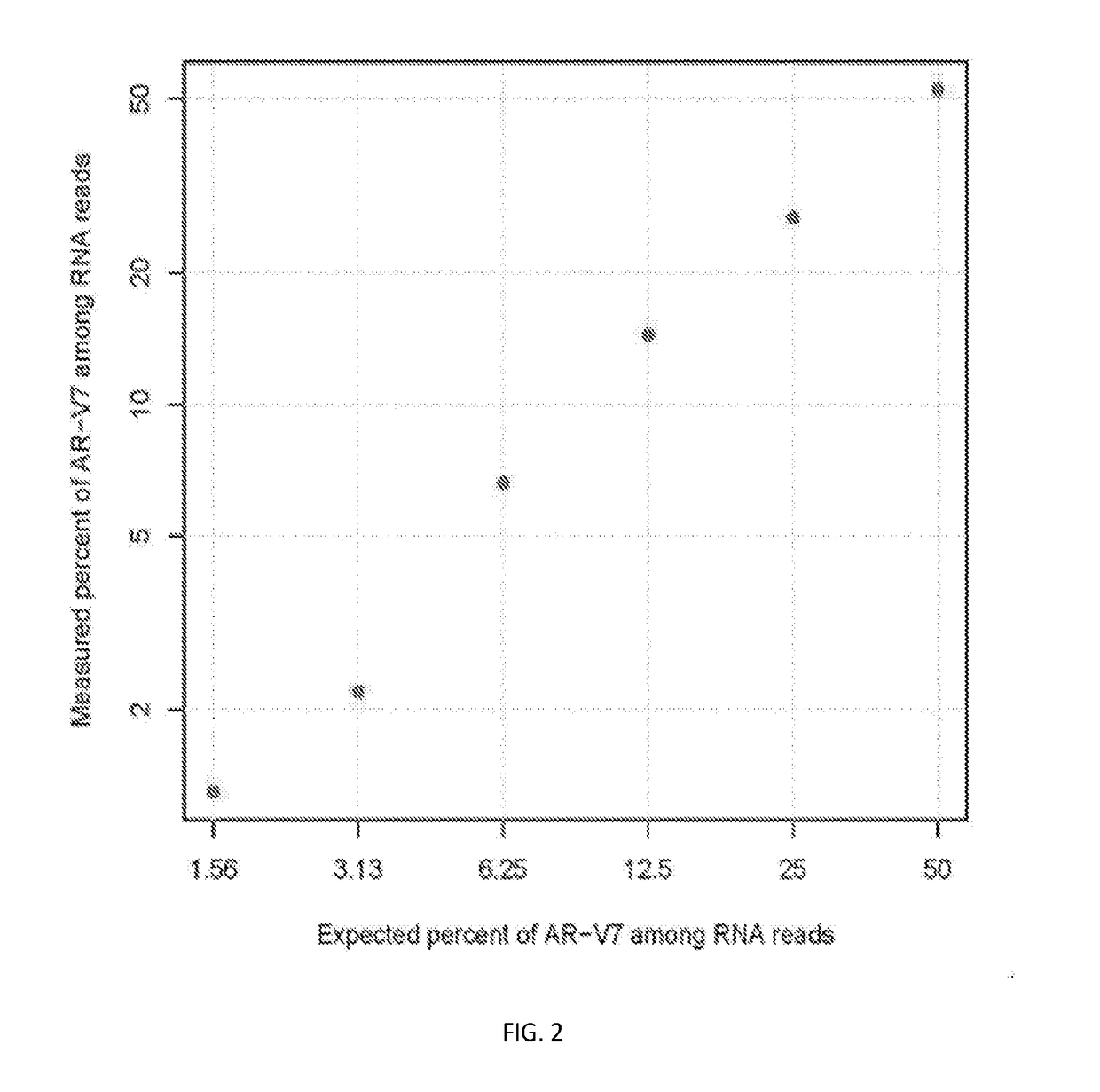
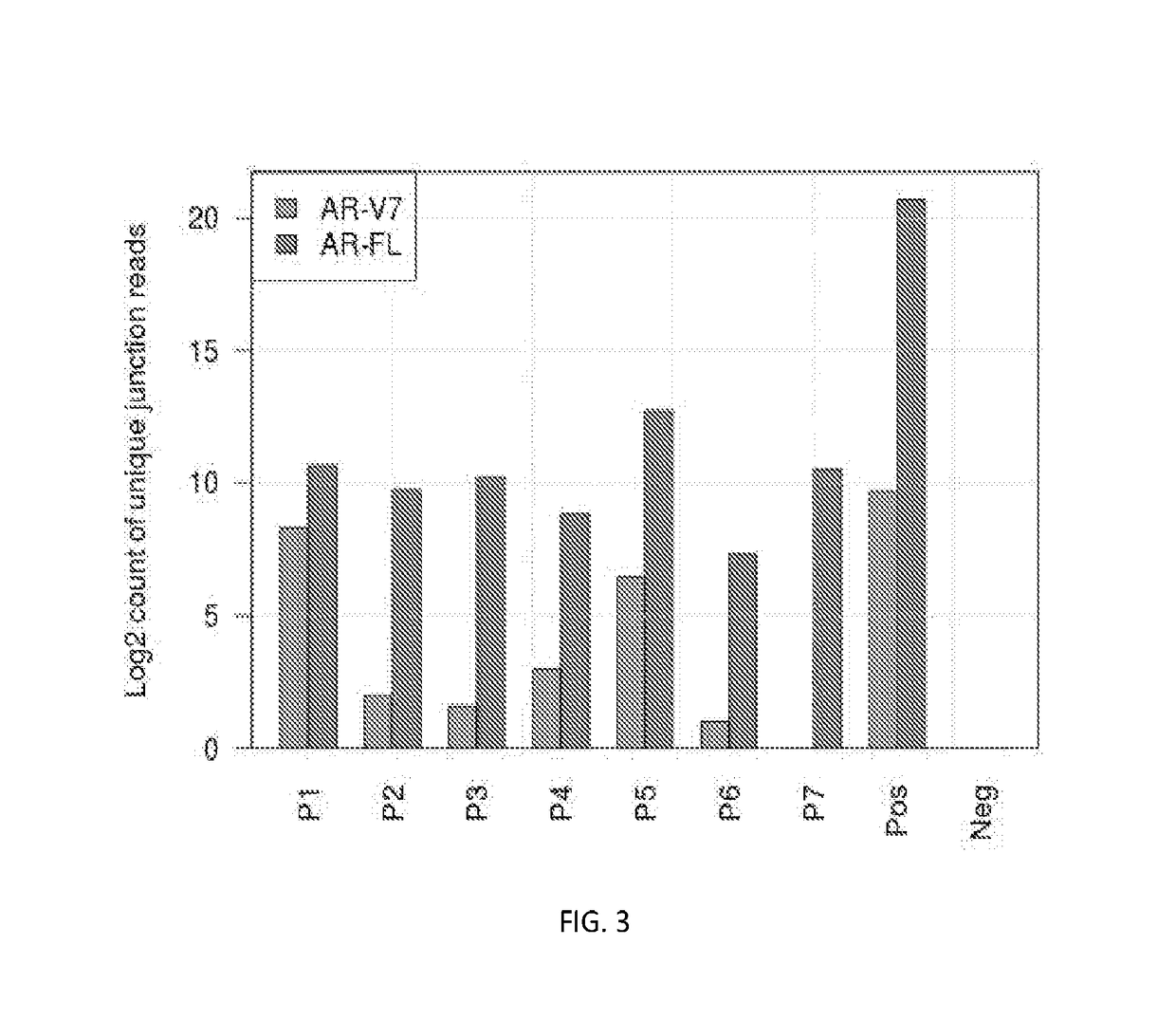
ActiveUS20190071732A1High sensitivityStrong specificityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGene splicingAndrogen Receptor Gene
Disclosed are systems and methods for detecting genetic alterations comprising androgen receptor gene splice variants (AR-Vs), mutations, indel, copy number changes, fusion and combination thereof, in a biofluid sample from the patient. The systems and methods are similarly applicable to the detection of gene alterations comprising gene splicing variants, mutations, indel, copy number changes, fusion and combination thereof of other genes of interest. The streamlined methods improve the consistency and simplicity of non-invasive detections of biomarkers.
Owner:PREDICINE INC
Ubiquitin ligase gene participating in symbiotic nodulation of leguminous plants, and application thereof
InactiveCN103290034APositive regulation of nodulationPositive regulation of symbiotic nodulationEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionCDNA librarySequence analysis
The invention discloses a ubiquitin ligase gene participating in symbiotic nodulation of leguminous plants and application thereof. A membrane outer part of crowtoe symbiotic receptor kinase serves as bait; partial sequence of the gene is screened from a crowtoe AD-cDNA library; and full-length sequence is obtained through amplification by gene splicing and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) methods according to two expression sequence tags Lj-G0027263 and Lj-G0032470 overlapped with the partial sequence. Gene cloning and sequencing comparative analysis proves that the gene is cloned from crowtoe genome and cDNA. Sequence analysis and in vitro ubiquitin activity test prove that the gene is novel ubiquitin ligase. According to the application of the gene to the leguminous plants, the biological function of the gene in a symbiotic nodulation process is researched by RNAi and overexpression methods. The results show that, compared with the control plants, the plants with he gene has the advantages that the number of root nodules is increased obviously after overexpression, and the number of root nodules is reduced obviously after RNAi, so the gene has an application prospect in symbiotic nitrogen fixation of the leguminous plants.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
A method and application for mining low-abundance expressed genes and systematically identifying splice variants using nested PCR combined with gene-specific primers for reverse transcription
InactiveCN102260670AImprove digging efficiencyEfficient enrichmentMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSequence analysisAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method for excavating a low-abundance expression gene and system identification splicing variants by using a reverse transcription technique combining nested PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) with gene-specific primers (GSP), and application thereof. The method is based on reverse transcription PCR of 3'GSP1, gradient PCR is utilized to search for the best annealing temperature of each gene for each primer pair combination, and whether it is a new splicing variant is judged on the basis of GSP nested PCR sequencing and sequence analysis. The method is simple and easy to implement, has the advantages of favorable repetitiveness, high stability and strong reliability, greatly saves the experimental cost, can be applied to excavation of eucaryote low-abundance expression gene under different physiopathological states, and identification and detection of high / low-abundance expression gene splicing variants, and can be used for excavating low-abundance expression gene and identifying and detecting splicing variants of high expression gene and low-abundance expression gene. The method can be used for detecting both known splicing variants of targeted genes and unknown splicing variants of genes, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Broad Spectrum of Streptococcus Lyase and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20180104316A1High activityIncrease enzyme activityAntibacterial agentsMilk preparationEscherichia coliBacteroides
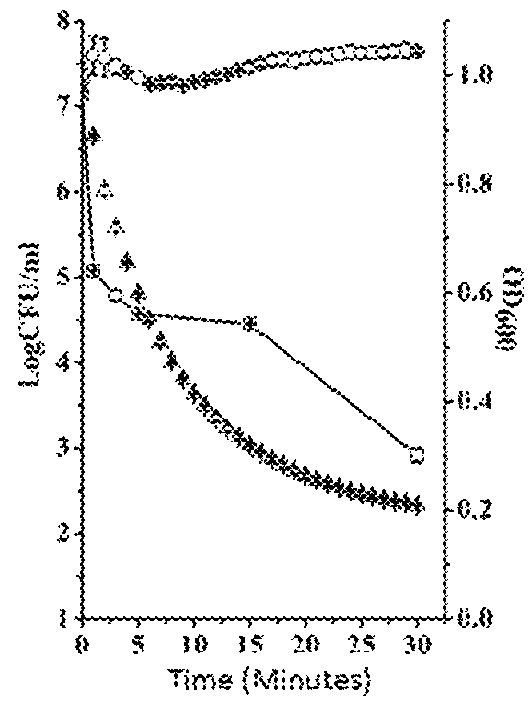
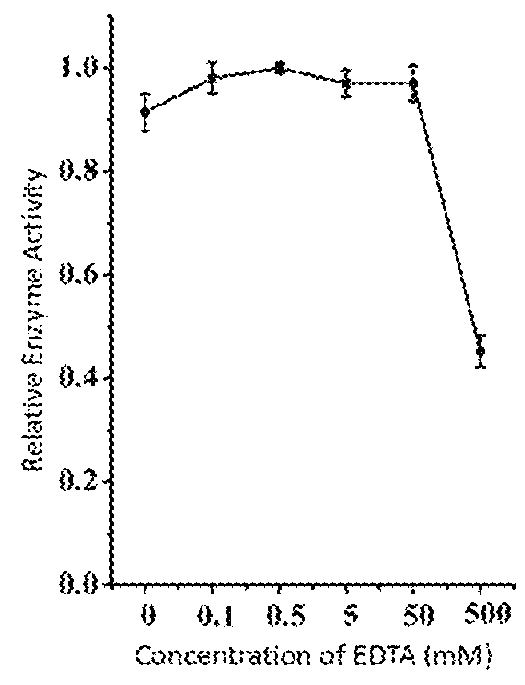
This invention discloses a lysin that can kill many species of Streptococci. A new lysin, ClyR, was constructed by the gene splicing method. The ClyR can effectively kill different species of Streptococci, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus suis, Streptococcus uberis, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus equi, and various Enterococci and Staphylococcus aureus. ClyR shows good stability and is not sensitive to EDTA and high concentration of NaCl. Moreover, the ClyR is active in a wide range of pH and maintains high activity in pH 5-11. Recombinant protein ClyR is well expressed in E. coli stain BL21 (DE3). High doses of ClyR showed no apparent toxicity in mice. Furthermore, administration of 0.8 mg per mouse once is able to completely protect the mouse infected with lethal doses of Group B Streptococci. The ClyR can be used alone or in combination with different forms of reagents and solutions, for the control of a variety of Streptococci and for the treatment of infections caused by these bacteria. It has a broad application prospect.
Owner:PHAGELUX INC
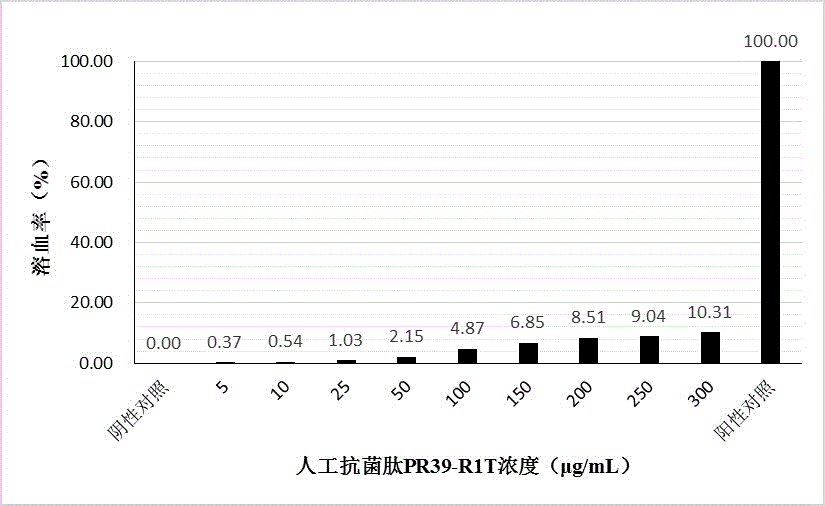
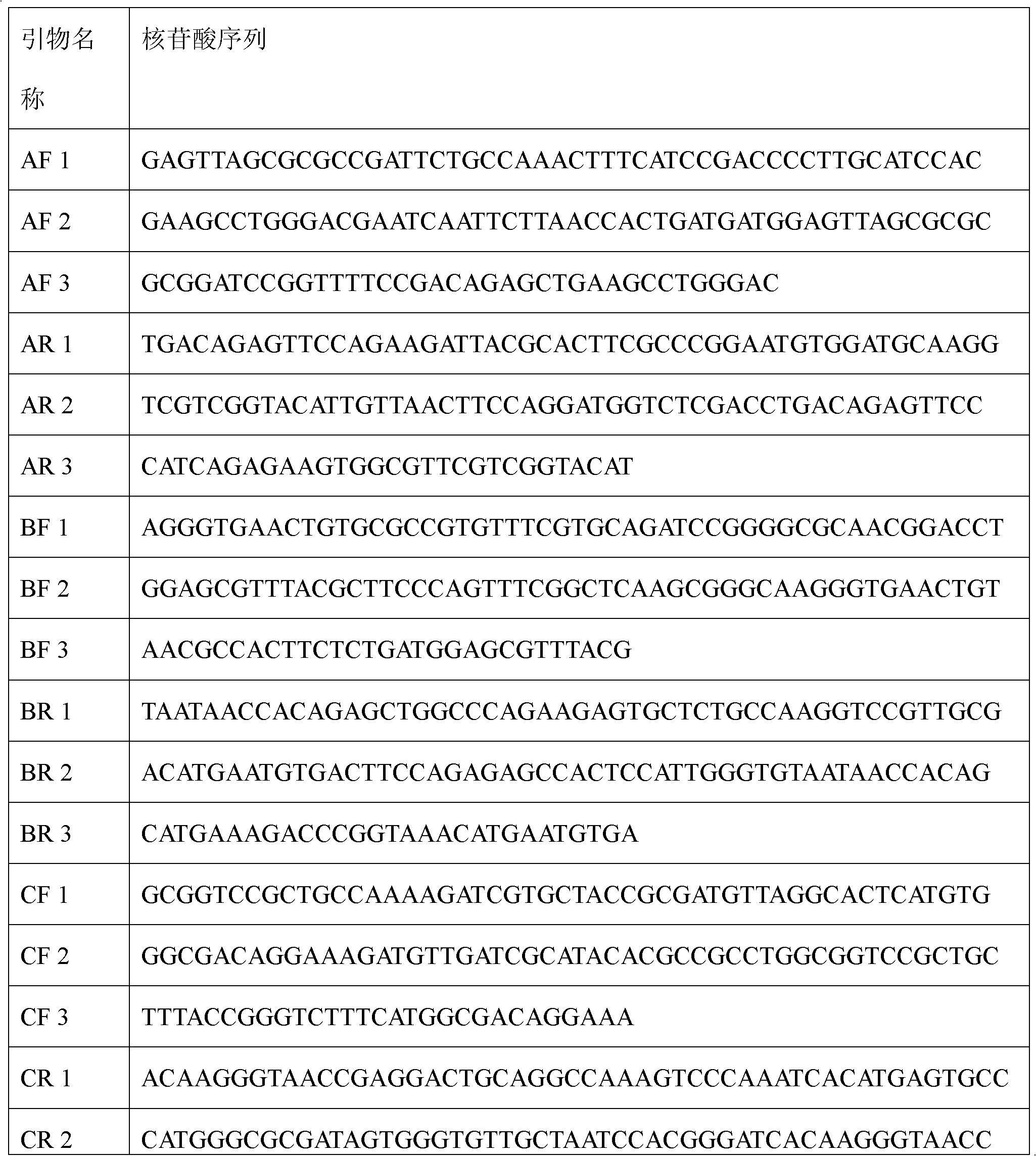
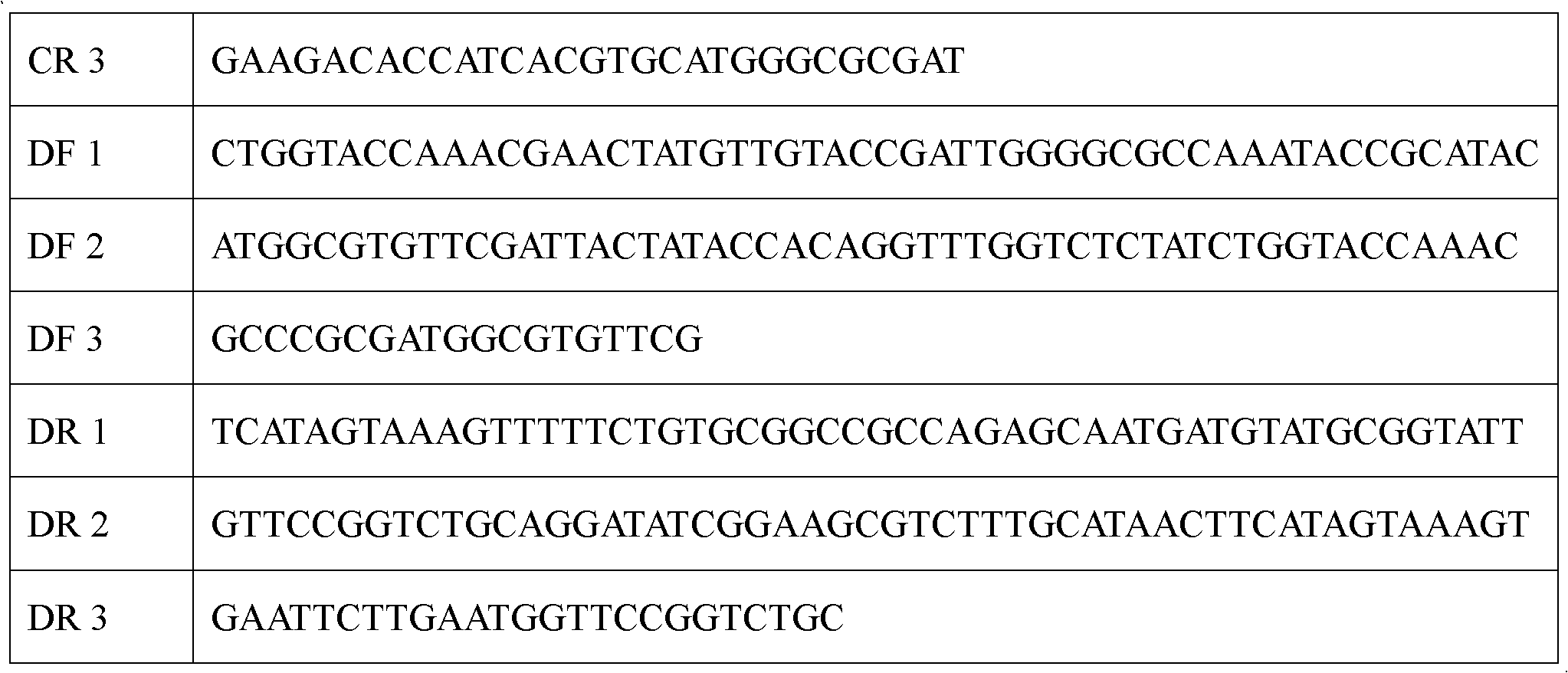
Preparation method of artificial antibacterial peptide PR39-R1T and application thereof
InactiveCN104987367AStrong broad-spectrum antibacterial activityNo hemolytic activityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliDisease
The invention relates to a preparation method of an artificial antibacterial peptide PR39-R1T and application thereof. Amino acid sequences of the artificial antibacterial peptide PR39-R1T are designed artificially, and escherichia coli preference codons are adopted for designing and coding the amino acid sequences of the artificial antibacterial peptide; an overlap region amplification gene splicing method is adopted for synthesizing target genes to construct a prokaryotic expression vector, and the prokaryotic expression vector is converted into escherichia coli BL21 or Rosetta for induction expression; enzyme digestion and nickel ion affinity chromatographic purification are performed on an expression product through enterokinase, and then the artificial antibacterial peptide PR39-R1T can be obtained. The antibacterial peptide has the high broad-spectrum antibacterial activity, can inhibit gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria and does not have the hemolytic activity. Therefore, the artificial antibacterial peptide can be used as a novel antibacterial agent, has the good application prospect on the aspects of food corrosion prevention, disease treatment and the like, and has the developing potential. The preparation method is high in expression efficiency, simple in separation and purification, low in production cost, good in stability and capable of being applied to large scale production.
Owner:刘诚
Enterovirus 71 capsid protein 3 recombinant antigen and application thereof
InactiveCN102628054ATo clarify the meaning of immunodiagnosisEfficient expressionBacteriaAntiviralsEscherichia coliAntigen
The invention discloses an enterovirus 71 capsid protein 3 recombinant antigen belonging to the technical field of virus detection and an application thereof. The gene nucleotide sequence of the recombinant antigen is showed in a sequence table SEQ ID NO: 1. The gene splicing technology is adopted, and through the annealing extending polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology, a VP3 gene for codon optimization escherichia coli is obtained, the optimization VP3 gene is efficiently expressed in escherichia coli, and a corresponding recombined EV71-VP3 gene is obtained through an affinity chromatography method in purification mode. The obtained EV71-VP3 antigen can have a specific immune response with serum of patients of hand-foot-and-mouth disease, and the recombinant antigen can improve detection sensitivity of hand-foot-and-mouth disease by combining with EV71-VP1 for use and can be used for clinical diagnosis of EV71 acute infection.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Mini-gene splicing reporter plasmid and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN107384917ASplicing effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDmd geneSplicing regulatory element
The invention provides a mini-gene splicing reporter plasmid and construction method and application thereof. A sequence of the mini-gene splicing reporter plasmid is as shown in a sequence table <400>1. Three non-continuous sequences on a DMD gene are obtained through PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and inserted to pcDNA 3.1 respectively to construct the mini-gene splicing reporter plasmid. The mini-gene splicing reporter plasmid can be used for identifying and analyzing splicing regulation elements in exons and introns and detecting whether micromutation (point mutation and microdeletion / repetition) affects splicing of the exons or not.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for quickly amplifying target genes from genome DNA
InactiveCN101798570AFast and accurate cloningUnlimited amplification lengthDNA preparationGene splicingExon
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, in particular to a method related to gene cloning. The method for quickly amplifying target genes from a genome DNA comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing the genome DNA; (2) designing amplification primers of gene exons; (3) carrying out exon amplification for respectively amplifying each exon; and (4) amplifying gene segments. In the invention, by using a special primer design method, required exons are firstly amplified from the genome and then purified and mixed, and the primers at both ends are used for amplifying the required target genes in a Touch-down program. The gene splicing method avoids the preparation of RNA and a process of synthesizing cDNA by reverse transcription, thus the gene cloning can be quickly and accurately finished within several hours. Meanwhile, any cDNA sequence the sequence information of which is known can be cloned by applying the method, and the amplification length is not limited.
Owner:北京良润生物科技有限公司
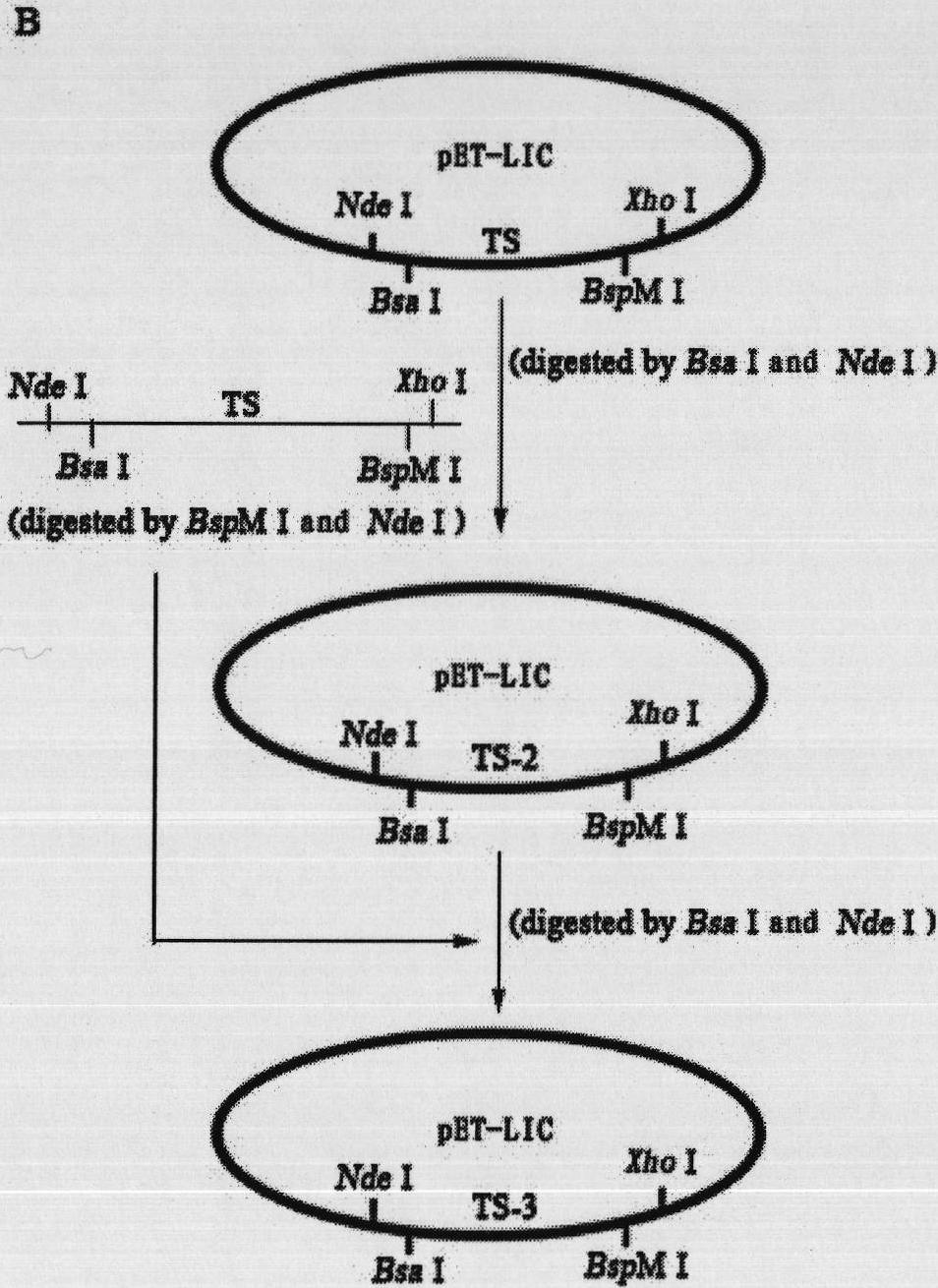
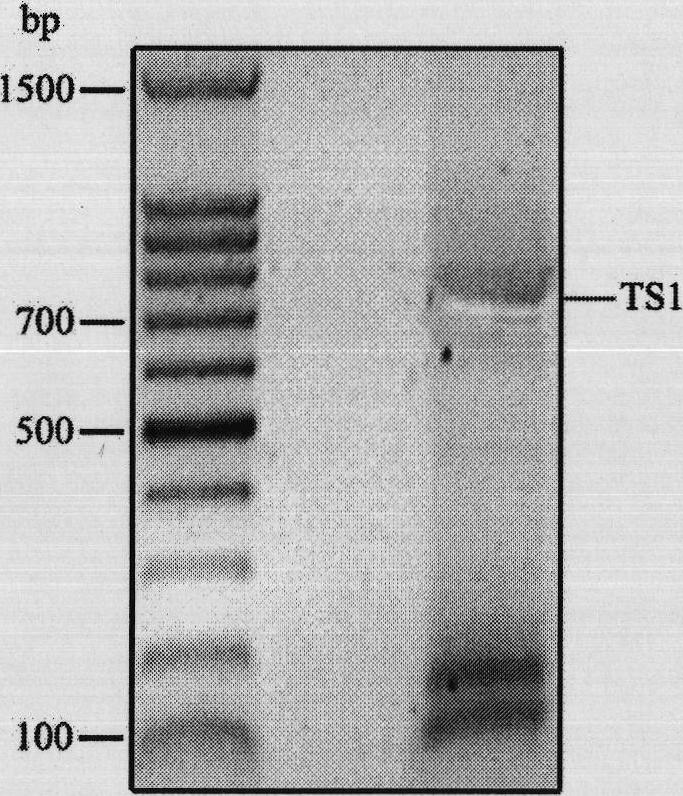
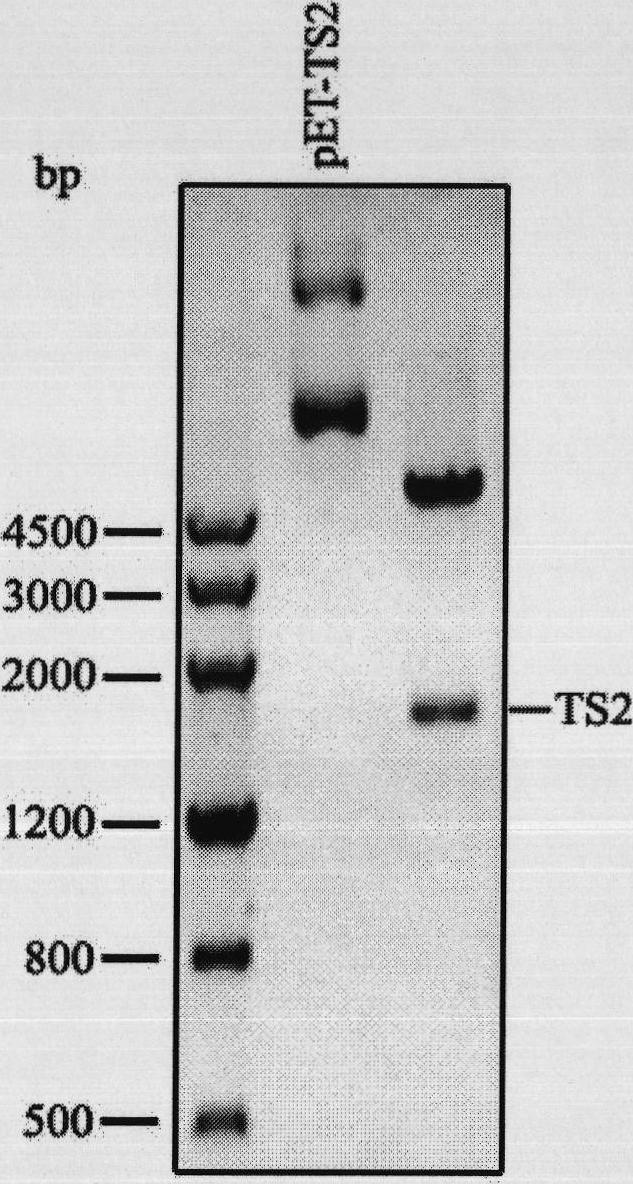
Repeated module gene-splicing method
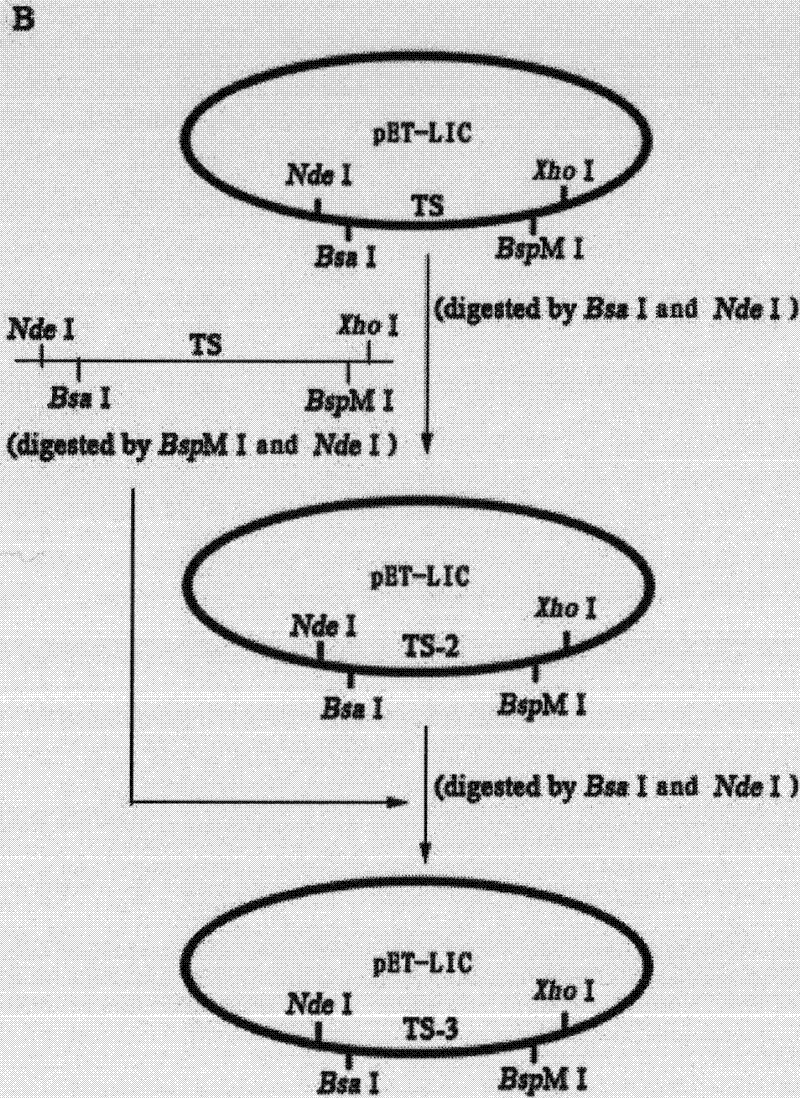
InactiveCN101805747ARealize repeated splicingRealize "seamless" connectionVector-based foreign material introductionRestriction Enzyme Cut SiteCompetent cell
The invention relates to a repeated module gene-splicing method, which includes the following steps: (1) two PCR primers are utilized to amplify target gene; (2) the PCR primers and plasmid pET-LIC are cut by double restriction enzymes, segments are connected with carrier, and after competent cells are transformed, plasmid pET-TS is obtained; (3) the plasmid pET-TS is cut by double restriction enzymes, and plasmid segments are recovered, and are then connected with the target gene segments to transform, so that plasmid pET-TS2 is obtained; (4) the plasmid pET-TS2 is cut by double restriction enzymes, and plasmid segments are recovered, and are then connected with the target gene segments to transform, so that plasmid pET-TS3 is obtained; (5) the plasmid and target gene PCR product are cut by double restriction enzymes, and the same method is utilized to continuously insert repeated segments. The invention repetitively splices a plurality of repeated module genes, moreover, no restriction enzyme cutting site residues are left between the modules, thereby the seamless connection between the repeated modules is truly realized, and moreover, splicing is directional.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
High-efficiency streptococcus pneumonia chimeric lyase and its mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN108823193AEfficient killingAvoid infectionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliStreptococcus pneumoniae
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and especially relates to high-efficiency streptococcus pneumonia chimeric lyase and its mutant and an application thereof. A gene splicing means is employed, a brand new chimeric lyase ClyJ is constructed, and the mutants ClyJ-1, ClyJ-2 and ClyJ-3 are constructed through gene fragment insertion and deletion. The ClyJ and its mutanthave good stability, and efficiently kill streptococcus pneumonia both in vitro and in vivo; the ClyJ and its mutant can better expressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3), and have latent prevention andtreatment capability for streptococcus pneumonia infection through high-efficiency cracking activity on streptococcus pneumonia. the ClyJ and its mutant can be individually used, or can be used as anadditive for compatibility with different forms of reagents and solutions, and have large application prospect for controlling the streptococcus pneumonia and treating infection due to streptococcuspneumonia.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for using polyethyleneimine to strengthen sensitivity and specificity of PCR gene splicing by overlap extension
InactiveCN106367414AEasy to synthesizeEfficient synthesisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGene splicingTrue positive rate
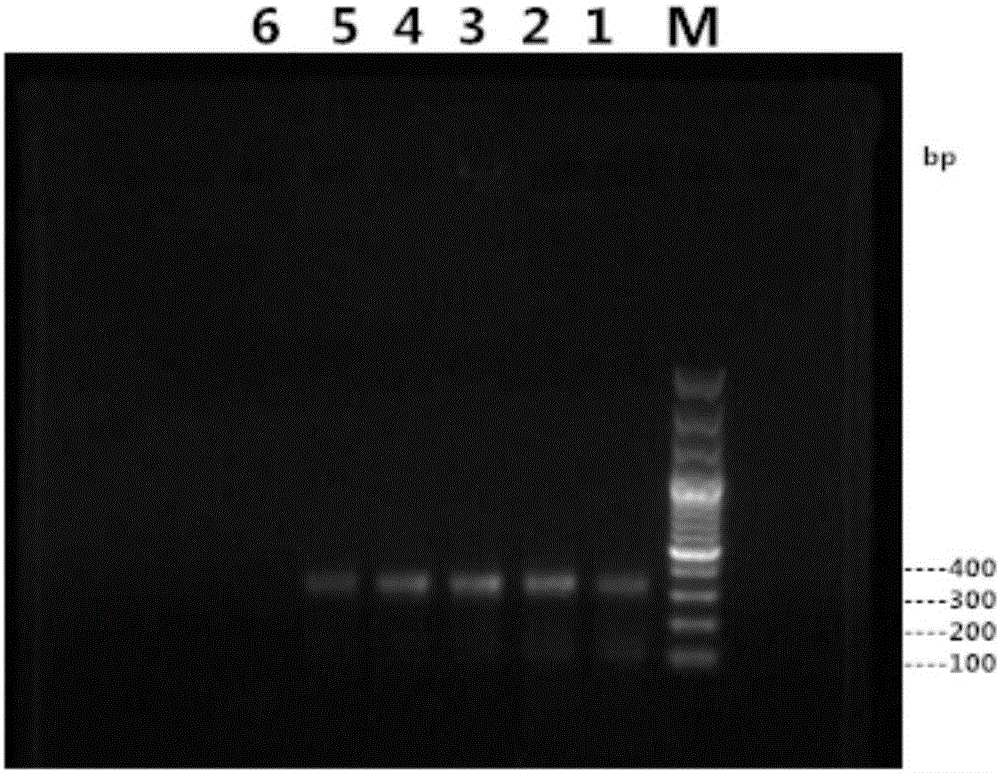
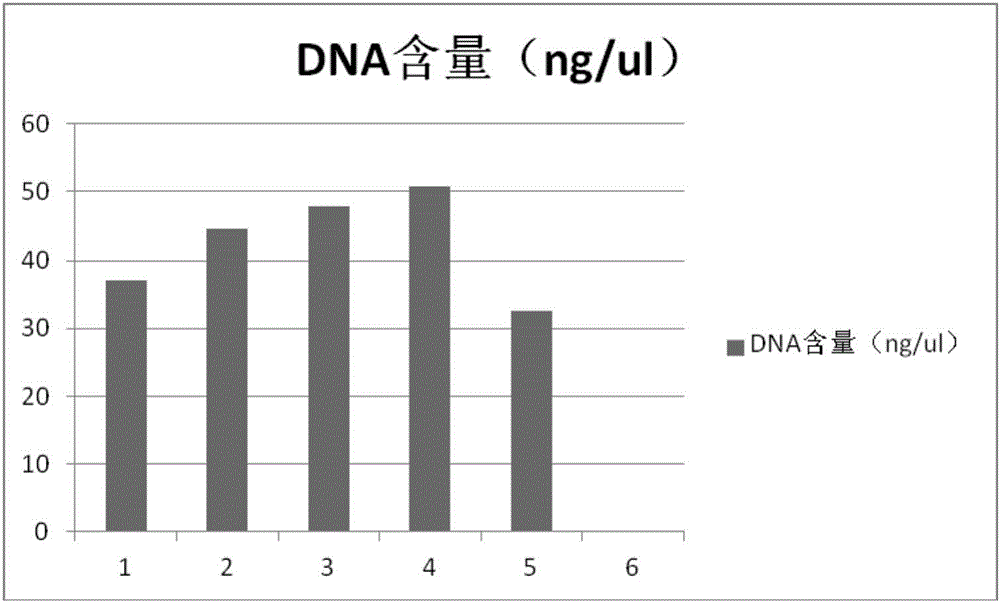
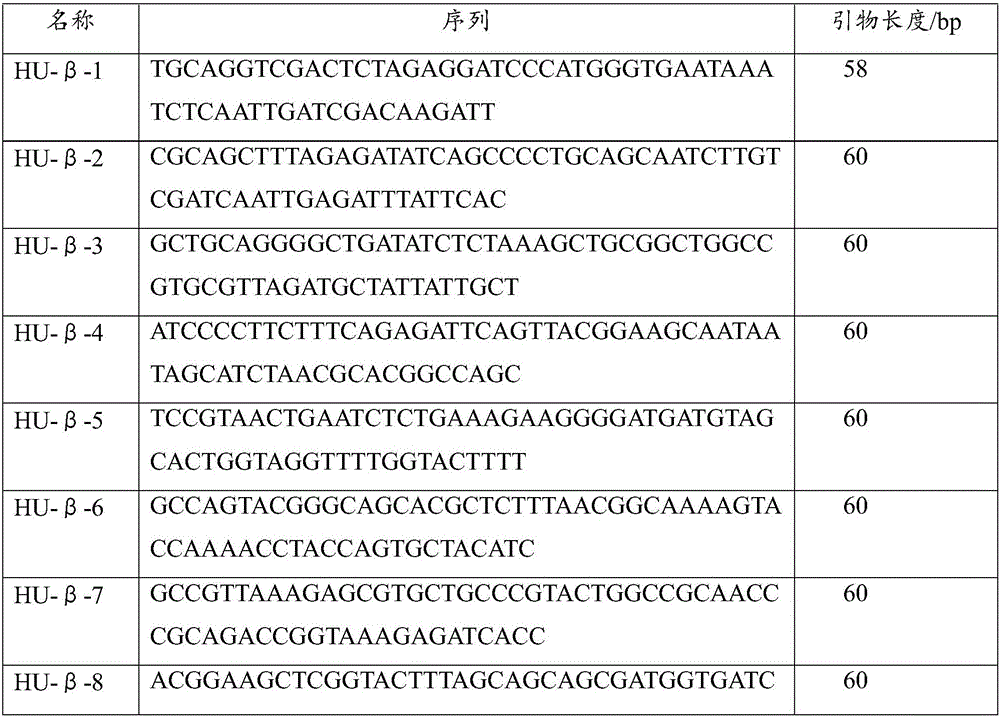
The invention discloses a method for using polyethyleneimine to strengthen sensitivity and specificity of PCR gene splicing by overlap extension. The method comprises the steps of designing an HU-Beta primer sequence which needs to be synthesized, and obtaining a blended overlapping oligonucleotides template, wherein every sequence contains 25bp overlapping oligonucleotides template so as to cover the entire DNA(200-1500 basic group) sequence; adding DNA polymerase, head and tail primer, and the solution of blended overlapping oligonucleotides which is used as a template in the last step into into PEI ,the volume of which should be 10<-5>-10<-13> that of the DNA polymerase, head and tail primer, and the solution of blended overlapping oligonucleotides; carrying out repeated circulation according to three steps of melting, annealing, extending of conventional PCR, synthesizing and amplifying the target nucleic acid segment. The method for using polyethyleneimine to strengthen sensitivity and specificity of gene splicing by overlap extension can specifically and efficiently synthesize and amplify the target nucleic acid sequences.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Broad spectrum of Streptococcus lyase and use thereof
ActiveUS9993532B2Increase enzyme activityHigh activityAntibacterial agentsMilk preparationEscherichia coliBacteroides
This invention discloses a lysin that can kill many species of Streptococci. A new lysin, ClyR, was constructed by the gene splicing method. The ClyR can effectively kill different species of Streptococci, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus suis, Streptococcus uberis, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus equi, and various Enterococci and Staphylococcus aureus. ClyR shows good stability and is not sensitive to EDTA and high concentration of NaCl. Moreover, the ClyR is active in a wide range of pH and maintains high activity in pH 5-11. Recombinant protein ClyR is well expressed in E. coli stain BL21 (DE3). High doses of ClyR showed no apparent toxicity in mice. Furthermore, administration of 0.8 mg per mouse once is able to completely protect the mouse infected with lethal doses of Group B Streptococci. The ClyR can be used alone or in combination with different forms of reagents and solutions, for the control of a variety of Streptococci and for the treatment of infections caused by these bacteria. It has a broad application prospect.
Owner:PHAGELUX INC
A kind of lyase and application thereof for internally lysing Escherichia coli
ActiveCN104762285BEfficient self-cleavageNo pollution in the processFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousBacteroides
The invention discloses a lyase of self-cleaving escherichia coli, and applications thereof. A brandnew lyase ClyN is constructed by adopting gene splicing means, the lyase can result in the self-cleaving of the host escherichia coli after being expressed in the escherichia coli, to release intracellularly expressed ATP and protein. Recombinant ClyN expression plasmid can be duplicated in the escherichia coli BL21(DE3), and express for 15 min under the induction of IPTG to observe the obvious phenomenon of inducing the escherichia coli to self-cleave, and the induced cleaving efficiency achieves 99.8%. When the host bacteria express heterologous enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP), EGFP can be released in solution after escherichia coli is cleaved, and the release efficiency is 89% of direct ultrasonic breaking efficiency. Therefore, the ClyN can be used for extracting and release of heterologous protein after expression in the escherichia coli, thus having wide application prospects.
Owner:靶抗生物医药科技股份有限公司
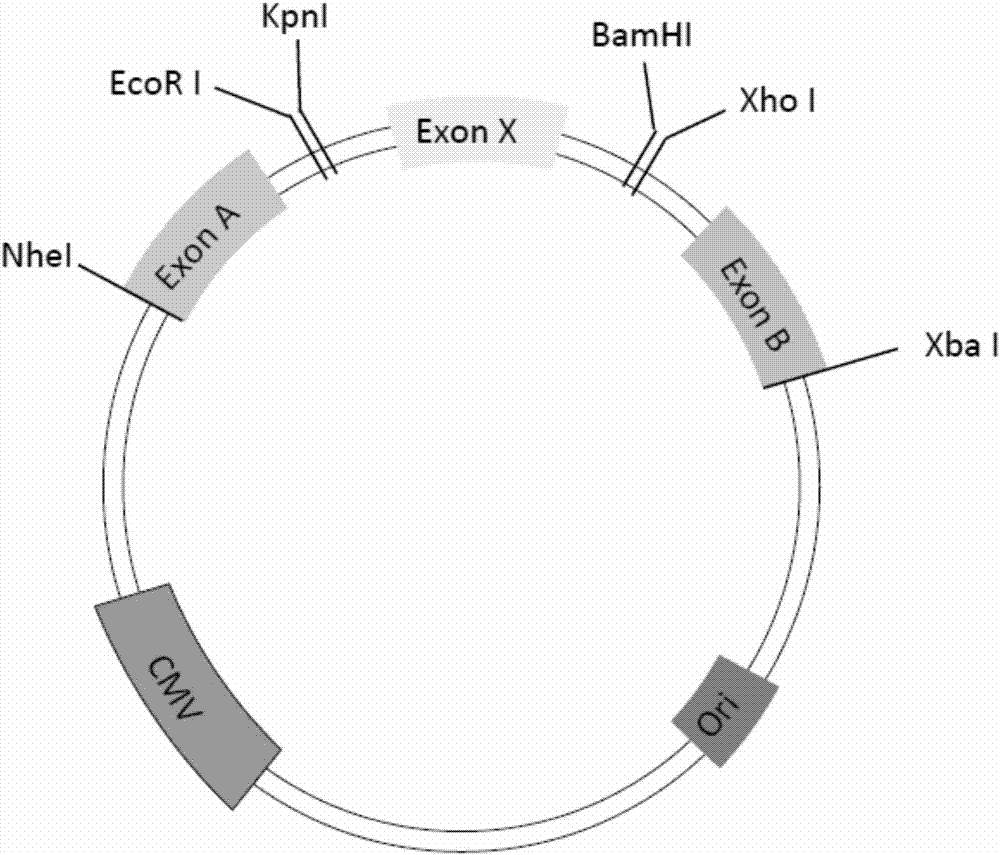
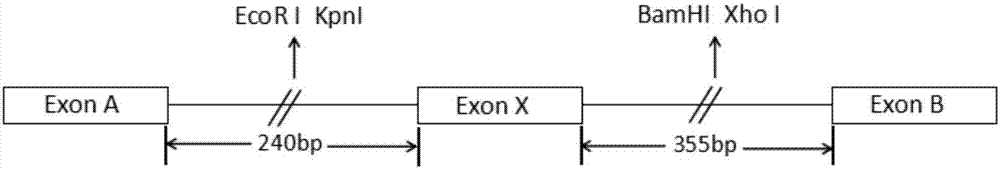
Plasmid for verifying influence of human gene Intron variation on gene splicing and construction method and application thereof
PendingCN113817772ACorrect splicingMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorGene splicingLiving body
The invention provides a plasmid for verifying the influence of human gene Intron variation on gene splicing. An Intron of a gene to be verified is used for replacing Intron1 or Intron2 of a variable splicing reporter plasmid pCDNA3.1-EGFP-AS to form a minigene plasmid containing the Intron of the gene to be verified. The invention further provides a construction method and application of the plasmid. By forming the minigene plasmid containing the Intron of the gene to be verified and combining cell transfection and cDNA detection, the influence of the gene Intron variation on gene splicing can be embodied at the cell level and the living body level, and variable splicing practice can be detected at the transcription level.
Owner:浙江赛微思生物科技有限公司
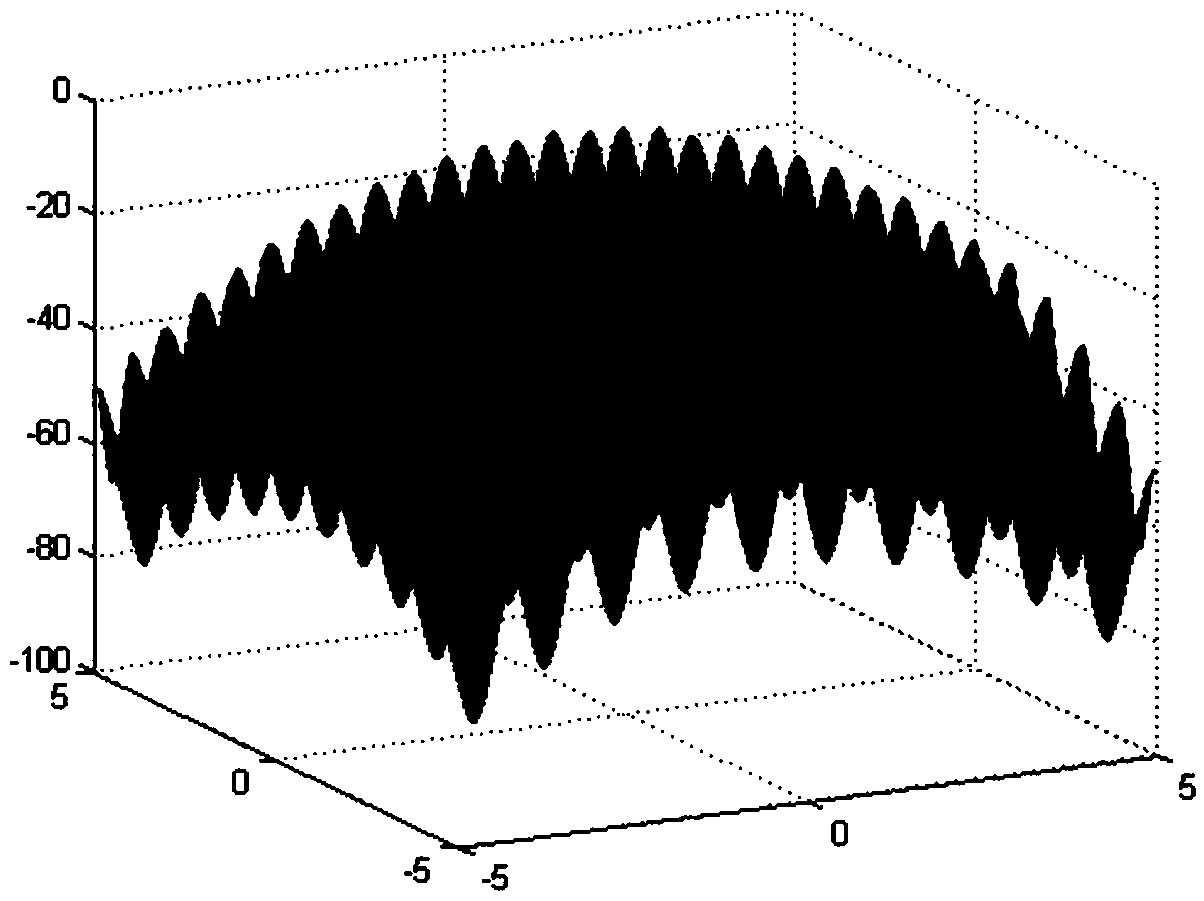
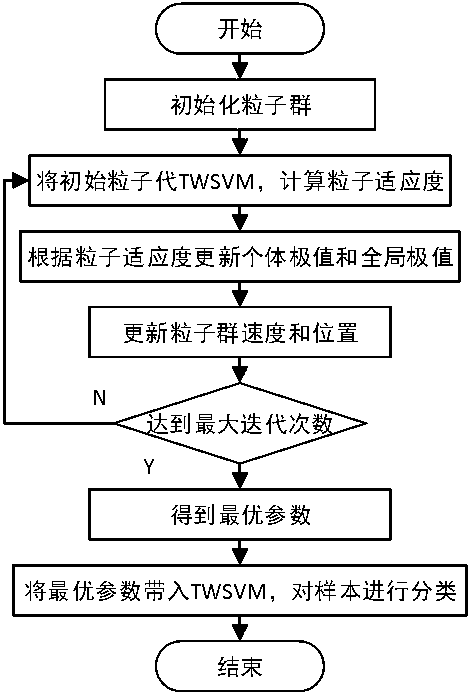
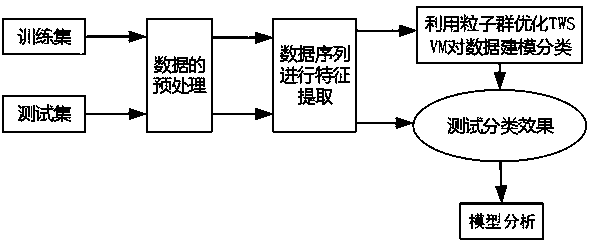
Gene splicing site identification model constructing method based on particle swarm optimization twin support vector machine
PendingCN111383710AImprove recognition accuracyOvercoming difficult setup problemsBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionGene splicingEngineering
The invention provides a gene splicing site identification model constructing method based on a particle swarm optimization twin support vector machine. Firstly splicing site identification is used asa two-class machine learning identification problem, and furthermore identification is finished through splicing sequence characteristic next to a site. Secondly, for aiming at a problem of relatively difficult twin support vector machine parameter setting in a class identification process, a particle swarm algorithm is used for parameter optimization of the twin support vector machine, thereby further improving the identification performance of the splicing site and preventing parameter selecting blindness. An experiment result verifies feasibility of the method and can effectively improve splicing site identification rate and accuracy.
Owner:MINJIANG UNIV
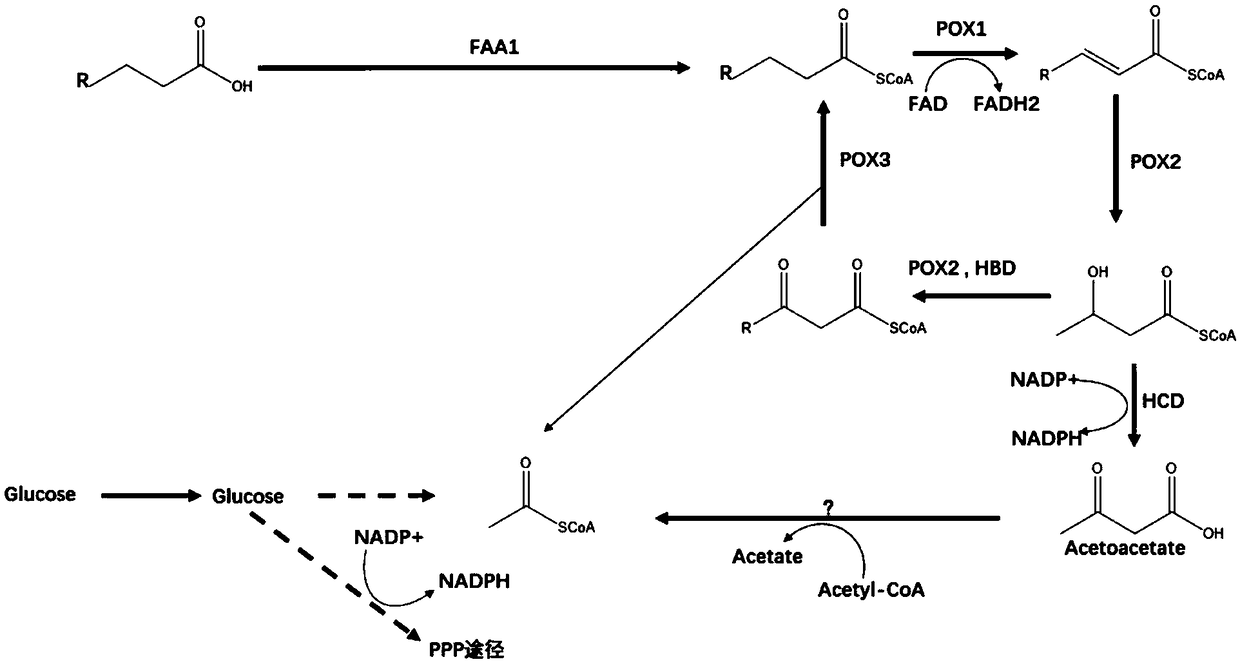
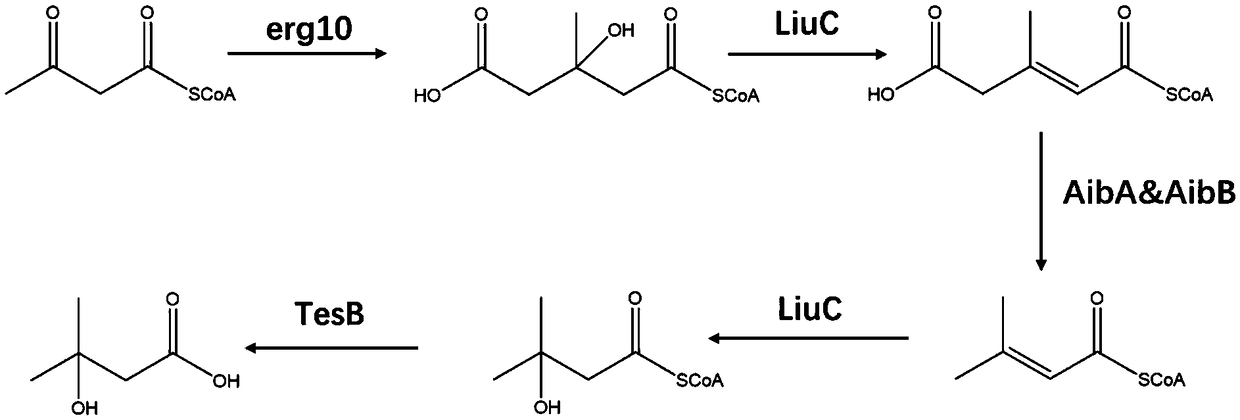
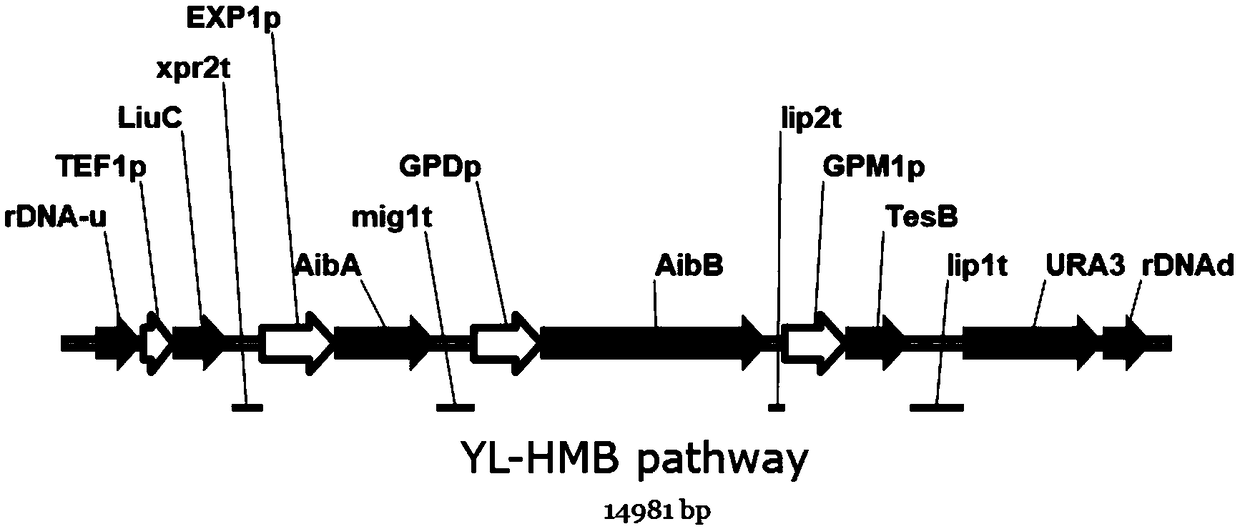
Construction method of engineering bacteria producing beta-hydroxy-beta-methyl butyric acid
ActiveCN109251940AIncrease productionWith industrial developmentFungiHydrolasesEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention discloses a construction method of engineering bacteria producing beta-hydroxy-beta-methyl butyric acid, which includes the following steps: by taking yarrowia lipolytica as chassis cells, interrupting and inactivating five genes involved in fatty acid degradation and metabolism in the genome of yarrowia lipolytica, i.e. pox2, pox3, hbd, hcd and faa1, to obtain a gene-splicing strain; and integrating genes of LiuC, AibA and AibB from myxococcus xanthus, and a TesB gene from Escherichia coli into the genome of the gene-splitting strain to obtain the engineering bacteria producingbeta-hydroxy-beta-methyl butyric acid. The engineering bacteria constructed by the invention can ferment and synthesize the target product HMB with glucose as a carbon source, and the maximum yield can reach 10g / L.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUARUI BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
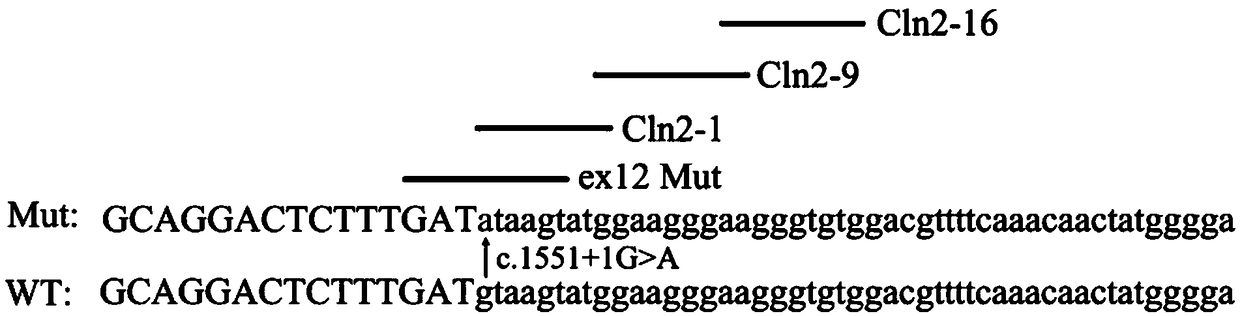
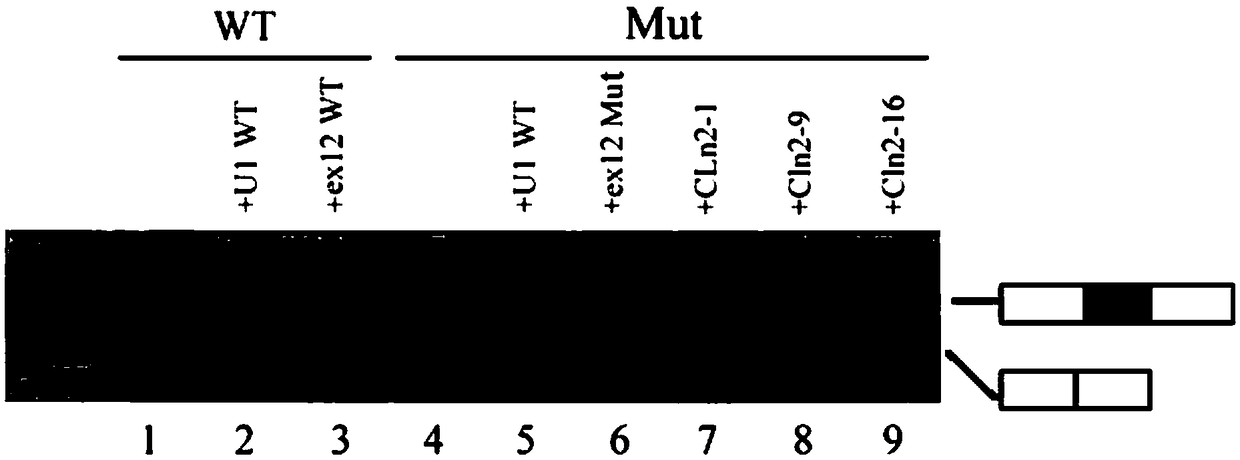
U1-snRNA for repairing TPP1 gene Pre-mRNA aberrant splicing and application of U1-snRNA
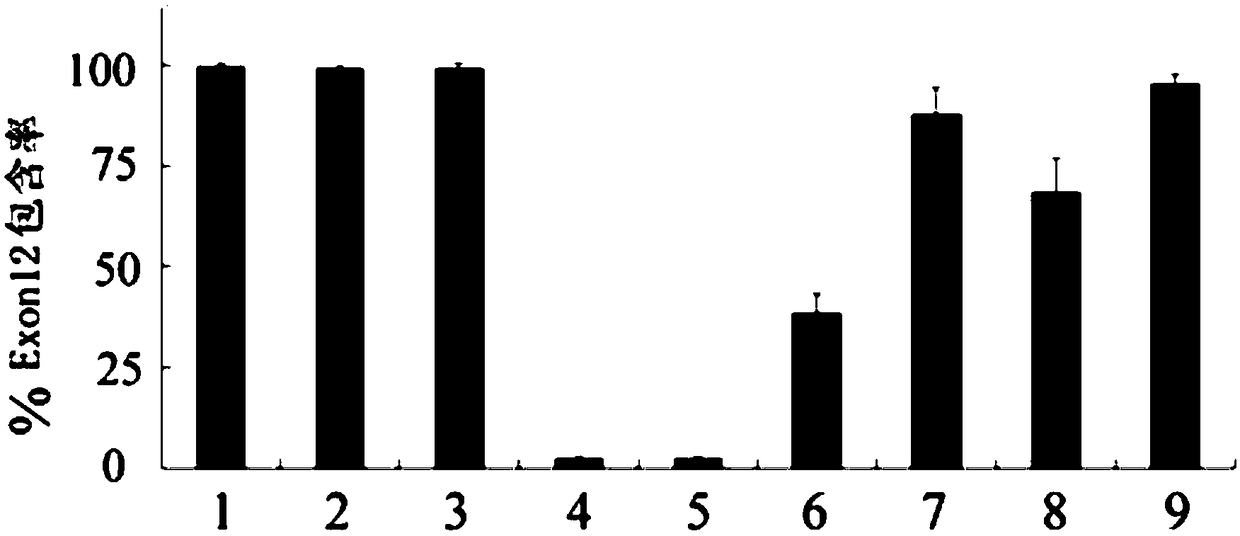
ActiveCN109486813AGain splicing repair efficiencyInhibit abnormal mRNA expressionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseSide effect
The invention discloses a U1-snRNA for repairing TPP1 gene splicing defects and a vector containing a base sequence for expressing the U1-snRNA. The base sequence for expressing the U1-snRNA sequentially comprises a U1-snRNA initial basic group, a sequence complemented with a TPP1 gene Exon12 donor splicing site or a downstream intron sequence target and a U1-snRNA downstream sequence, and the U1-snRNA downstream sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.20. The U1-snRNA is from a nucleic acid molecule prepared according to a TPP1 gene donor splicing site or donor splicing site downstream intron sequence. By the aid of a U1-snRNA technique, U1-snRNA of a target gene serves as a target medicine, and repairing is implemented in the splicing process of Pre-mRNA, so that aberrant mRNA expression caused by splicing site mutation is effectively restrained. The U1-snRNA has the advantages of high specificity, high efficiency and small side effect, can make up for the deficiency of current treatment means of diseases caused by aberrant splicing and possibly serves as a new method for treating specific types of diseases in the near future.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Repeated module gene-splicing method
InactiveCN101805747BRealize repeated splicingRealize "seamless" connectionVector-based foreign material introductionCompetent cellRestriction Enzyme Cut Site
The invention relates to a repeated module gene-splicing method, which includes the following steps: (1) two PCR primers are utilized to amplify target gene; (2) the PCR primers and plasmid pET-LIC are cut by double restriction enzymes, segments are connected with carrier, and after competent cells are transformed, plasmid pET-TS is obtained; (3) the plasmid pET-TS is cut by double restriction enzymes, and plasmid segments are recovered, and are then connected with the target gene segments to transform, so that plasmid pET-TS2 is obtained; (4) the plasmid pET-TS2 is cut by double restriction enzymes, and plasmid segments are recovered, and are then connected with the target gene segments to transform, so that plasmid pET-TS3 is obtained; (5) the plasmid and target gene PCR product are cutby double restriction enzymes, and the same method is utilized to continuously insert repeated segments. The invention repetitively splices a plurality of repeated module genes, moreover, no restriction enzyme cutting site residues are left between the modules, thereby the seamless connection between the repeated modules is truly realized, and moreover, splicing is directional.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Murine IL-27 recombinant protein eukaryotic expression vector and construction method
InactiveCN102816794AHigh expression efficiencyEasy to purifyVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
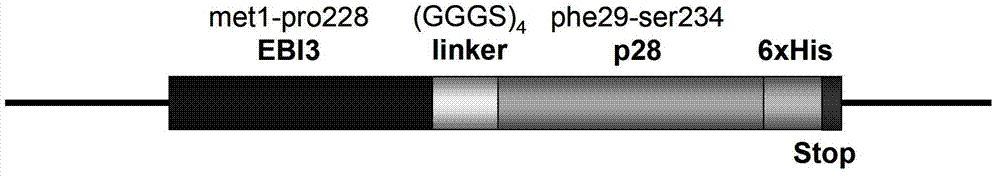
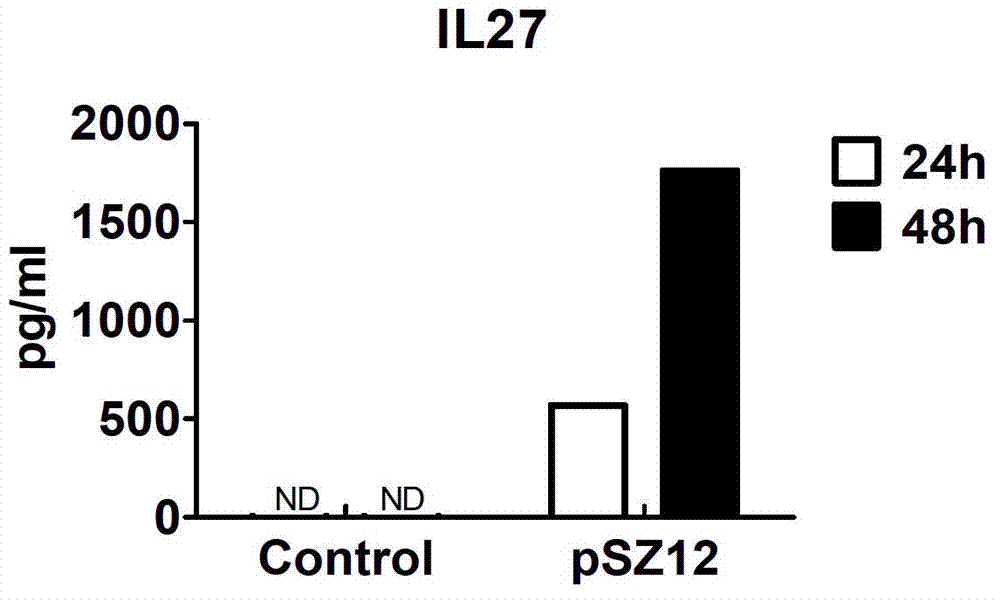
The invention discloses a murine IL-27 recombinant protein eukaryotic expression vector and a construction method. The construction process comprises the following steps that primers are designed to amplify the cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of encoding mouse EBI3 amino acids 1-228 and the cDNA sequence of encoding mouse p28 amino acids 29-234; and then an integrated DNA fragment is obtained by an SOEPCR (gene splicing by overlap extension polymerase chain reaction) method. The fragment is connected with a pcDNA3.1 + vector to obtain a murine IL-27 recombinant protein eukaryotic expression vector pSZ12. EBI3 and p28 are connected by the pre-designed amino acid encoding sequence. The vector constructed by the invention can not only effectively express a heterodimer IL-27 formed by EBI3 and p28, but also contain 6 * histidine encoding sequences to greatly facilitate the purification of recombinant protein. The key fragment can be cloned to other vectors so as to facilitate the application of protein expression in different cases, and an effective tool is provided for the study of the IL-27 function and the gene therapy method.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
High-temperature polyphenol oxidase and application thereof in phenol-containing wastewater treatment
ActiveCN113462701AHigh catalytic efficiencyImmobilised enzymesBacteriaMembrane enzymesOxidative enzyme
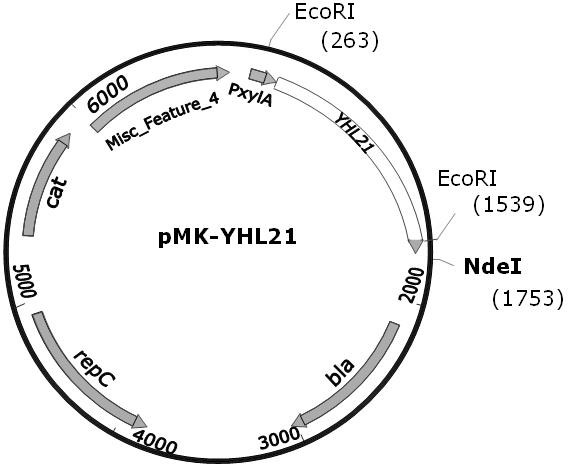
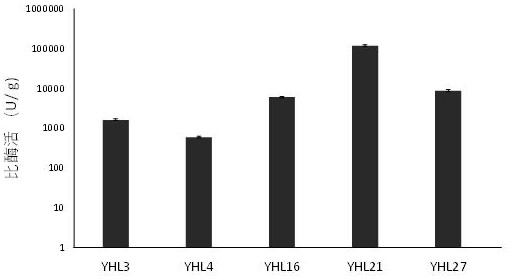
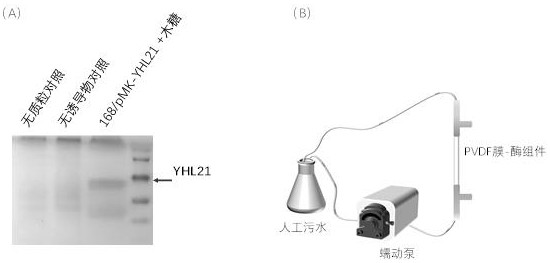
The invention discloses a gene and a polypeptide sequence of polyphenol oxidase YHL21. The polyphenol oxidase is confirmed by gene splicing and high-throughput screening of enzyme performance, and has the advantages of wide temperature-resistant range, strong high-temperature catalytic performance, easy membrane immobilization and the like, wherein functional enzyme is constructed by a single peptide fragment. The invention also discloses a method for carrying out recombinant expression and secretion production on the polyphenol oxidase YHL21 in a bacillus subtilis strain 168, and a method for immobilizing the recombinant polyphenol oxidase on the surface of a membrane by utilizing a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane, and the membrane enzyme composite system can stably and efficiently degrade organic matters such as phenol, parachlorophenol and the like in an aqueous solution. Enzyme engineering optimization is carried out through gene splicing, polyphenol oxidase capable of efficiently degrading phenolic pollutants is obtained, recombinant secretory expression is carried out through bacillus subtilis, enzyme immobilization is carried out through PVDF, and the catalytic efficiency of enzyme is improved.
Owner:FOSHAN YUHUANG ECOLOGICAL ENVIRONMENT TECH
A one-step, seamless, non-homologous, multi-segment gene splicing transformation method and its kit
ActiveCN106754883BLow costGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGene splicingPhosphorylation
The invention discloses a one-step seamless, non-homologous and multi-fragment gene splicing method. The steps of DNA fragment phosphorylation, DNA fragment bridging and exponential type amplification of a ligation product are finished in one pipe through thermal cycling similar to PCR. The method has the following advantages: (1) ligation reaction is finished by one step, so that high cost caused by using a phosphorylation primer is avoided; (2) the concentration of DNA, the concentration of a bridging primer and components and a proportion of a buffer solution are optimized, and the ligation reaction with high reliability and good repeatability is reached; (3) DNA fragments are seamlessly ligated with one another without introduction of excess nucleotide; (4) non-DNA sequence dependency is realized; (5) the multi-fragment gene splicing ability is efficient; (6) the ligation product is amplified while ligation, so that the concentration of a product is greatly increased, and efficient conversion and subsequent experiment needs are guaranteed; and (7) the cost is low compared with that of the conventional restriction enzyme ligation method.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Hog cholera antibody ELISA diagnosis reagent kit
The invention relates to an ELISA diagnosis kit for swine fever virus. In the invention, by gene splicing technology, the swine fever virus E2 is jointed with secretion signal peptide sequence and purification label at two sides and is inserted into the autographa californica nucleopolyhedrosis virus expression vector so as to construct recombinant autographa californica nucleopolyhedrosis virus CGMCC No.2671 and to obtain coated ELISA swine fever virus Shimen Strain E2 gene soluble expression antigen. The kit of the invention is rapid, sensitive, and specific to the diagnosis and the immune evaluation of swine fever virus, and the diagnosis can be completed once within 2 hours.
Owner:CHINA INST OF VETERINARY DRUG CONTROL
Systems and methods for combined detection of genetic alterations
ActiveUS11174503B2Suppression of the sequencing and PCR errorsIncrease diversityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGene splicingSolid tissue
Owner:PREDICINE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com