Mini-gene splicing reporter plasmid and construction method and application thereof
A technology of reporter plasmid and construction method, applied in the field of mini-gene splicing reporter plasmid and its construction, can solve problems such as difficulty in grasping the relationship between mutation, splicing and splicing and diseases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Construction process of minigene splicing reporter plasmid
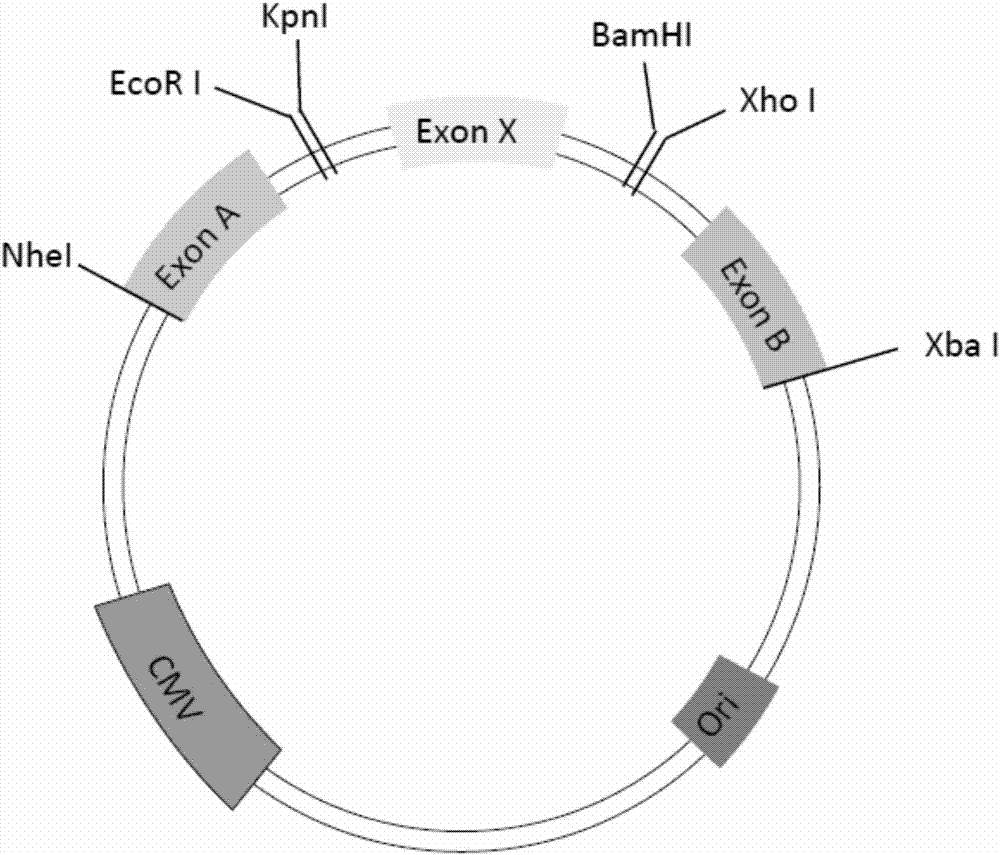
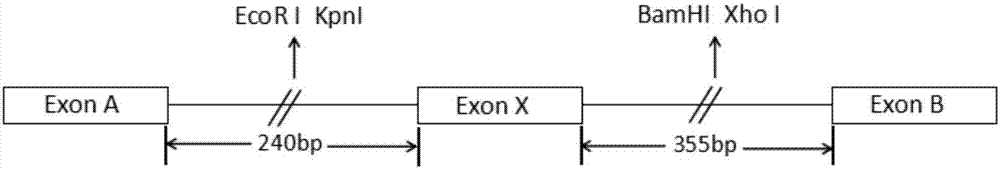
[0038] The non-contiguous sequences on the three DMD genes were obtained by PCR amplification, and were respectively inserted into pcDNA3.1 to construct the minigene reporter plasmid NKU-YC-1.
[0039] Materials and Reagents:
[0040] The vector pcDNA3.1 was purchased from Invitrogen, the LB culture plate and culture medium were purchased from Shanghai Sangon Biological Company, the competent Trans1-T1 was purchased from Quanshijin Bio Company, and the agarose recovery kit and T4 ligase were purchased from NEB Bio Company , the restriction endonucleases used in the experiment were purchased from TAKARA Biological Company.
[0041] (1) Using the genomic DNA of a normal person as a template, design primers Y1F-NheI (sequence shown in Sequence Listing 3) and Y1R-KpnI (sequence shown in Sequence Listing 4) for PCR amplification. The primers are as follows (where the underline is the restriction site):
[0042] ...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Construction method of mutant mini-gene
[0061] Design primers M-F: GTGGGCAGTAGATAAAGAATGAAGC
[0062] M-R:CTTTATCTACTGCCCACCTTCATTG
[0063] Using the NKU-YC-1 plasmid as a template, design primers M-F (sequence shown in Sequence Listing 9) and M-R (sequence shown in Sequence Listing 10) for PCR amplification. The primers are as follows:
[0064] M-F: GTGGGCAGTAGATAAAGAATGAAGC
[0065] M-R:CTTTATCTACTGCCCACCTTCATTG
[0066]
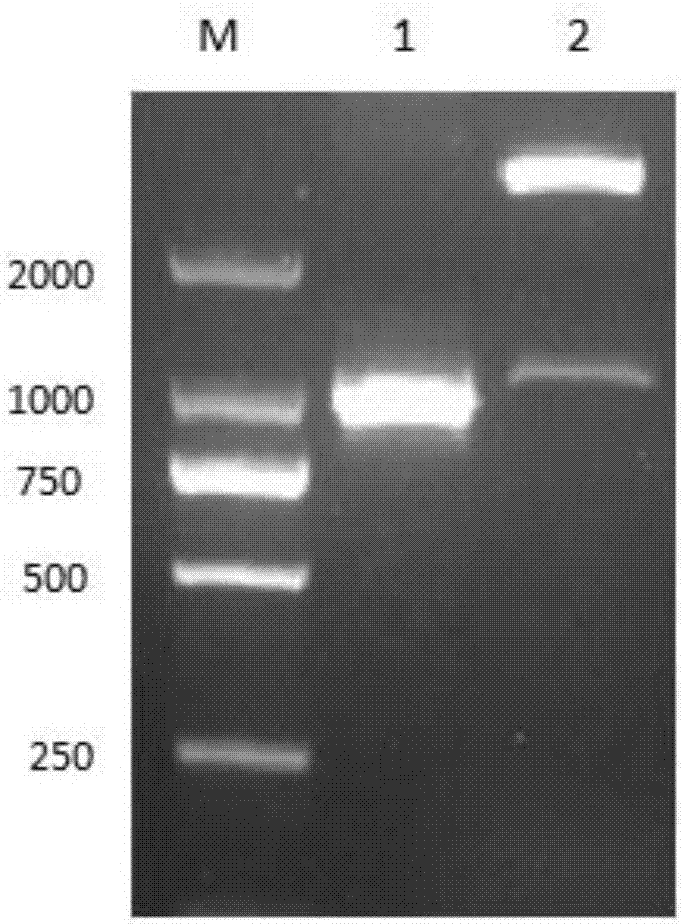
[0067] After mixing the components, put them into the PCR machine. PCR reaction parameters: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5min, denaturation at 94°C for 30s, annealing at 60°C for 30s, extension at 72°C for 10min, 35 cycles, and stop extension at 72°C for 5min. After the reaction was completed, 5 ul of the PCR product was taken for electrophoresis to detect the amplified product fragment, and the fragment size was about 5 kb. Take 20ul of the PCR product for DpnI enzyme digestion and digestion. The enzyme digestion system is as follows:
...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Functional validation of a mini-gene splicing reporter system
[0072] 1) The plasmid NKU-YC-1 was transfected into Hela cells by a liposome-mediated method. The transfection reagent used liposome Lipo2000 from Invitrogen Company. The transfection method refers to the instructions of the transfection reagent. The specific operations are as follows:
[0073] The night before, add 0.5ug plasmid and 8ul transfection reagent to 200ul serum-free medium, incubate at room temperature for 5min, so that the liposomes can fully wrap the plasmid, then add it to 2ml well-grown Hela cells, place in The incubator was cultured overnight, and the serum-free medium was replaced with serum-containing medium the next morning to continue culturing.
[0074] 2) RNA extraction: 48 hours after transfection, aspirate the culture medium, wash twice with PBS, add 500ul Trizol to wash repeatedly, and transfer to a 1.5ml centrifuge tube. Add 100ul of chloroform, shake vigorously for 15s, let stan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com