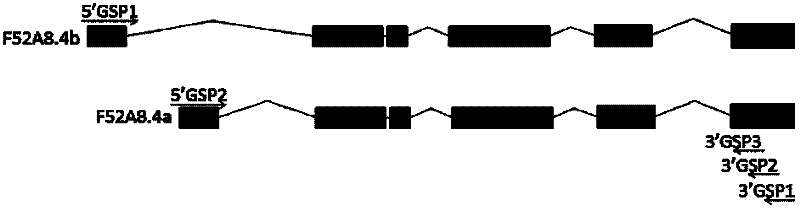
A method and application for mining low-abundance expressed genes and systematically identifying splice variants using nested PCR combined with gene-specific primers for reverse transcription
A technology for expressing genes and specific primers, applied in the field of biotechnology applications, can solve the problems of high false positives, high cost, no mining of low-abundance expressed genes, and systematic identification of splice variants.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1: Design of gene-specific primers (GSP) for mining low-abundance expressed genes and systematically identifying splice variants
[0042] The design of gene-specific primers (GSP) is automatically completed by the Primer3 program, and the main idea of the program design is as follows:
[0043] 5) Obtain the sequence of a gene splicing variant from the NCBI GenBank database, and analyze its gene structure according to the GenBank database records or using software such as splign, gmap, blat, blast;
[0044] 6) Search for possible candidate primer regions within the full-length cDNA sequence;
[0045] 7) Scoring the candidate primers, which consists of three parts, namely S=S basic +S end +S genome :
[0046] a) Primer quality basic score (S basic ): Scored according to the conventional primer quality evaluation system, that is, the primer length is 18-25bp, the GC content is about 50%, and the Tm is about 58°C. The closer to these parameters, the higher th...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2: Application of gene-specific primers (GSP) in combination with nested PCR technology in identification and discovery of low-abundance expression genes
[0061] Using gene-specific primers (GSP, taking the primers designed in Example 1 as an example) in combination with the application of nested PCR technology in the identification and discovery of low-abundance expression genes, the specific method includes the following steps (the flow chart is as follows: figure 1 shown):
[0062] 1. 3’GSP1-dependent RNA reverse transcription
[0063] Extracted total RNA (wild-type Caenorhabditis elegans N 2 strain or mouse) as a template, the first strand of cDNA of the corresponding gene was reverse transcribed. The 20 μl reverse transcription system and reverse transcription method based on 3’GSP1 are as follows (the reagents used are purchased from TOYOBO): (1). Total RNA 1 μg, corresponding gene 10 pmol / L 3’GSP1 1 μl, RNase Free H 2 O make up to 12μl, mix well, 65°C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com