Important effects of CaV2.1 channel in Ca<2+> dependent ischemic models
An ischemia, dependence technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problem of different severity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Ca v 2. Expression pattern of 1α1 subunit mRNA
[0038] We used in situ hybridization to assess Ca v 2. The distribution of 1α1 mRNA in wild-type mice (n=6), Rolling Nagoya (n=5) and Leaner mice (n=5); the distribution in the three mice is the same (data not shown). We detected a widespread expression of α1 subunit in the brains of all three mice using antisense probes, especially in the olfactory bulb neurons, cerebral cortex neurons, hippocampus neurons and cerebellum neurons There are strong expressions. However, no signal was detected after using the sense probe. We use real-time qRT-PCR to detect Ca V 2. The expression levels of 1α1 mRNA in the olfactory bulb, cerebral cortex, caudate putamen, hippocampus, cerebellum and liver in these three kinds of mice. In the olfactory bulb, cerebral cortex, caudate putamen, hippocampus, and cerebellum of these three mice, total Ca V 2. The relative expression level of 1α1 was not significantly different (the values of ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Ca V 2.1α1 Gene Mutant Mice Reduced Infarct Volume in In vivo Ischemia Model
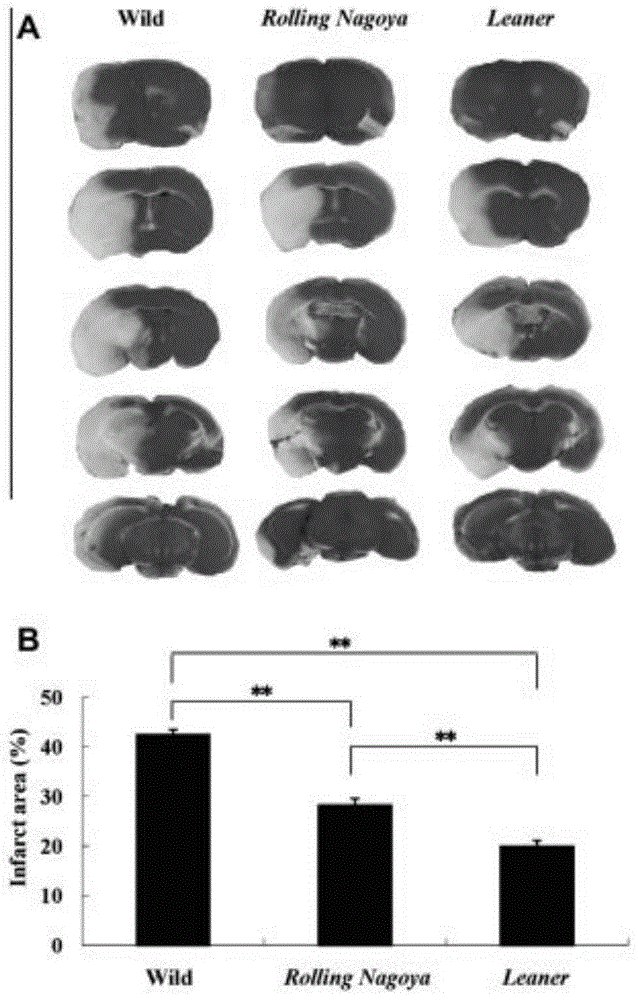
[0041] Wild-type mice (n=12), Rolling Nagoya (n=11) and Leaner mice (n=12) were treated with middle cerebral artery occlusion. We distinguish cerebral infarction from the color, which is a white unstained area surrounded by red living tissue. figure 1 A is a group of representative experimental results, which are the results obtained by staining for 24 hours after the infarct part was permanently occluded with TTC. After treatment with middle cerebral artery occlusion, the infarct area was significantly different in the three mice. The proportion of the infarct region to the total brain volume was 27.1 ± 3.5% in RollingNagoya, 20.2 ± 3.5% in Leaner mice, and 42.9 ± 4.5% in wild-type mice.
Embodiment 3
[0043] Ca V 2.1α1 Gene Mutant Mice Reduce Calcium Ion in Vitro Ischemia Model
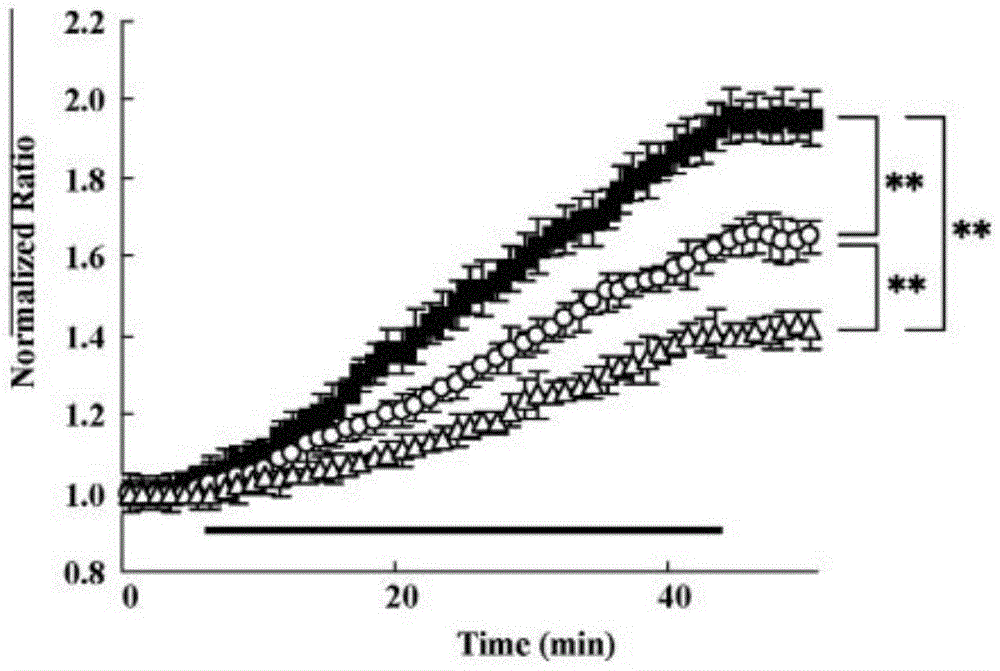
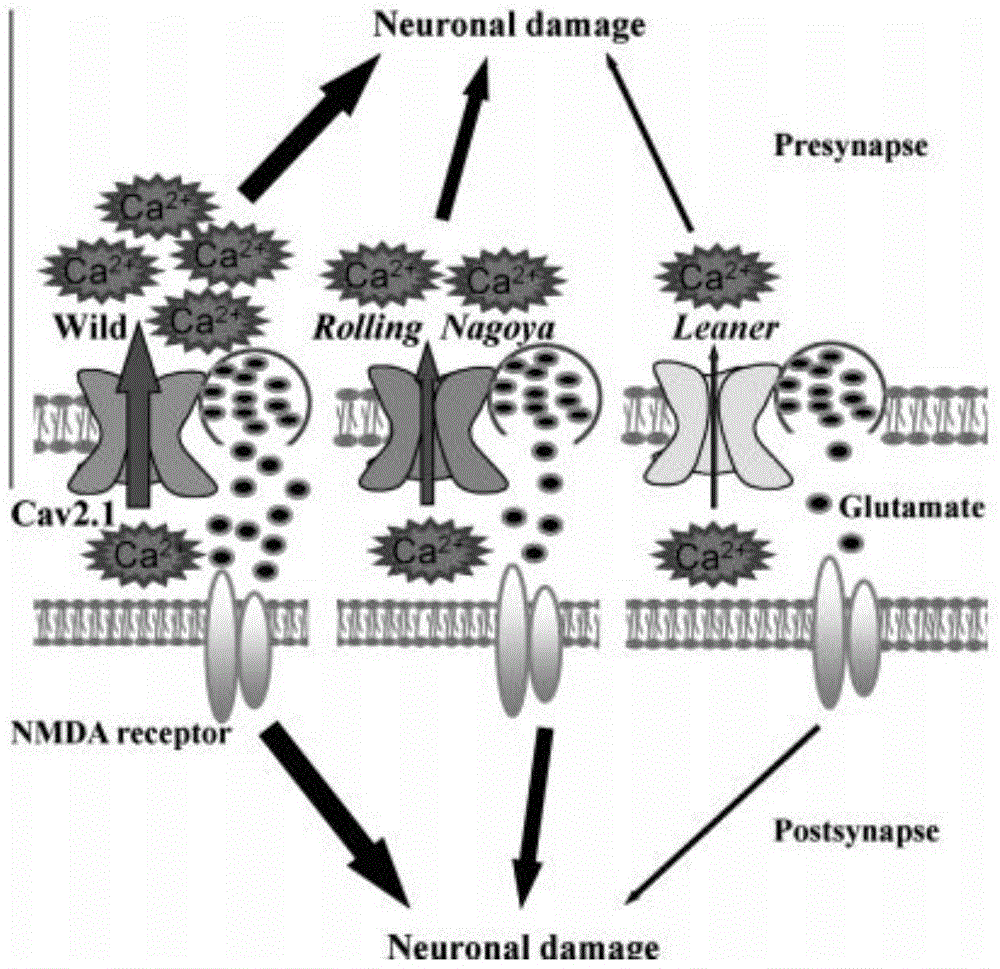
[0044] To investigate whether the reduction in infarct volume in mutant mice is related to neuronal calcium signaling, we used hippocampal slices to examine calcium changes following OGD treatment, which induces ischemia. Ca V The 2.1 channel is strongly expressed in the hippocampal region. Before OGD treatment, there was no significant difference in the basal ratio of the pyramidal cell layer in the CA1 region in these three mice (wild type: 0.847 ± 0.011; Rolling Nagoya: 0.827 ± 0.022; Leaner mice: 0.803 ± 0.013) . Once OGD treatment started, calcium ions increased, and within 4 minutes after treatment, the normalized index of wild-type mice was much higher than that of mice in the other two groups. The maximum rate of increase was also different among the three mice. The rate of increase was 0.083 ± 0.007 / min (p < 0.01) in Rolling Nagoya, 0.062 ± 0.006 / min (p < 0.01) in Leaner mice, and 0.105...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com