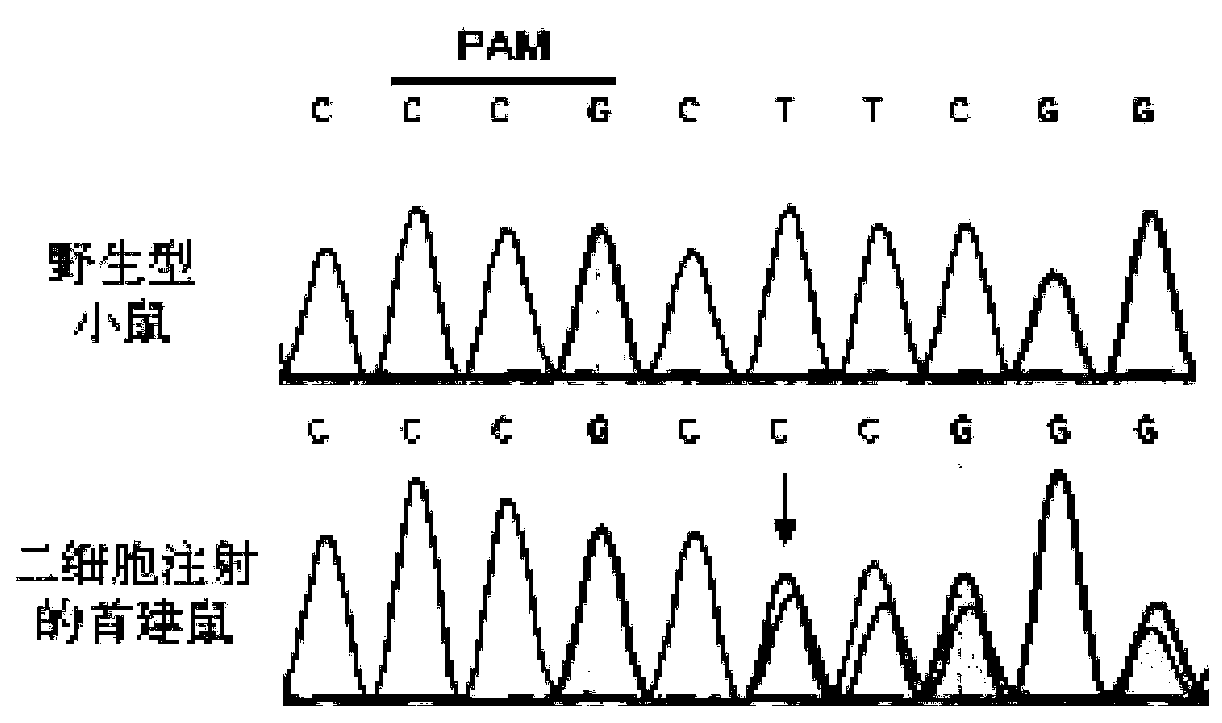
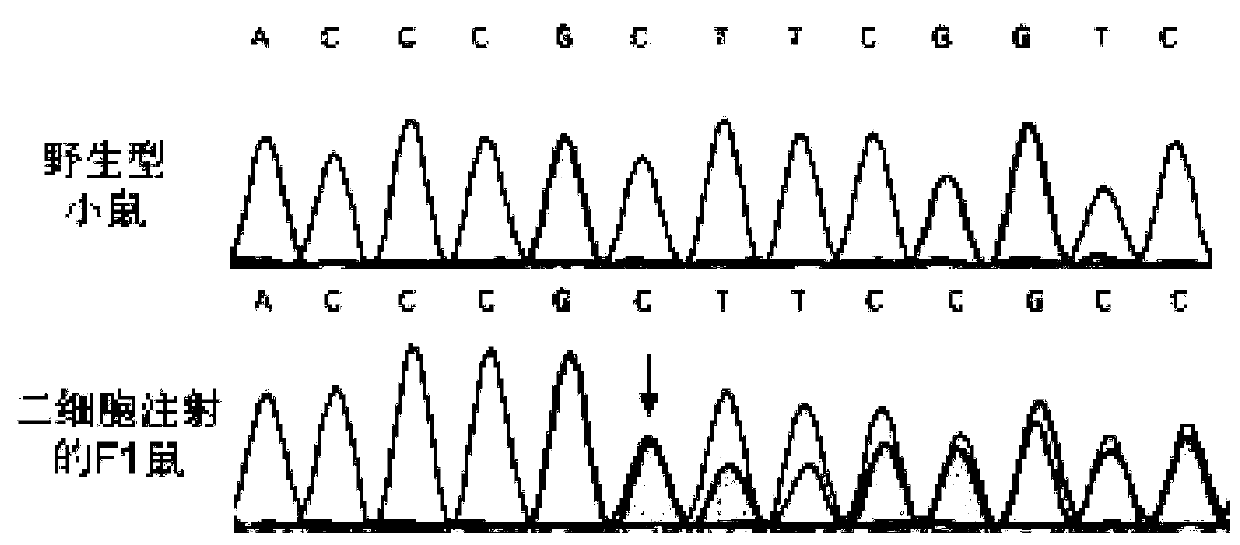
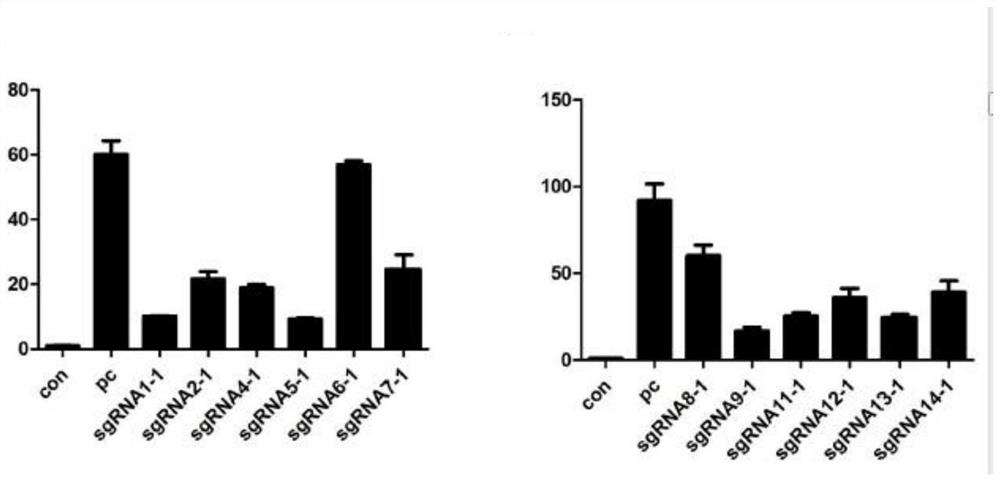
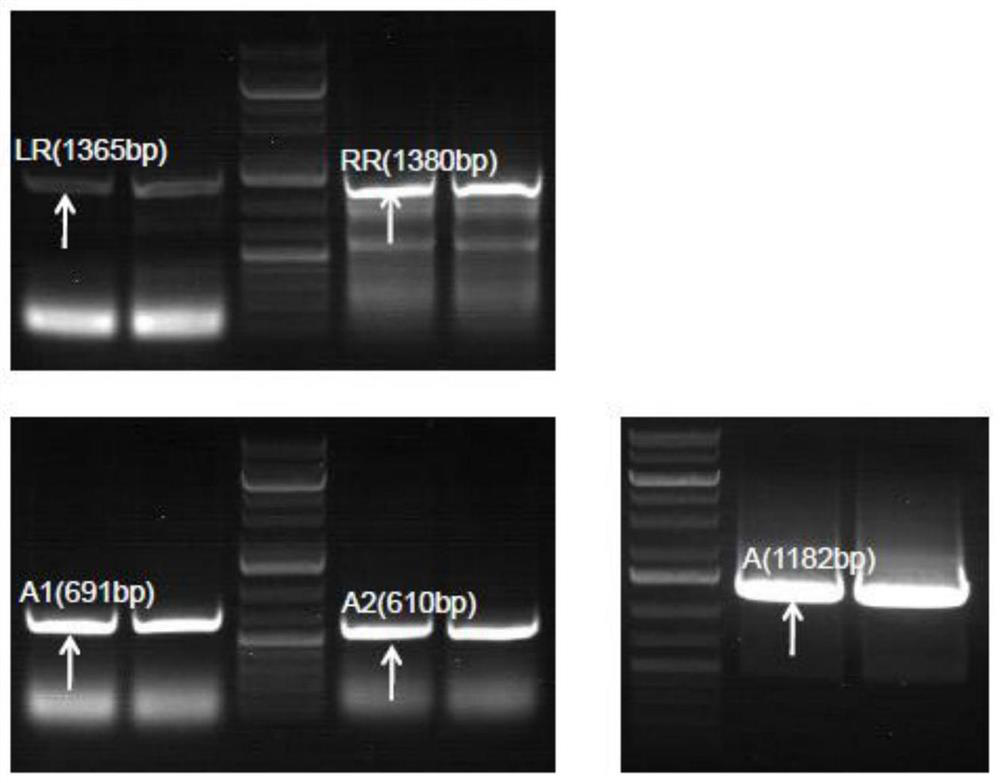
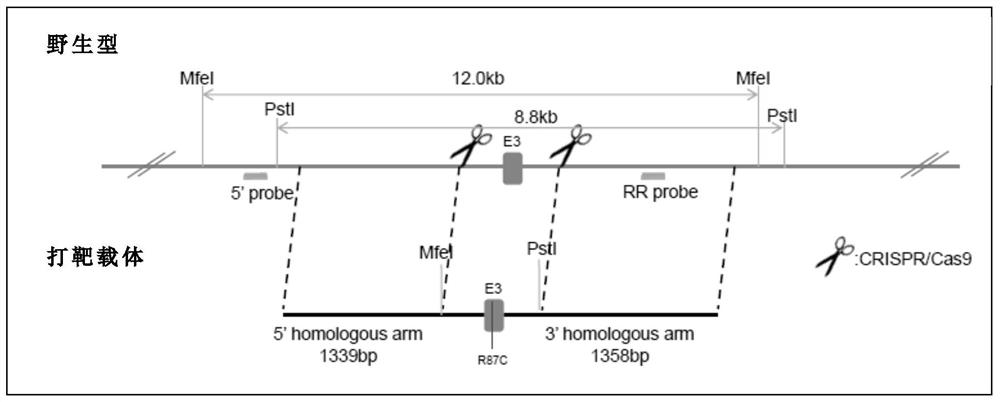
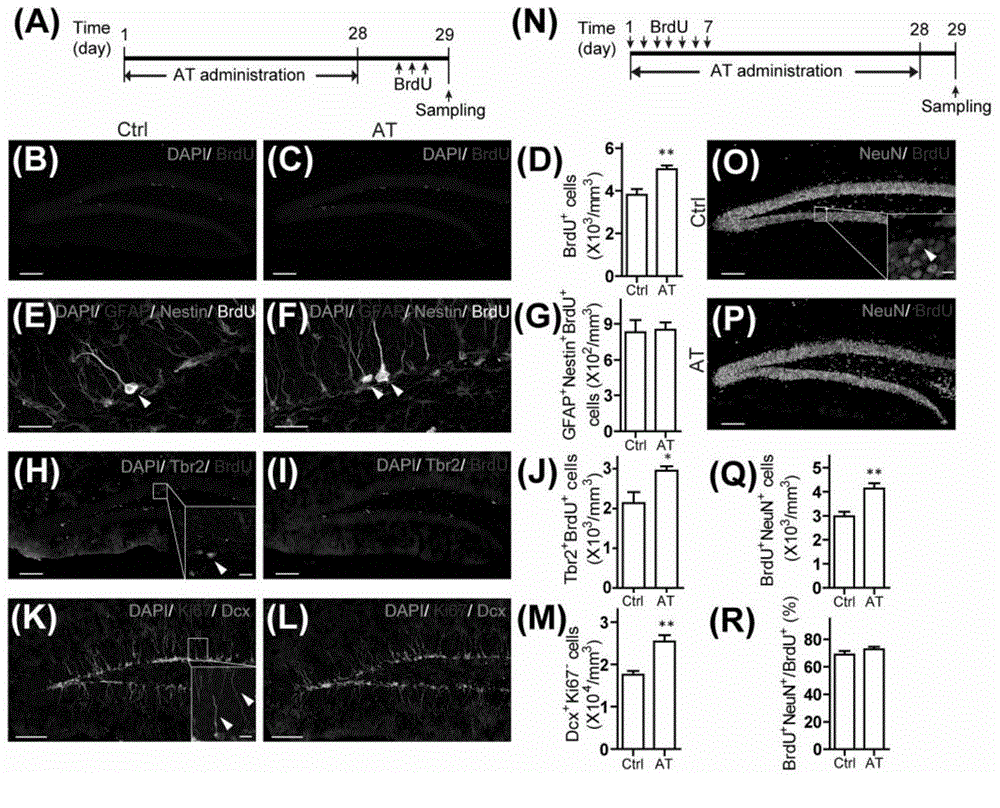
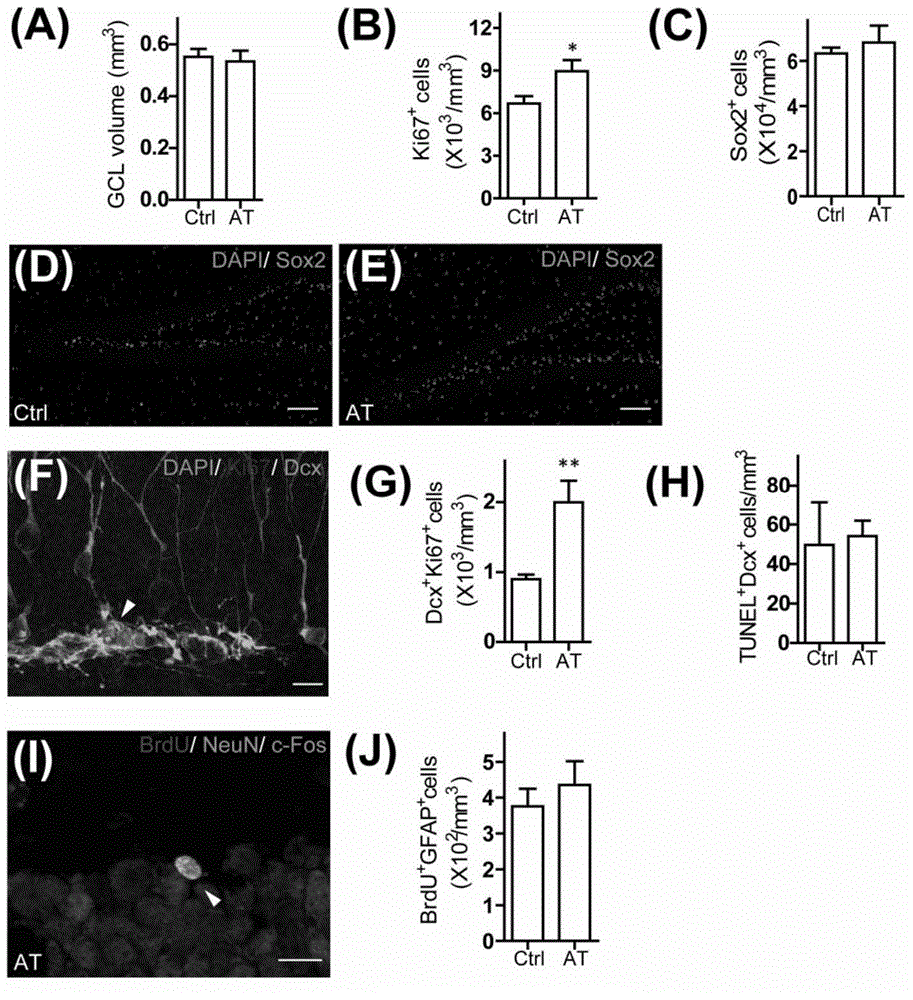
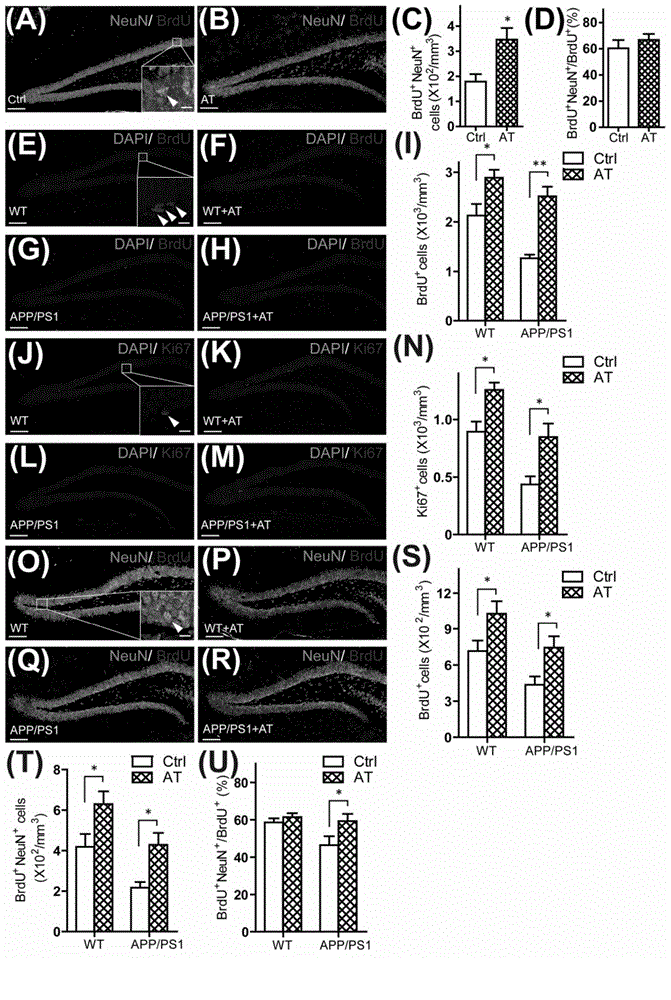
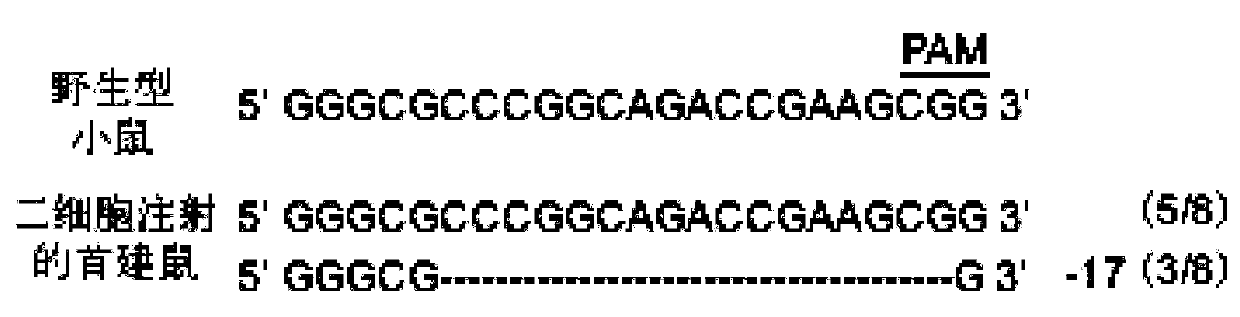Patents
Literature
75 results about "Wild Type Mouse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
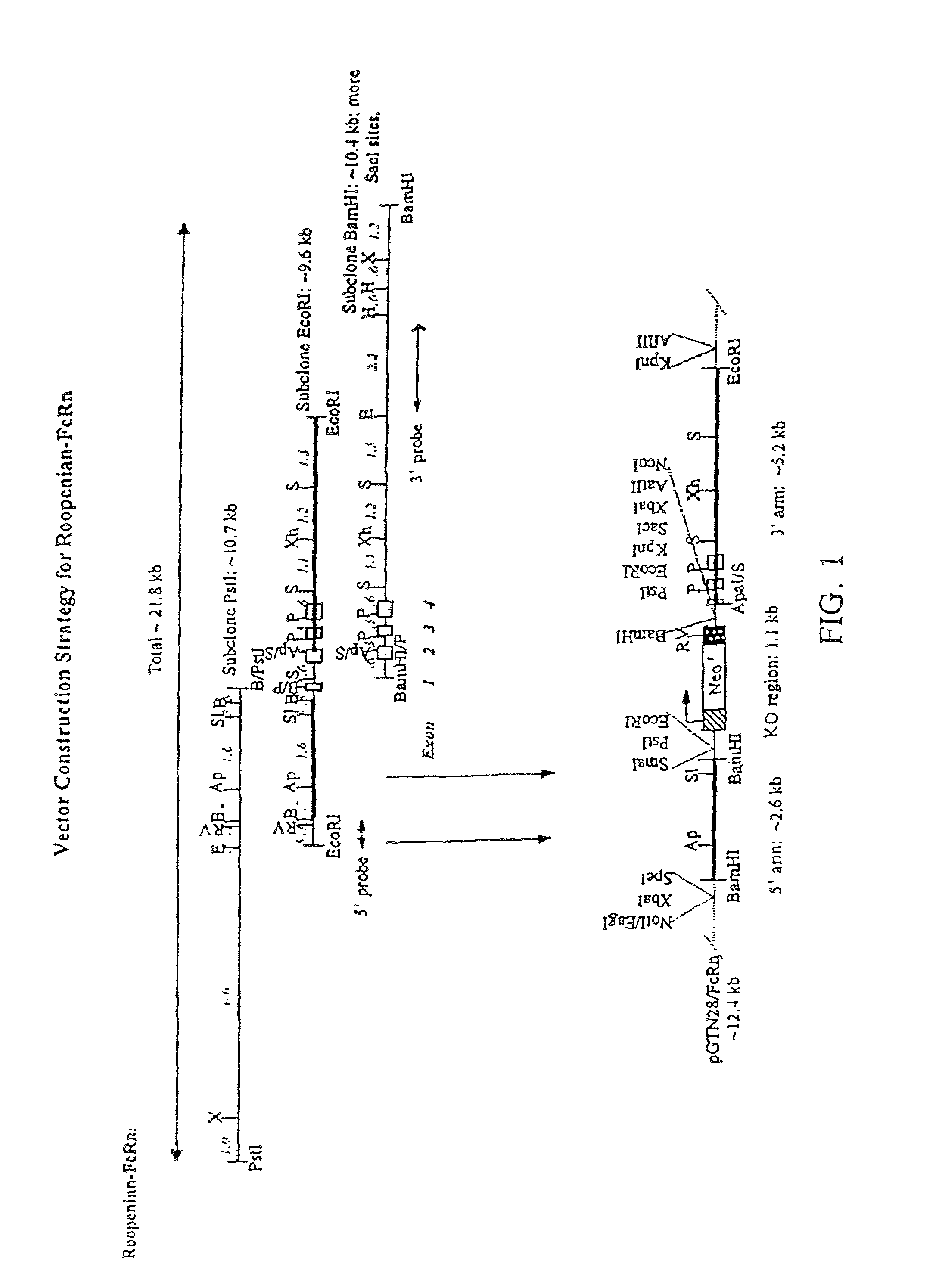
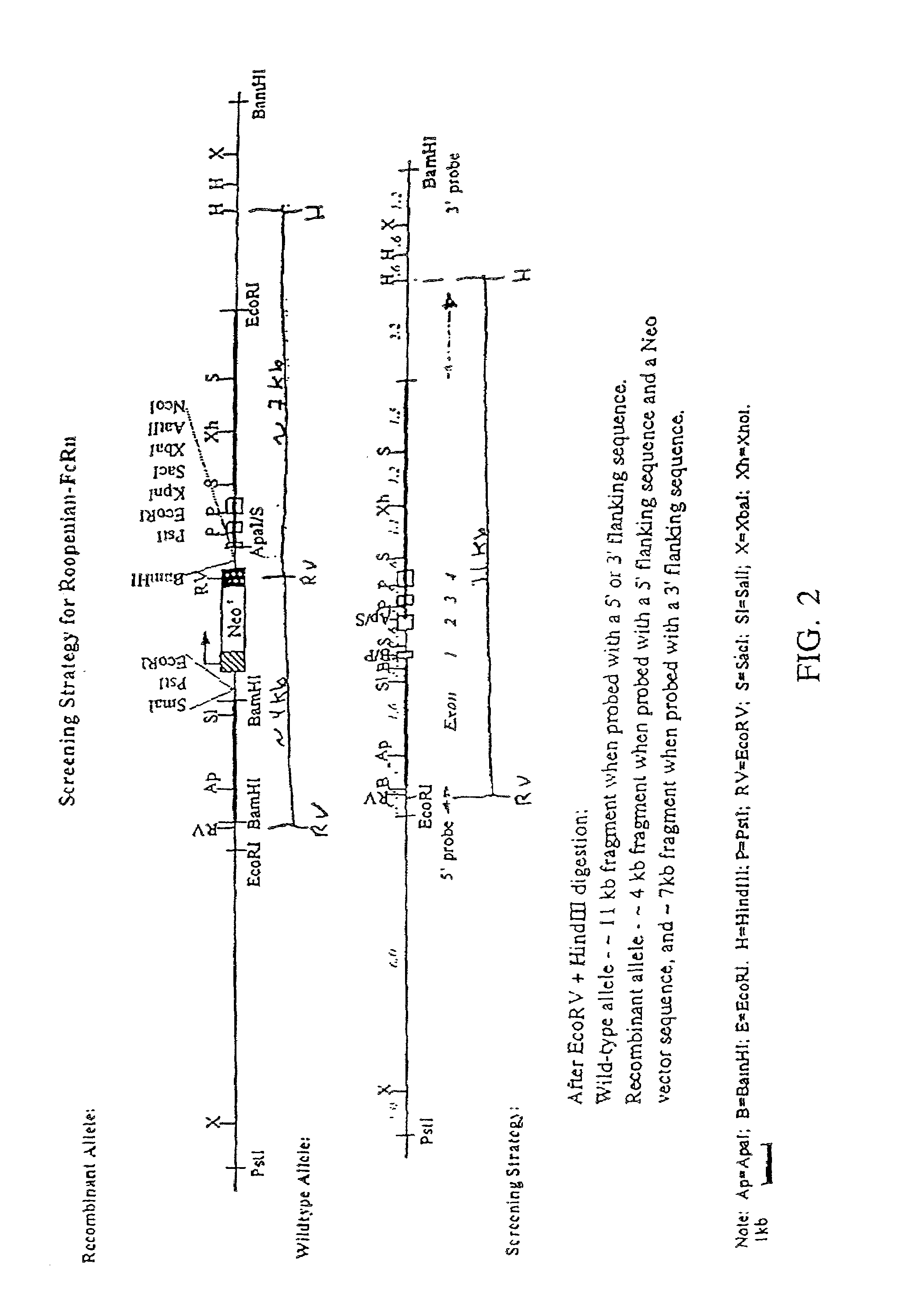
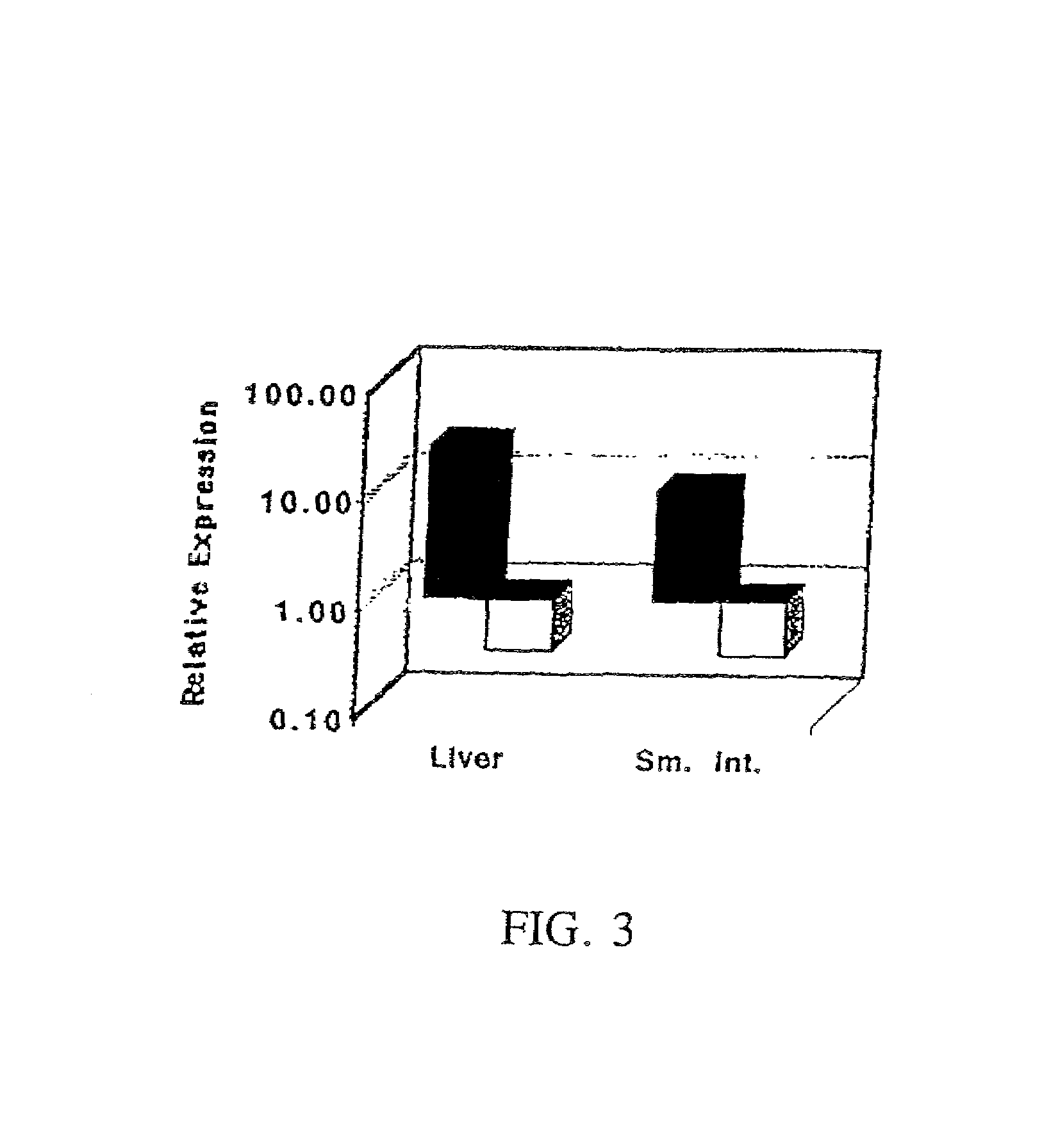
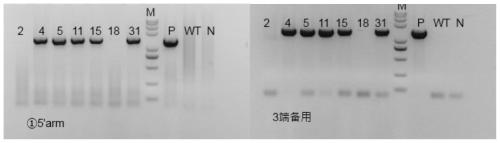
FcRn-based therapeutics for the treatment of auto-immune disorders
InactiveUS6992234B2Increased catabolismShort livedAntibody ingredientsDepsipeptidesDiseaseTransgenic knockout
Owner:JACKSON LAB THE
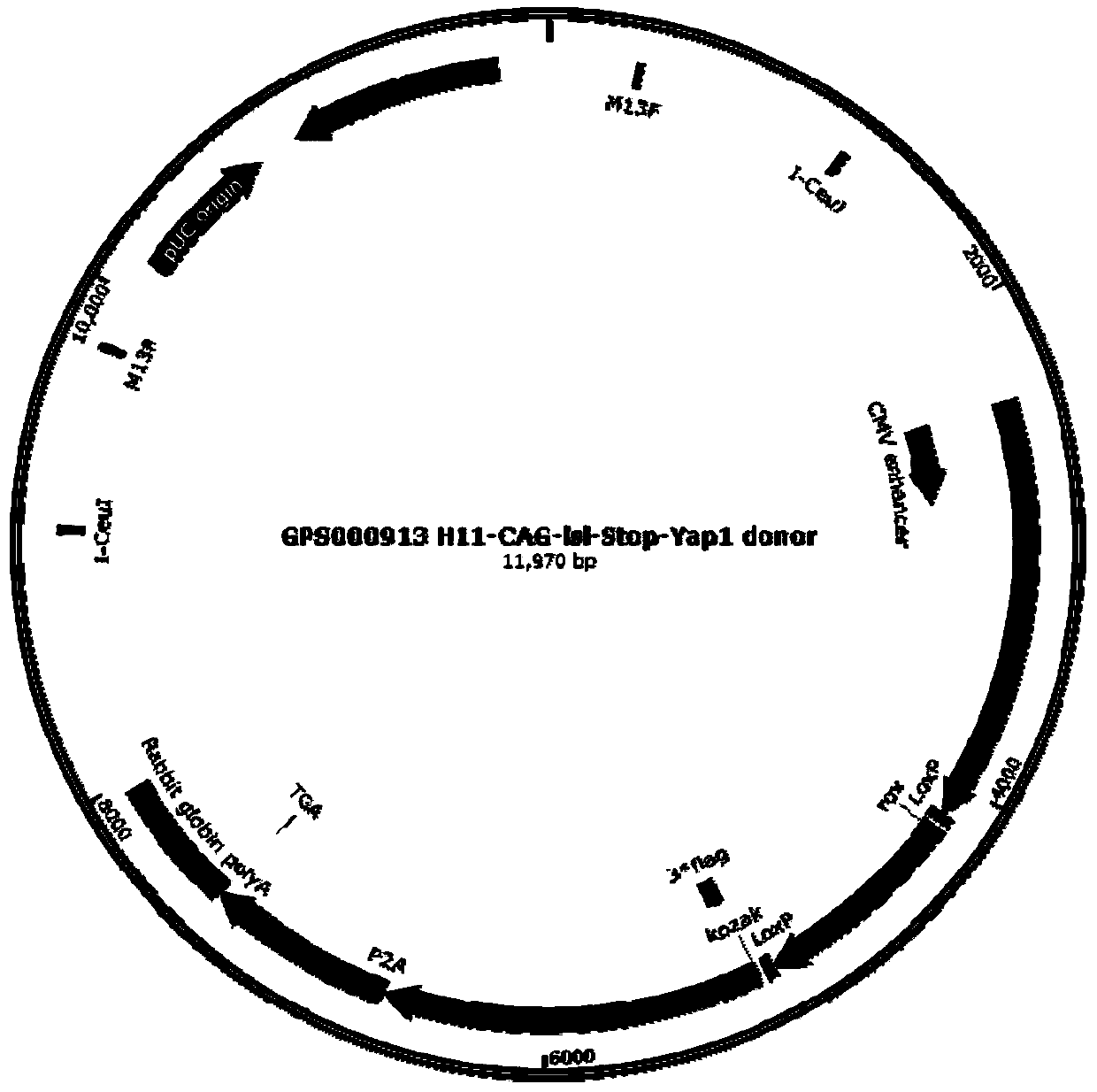
Construction method for conditional overexpression Yap1 gene mice model at H11 locus
InactiveCN110093369AHigh precisionReduce dependenceAnimals/human peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionDevelopmental stageHippo signaling
The invention discloses a construction method for a conditional overexpression Yap1 gene mice model at an H11 locus. The construction method comprises the steps: firstly, obtaining an inducible Yap1 overexpression transgenic vector; then, obtaining transgenic F0-generation mice; next, enabling the F0-generation mice to mate with wild-type mice, carrying out passage and line establishment, and thusobtaining F1-generation mice; and carrying out expanding propagation of positive F1-generation mice, then mutually mating, and thus obtaining the conditional overexpression mice Yap1 animal model. The transgenic mice model constructed by the method can be used for studying the function of Yap1 in different tissues and different developmental stages and the action mechanism of Hippo signaling pathways, can also be used for studying the function of the Hippo signaling pathway in animal development, biotumorigenesis, regenerative medicine and other disciplines, and has important guiding significance on biological signal transduction studies.
Owner:成都药康生物科技有限公司
Method for constructing lethal gene systemic knockout mouse model with CRISPR/Cas9 system
InactiveCN109777837ALong production cycleThe production steps are cumbersomeHydrolasesStable introduction of DNASTATH geneKnockout animal
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, in particular to a method for constructing a lethal gene systemic knockout mouse model with a CRISPR / Cas9 system. The method includes the followingsteps that 1, an sgRNA sequence for efficiently identifying a lethal gene PAM region after knockout is designed; 2, mRNA or protein of Cas9 is mixed with the sgRNA designed in step 1, microinjectionis performed on any blastomere cell in a mouse two-cell embryo with the mixture, embryo transplantation is performed after injection, and strain gene identification is performed to obtain a chimeric positive founder with the lethal gene knocked out; 3, the positive founder and a wild-type mouse are mated to generate an F1 generation, a heterozygous F1-generation mouse with the lethal gene systemically knocked out is finally obtained after gene identification, and construction of the mouse model capable of realizing passage propagation is completed. Compared with the prior art in which a lethalgene systemic knockout mouse model is constructed by ES cell gene targeting, the method in the technical scheme has the advantages that the operation steps are simple, the operation difficulty is low, the production cycle is short, and the cycle is only about 4 months.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
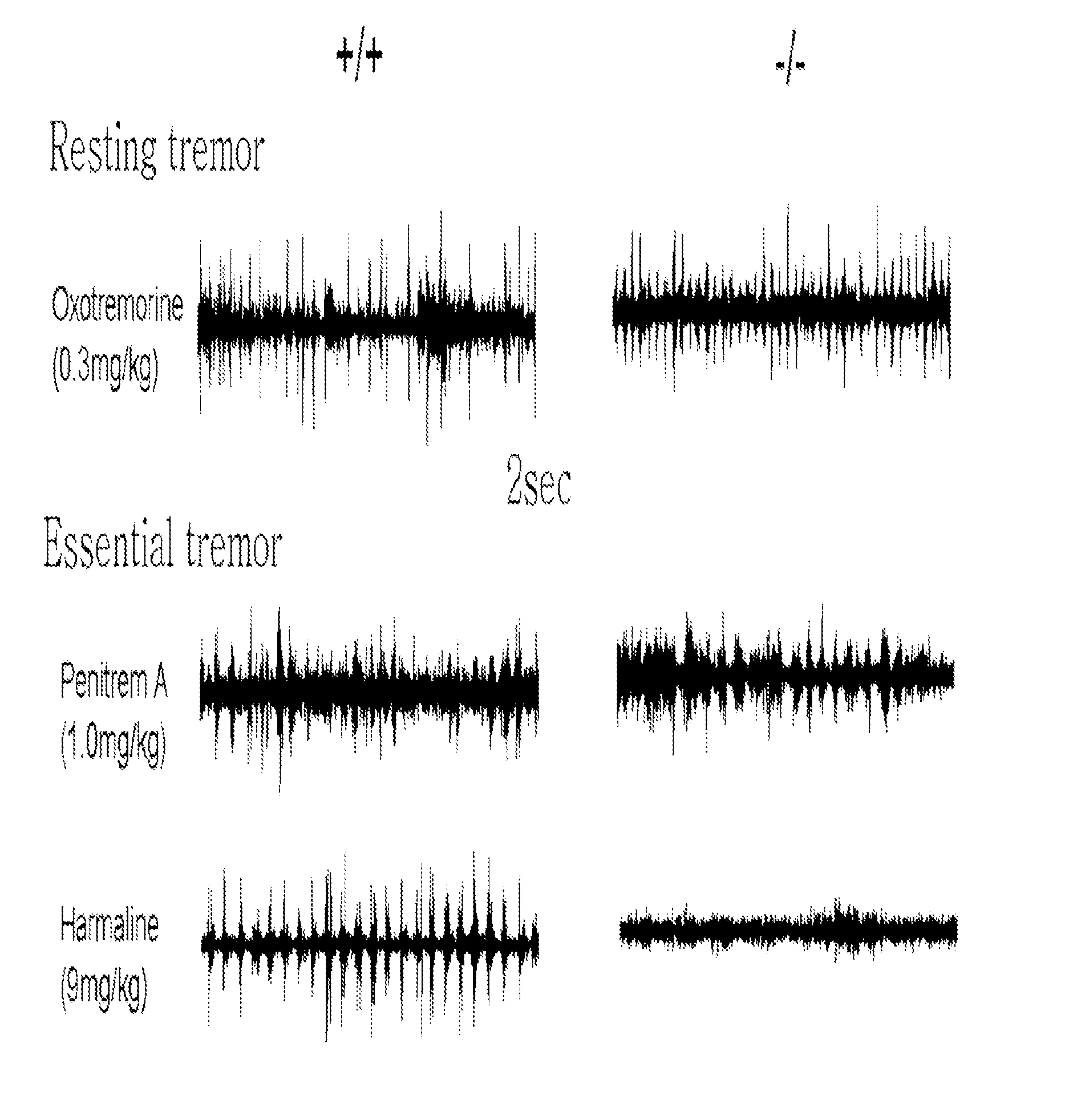
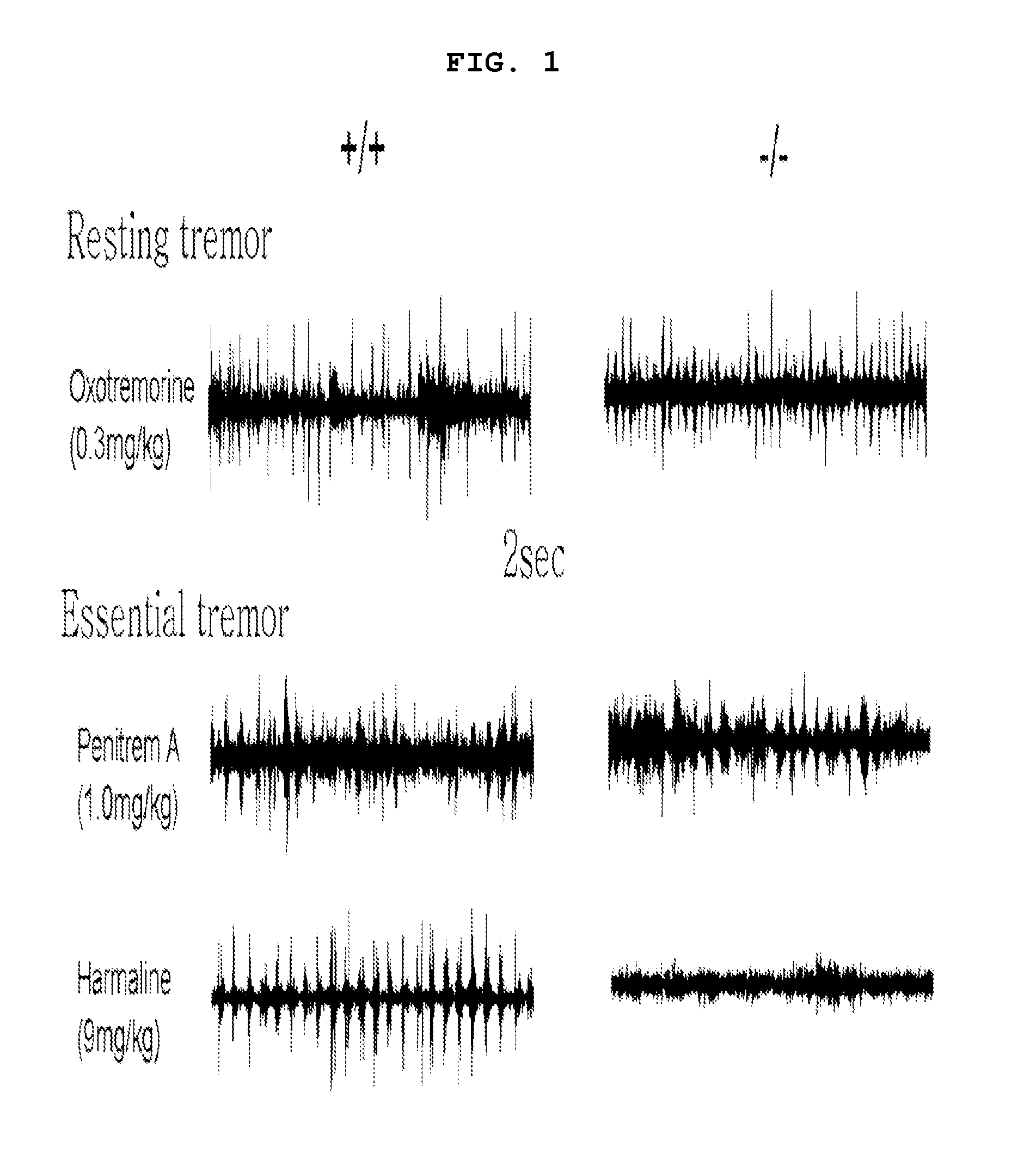
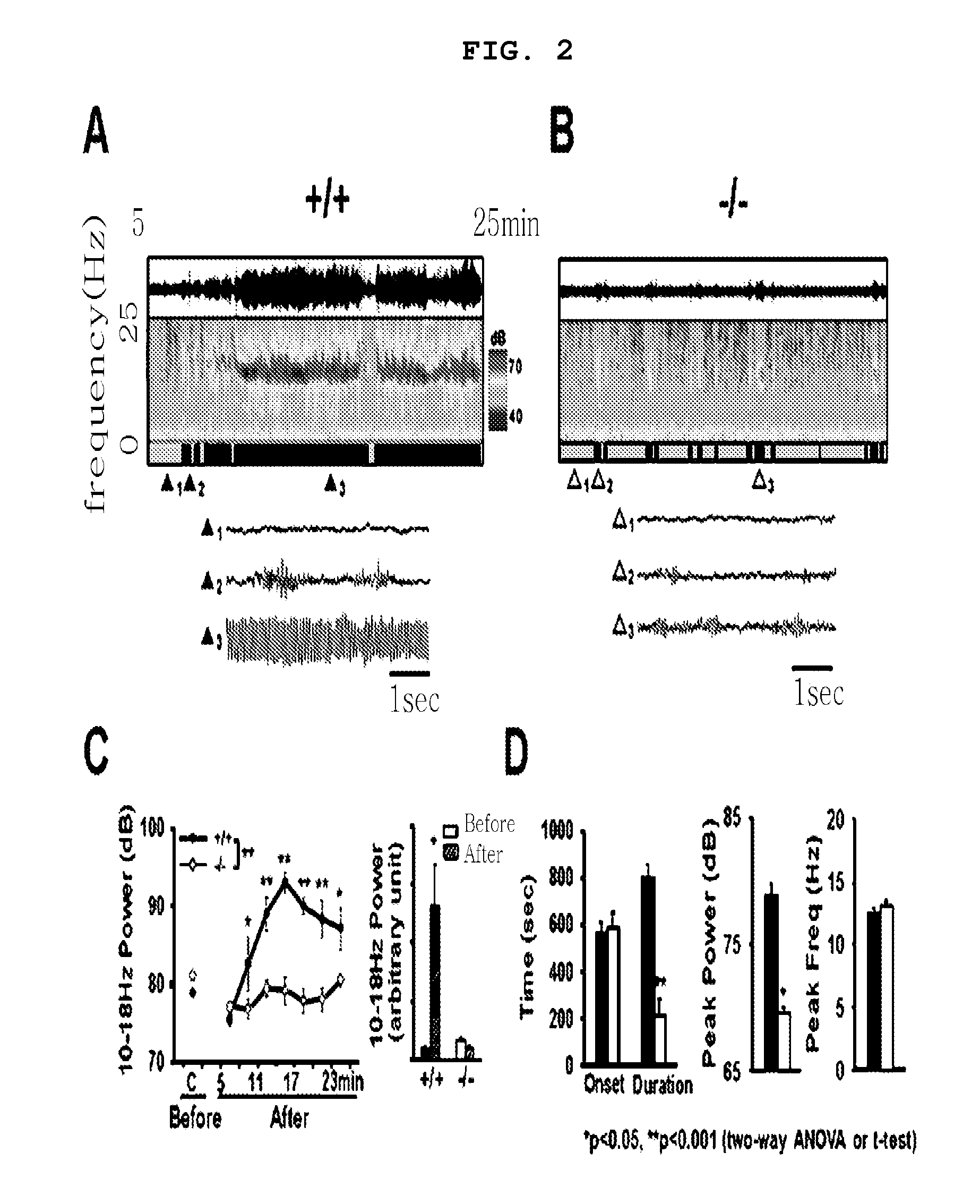
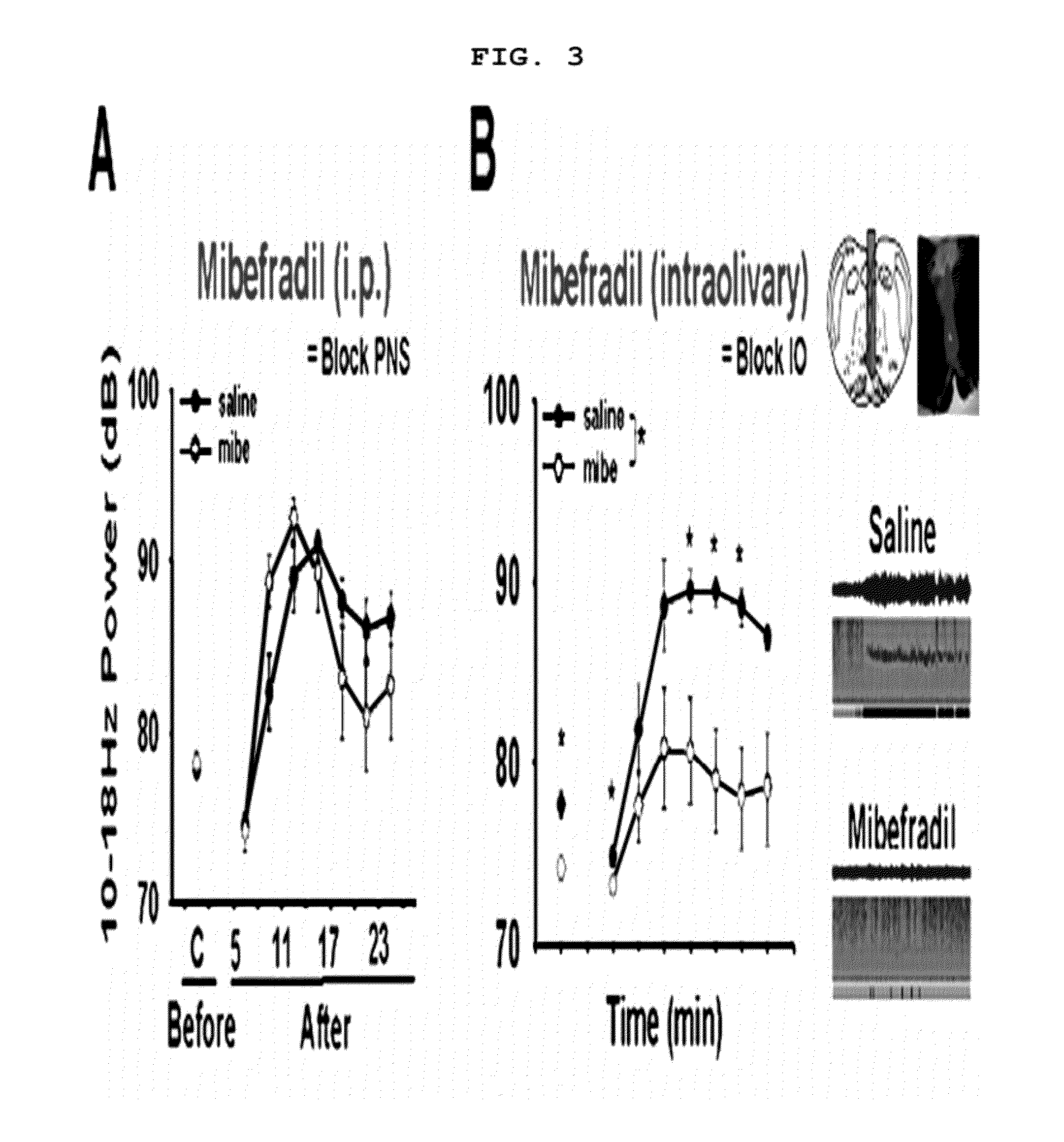
Method for the prevention and treatment of essential tremor by regulating alpha1g t-type calcium channel or by t-type calcium channel blockers
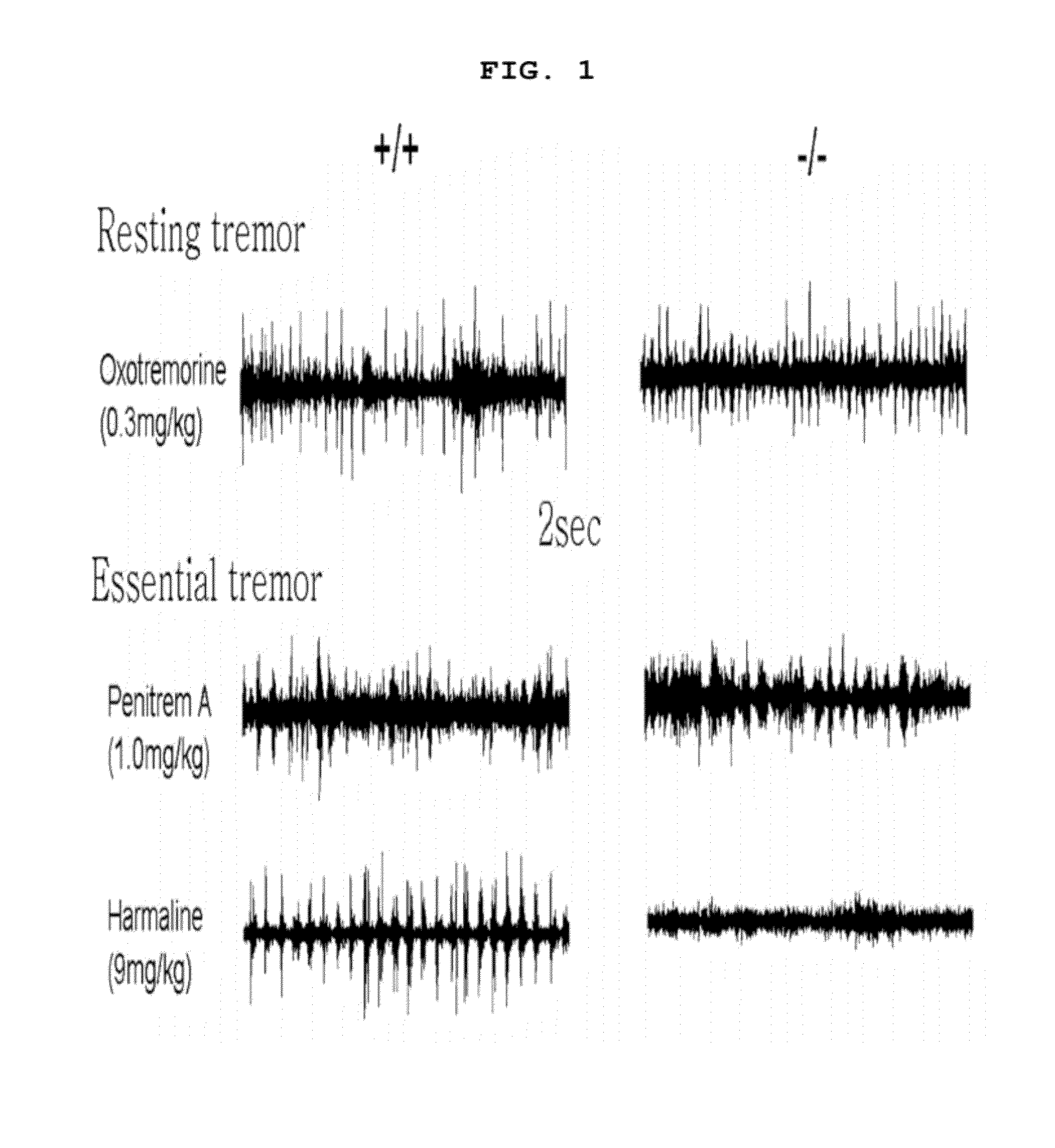
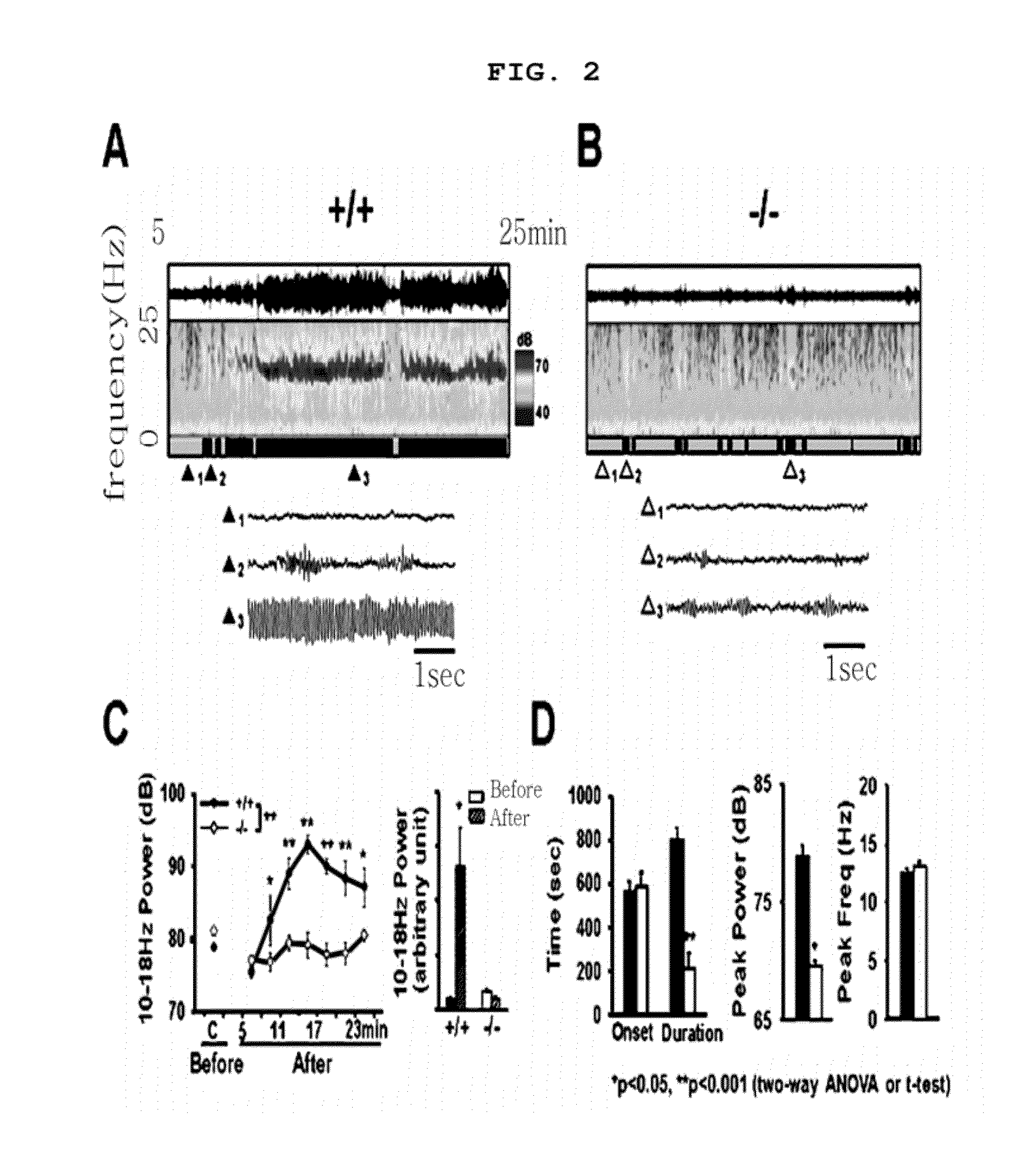
The present invention relates to a method for the prevention and treatment of essential tremor by blocking α1G T-type calcium channel, a preventive and therapeutic agent for essential tremor containing the α1G T-type calcium channel blocker as an active ingredient, and a screening method of a preventive and therapeutic agent for essential tremor by investigating α1G T-type calcium channel blocking activity. More precisely, the present invention relates to a method for the prevention and treatment of essential tremor by using α1G T-type calcium channel blocker, for which the inventors confirmed that the α1G T-type calcium channel knock out mice (α1G − / −) had resistance against essential tremor and when the T-type channel blocker was administered to the wild type mice (α1G + / +), they gained resistance against essential tremor.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
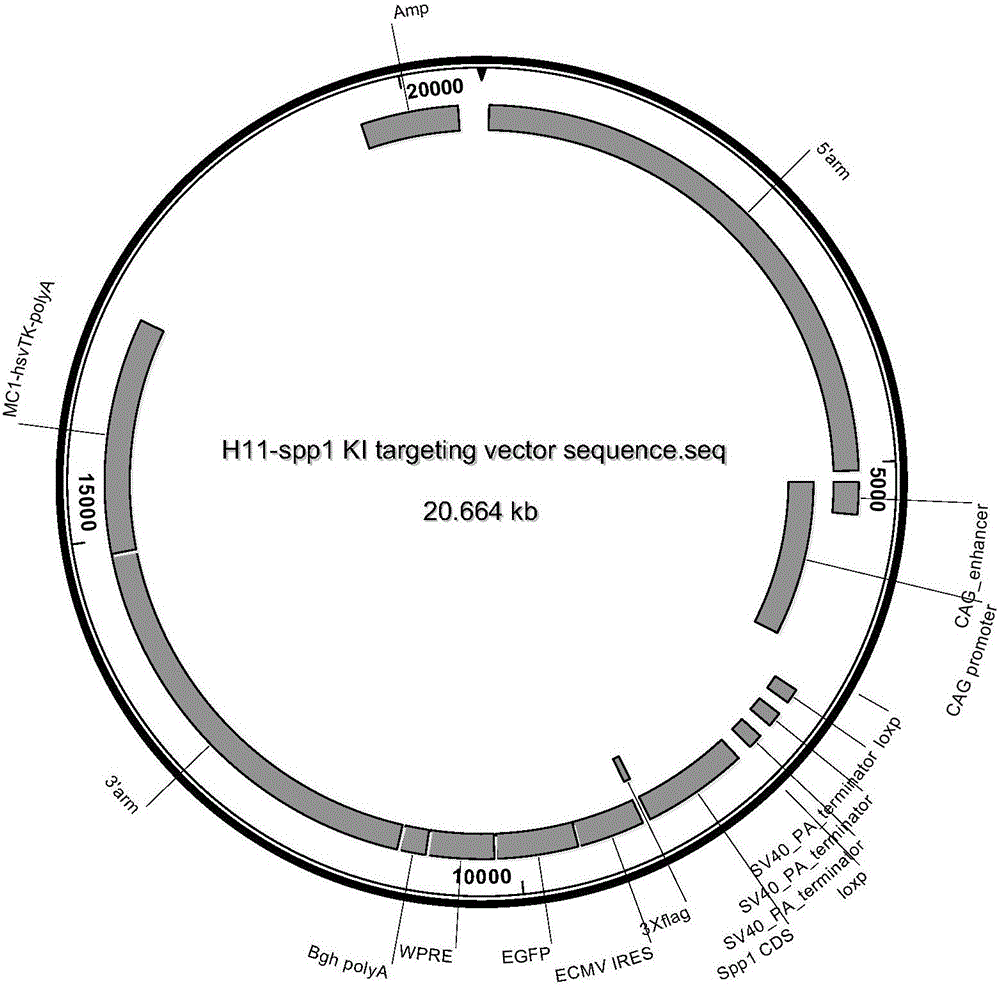
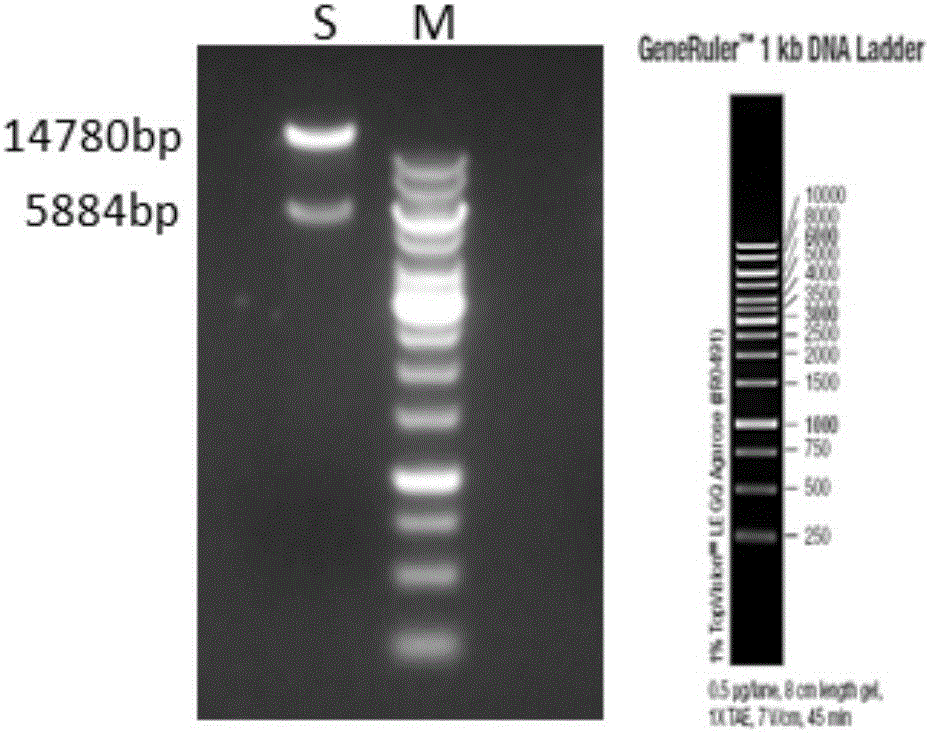
H11 fixed-point knock-in heterozygous mice model of conditional overexpression Spp1 gene and construction method of H11 fixed-point knock-in heterozygous mice model of conditional overexpression Spp1 gene
ActiveCN106480099AImprove controllabilityControl the onset timeFermentationGenetic engineeringWild typeGenetically modified mouse
The invention discloses an H11 fixed-point knock-in heterozygous mice model of a conditional overexpression Spp1 gene and a construction method of the H11 fixed-point knock-in heterozygous mice model of the conditional overexpression Spp1 gene. The construction method includes obtaining an inducible Spp1 overexpression transgenic vector; obtaining transgenic F0-generation mice; enabling the transgenic F0-generation mice to mate with wild-type mice for passage and line establishment so as to obtain F1-generation mice; selecting the F1-generation mice high in expression in terms of bone marrows, spleens, lymph nodes and thymus glands as a subsequent laboratory strain so as to obtain transgenosis tool mice; enabling the transgenosis tool mice to mate with Cre transgenic mice so as to obtain the H11 fixed-point knock-in heterozygous mice model. The H11 fixed-point knock-in heterozygous mice model, a transgenosis mice model, is an inducible leukemia model characterized in that Spp1 isn't in expression and causes no leukemia in the absence of an inducer and is in expression and causes leukemia in the presence of the inducer, thereby being higher in controllability than a conventional transgenosis mice model and capable of adjusting the quantity of species needing to be maintained according to experiment needs.
Owner:赣南医学院第一附属医院
Composition based on main components of Pu'er tea and application thereof
InactiveCN103070983APrevent biological hazardsAvoid deathAntinoxious agentsAntineoplastic agentsApoptosisTumor chemotherapy
The invention discloses composition based on main components of Pu'er tea and the application thereof. The composition comprises tea brown pigment, tea polysaccharide, tea polyphenol, caffeine, gamma-aminobutyric acid and gallic acid. A wild type mouse embryo fibroblast is utilized to test the killing effect of DNA toxicity chemical substance to normal cells and the effect that the composition provided by the invention protects the normal cells from DNA damage and prevents apoptosis; the result shows that the composition provided by the invention can effectively prevent the normal cell death caused by DNA toxicity chemical substance; and further research shows that the composition provided by the invention does not protect tumor cell death caused by the DNA toxicity chemical compound, conversely, the composition provided by the invention can promote the killing effect of the DNA toxicity chemical compound to the tumor cells. Therefore, the composition can be used for protecting the normal cells during the chemotherapy of tumor patients and alleviating toxic side effects caused by tumor chemotherapy, and meanwhile sensibilizes chemotherapy drug, enhances chemotherapy effect, and improves survival quality of chemotherapy patients.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +2
Application of macrophage beta-profilin-1 to preparation of drug for preventing or treating atherosclerosis
InactiveCN105561297AImprove securityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsKnockout animalAbnormal macrophage
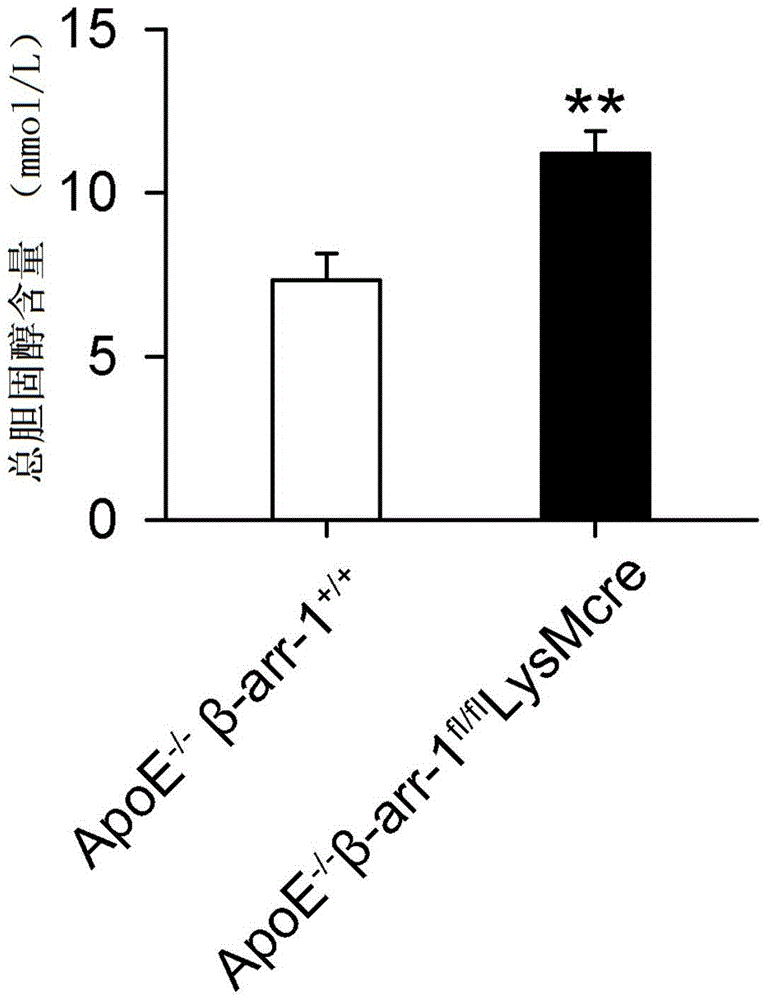
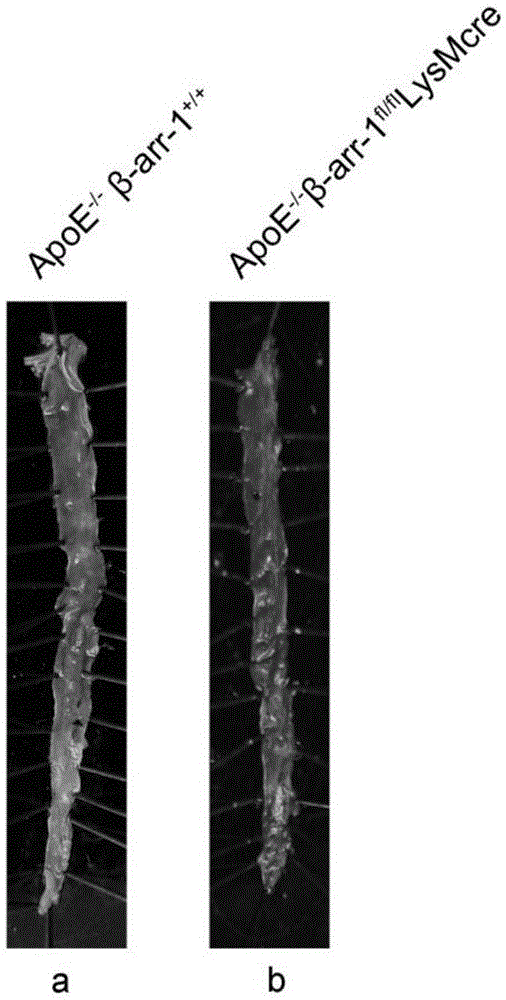
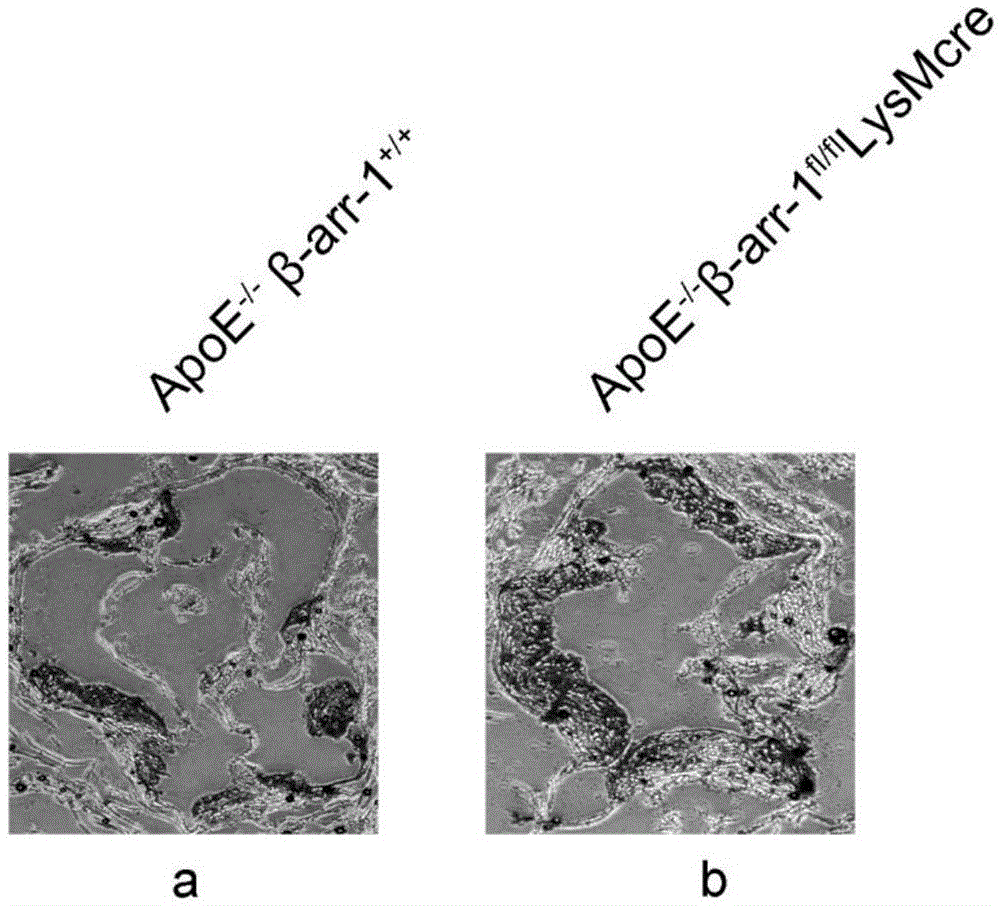
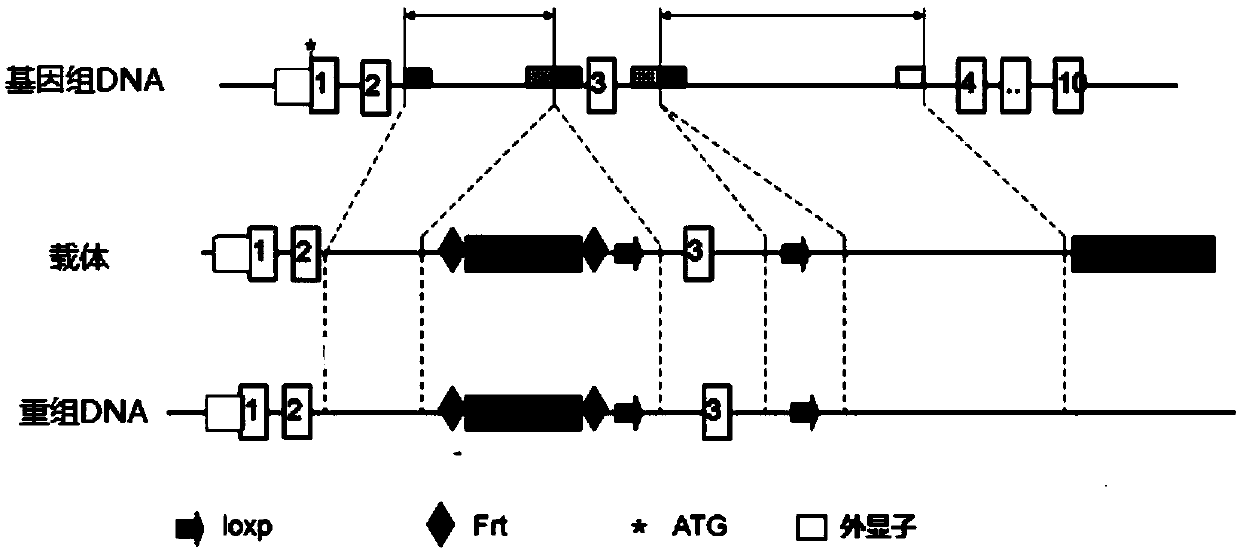
The invention relates to the technical field of medicine, and provides new application of macrophage beta-profilin-1, namely application of macrophage beta-profilin-1 to preparation of a drug for preventing or treating atherosclerosis. It is proved through experiments that in comparison with wild type mice, the serum total cholesterol content of macrophage beta-arrestin-1 specificity myelogenous knockout mice is remarkably increased, and it is found through oil red O dyeing that the aorta overall plaque area and the plaque area of aorta roots are obviously increased compared with those of the wild type mice. By changing the macrophage beta-arrestin-1 gene expression level through virus transfection, and it is found that macrophage phagocytosis lipid is increased by interfering beta-arrestin-1 expression and is decreased by overexpressing beta-arrestin-1. The results show that the beta-arrestin-1 gene has a protective effect on the severity degree and prognosis of atherosclerosis.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Construction method of VDR gene conditionality knockout floxed mouse model
PendingCN110408653AAvoid fatal restrictionsControl time specificityCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsVector-based foreign material introductionSusceptibility/Resistance GeneMolecular biology
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a construction method of a VDR gene conditionality knockout floxed mouse model. According to the method, a gene targeting technique and an ES cell recombination technique are utilized, an Frt-neo-Frt-loxP sequence and an loxP sequence are respectively put on two sides of a VDR gene exon 3 of a bacterium artificial chromosome,a VDR-floxed carrier is constructed, and ES cells are guided through electric shock; after positive ES cells screened out through drug-resistant genes are cloned, through sequencing determination withPCR and a product thereof, the positive ES cells are transplanted in the body of a surrogacy female mouse, and a chimera mouse containing ES cell sources is produced; a male chimera mouse and a female wild type mouse intercross to generate an F1-generation mouse, and through sequencing confirmation with the PCR and the product thereof, a VDR-floxed heterozygote mouse containing Neo genes is obtained; and then the VDR-floxed heterozygote mouse containing Neo genes and an Flp mouse hybridize so that a VDR-floxed heterozygote mouse without neo genes is obtained. Through experimental verification, the VDR-floxed mouse model constructed by the construction method can lead to knockout of a VDR gene exon 3 region, and lead to deletion of VDR expression.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Construction method and application of SDK2 gene mutation mice mice
ActiveCN111778246AGenetic stabilityConvenient researchAnimal reproductionLuminescence/biological staining preparationWild typeWild Type Mouse
The invention provides a construction method of an SDK2 gene mutation mice model. The mice model comprises the following steps of designing and constructing sgRNA capable of specifically identifying an SDK2 gene on the basis of a CRISPR / Cas9 system, injecting the sgRNA and a targeting vector constructed on the basis of the sgRNA into a mice fertilized egg; and after embryo transplantation, screening out F0-generation mice with SDK2 gene mutation from the output mice, and hybridizing the F0-generation mice with wild type mice to obtain an F1-generation mice model with SDK2 gene mutation. The mice model constructed by the method can be stably passaged, the action mechanism of the SDK2 gene in mice hereditary cataract can be conveniently researched in practical application, and under the condition that human patient research materials are not easy to obtain and are restricted by medical ethics, the SDK2 gene can be stably cloned. The mice model provided by the invention can become an important tool in the research of hereditary cataract, and a research model capable of realizing stable heredity is provided in the research of pathogenesis, treatment methods, drug screening, cataract surgery and the like.
Owner:BEIJING TONGREN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
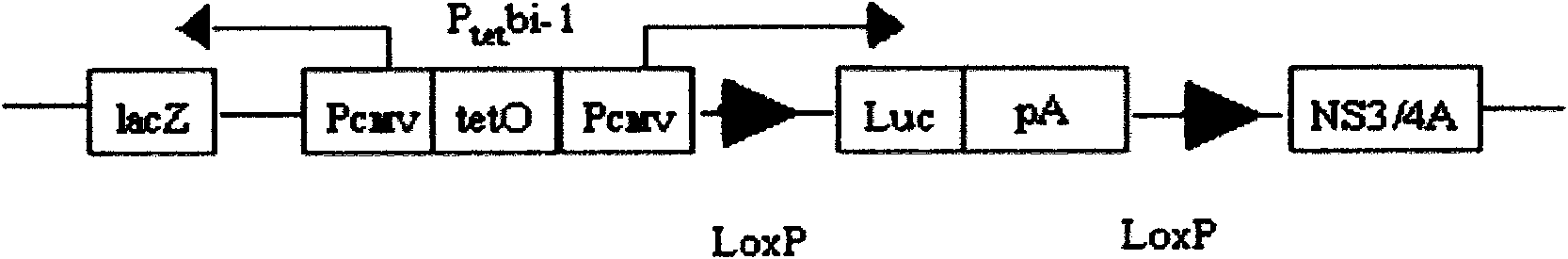
Method for constructing the regulation and expression of hepatitis C virus NS3/NS4A protease
InactiveCN101671694AImmune tolerance does not developHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementWild typeWild Type Mouse
The invention relates to a method for constructing the regulation and expression of a protease, in particular to a method for constructing the regulation and expression of a hepatitis C virus NS3 / NS4A protease; the genome of transgenic animals contains a transgene DNA of a coding hepatitis C virus NS3 / NS4A, moreover a regulating gene sequence and a report gene sequence are added before a purpose gene HCV NS3 / 4A DNA so as to be capable of expressing the active NS3 / NS4A protease on the condition of a regulating factor. The method for constructing the regulation and expression of the hepatitis Cvirus NS3 / NS4A protease comprises the following contents: (1) constructing a eukaryotic expression vector which contains regulating sequences such as LoxP locus, Luciferase, and polyA and the like, is dually regulated by Tet and Cre / LoxP systems, and expresses the HCV NS3 / 4A protease; and (2) obtaining an NS3 / 4A mouse and a transgenic heterozygous mouse with the genetic background basically similar to the wild type mouse. The HCV NS3 / NS4A transgenic mouse model obtained can be used for the hybridization with a double-transgenic mouse, and further obtains a three-transgenic mouse and is applied to the HCV pathogenesis research and drug screening as well as evaluation.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
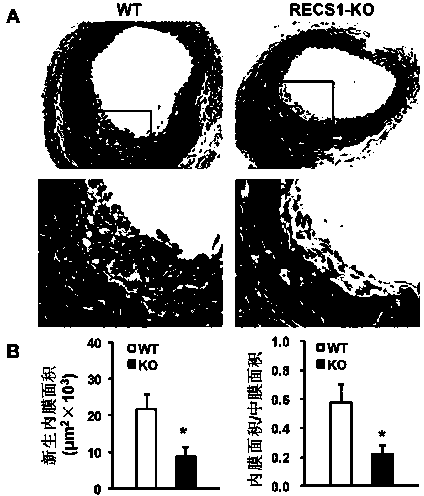
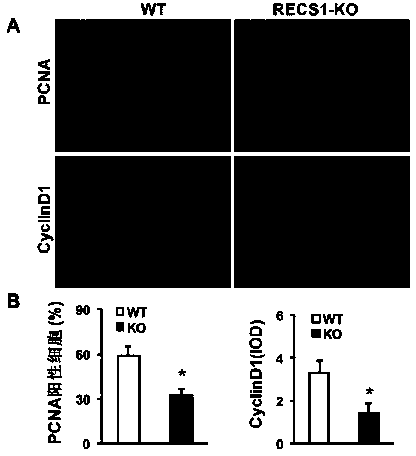
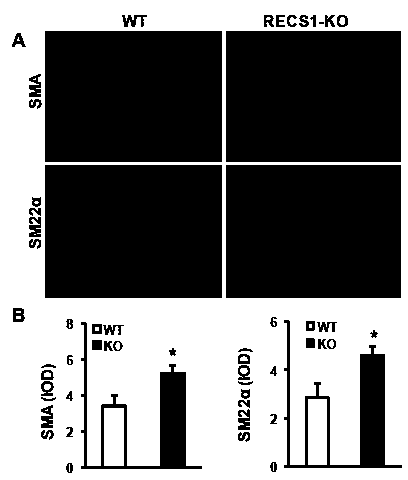
Functions and application of responsive to centrifugal force and shear stress gene 1 (RECS1) to treatment of restenosis after vascular injury
ActiveCN104198697APromote restenosisPro-restenosisGenetic material ingredientsSurgeryCell phenotypeDisease
The invention discloses functions and application of responsive to centrifugal force and shear stress gene 1 (RECS1) to treatment of restenosis after vascular injury. An RECS1 knockout mouse and a wild type mouse are taken as experimental subjects, and detection on mouse internal membrane regeneration, vessel wall cell proliferation level and smooth muscle cell phenotype transformation is carried out by a vascular injury model. Detection results prove that by virtue of RECS1 knockout, internal membrane regeneration and cell proliferation can be obviously inhibited, and smooth muscle cells are inhibited to be transformed into synthetic phenotype from contractile phenotype. Therefore, the functions of the RECS1 to the restenosis after vascular injury are mainly embodied in that internal membrane regeneration, cell proliferation and smooth muscle cell phenotype transformation are promoted by the RECS1. Aiming at the functions of the RECS1, the RECS1 can be used as a drug target for screening medicines for preventing, relieving and / or treating the disease of restenosis after vascular injury; an inhibitor of the RECS1 can be used for preparing medicines and arterial stents for preventing, relieving and / or treating the restenosis after vascular injury.
Owner:武汉惠康基因科技有限公司
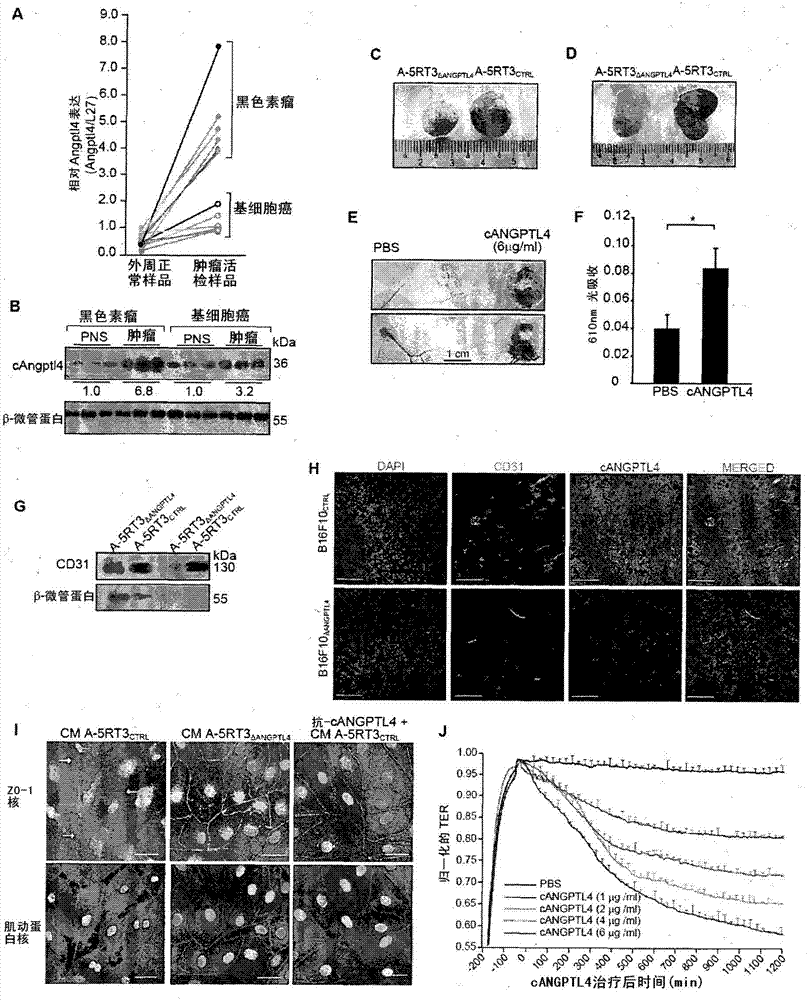
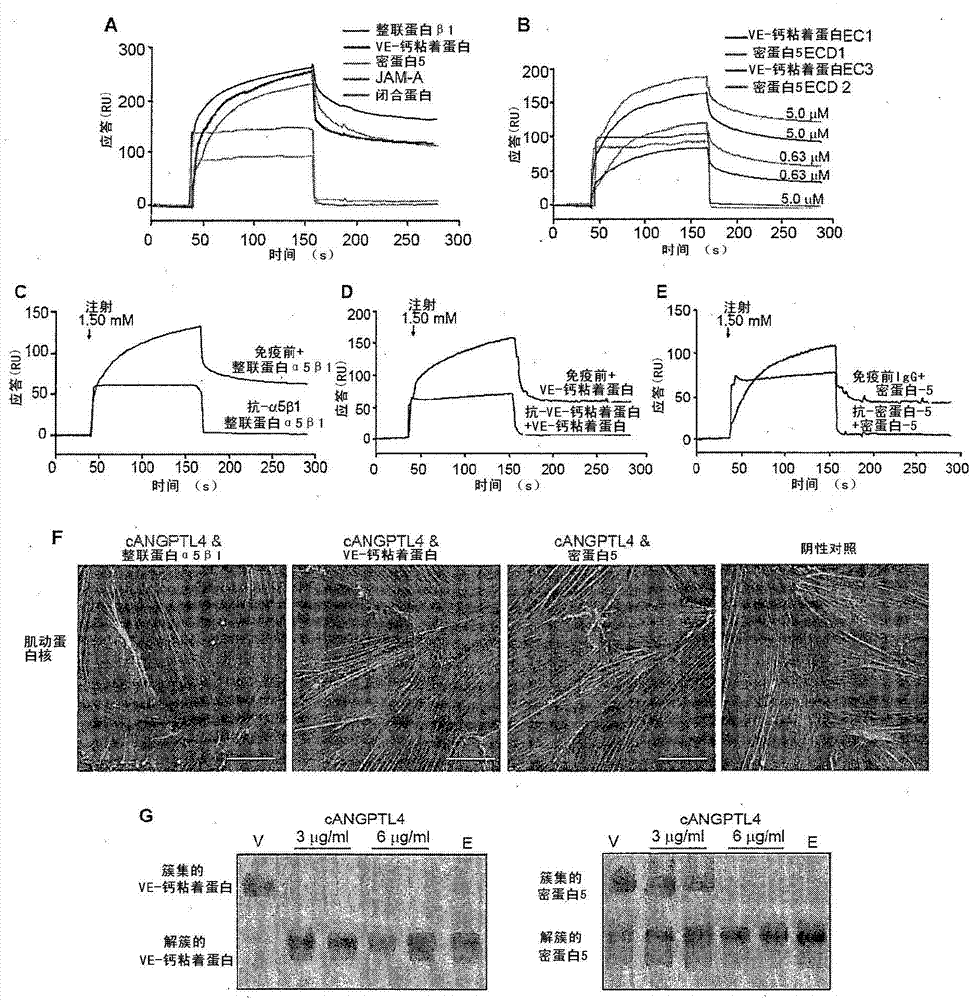
Angiopoietin-like 4 and its use in modulating cell leakiness
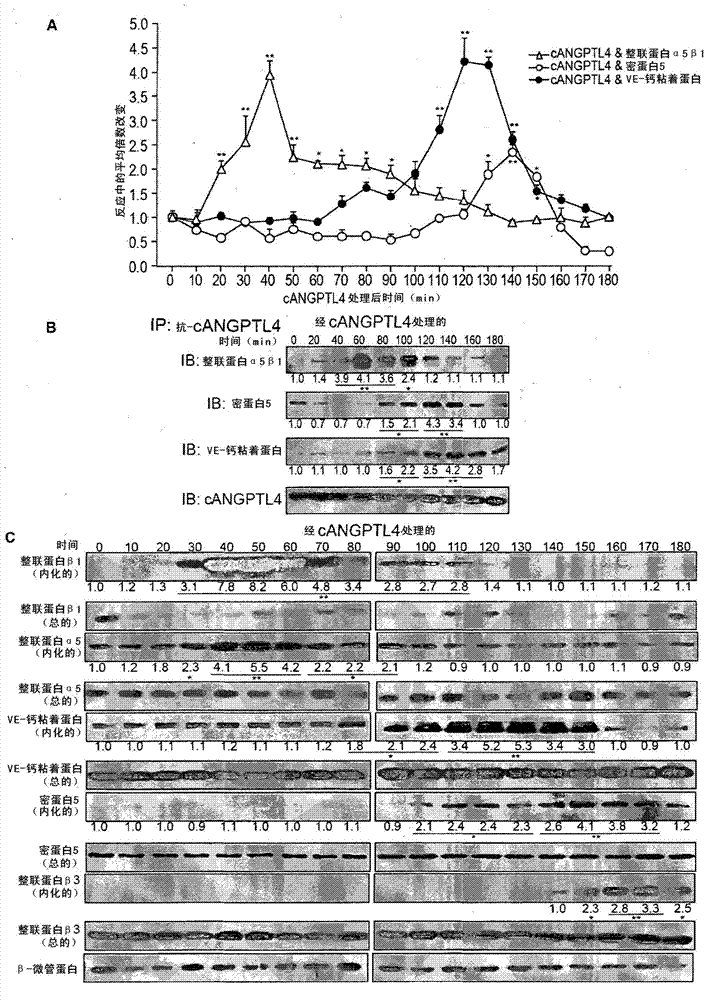
Vascular disruption induced by interactions between tumor-secreted permeability factors and adhesive proteins on endothelial cells facilitates metastasis. The role of tumor secreted angiopoietin-like 4 (cANGPTL4) in vascular leakiness and metastasis is controversial due to the lack of understanding of how cANGPTL4 modulates vascular integrity. Here, we show that cANGPTL4 instigated the disruption of endothelial continuity by directly interacting with three novel binding partners, integrin [alpha]5[beta]1, VEcadherin and claudin-5, in a temporally sequential manner, thus facilitating metastasis. We showed that cANGPTL4 binds and activates integrin [alpha]5[beta]1-mediated Rac1 / PAK signaling to weaken cell-cell contacts. Subsequently, cANGPTL4 is associated with and declusters VE-cadherin and claudin-5, leading to endothelial disruption. Interfering with the formation of these cANGPTL4 complexes delayed vascular disruption. In vivo vascular permeability and metastatic assays performed using ANGPTL4-knockout and wild-type mice injected with either control or ANGPTL4-knockdown tumors confirmed that cANGPTL4 induced vascular leakiness and facilitated lung metastasis in mice. Therefore, our findings elucidate how cANGPTL4 induces endothelial disruption. Our findings have direct implications for targeting cANGPTL4 to treat cancer and other vascular pathologies.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
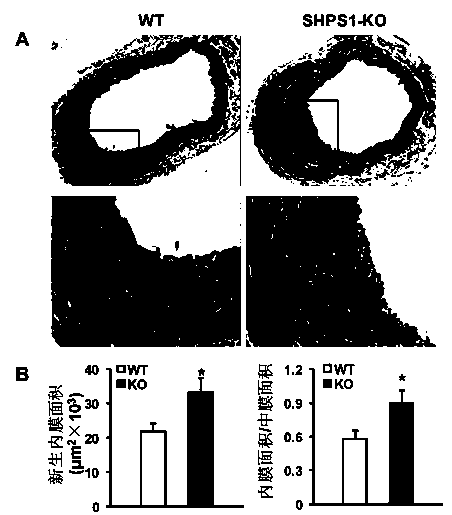
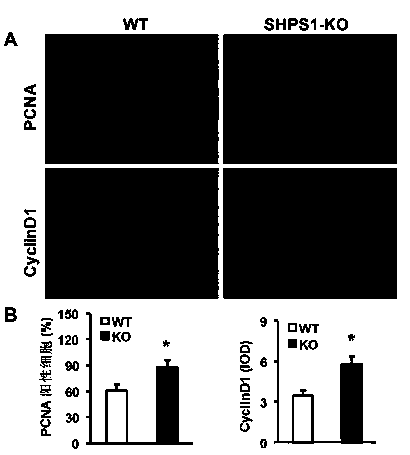
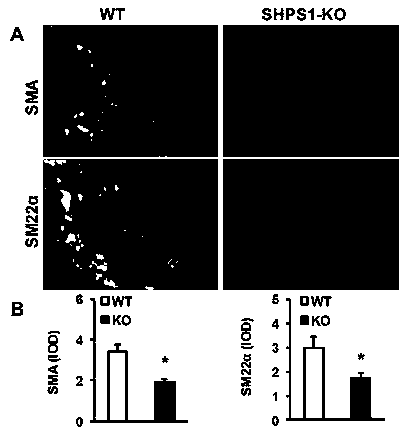
Functions and application of SHPS1 in treatment of post-vascular injury restenosis
ActiveCN104174010APrevent restenosisPrevent stenosisPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCell phenotypeNeointima
The invention discloses functions and application of SHPS1 in treatment of post-vascular injury restenosis, belonging to the field of functions and applications of genes. SHPS1 gene knockout mice and wild type mice are taken as experimental subjects, and due to a vascular injury model, the mouse neointima formation, vascular wall cell proliferation level and smooth muscle cell phenotype transform are detected. The result proves that SHPS1 gene knockout can obviously promote neointima neogenesis and cell proliferation and promote transformation of smooth muscle cells from a shrinkage manner to a synthetic manner. Thus the functions of SHPS1 in post-vascular injury restenosis are realized, which mainly shows that SHPS1 has the functions of inhibiting neointima formation and cell proliferation and inhibiting smooth muscle cell phenotype transformation. Aiming at the functions of the SHPS1, the SHPS1 can be used for preparing medicines and arterial stents for preventing, relieving and / or treating the post-vascular injury restenosis.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
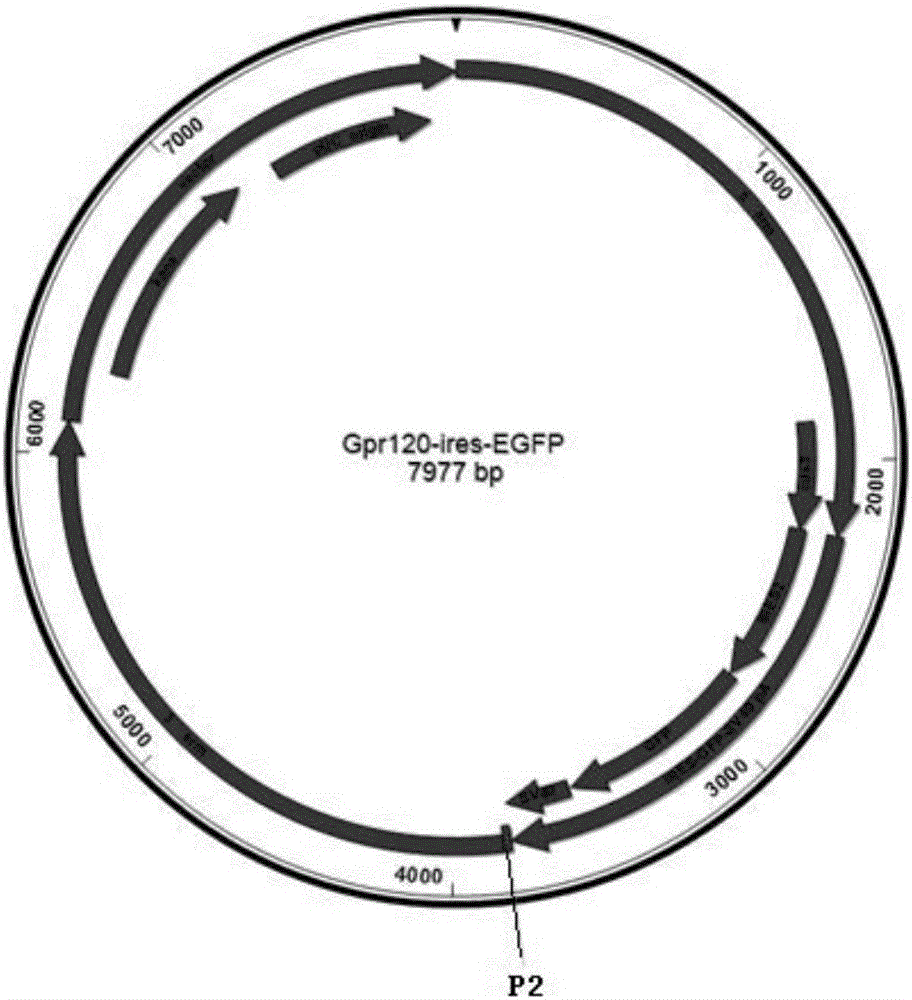
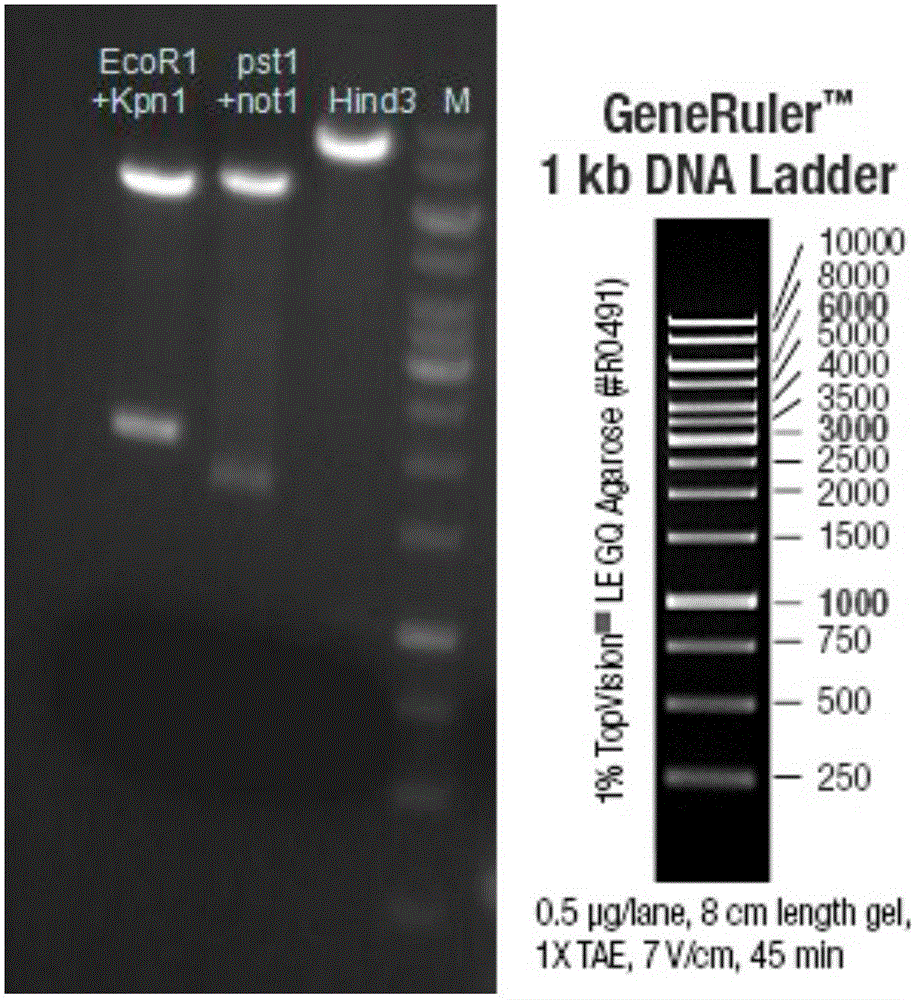
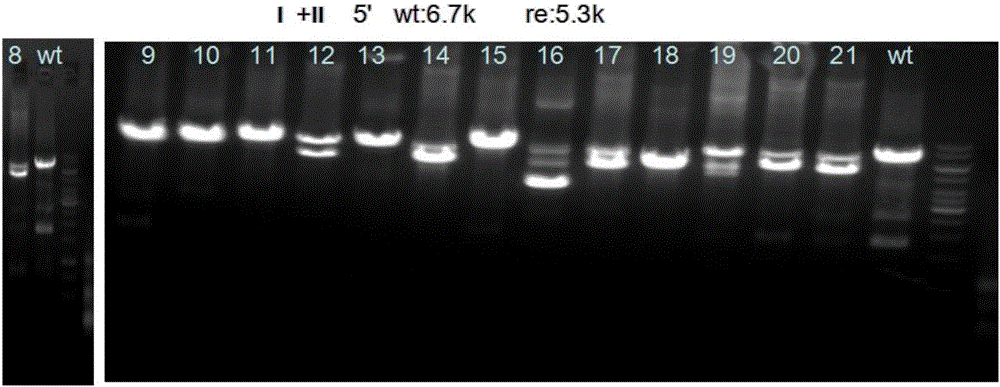
Mouse model construction method of eGFP-labeled GPR120 positive cells
InactiveCN106086072AFunctionality is not affectedCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationF1 generationWild type
Provided is a mouse model construction method of eGFP-labeled GPR120 positive cells. A guideRNA target sequence aiming at a target locus genome is designed, and in vitro transcription is carried out to obtain guideRNA aiming at the genome; donor DNA recombinant plasmid is constructed; the guideRNA and the donor DNA recombinant plasmid are subjected to oosperm injection to obtain F0-generation mice, and the genotype of the F0-generation mice is identified to obtain positive F0-generation mice achieving correct homologous recombination; the F0-generation mice and wild type mice are copulated to obtain F1-generation mice, and the genotype of the F1-generation mice is identified to obtain positive F1-generation mice achieving correct homologous recombination; positive transgenic mice in the generation F1 are subjected to sib mating to obtain F2-generation mice, and homozygous transgenic mice are obtained through screening and identifying. According to the method, GPR120 expression cell express eGFP at the same time, and therefore GPR120 positive cells are distinguished under laser excitation.
Owner:XIAN MEDICAL UNIV
New application of dcf1 gene
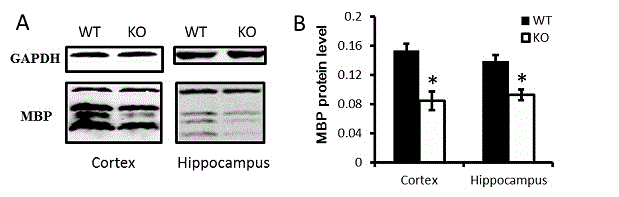
The invention relates to new application of a dcf1 gene. A wild type mouse (serving as contrast) and a mouse with the dcf1 deleted are mainly adopted; western blotting is used for detecting reducing of myelin basic protein; immunohistochemistry and a transmission electron microscope are used for observing changing of the form of a myelin sheath; and then a behavioral experiment is used for showing that the mouse with the dcf1 deleted can simulate clinical symptoms of multiple sclerosis, then the mouse with the dcf1 deleted is subjected to rescue, and it is discovered that the dcf1 can cause myelin sheath remodeling and regeneration.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for screening PTPzeta activity promoter or inhibitor
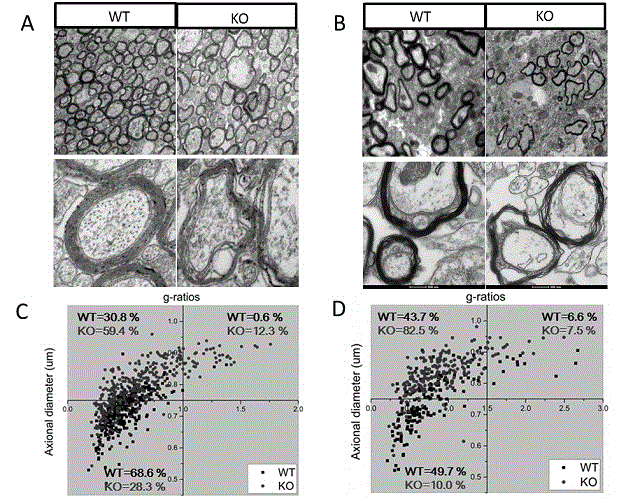
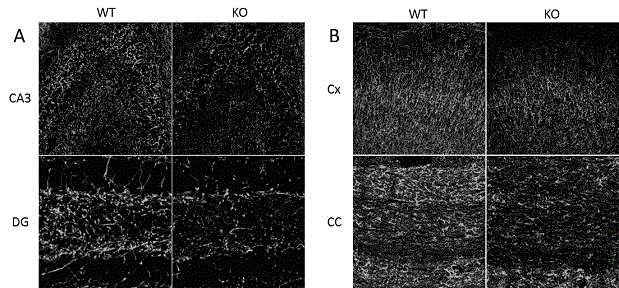
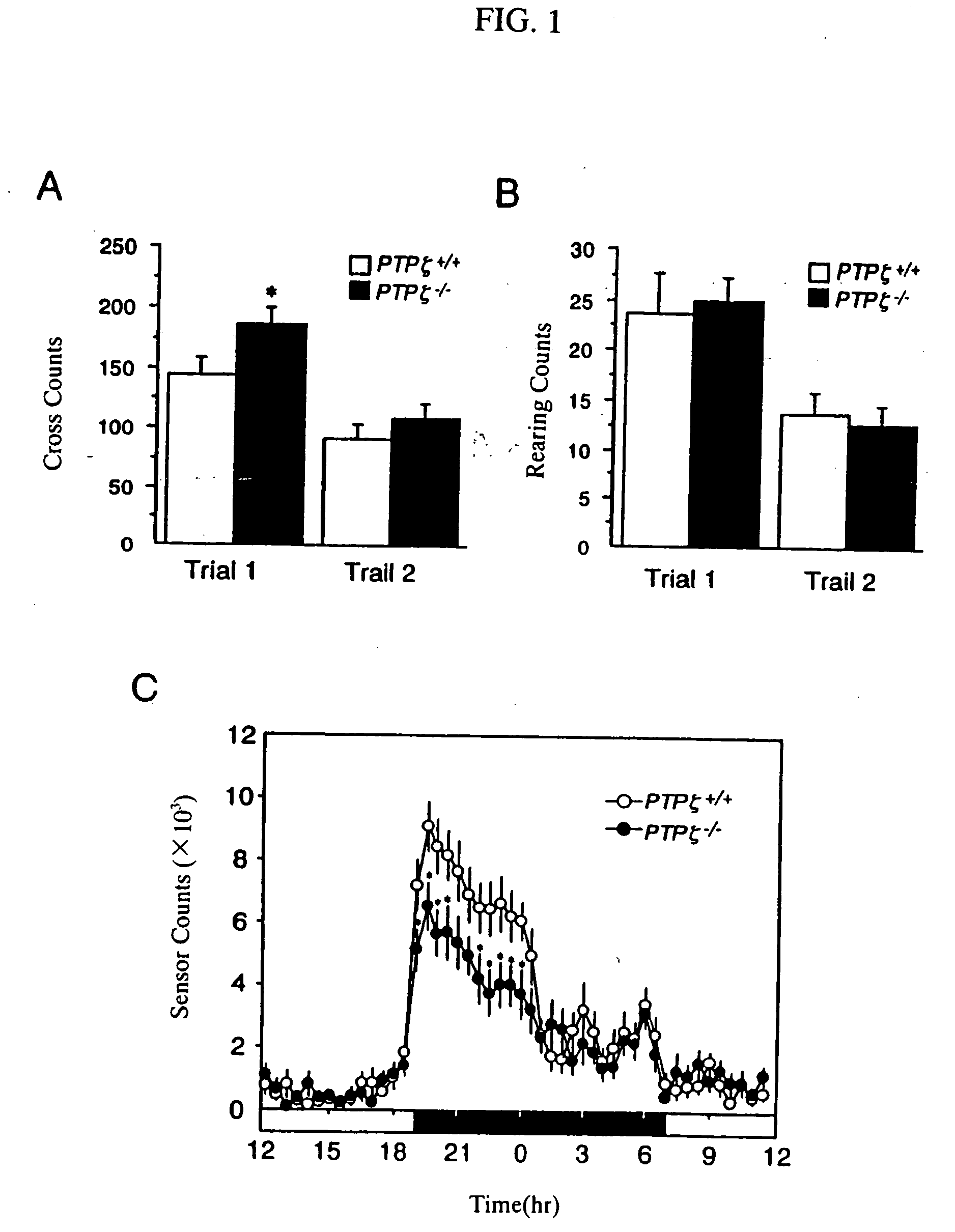
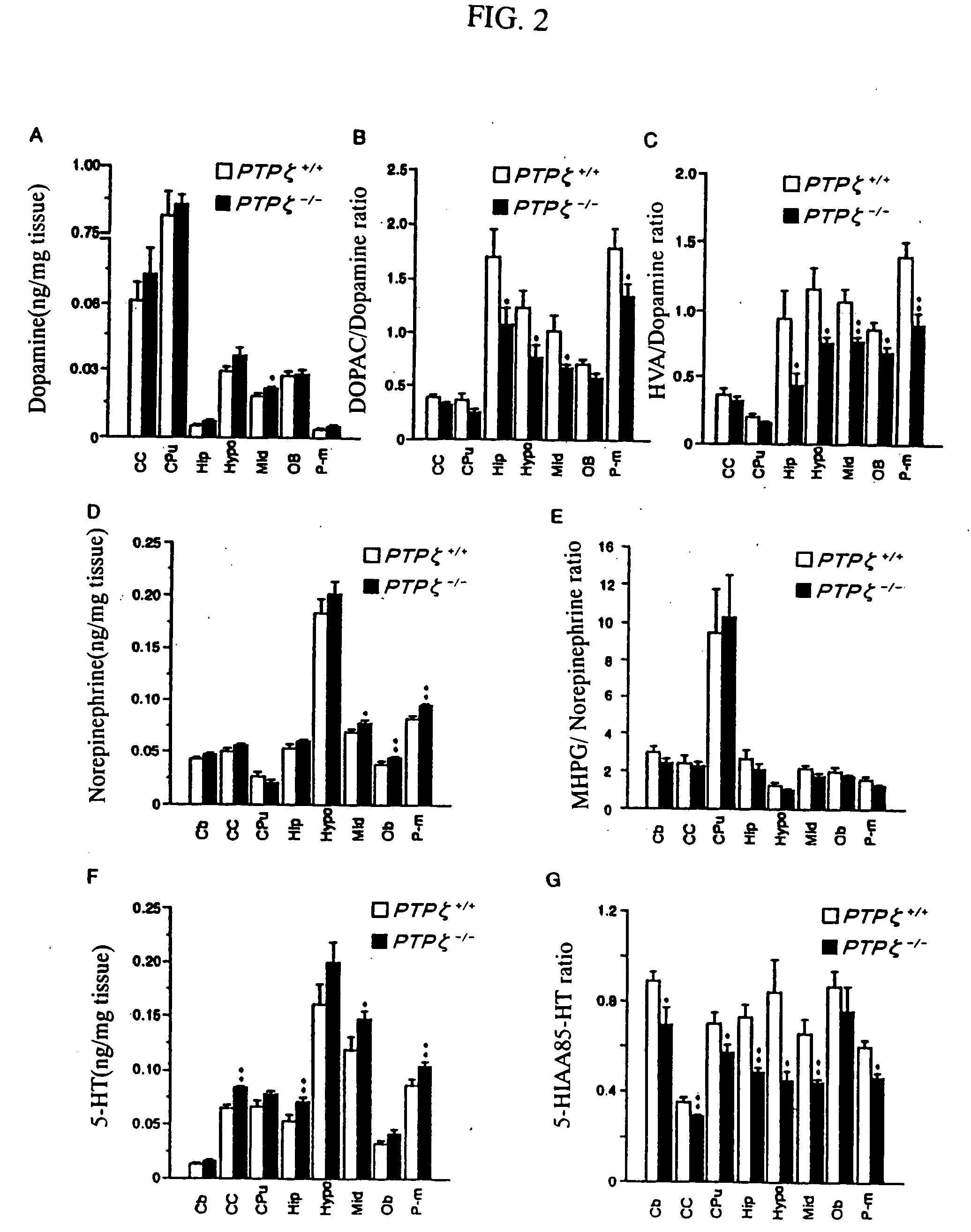
An object of the present invention is to provide a remedy for dysfunction of central monoamine pathway, a method for screening a PTPζ inhibitor or activator, which is useful as a remedy for gastric ulcer caused by Helicobacter pylori or pleiotrophin which is a heparin-binding secretory protein, and a non-human model animal being hyposensitive to a stimulant drug, VacA which is a toxin of Helicobacter pylori, or pleiotrophin by utilizing the physiological function of PTPζ. After administering a subject material to PTPζ knockout mice and wild-type mice, PTPζ activity in the PTPζ knockout mice and the wild-type mice is compared and evaluated to screen a PTPζ inhibitor or activator. Examples of the comparison and the evaluation of the PTPζ activity include the comparison and the evaluation of the function of central monoamine pathway such as changes in the level of central monoamine metabolism, sensitivity to a stimulant drug, the presence of dysfunction of mesolimbic dopamine pathway, level of acclimation to new circumstances, or stress-responsiveness, and the comparison and the evaluation of the level of binding to VacA, a toxin of Helicobacter pylori, or pleiotrophin.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Function of tumor progress site 2 in treatment of fatty liver and type 2 diabetes as well as application thereof
InactiveCN106512014AWith deteriorating fatty liverType 2 diabetes mellitusMetabolism disorderDigestive systemIntraperitoneal routeHepatic dysfunction
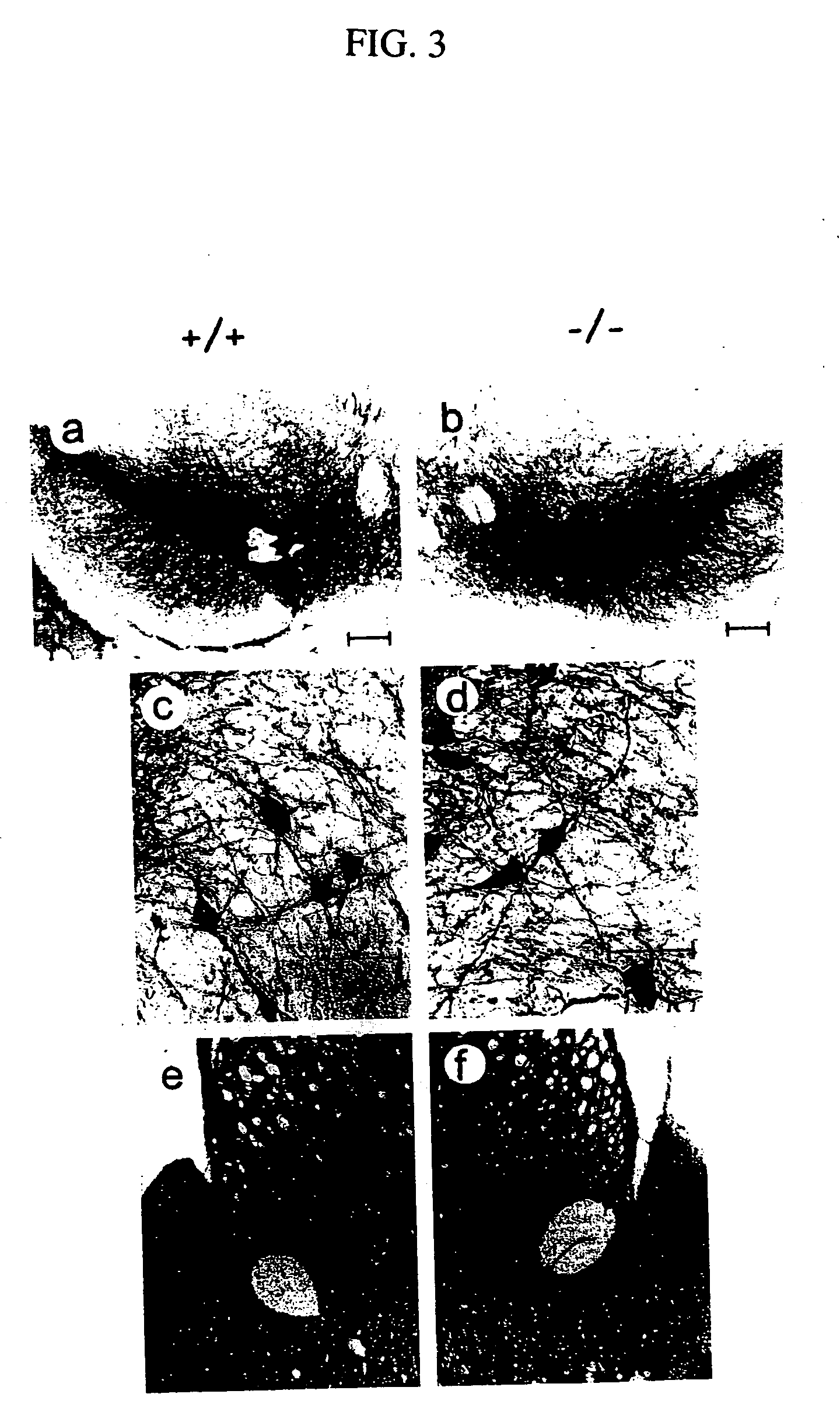
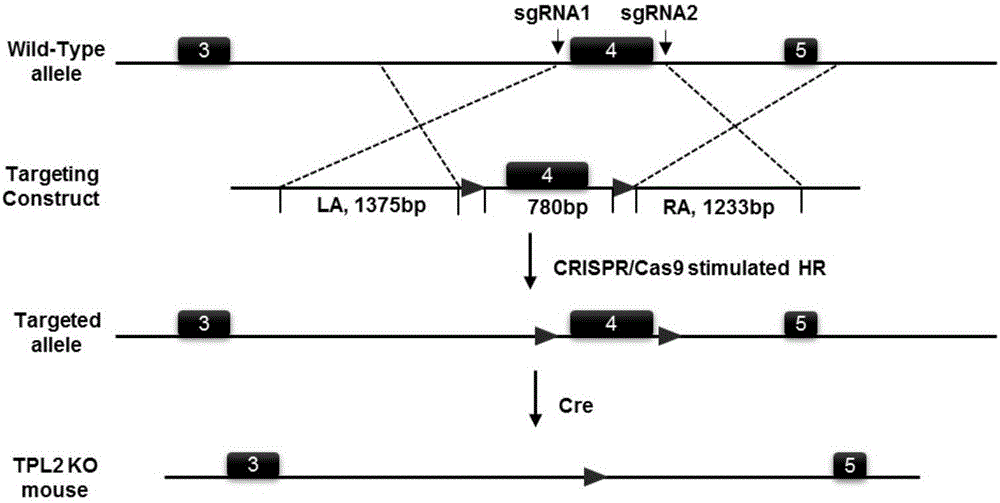
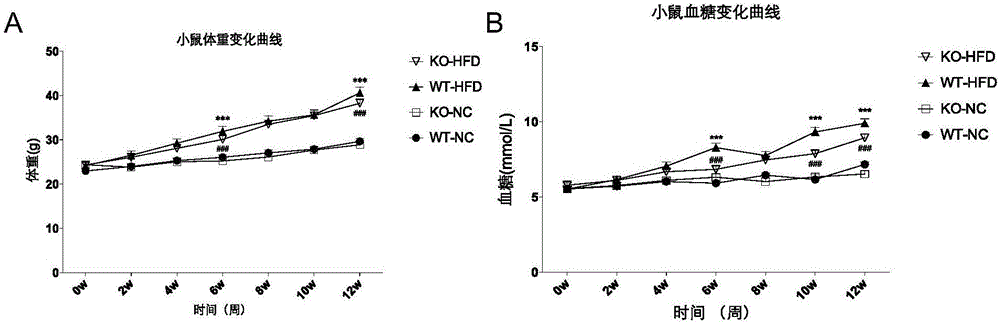
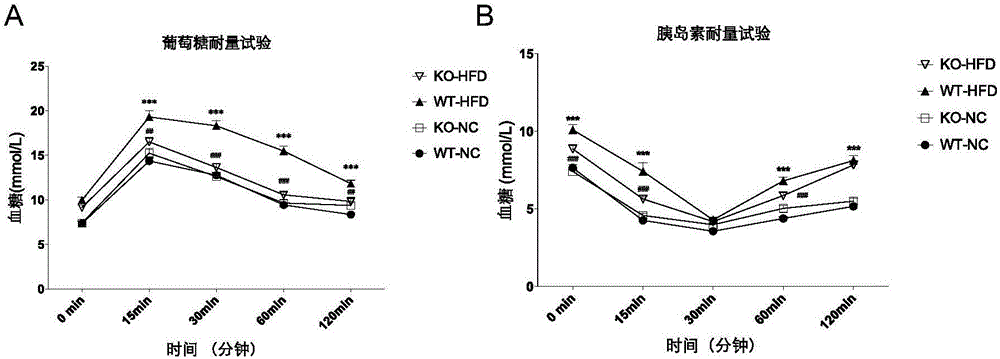
The invention discloses a function of tumor progress site 2 in treatment of fatty liver and type 2 diabetes as well as an application thereof. According to the invention, TPL2 gene knockout mice and wild type mice are taken as the experiment objects, through a high-fat diet-induced obesity mice model, the result shows that compared with the wild type C 57 mice, body weight of the TPL2 gene knockout mice is mitigated, the fasting blood glucose level is lower than that of a control group WT mice, and the hepatic dysfunction is obviously mitigated. Through intraperitoneal glucose tolerance experiment, the endurance of the TPL2 gene knockout mice on glucose is obviously enhanced. the mice liver tissue cholesterol content change result instructs that TPL2-KO mice fatty liver pathology of a HFD group (High fat diet) is obviously mitigated, and the lipid accumulation is obviously reduced. TPL2 can be taken as a drug target for treating fatty liver and / or type 2 diabetes, and its inhibitor can be used for preparing a drug to treating fatty liver and / or type 2 diabetes.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Application of asarol or substance containing asarol to preparation of medicine for promoting neural stem cell proliferation
PendingCN106176696APromote regenerationPromote proliferationNervous disorderEther/acetal active ingredientsDiseaseERK cascade
The invention belongs to the field of drug research and development, and in particular relates to the use of asarone or a substance containing asarone in the preparation of drugs for promoting the proliferation of neural stem cells. The present invention finds for the first time that oral administration of Shichangpu can promote hippocampal nerve regeneration in wild-type mice, transgenic AD model mice and aged mice. In vitro and in vivo experiments, Shichangpu and its active ingredient asarone promote the proliferation of neural stem cells. Calamus calamus and asarone activate ERK cascade without affecting Akt cascade. The research of the present invention shows that oral administration of calamus and asarone can not only prevent, but also act as a therapeutic means to promote nerve regeneration, to resist the decline of cognitive function related to aging and neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
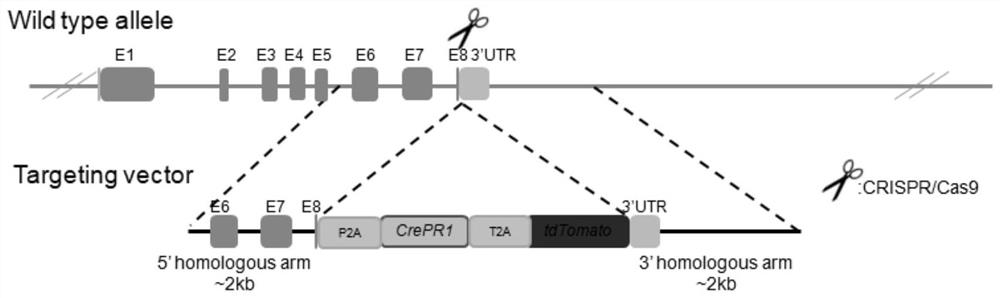
Construction and application of KRT10 site-directed gene knock-in P2A-CrePR1-T2A-tdTomato mouse model
Owner:THE FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF FOSHAN +1
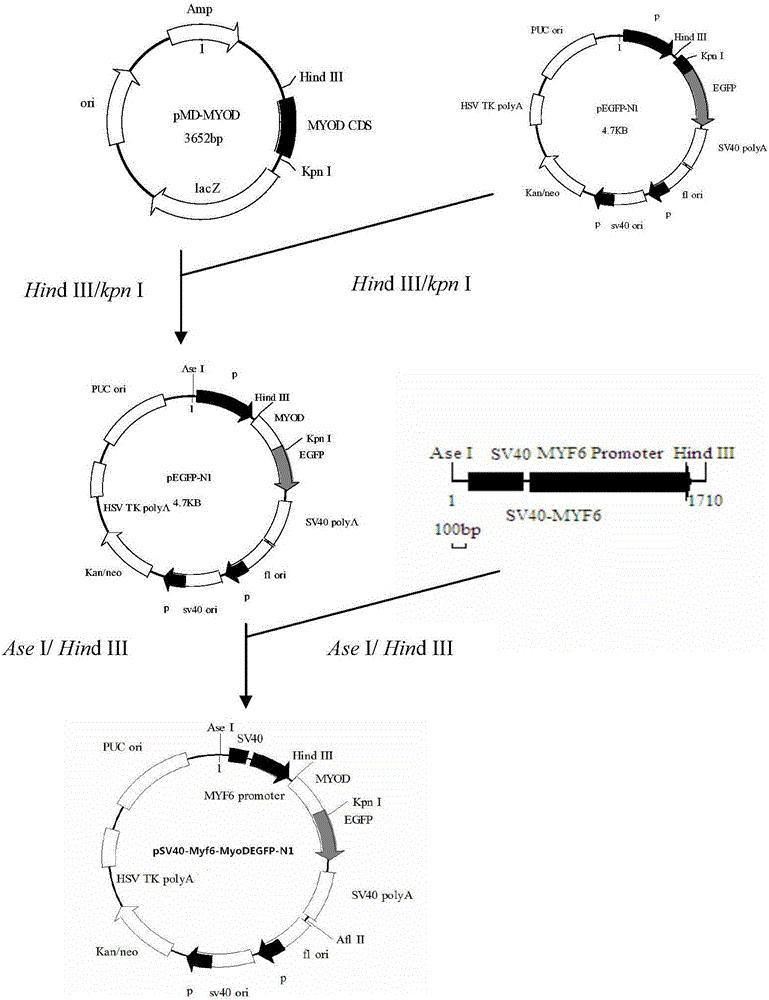
Application of Myf6 promoter in driving expression of MyoD gene in muscular tissue
InactiveCN105039340AImprove lean meat percentagePromote growthFermentationPlant genotype modificationFiberWild type
The invention belongs to the field of animal genetic engineering, and in particularly relates to an application of a promoter region of a specific expression gene Myf6 of skeletal muscle of pigs in level verification of a model animal transgenic mouse living body. According to the invention, a constructed eukaryotic expression vector pSV40-Myf6-MyoDEGFP-N1 is subjected to linear treatment, and a transgenic mouse is prepared through micro-injection; MyoD gene expression conditions in different tissues of the positive transgenic mouse are verified, a tissue expression profile is established, and the horizontal expression conditions of MyoD in skeletal muscle of the transgenic mouse and wild type mouse in mRNA and protein are verified, the result shows that Myf6 gene promoter can specifically up-regulate the overexpression of the MyoD gene in the skeletal muscle; and the growth condition of muscle fiber is observed through a muscular tissue slice, the result shows that the area and the diameter of the muscle fiber in the muscular tissue slice of the transgenic mouse are significantly higher than those of the wild type mouse, and the density of the muscle fiber in unit area is obviously lower than that of the wild type mouse.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
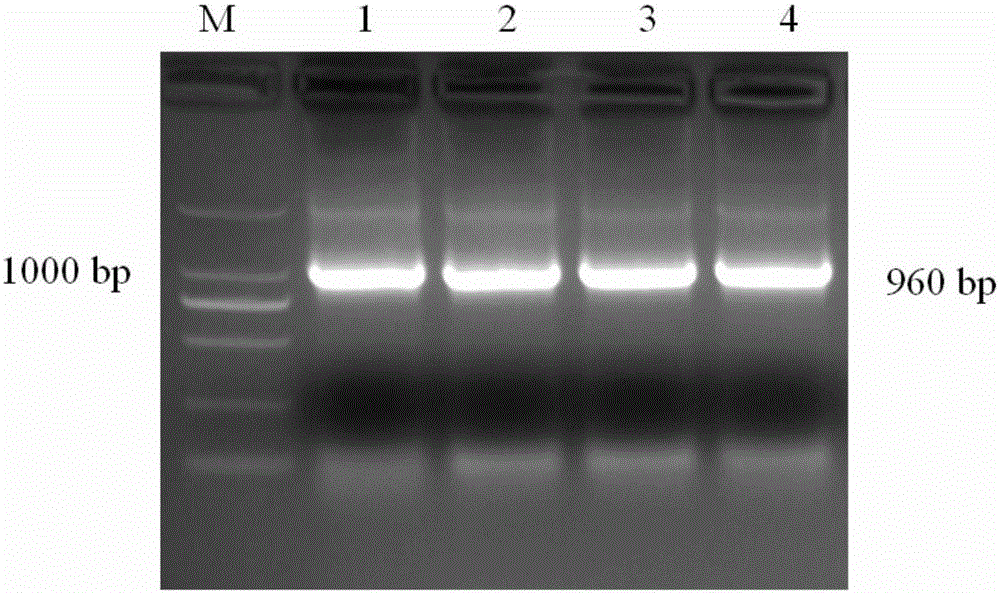
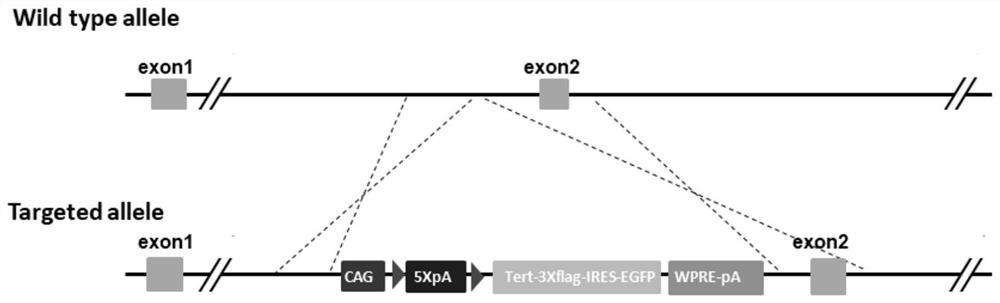
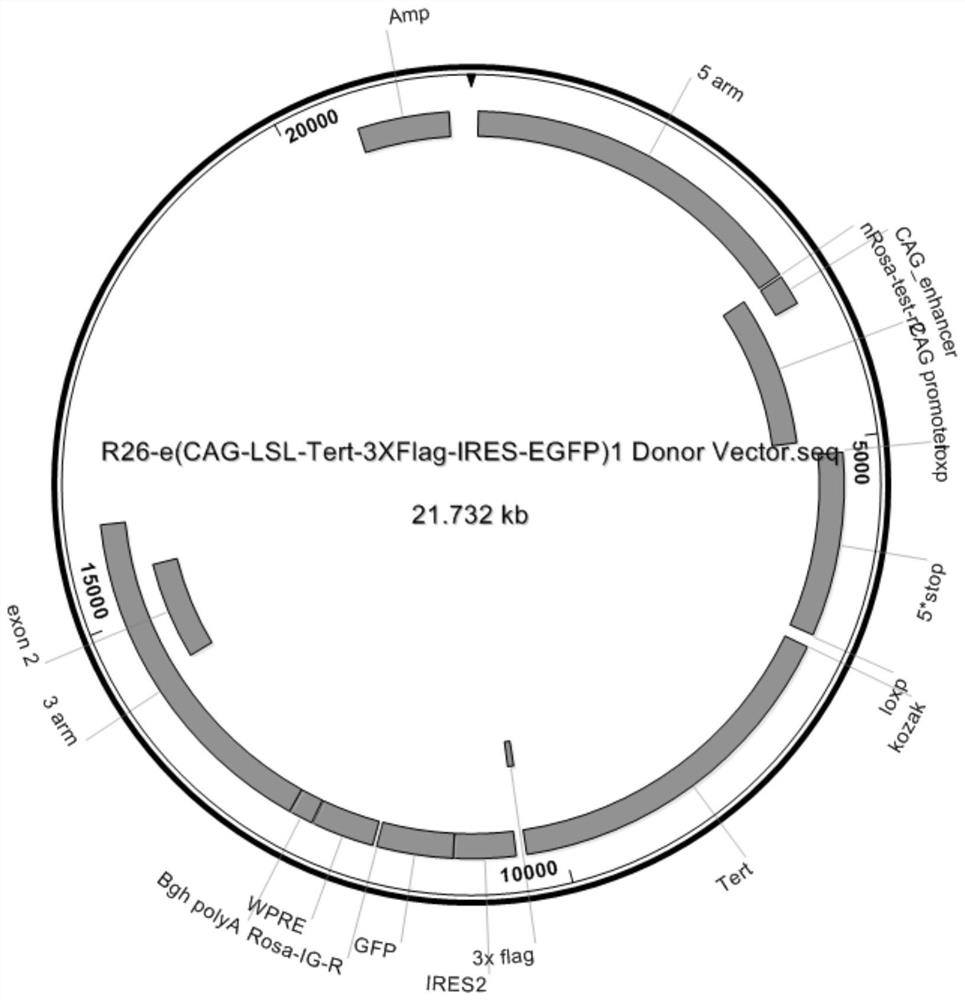
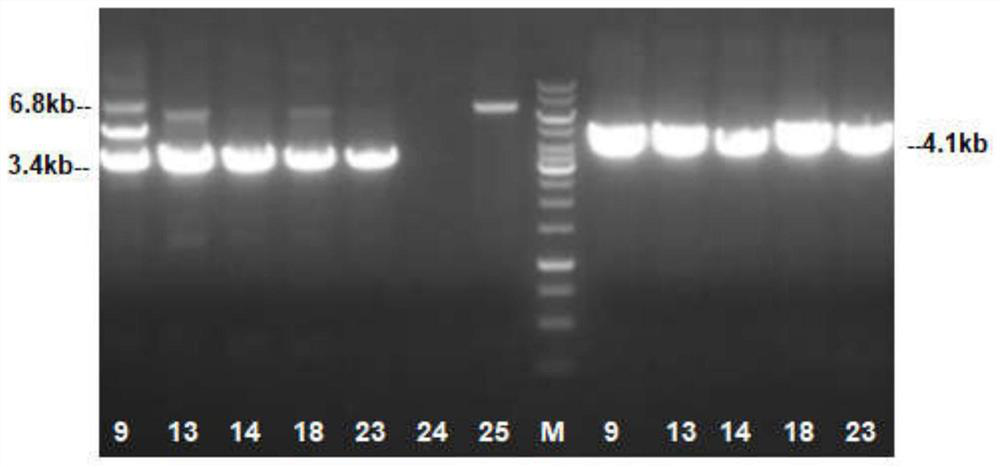
Construction method of a mouse model with conditional mTERT overexpression and application thereof
The invention provides a construction method of a mouse model with conditional mTERT overexpression and an application thereof. The construction method comprises the following steps: constructing a targeting vector through a seamless cloning technology, wherein the targeting vector comprises a 3.3 kb 5'homologous arm, a CAG promoter, loxp-stop-loxp, TERT-3XFlag-IRES-EGFP-WPRE-polyA and a 3.3 kb 3'homologous arm; cas9 mRNA, gRNA and the targeting vector are microinjected into fertilized eggs of wild type mice to obtain F0-generation mice, homologous recombination positive F0-generation mice are identified, F1-generation mice are obtained through breeding after backcross, and the F1-generation mice are conditional mTERT overexpressed mouse models. The mouse constructed by the construction method provided by the invention can mate with different Cre tool mice to realize specific overexpression in various tissues, organs and cell types of the whole body. The mouse can be used for modeling various transgenic models for researching embryo and nerve development, senescence, wound repair, tumor occurrence, development and treatment, and the mating of the mouse and a CreERT tool mouse can control the time of TERT overexpression through tamoxifen.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT
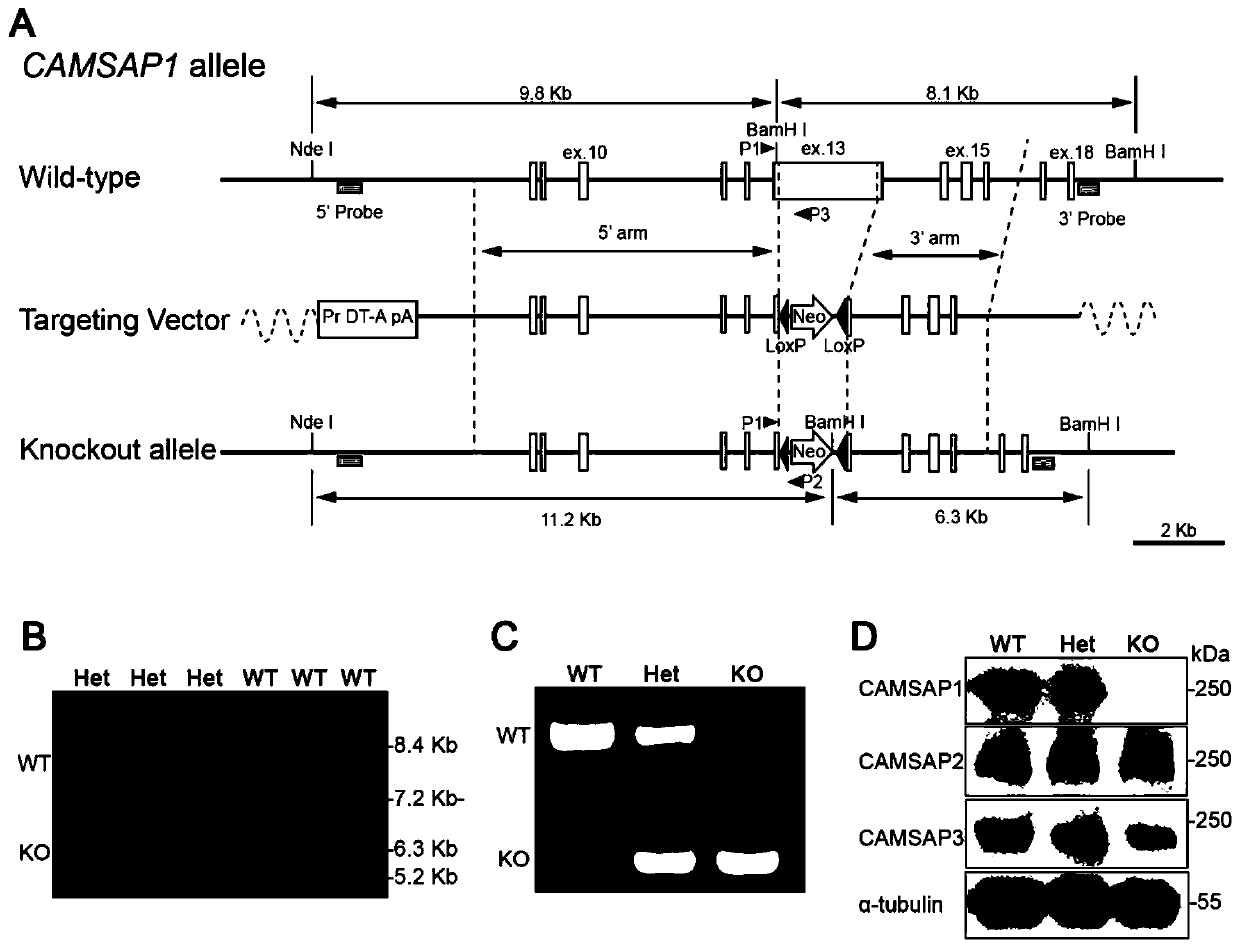
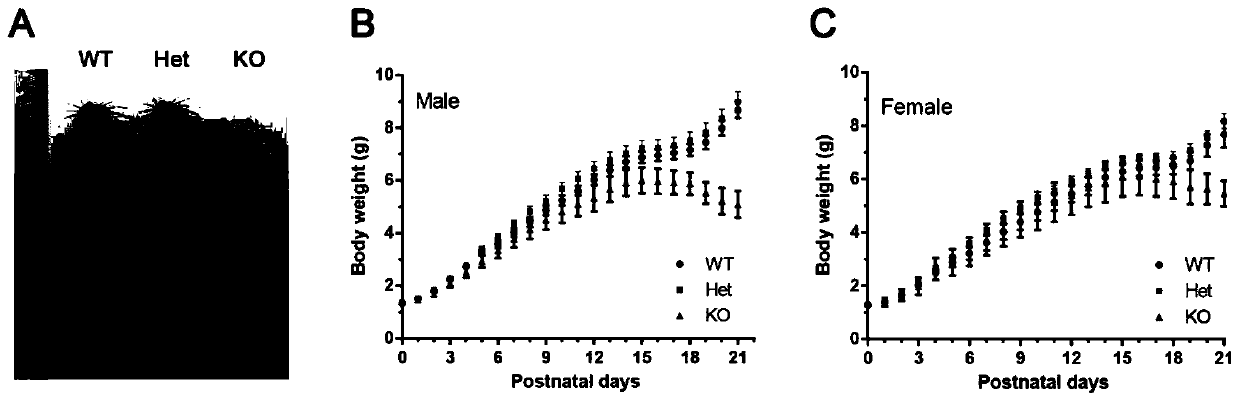
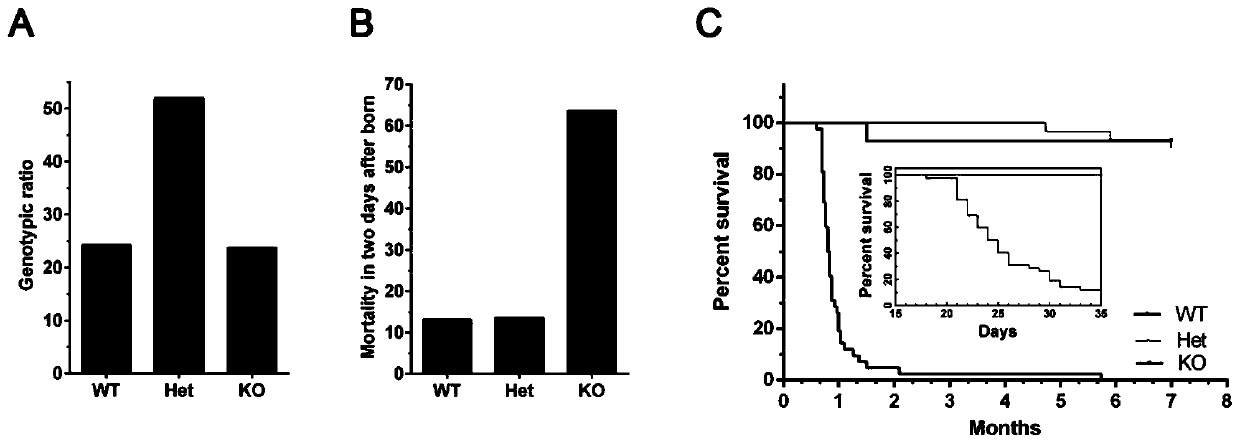
CAMSAP1 protein and application of gene thereof as epileptic drug target
InactiveCN110865195AIncreased mortalityCompounds screening/testingCompound screeningRadial glial cellPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses a CAMSAP1 protein and the application of a gene thereof as an epileptic drug target. The 13th exon of CAMSAP1 is selected as a target site, and a wild mouse is knocked out through a homologous recombination method to acquire a knocked-out mouse. Experiments prove that compared with wild type mice, the knocked-out mouse is small in size and light in weight, and the death rate is increased. The CAMSAP1 protein is knocked out to change the polarity of neurons. The knocked-down CAMSAP1 protein can influence the transformation of neurons from multipolar cells to bipolar cells, resulting in abnormal migration of neurons along radial glial cells (the migration of neurons is influenced), and abnormal layered arrangement of neurons in cerebral cortex. The knocked-out CAMSAP1protein can cause epilepsy. Therefore, the CAMSAP1 protein can maintain normal growth of neurons and prevent and / or treat epilepsy. The CAMSAP1 protein and the application, which are provided by theinvention, have an important application value.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
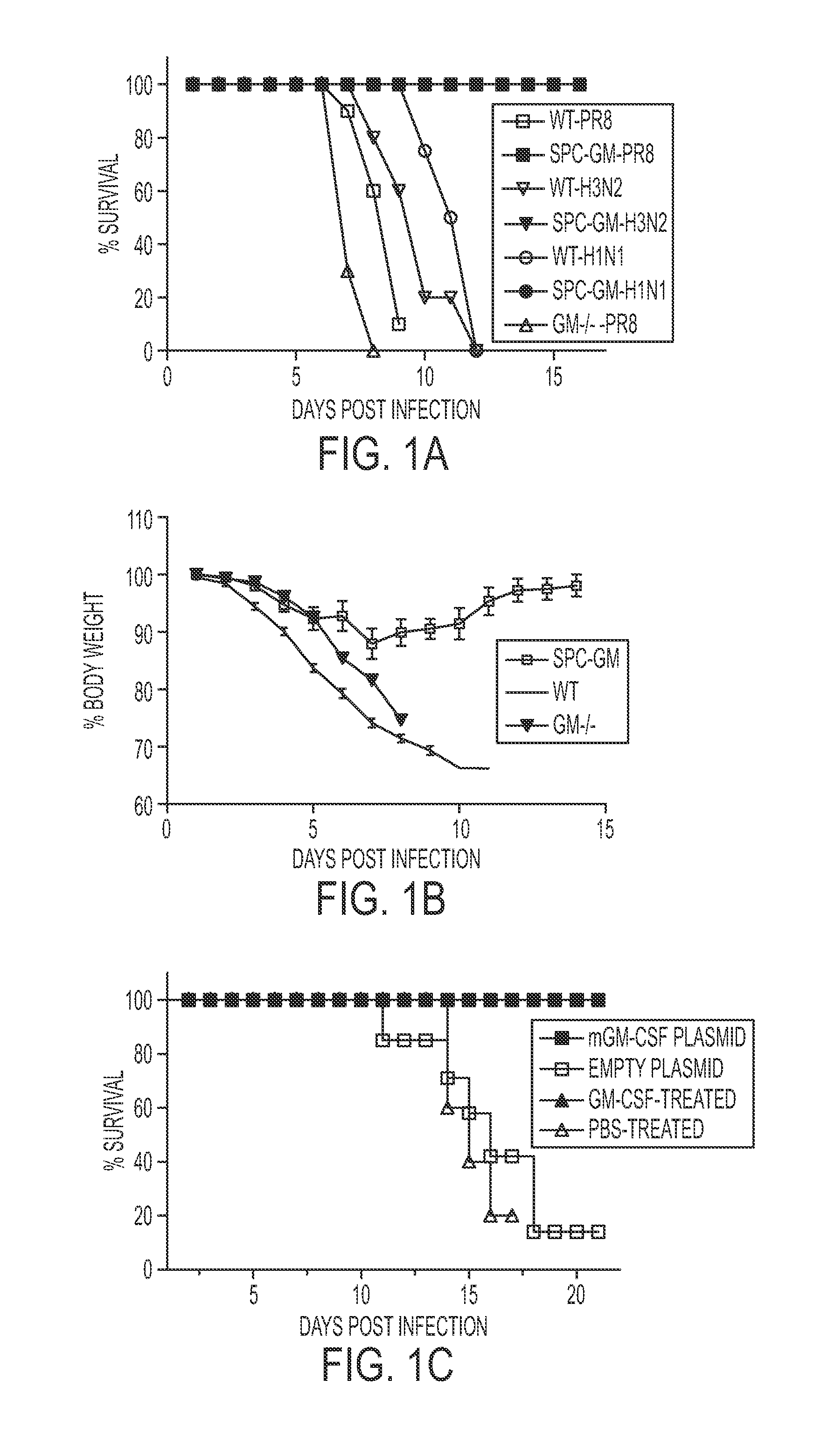
Protection against influenza infection by granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor
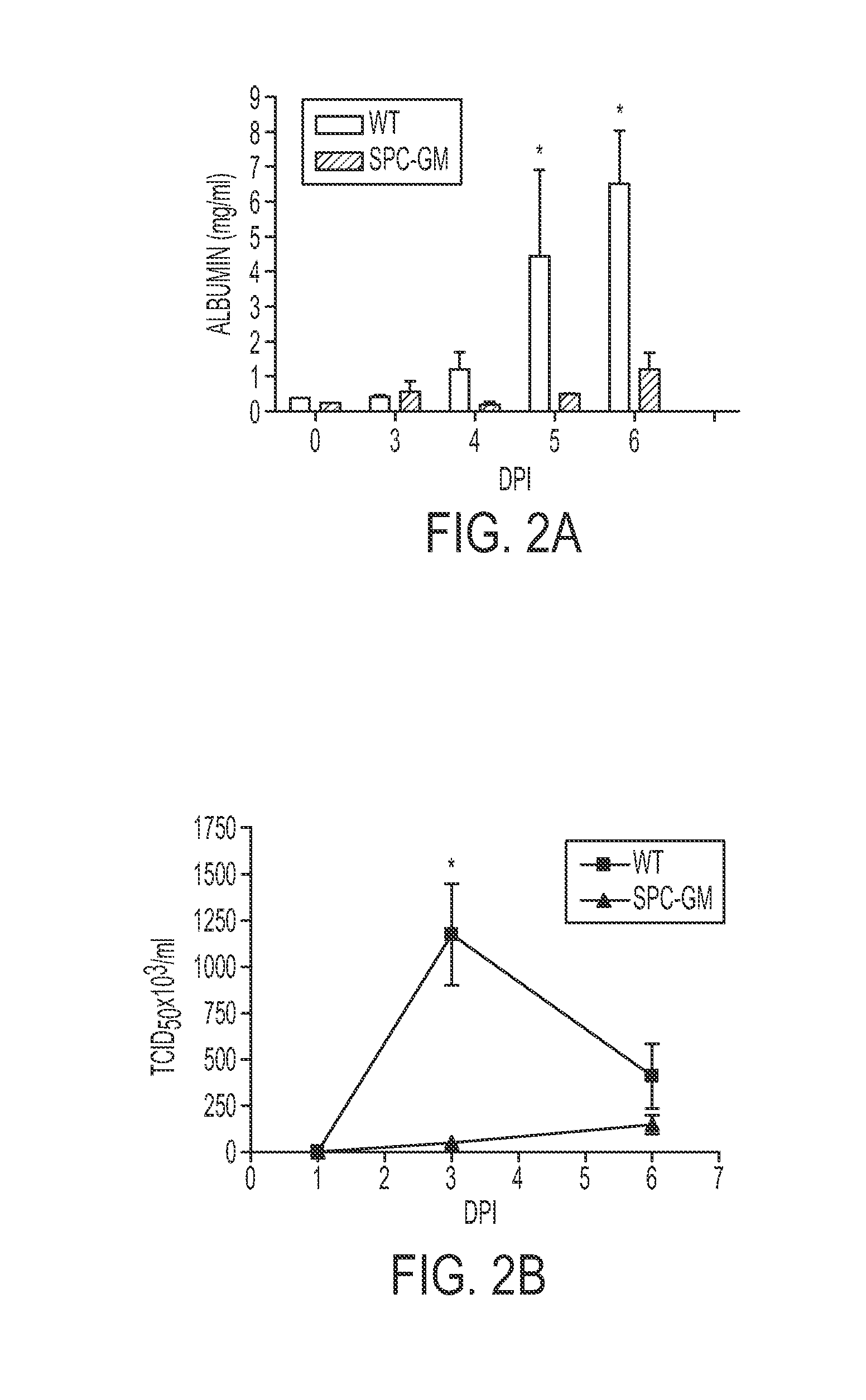
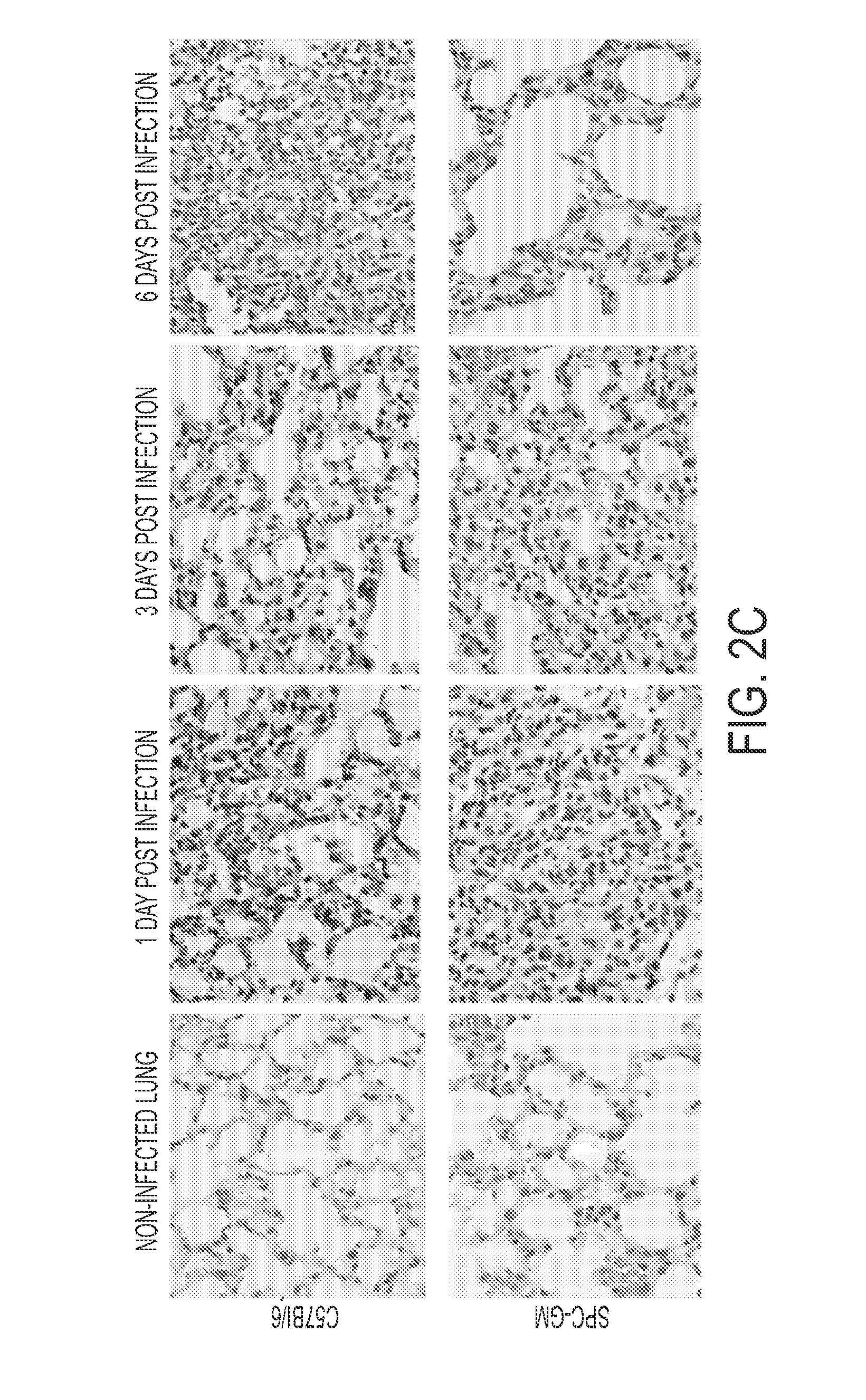
ActiveUS20140193506A1Optimization mechanismImprove balancePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsPulmonary infectionApoptosis
Alveolar macrophages contribute to host defenses against influenza. Enhancing their function contributed to protection against influenza and other acute lethal pulmonary infections. Wild-type mice and Tg mice expressing GM-CSF in the lung were infected with influenza virus, and lung pathology, weight loss and mortality were measured. GM-CSF was also administered to lungs of wild-type mice that were infected with influenza virus. All Tg mice expressing GM-CSF in the lungs survived with greatly reduced weight loss and lung injury and histologic evidence of a rapid host inflammatory response that controlled infection vs. wild-type mice not expressing GM-CSF in the lungs. This resistance to influenza was abrogated by elimination of alveolar phagocytes, but not by depletion of T cells, B cells or neutrophils. Tg mice had far more alveolar macrophages than wild-type mice and were more resistant to influenza-induced apoptosis. Delivery of intranasal GM-CSF to wild-type mice also conferred influenza resistance. Therefore, GM-CSF confers resistance to influenza by enhancing innate immune mechanisms that depend on alveolar macrophages. Pulmonary delivery of GM-CSF is therefore useful for reducing the significant morbidity and mortality due to influenza virus and is similarly useful in pulmonary infection caused by other infectious viral and bacterial agents.
Owner:SHAMS HOMAYOUN
Construction method of congenital cataract disease animal model and application
ActiveCN112608940AFacilitate later reproductionCompounds screening/testingNucleic acid vectorDiseasePhysiology
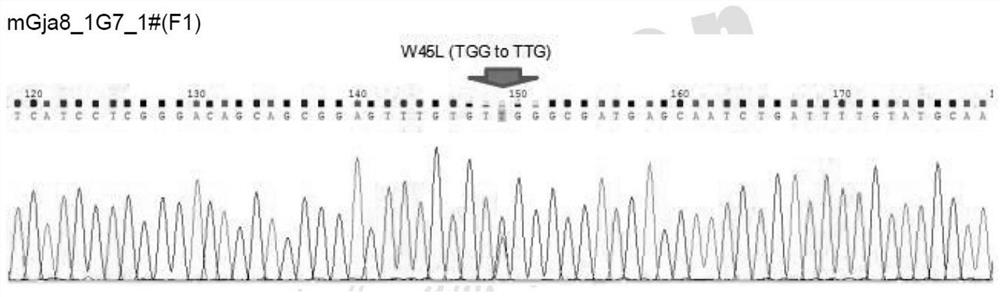
The invention relates to a construction method of a congenital cataract disease animal model, which comprises the steps of firstly, designing a gRNA target site sequence for a second exon region of a mouse GJA8 gene, amplifying a homologous arm and a cKO region, and respectively connecting the homologous arm and the cKO region to a vector; injecting positive clones into blastula by electroporation ES cells of the constructed plasmids, transferring the blastula into a mouse body, and obtaining a first builder mouse after a birth mouse is mature; mating with a wild type mouse to obtain a heterozygote mouse F1 generation with gene mutation; finally, mating the F1 generation of heterozygote mice with the same genotype to obtain F2 generation of gene mutation homozygote mice. According to the construction method of the congenital cataract disease animal model provided by the invention, typical characteristics of congenital cataract, such as crystalline lens degeneration opacity and crystalline lens epithelial apoptosis, can be obtained, the animal model can be used for researching congenital cataract diseases and screening medicines for treating the congenital cataract diseases, and application prospect is promising.
Owner:中国人民解放军陆军特色医学中心
Application of PSMB8 and PSMB8 inhibitor to preparation of medicine for treating fatty liver and related diseases
ActiveCN108130370AWith deteriorating fatty liverWith associated diseasesMicrobiological testing/measurementDigestive systemWild typeHigh fat
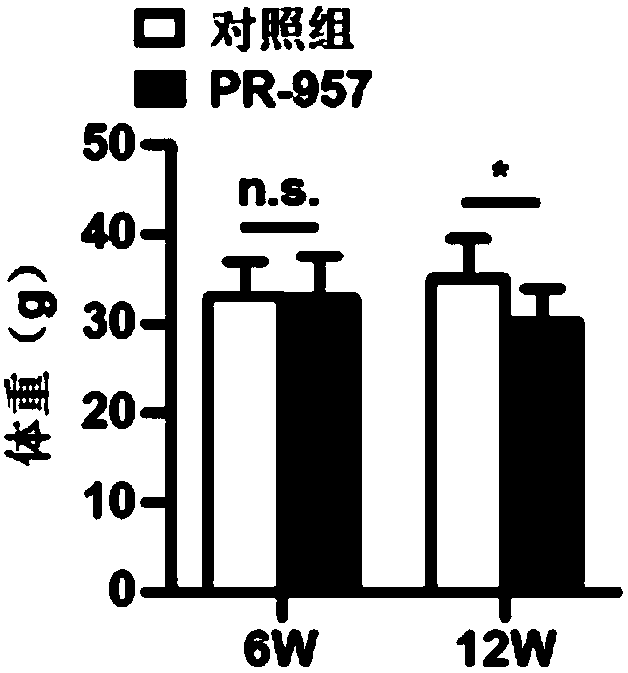
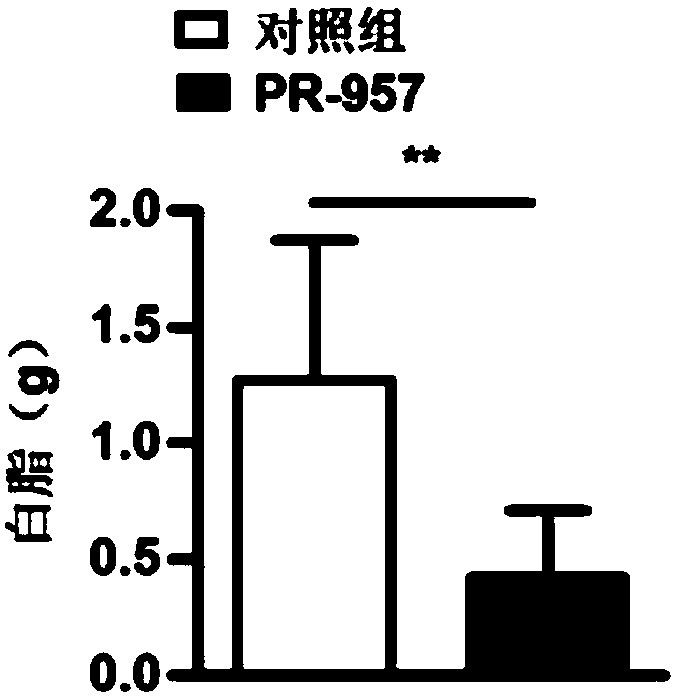
The invention discloses application of PSMB8 and a PSMB8 inhibitor to preparation of medicine for treating fatty liver and related diseases. Primary hepatocytes of C57BL / 6 wild type mice and PSMB8 knock-down C57BL / 6 mice are separated; the functions of PSMB8 gene are studied by a palmitate and oleic acid stimulation induced liver cell lipid accumulation model. The result proves that when the PSMB8expression is lowered, the PA+OA stimulation induced primary hepatocyte lipid accumulation is obviously reduced, i.e., the PSMB8 gene can promote the development and progression of fatty liver and related diseases; in an HFHC (high fat and high cholesterol) induced WT mouse fatty liver disease model, PR-957 can obviously inhibit HFHC induced weight increase, white grease increase and liver lipidaccumulation; the development and progression of the fatty liver and related diseases are inhibited. Therefore the PSMB8 provides a target for developing medicine for preventing, relieving and / or treating the fatty liver and related diseases.
Owner:武汉惠康达科技有限公司
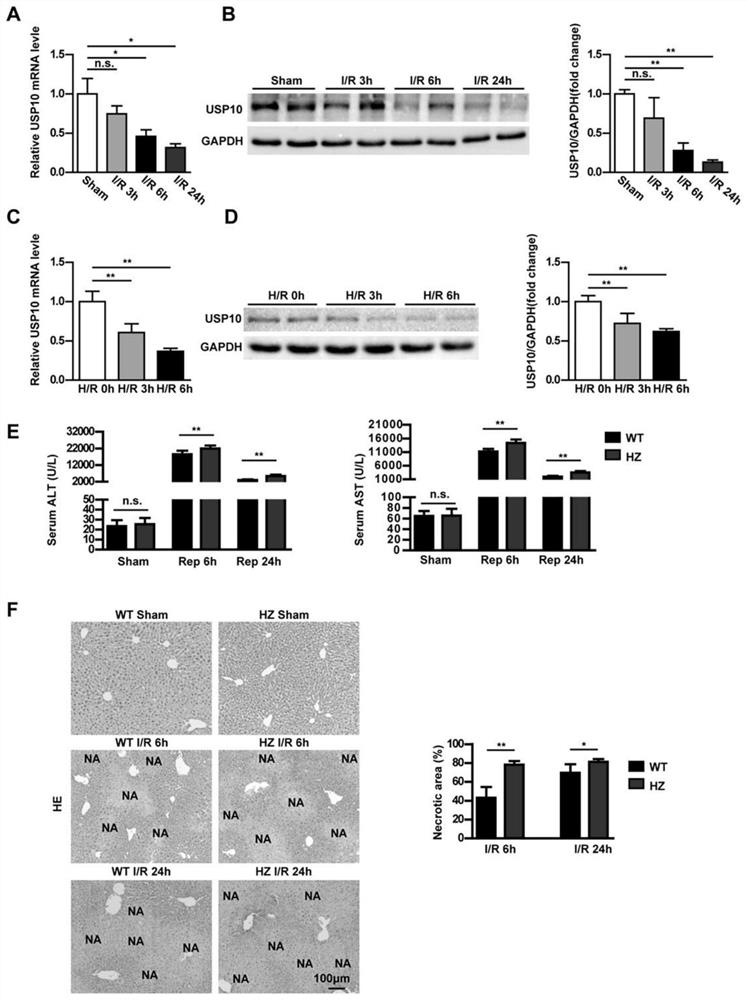
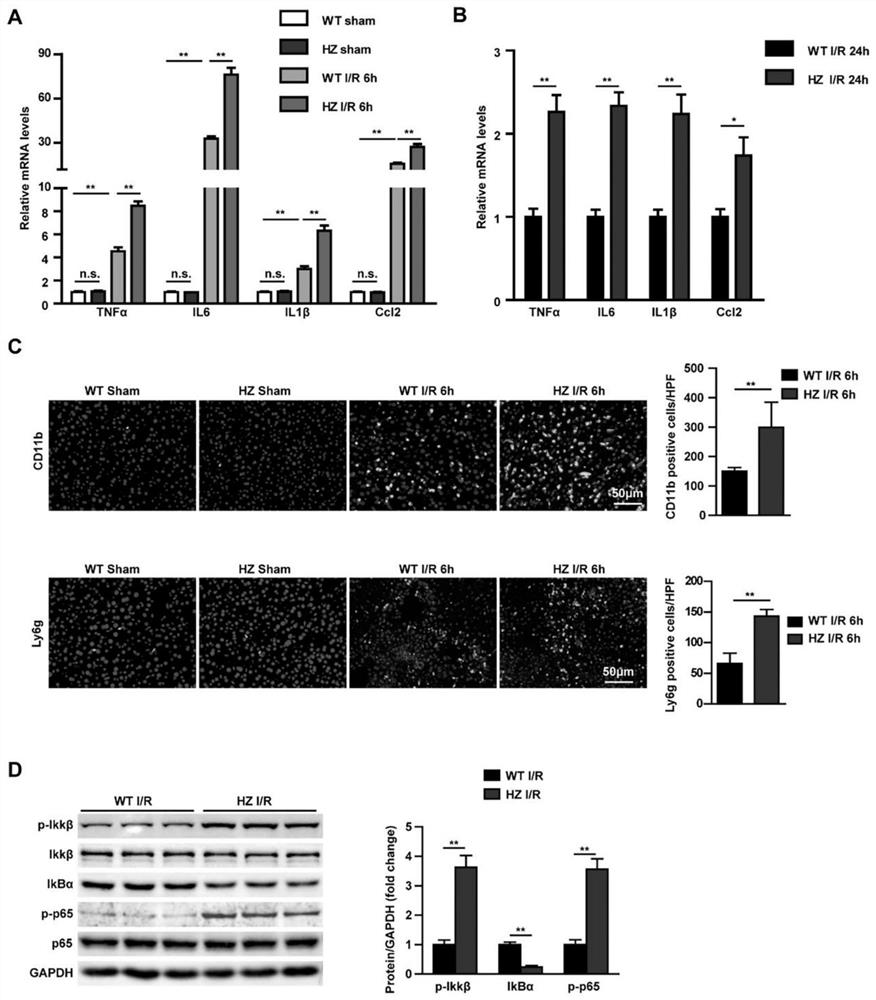
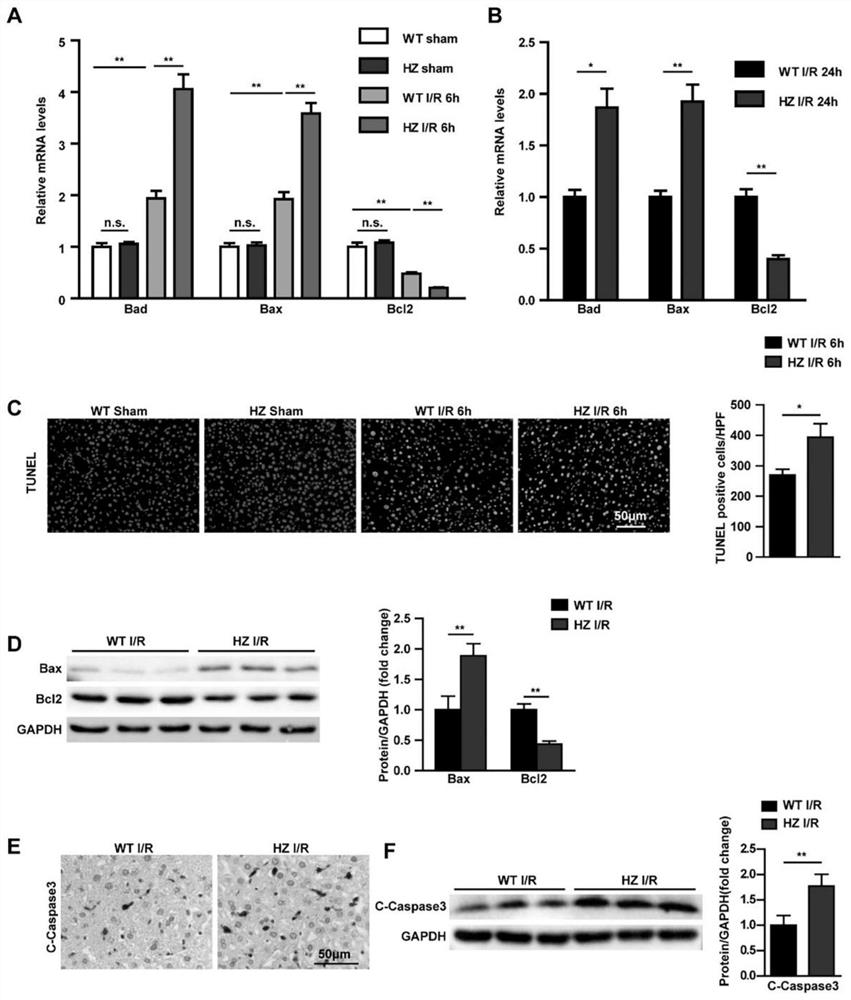
Application of USP10 in hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury
InactiveCN112933231AReduce ischemia-reperfusion injuryDigestive systemPharmaceutical active ingredientsApoptosisIschemic reperfusion injury
The invention discloses an application of USP10 in hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury. A USP10 gene knockout mouse and a C57BL / 6 wild type mouse are selected as experimental subjects, mouse hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury models are constructed respectively, the function of USP10 in hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury is researched, the new function of the USP10 gene in hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury is found, and the application of the USP10 gene in hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury is developed. The over-expression of the USP10 can relieve the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting inflammation and cell apoptosis, so that the USP10 can be applied to the preparation of the medicine for preventing / treating the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury, and a new medicine target is provided for the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
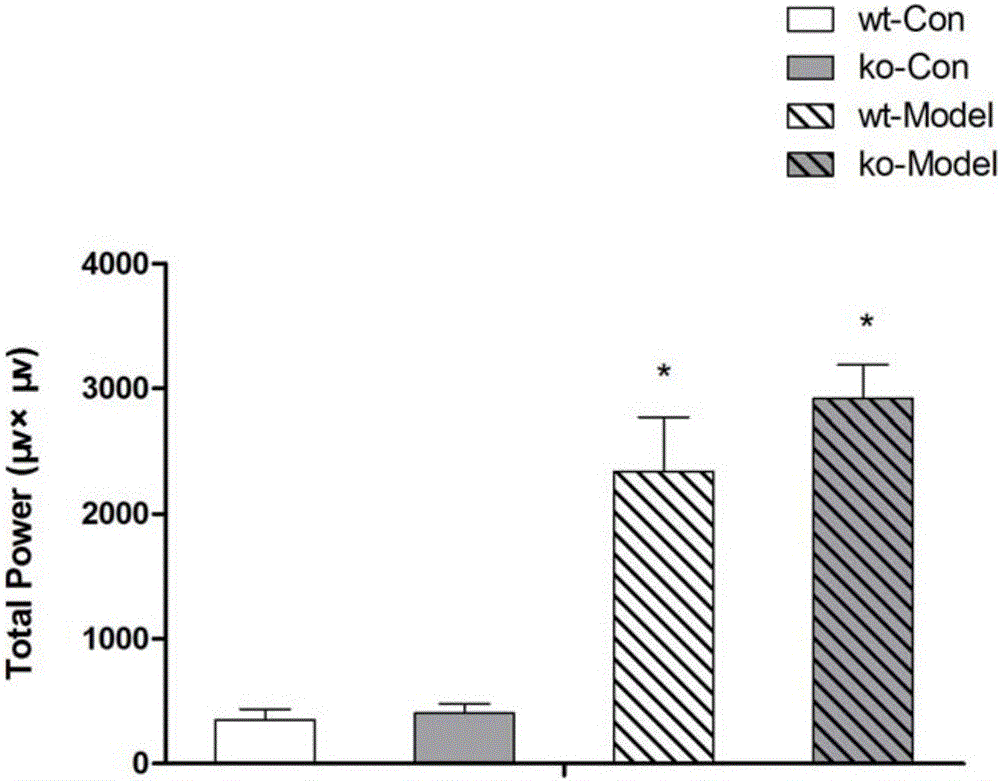
Application of gama-aminobutyric acid (GABA) translocator isoform I gene knockout mouse system in building novel drug induced epilepsy animal model
InactiveCN105687202AHigh induction success rateHigh grade epilepsyCompounds screening/testingGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseWild type
The invention relates to application of a gama-aminobutyric acid (GABA) translocator isoform I gene knockout mouse system in building a novel drug induced epilepsy animal model. According to the invention, a GAT1 gene knockout mouse is adopted to build an animal epilepsy model, the effect is compared with modeling by adopting wild type mice, and the method provided by the invention is proved to be with high success rate, high epilepsy level, stable state, difficulty in death and good repeatability, and can well meet the requirement of epileptic disease research. The result provided by the invention also proves that after GAT1 gene knockout, the mouse epilepsy susceptibility is increased, the GAT1 gene or protein can be used as a therapeutic target for epilepsy, and the level of the GAT1 gene or protein can be used as a biomarker for epilepsy diagnosis.
Owner:JINSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
METHOD FOR THE PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF ESSENTIAL TREMOR BY REGULATING alpha1G T-TYPE CALCIUM CHANNEL OR BY T-TYPE CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS
The present invention relates to a method for the prevention and treatment of essential tremor by blocking α1G T-type calcium channel, a preventive and therapeutic agent for essential tremor containing the α1G T-type calcium channel blocker as an active ingredient, and a screening method of a preventive and therapeutic agent for essential tremor by investigating α1G T-type calcium channel blocking activity. More precisely, the present invention relates to a method for the prevention and treatment of essential tremor by using α1G T-type calcium channel blocker, for which the inventors confirmed that the α1G T-type calcium channel knock out mice (α1G− / −) had resistance against essential tremor and when the T-type channel blocker was administered to the wild type mice (α1G+ / +), they gained resistance against essential tremor.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
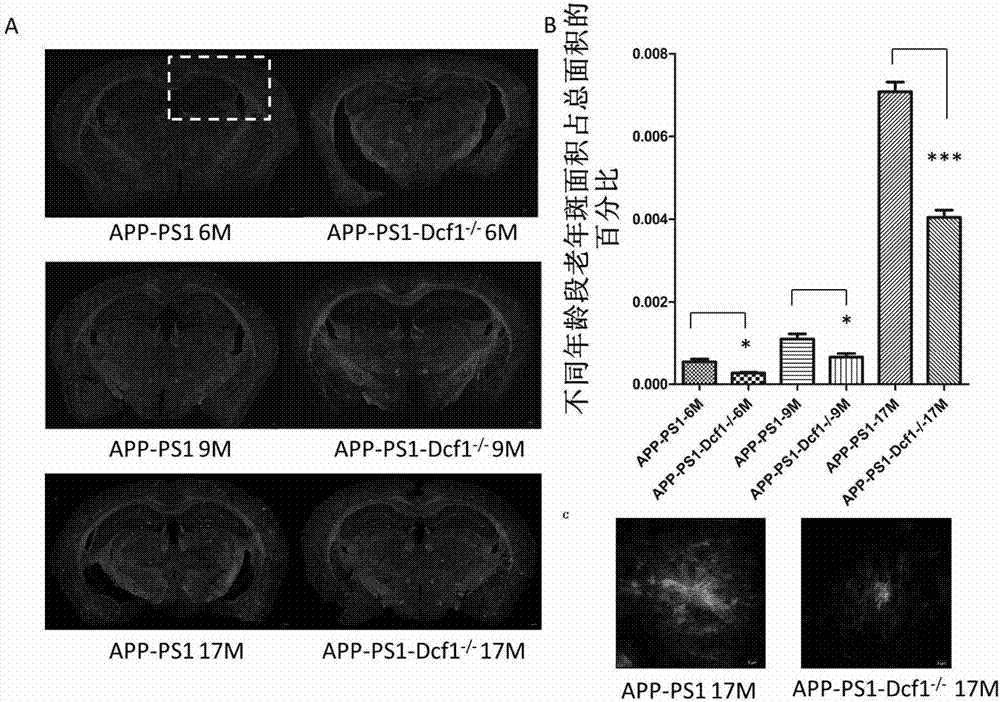
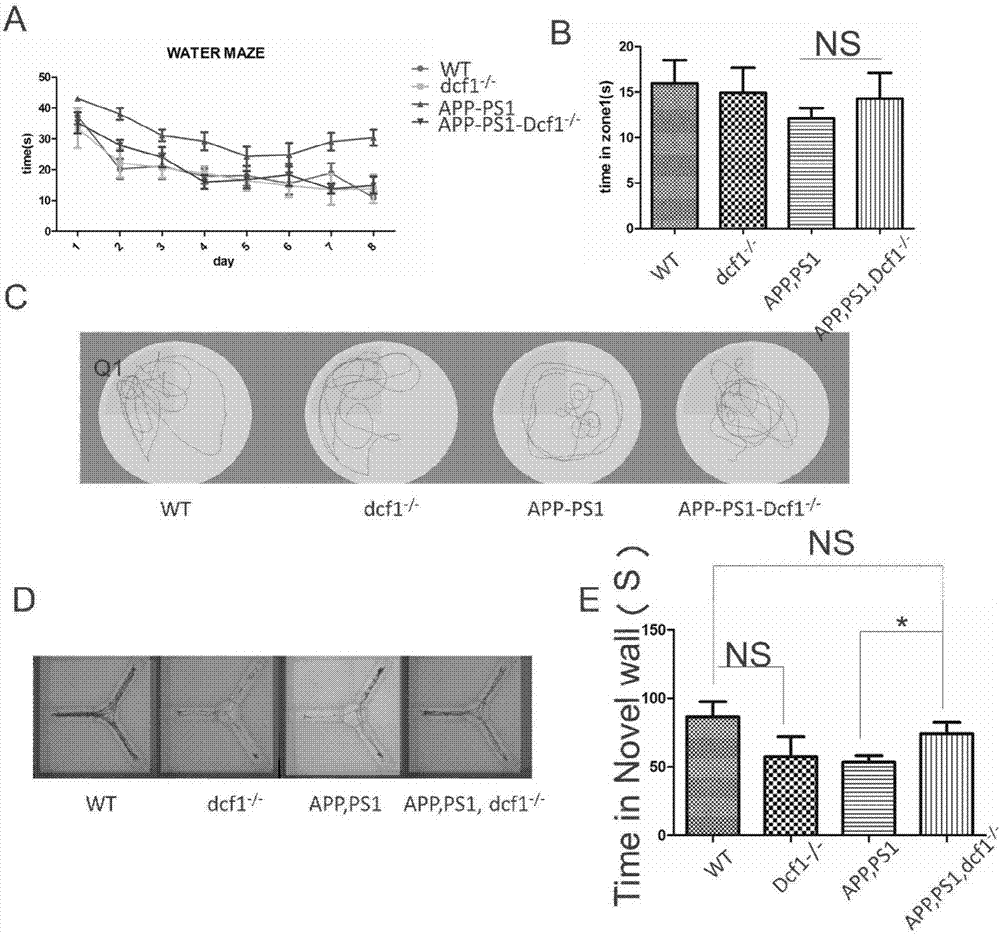
Applications of DCF1 gene knockout in preparation of drugs for alleviating Alzheimer's disease
InactiveCN106983864AReduce depositionImprove learning and memory abilityNervous disorderPharmaceutical active ingredientsDiseaseGene targets
The present invention relates to applications of DCF1 gene knockout in preparation of drugs for alleviating Alzheimer's disease. According to the present invention, mainly wild type mice, dcf1 knockout mice and AD model mice are adopted as control, and Dcf1 gene knockout AD model mice are adopted as a research object; the thioflavine staining results of the mouse brain freezing slices show that the deposition of senile plaques can be reduced after DCF1 gene knockout; the observation results of the mouse spatial learning and memory ability from the ethology prove that the learning and memory ability of the mouse can be enhanced after DCF1 gene knockout; and the results show that the DCF1 gene knockout can alleviate Alzheimer's disease, and the gene target is provided for the development of the new AD treatment drug.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
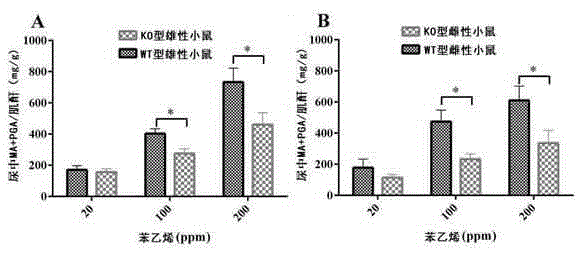
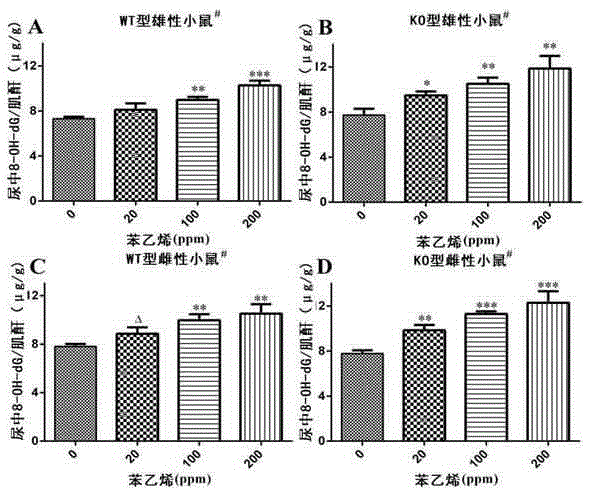
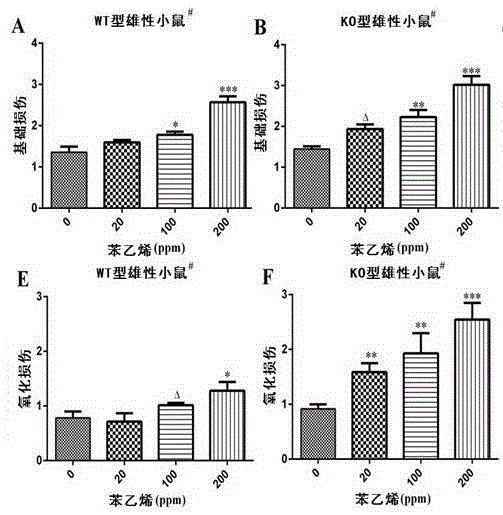
Application of ALDH2 genes to preparation of medicine for preventing genetic toxicity caused by styrene
InactiveCN105251025AMitigation of genotoxicityGenetic material ingredientsAntinoxious agentsMetaboliteWild type
The invention discloses application of ALDH2 genes to preparation of medicine for preventing genetic toxicity caused by styrene and belongs to the field of functions and application of genes. According to the application, an Aldh2 gene knockout type and wild type mouse is used as a model; after the mouse is exposed in styrene by inhaling styrene, the concentrations of mandelic acid and phenylglyoxylic acid, final metabolites of styrene, in the mouse are detected, and multiple biological indexes, representing genetic toxicity, of DNA basic damage, oxidative damage and 8-hydroxyl deoxyguanosine (8-OH-dG) are used for quantization of genetic toxicity caused by styrene. Results clearly show that the ALDH2 genes have an adjusting effect on genetic toxicity caused by styrene, metabolism of styrene may be enhanced through the ALDH2 genes, and therefore genetic toxicity caused by styrene is reduced. As a result, targeting the metabolic detoxication function of the ALDH2 genes, the ALDH2 genes can be used for preparing healthcare products or medicine for preventing genetic toxicity caused by styrene.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com