Method for preparing biomedical magnesium alloy wire
A biomedical and magnesium alloy technology, applied in the field of preparation of biomedical magnesium alloy wire, can solve the problems of many drawing passes, low deformation, low wire plasticity, etc., and achieves clear preparation principle, improved corrosion resistance, The effect of meeting the requirements of strength and plasticity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0020] A method for preparing a biomedical magnesium alloy wire, comprising the following steps:
[0021] (1) Metal magnesium and metal zinc are melted into liquid metal;
[0022] (2) Stirring and refining the liquid metal in step (1) to obtain refined liquid metal, mechanically stirring the molten metal for 3 to 5 minutes, then allowing the molten slag to float and then removing the slag;
[0023] (3) casting the refined liquid metal in step (2) into an alloy ingot;
[0024] (4) Perform homogenization heat treatment on the alloy ingot obtained in step (3) or directly perform equal-channel extrusion without heat treatment, the homogenization treatment temperature is 300-350 ° C, and the time is 2-6 hours; equal-channel angular extrusion The pressing temperature is between 200°C and 300°C, and the cumulative deformation is required to be over 400%;
[0025] (5) The material after medium channel extrusion in step (4) is processed into wire by multi-pass drawing. Before drawing...
Embodiment 1
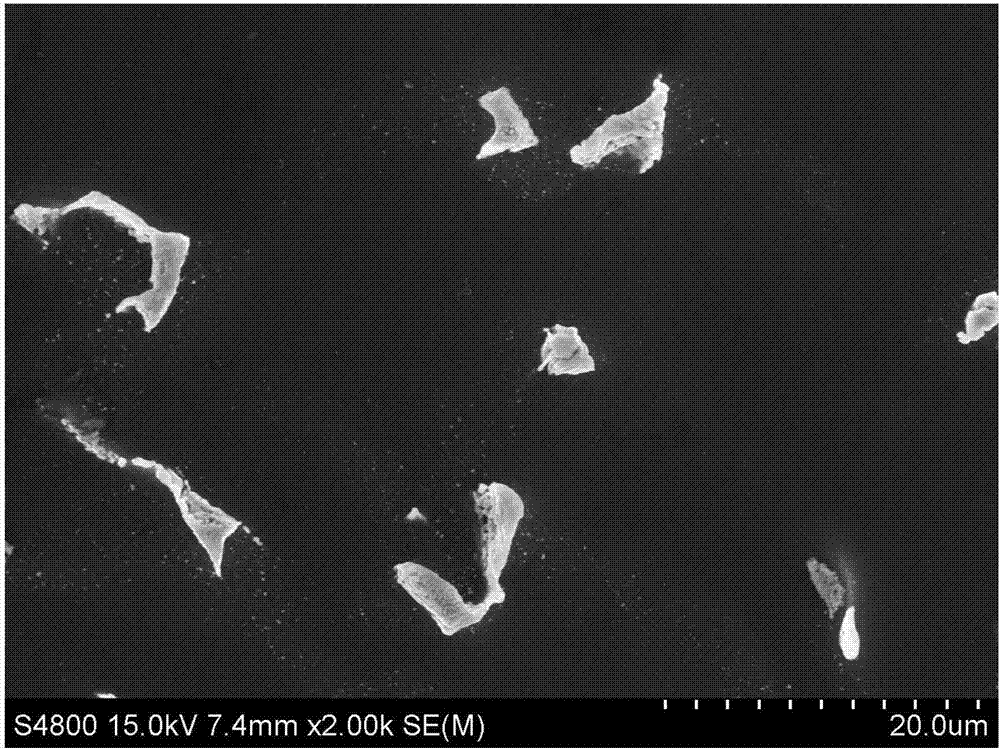
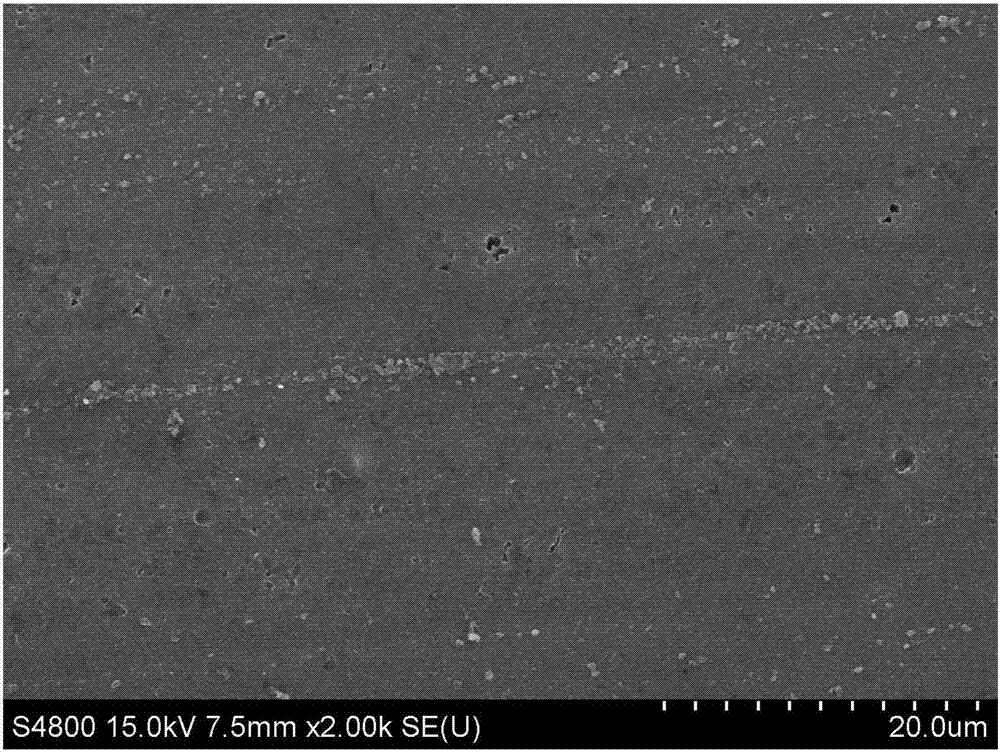
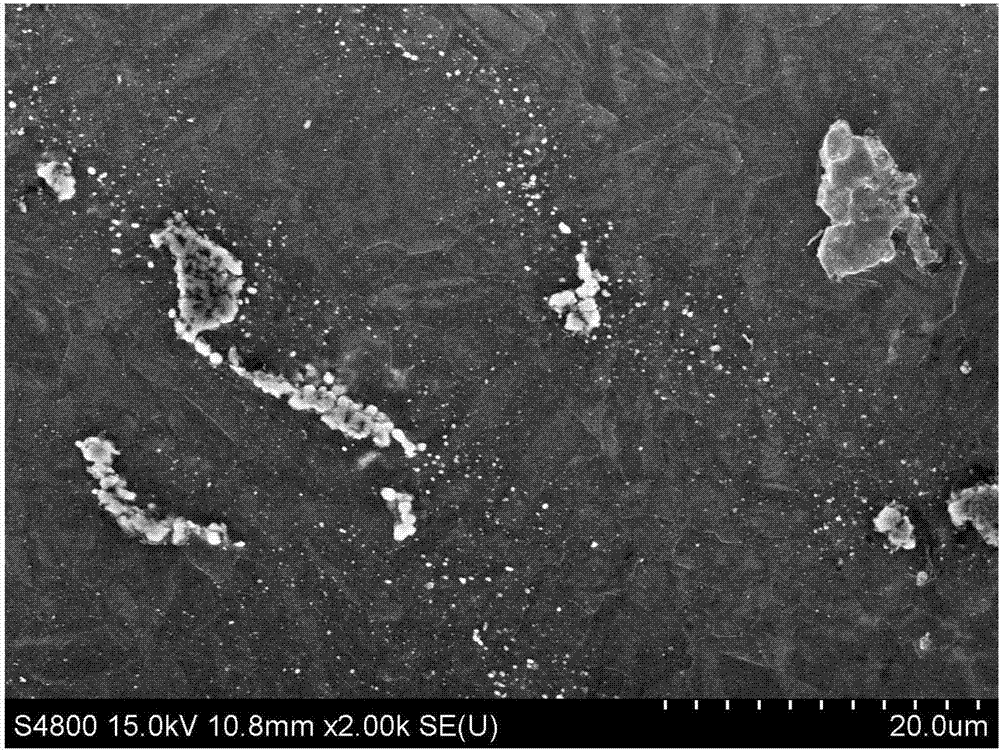
[0029] Such as Figure 1~4 Shown, a kind of preparation method of biomedical magnesium alloy wire, Mg-6%wt.Zn alloy casts and there is bulk eutectic phase in the tissue after extrusion, such as figure 1 As shown, after the extruded sample was subjected to 200°C, 6-pass equal-channel extrusion treatment, the number of mesophases decreased, the size decreased, and a large number of fine precipitates were precipitated, such as figure 2 shown. After the extruded sample is drawn into a wire with a diameter of 0.3mm, there are a large number of mesophases distributed in bands in the microstructure, and the area between the mesophases distributed in bands appears due to uneven deformation. microcracks and holes, such as image 3 shown. However, the microstructure of the wire drawn after multi-channel equal channel extrusion has almost no second phase precipitation, the structure is uniform, and there are no cracks and holes, such as Figure 4 shown.
[0030] Such as Figure 5 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com