Standard detection method and application of DNA bar code for identifying tridacna
A bar code, Tridacina technology, applied in recombinant DNA technology, DNA/RNA fragment, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problem of difficulty in accurately identifying Tridacina, achieve automation and standardization, break through excessive dependence, and quickly price Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1: Screening of DNA barcodes of Tridacnaceae shellfish
[0036] 1) The sequence used to screen the DNA barcodes of Tridacnaceae molluscs:
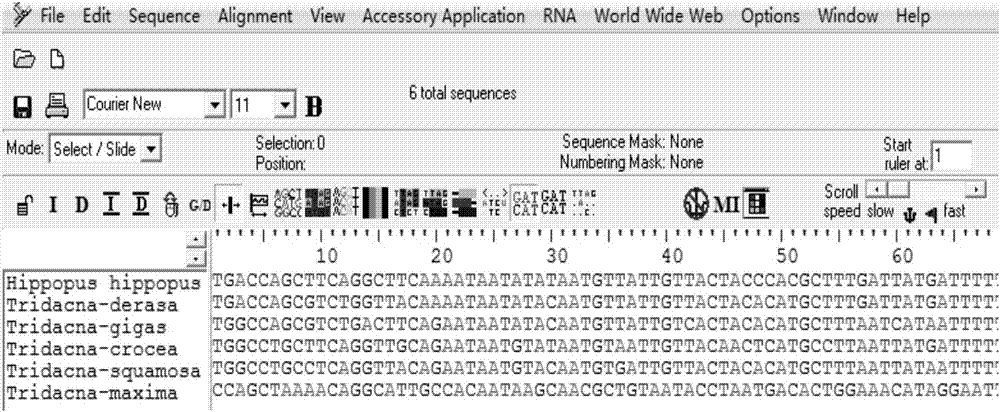
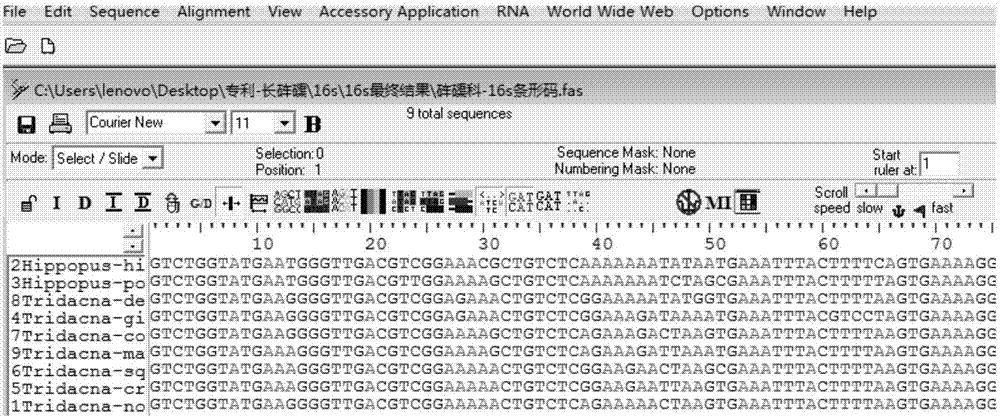
[0037] Query the mitochondrial gene sequences of Tridacnaceae shellfish on the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI, http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ), among which there are 2028 CO1 sequence records; 192 16s rRNA records; 122 18s rRNA records; 3 12s rRNA records. Among them, 12s rRNA only contains two species of giant clam (Tridacnasquamosa) and giant clam (T.maxima), which do not meet the conditions for DNA barcodes.
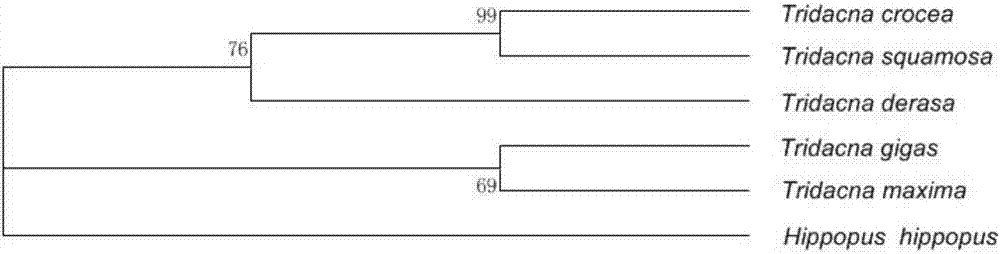
[0038] After analysis, the CO1 gene sequence of the following species was obtained: (Hippopus hippopus), giant clam (T.derasa), giant clam (T.gigas), giant clam (T.maxima), scaled clam (T.squamosa), saffron clam (Tridacna crocea) . Among them, 10 sequences (HE995483.1-HE995487.1, FM244530.1-FM244534.1) were downloaded from giant clam (T.maxima) and 10 sequences from giant clam (T.squamosa) (H...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Example 2: Universal primer pairs for amplifying the above DNA barcodes
[0087] 1) Sequence alignment: use BioEdit software to align (Hippopus hippopus), giant clam (T.derasa), giant clam (T.gigas), giant clam (T.maxima), scaled giant clam (T.squamosa), saffron giant clam (Tridacna crocea) Compare the CO1 sequences to find the sequence fragments that are relatively conservative and have the least base variation.
[0088] 2) Primer synthesis: According to the above comparison results, a pair of amplification primers was designed in the sequence fragment with the smallest base variation by using the primer design software Primer5. The primer sequence is
[0089] COI-F: 5'CTACTCCACCCGCTACCAAT 3' (SEQ ID NO: 7);
[0090] COI-R: 5'GATGCTCTACAATGTGCGAAAC 3' (SEQ ID NO: 8).
[0091] 3) Primer amplification: the above-mentioned amplification primers were respectively applied to PCR amplification of known giant clam samples. Set the PCR thermal cycle annealing temperature...
Embodiment 3
[0095] The shellfish collected from Quanfu Island in the South China Sea is preliminarily determined to be a type of giant clam from the appearance observation, but it is not clear which species it belongs to. The barcodes obtained by screening of the present invention are used for identification.
[0096] Specific steps are as follows:
[0097] 1) Utilize conventional method to extract the DNA of the sample to be tested for use;
[0098] 2) PCR amplification: use the designed degenerate primers to perform PCR amplification on the individuals of Tridacnaceae to be tested. The annealing temperature range is 48-52°C;
[0099] 3) Sequencing results: the amplified product is subjected to two-way sequencing; the determined nucleotide sequence is:
[0100] AAATCAAAATAAATGTATAAATAAAACCGGATCTCCACCGCCAACAGGATCAAAAAATGATGTAGCAAAATTACGATCAAATAATAATATGGTTAAAGCCCCAGCTAAAACAGGCATTGCCACAATAAGAAGCAACGCTGTAATACCTAATGACACTGGAAACATAGGAATTTTATGGAAACCACGTTTTTGATGCCGTATATTAGCCACAGTCCTTGCAAAATTTA...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com