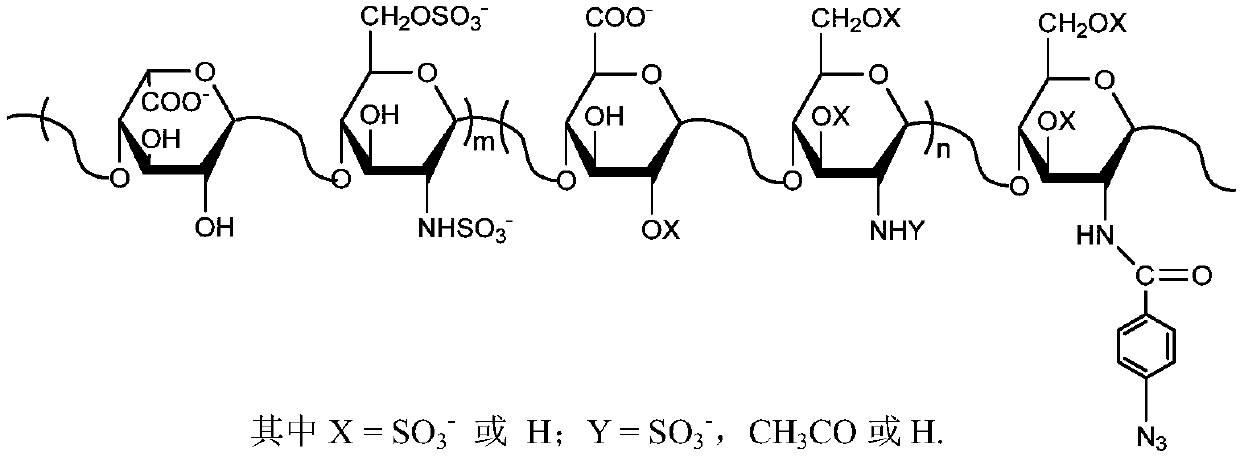
A kind of azide modification method of heparin, azide heparin and application
A modification method, a technology for nitriding heparin, applied in the field of biological materials, can solve the problems of increasing the material synthesis process and cost, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
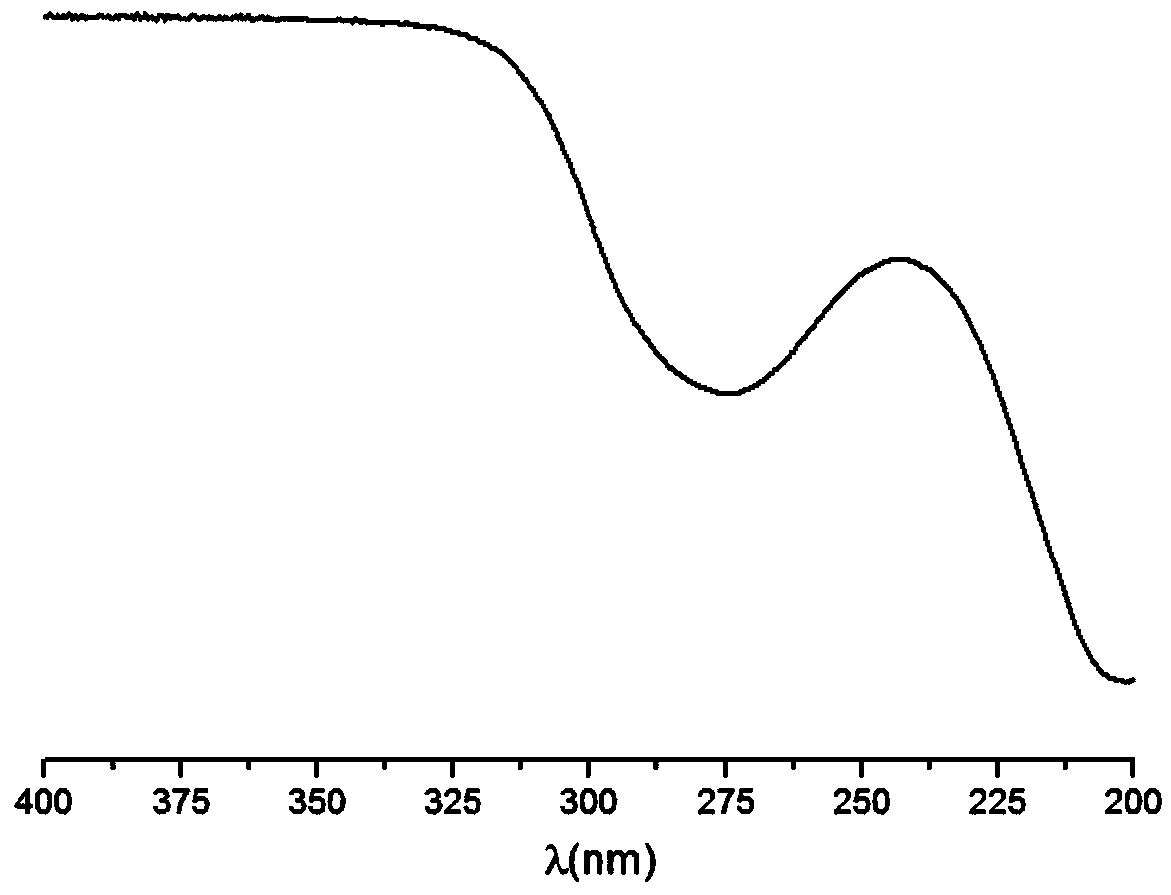
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Add 0.815g of p-azidobenzoic acid, 0.958g of EDC.HCl, 0.575g of NHS in sequence to a container with 20ml of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, containing water), stir well and then adjust with 0.1M dilute hydrochloric acid solution After the pH reaches 4.7, place it in a 4°C environment with magnetic stirring, avoid light reaction (to prevent the azide group from being decomposed by light) for 4 hours; add 10ml (0.1g / ml) of heparin sodium (molecular weight: 12000) After adjusting the pH of the NaOH solution to 7.4, place it in an environment at 4°C and avoid light for 6 hours; finally, pour the reaction solution into a dialysis bag (3.5K), dialyze it with water until there is no azido-terebenzoic acid, filter it, and put the reaction solution in Freeze-dry at -25°C to obtain the product, ie heparin azide, with an azide group content of 8.8‰ (g / g) and a yield of 95%.
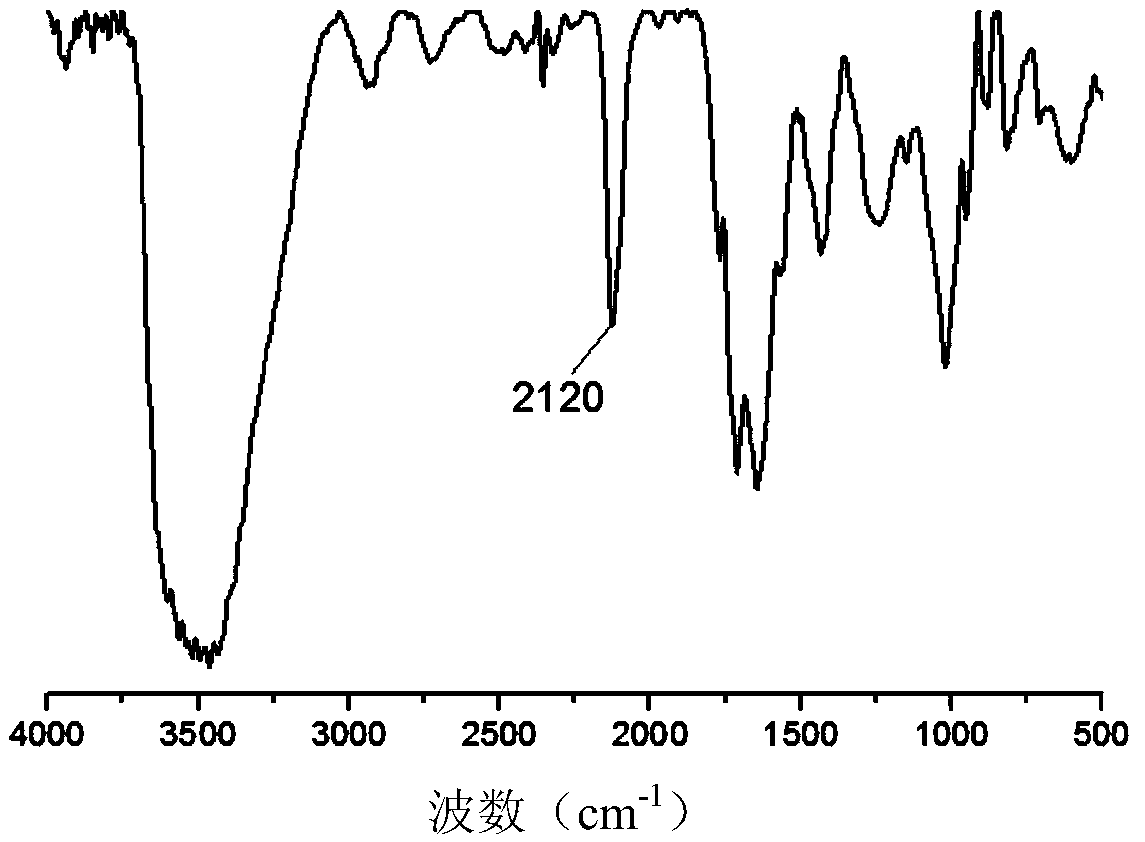
[0036] The infrared absorption spectrum of the heparin azide synthesized in this embodiment is as follows: figu...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Add 0.955g of 3-(4-azidophenyl)propionic acid, 1.916g of EDC.HCl, and 2.170g of sulfo-NHS in sequence to a container containing 20ml of dimethylformamide (DMF, containing water), and stir thoroughly After adjusting the pH to 4.7 with 0.1M dilute hydrochloric acid solution, place it in a 6°C environment with magnetic stirring, and react in the dark for 4 hours, add 10ml (0.05g / ml) of heparin lithium (molecular weight: 20000) aqueous solution, and use 0.01M NaOH After the pH of the solution was adjusted to 7.4, it was placed in a 6°C environment and protected from light for 6 hours; finally, the reaction solution was poured into a dialysis bag (3.5K) and dialyzed with water until there was no 3-(4-azidophenyl)propionic acid. After filtering, the reaction solution was freeze-dried at -25°C to obtain the product, namely heparin azide, with an azide group content of 5.5‰ and a yield of 90%.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Add 0.155g of 4-azidobutanoic acid, 0.258g of EDC.HCl, and 0.345g of sulfo-NHS to a container containing 40ml of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, containing water) in sequence. After adjusting the pH of the dilute hydrochloric acid solution to 5.0, place it in a 10°C environment with magnetic stirring, and react in the dark for 6 hours; add 10ml (0.1g / ml) of heparin calcium (molecular weight: 20000) aqueous solution, and use 0.01M NaOH solution to adjust the pH to After 7.4, place it in a 10°C environment to avoid light for 6 hours; finally, pour the reaction solution into a dialysis bag (3.5K), dialyze with water until there is no 4-azidobutyric acid, filter, and store the reaction solution at -30°C After lyophilization, the product, namely heparin azide, was obtained. The azide group content of the product was 2.0‰, and the yield of the product was 85%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com