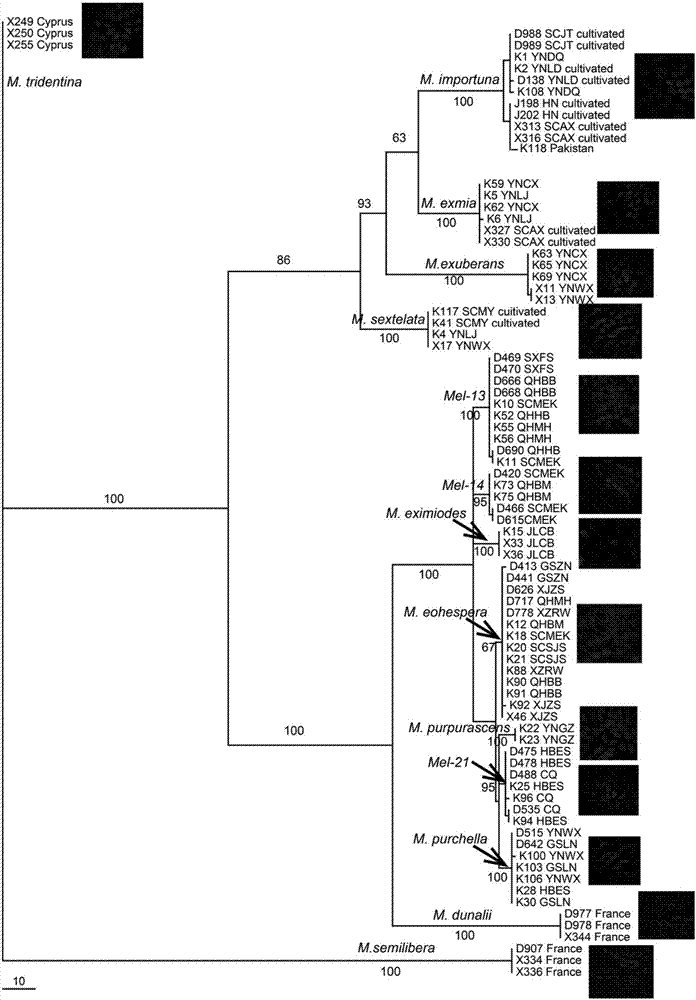
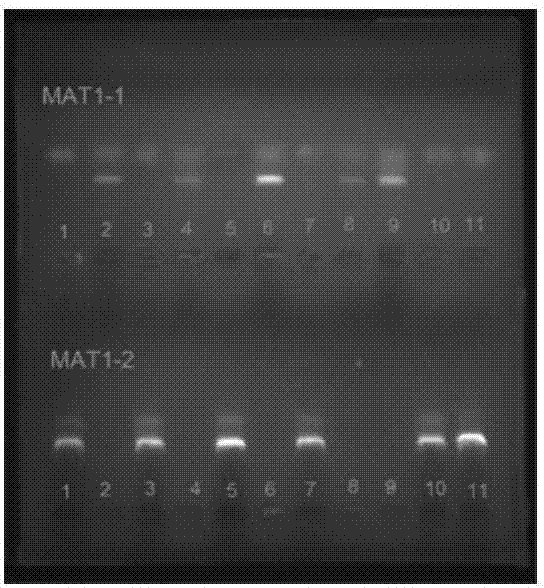
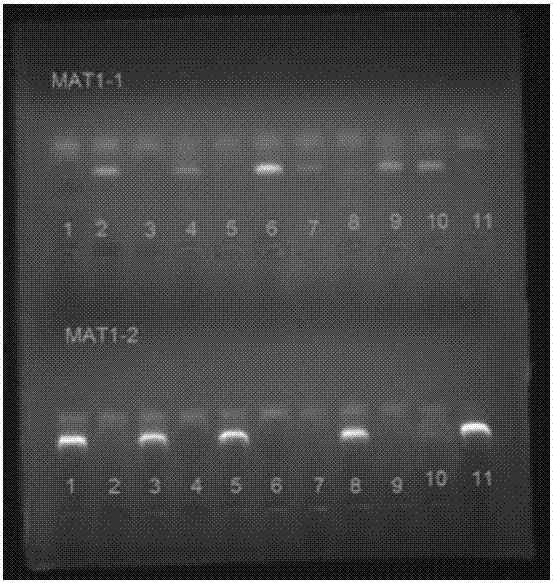
Method for authenticating mating type of eleven varieties in black morchella group
A kind of technology of mating type and Morchella, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve problems such as being unable to identify whether Morchella strain is reliable, and achieve the effects of stable and reliable results and simple and convenient method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Neutral Morchella (M.tridentina) X255 monoascospore strain mating type identification Neutral Morchella monoascospore strain X255-1—X255-11 was inoculated on PDA medium, cultured at 24°C for 7 days, and an appropriate amount of mycelium was picked , DNA was extracted by the CTAB method, and 4 μL was electrophoresed on a 1% (W / V) agarose gel to detect the quality and concentration of the DNA.
[0056] Using the DNA of X255-1—X255-11 as a template, PCR amplification was performed on MAT1-1L / MAT1-1R or 1L / 1R with primers: 25 μL amplification system included 12.5 μL of 2×PCRmix (TIANGENBioInc), 5 μM MAT1 -1L, 1 μL of MAT1-1R primers, 1 μL of DNA template, ddH 2O 9.5 μL. The PCR amplification program was: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 3 min; denaturation at 94°C for 1 min, annealing at 50°C for 30 sec, extension at 72°C for 1 min, 35 cycles; extension at 72°C for 10 min.
[0057] Using the DNA of X255-1—X255-11 as a template, PCR amplification was performed on MAT1-2L / MAT1-...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Identification of mating type of M. semilibera monoascospore strain D907-1—D907-11 monoascospore strains of M. semilibera were inoculated on PDA medium, cultured at 24°C for 7 days, and picked Take an appropriate amount of mycelium, extract DNA by CTAB method, and take 4 μL to detect DNA quality and concentration by electrophoresis on 1% (W / V) agarose gel.
[0061] Using the DNA of D907-1—D907-11 as a template, PCR amplification was performed on MAT1-1L / MAT1-1R or 1L / 1R with primers: 25 μL amplification system included 2×PCRmix (TIANGENBioInc) 12.5 μL, 5 μM MAT1 -1L, 1 μL of MAT1-1R primers, 1 μL of DNA template, ddH 2 O 9.5 μL. The PCR amplification program was: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 3 min; denaturation at 94°C for 1 min, annealing at 50°C for 30 sec, extension at 72°C for 1 min, 35 cycles; extension at 72°C for 10 min.
[0062] Using the DNA of D907-1—D907-11 as a template, PCR amplification was performed on MAT1-2L / MAT1-2R or 2L / 2R with primers. The 25 μL am...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Mating type identification of M. exuberans K63 monoascospore strain M. exuberans K63-1—K63-11 monoascospore strains were inoculated on PDA medium, cultured at 24°C for 7 days, and appropriate amount of bacteria were picked. Silk, DNA was extracted by CTAB method, and 4 μL was electrophoresed on 1% (W / V) agarose gel to detect the quality and concentration of DNA.
[0066] Using the DNA of K63-1—K63-11 as a template, PCR amplification was performed on MAT1-1L / MAT1-1R or 1L / 1R with primers: 25 μL amplification system included 2×PCRmix (TIANGENBioInc) 12.5 μL, 5 μM MAT1 -1L, 1 μL of MAT1-1R primers, 1 μL of DNA template, ddH 2 O 9.5 μL. The PCR amplification program was: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 3 min; denaturation at 94°C for 1 min, annealing at 50°C for 30 sec, extension at 72°C for 1 min, 35 cycles; extension at 72°C for 10 min.
[0067] Using the DNA of K63-1—K63-11 as a template, PCR amplification was performed on MAT1-2L / MAT1-2R or 2L / 2R with primers. The 25 μL ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com