Three-Level SVPWM method with neutral-point balancing and common-mode voltage suppression capabilities
A technology of common mode voltage and rejection capability, applied in the field of three-level SVPWM, can solve problems such as excessive common mode voltage, increase in harmonic components of inverter output power, decrease in motor life and stability, and achieve good real-time performance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0054] The present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0055] The present invention provides a three-level SVPWM method with midpoint balance and common mode voltage suppression capability, which specifically includes the following steps:
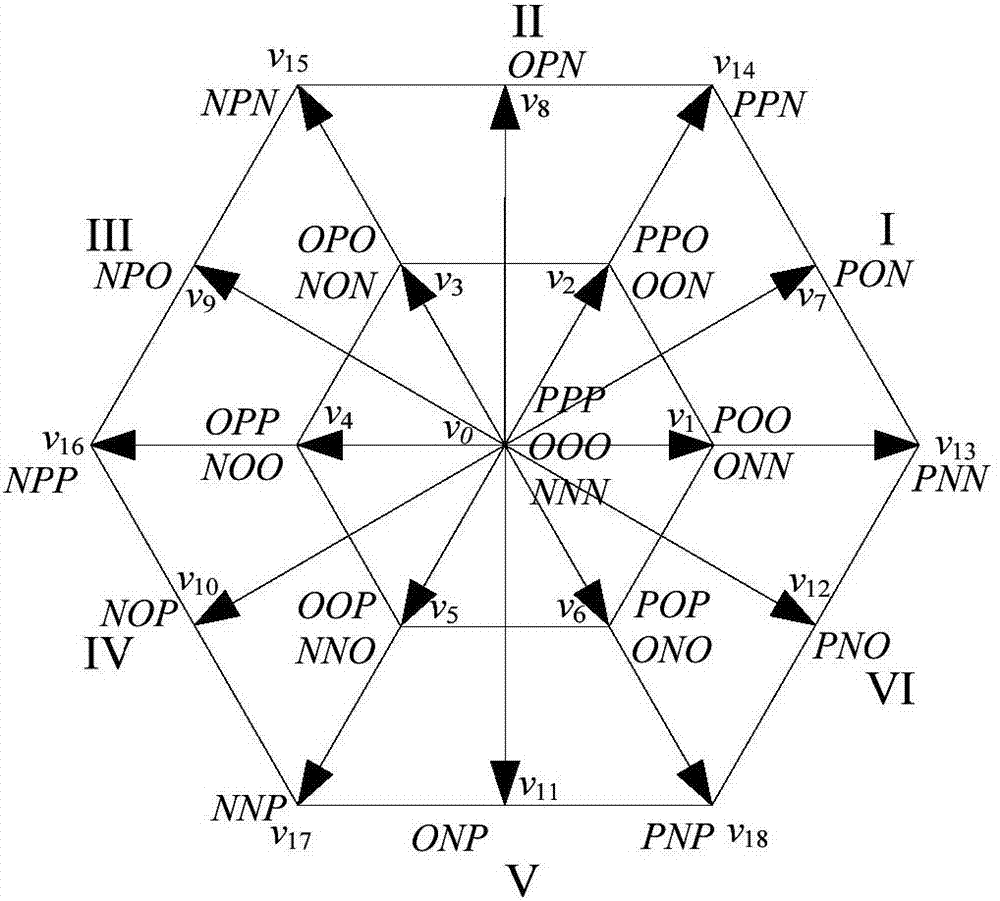
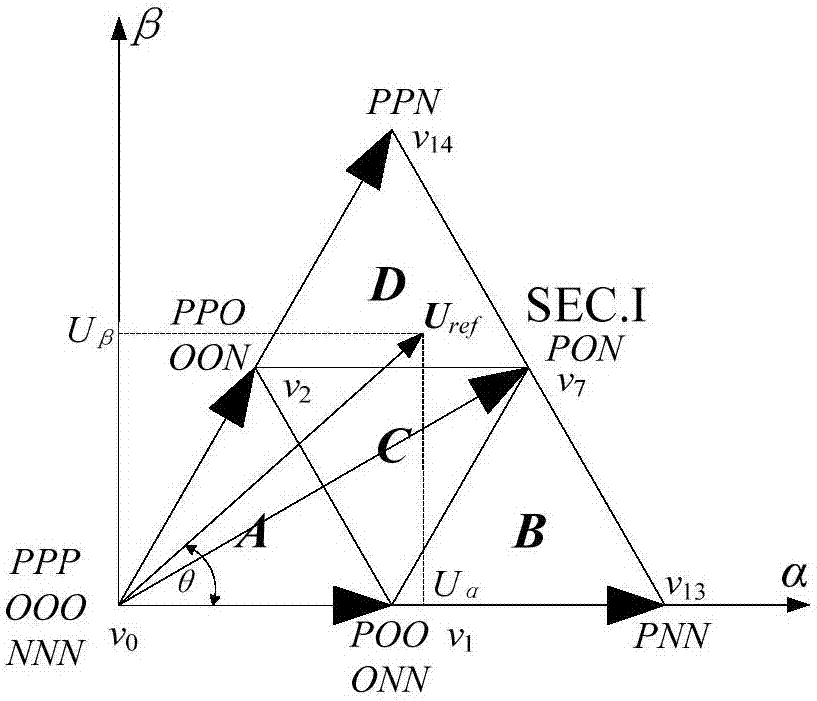
[0056] Step 1: Classification and Numbering of Voltage Space Vectors
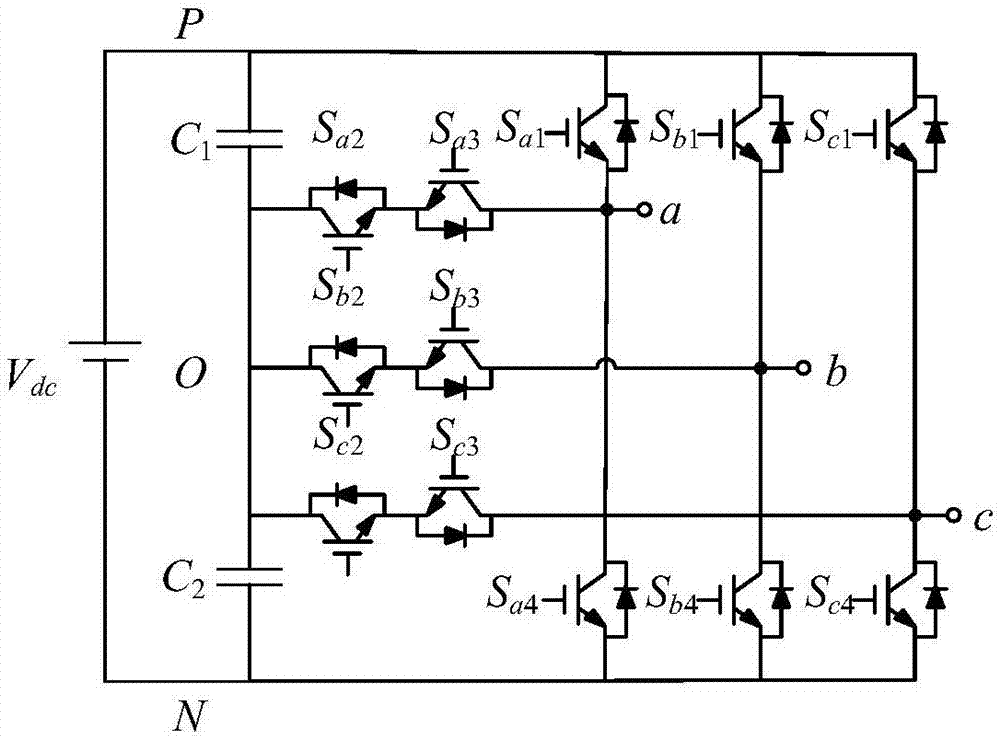
[0057] like figure 1 , there are three output states for each phase of the three-level inverter, namely P, O, and N. Define the function T representing the three output level states on the three-phase x (x=a,b,c), corresponding to the switching states of the 4 switches of each phase, expressed as:
[0058]
[0059] Among them, 1 means that the corresponding switch tube is closed, 0 means that the corresponding switch tube is open, and T a Indicates the output level state of phase a, T b Indicates the output level state of phase b, T c Indicates the output level state of phase c, S a1 ~S a4 In...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com