Recombinant hbv cccdna, the method to generate thereof and the use thereof
A genome and site technology, applied in the field including HBV genome, can solve the problems of poor physiological correlation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
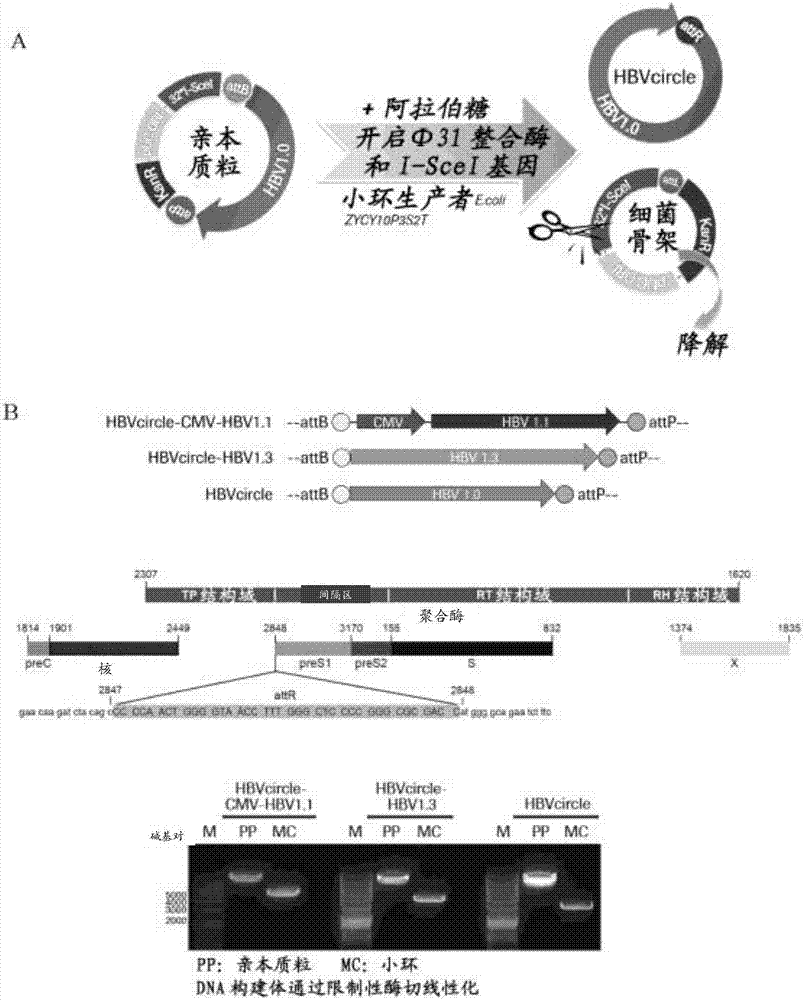
[0192] Design and production of HBVcircle
[0193] The plasmid pBR322-HBV1.3 containing the 1.3-unit-length genotype D-type HBV genome (GeneBank JN664917.1) and the sequence of the plasmid are listed as SEQ ID NO:7. The parental minicircle DNA vector plasmid pMC.CMV-MCS-SV40polyA was purchased from System Biosciences (catalogue number MN501A1, sequence number is SEQ ID NO: 13).
[0194] For the parental HBVcircle-CMV-HBV1.1 construct, the HBV genome with a length of 1.1 units starting from nucleotides 1805 to 3182 and 1 to 1990 of the genotype D HBV genome was extracted by PCR from pBR322-HBV1.3, and then used The SalI and NheI sites were cloned into pMC.CMV-MCS-SV40polyA vector. The sequence of the parental HBVcircle-CMV-HBV1.1 construct is set forth in SEQ ID NO:8.
[0195] For the parental HBVcircle-HBV1.3 construct, the pMC.CMV-MCS-SV40 polyA vector was digested with SmaI and KpnI (purchased from New England Biolabs Ltd). To generate an HBV genome insert of 1.3 units in...
Embodiment 2
[0203] Evaluation of HBV replication after HBVcircle transfection in vitro
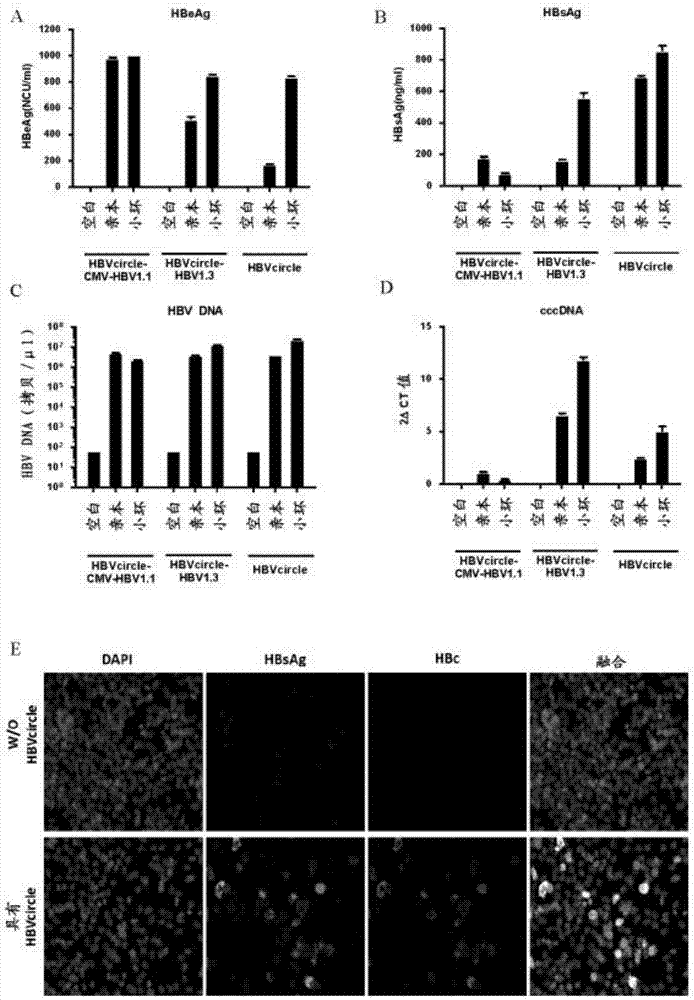
[0204] HBVcircle, HBVcircle-CMV-HBV1.1 and HBVcircle-HBV1.3 and their parental plasmids were transiently transfected into HepG2 cells for virus replication detection. 72 hours after transfection, cell culture supernatants were collected and analyzed by ELISA and qRT-PCR. HBeAg, HBsAg, and HBV DNA were highly abundant in the supernatant, indicating robust viral replication ( figure 2 A, B and C). Cells were lysed and total DNA was extracted, and cccDNA was quantified using real-time PCR with cccDNA-specific primer and probe sets ( figure 2 D). Compared with the parental HBVcircle-HBV1.3 plasmid carrying the traditional 1.3-unit HBV genome ultra-length design, HBVcircle showed at least comparable or higher expression of HBV markers.
[0205] In addition, HBsAg and HBV core (HBc) proteins were readily detectable in HBVcircle transfected cells by immunofluorescent staining ( figure 2 E). In order...
Embodiment 3
[0208] In vitro assessment of cccDNA markers
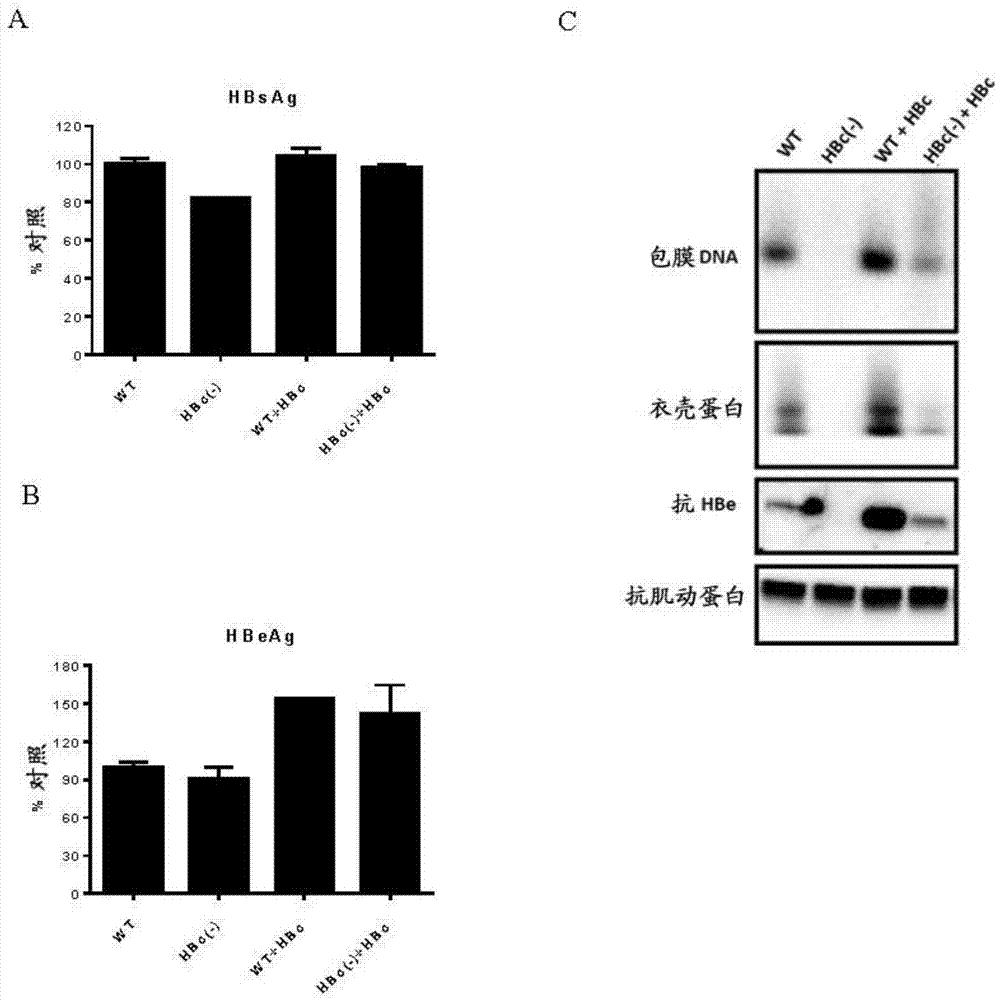
[0209] The presence of cccDNA in the nucleus is a unique feature of HBV. To determine whether HBVcircle is capable of forming cccDNA in hepatic nuclei, Southern blot and CHIP analysis were performed. For Southern blot analysis, parental HBVcircle or HBVcircle was first transfected into HepG2 cells, and then Hirt DNA was prepared (Cai et al., 2013, Methods Mol Biol, 1030:151-61). Supercoiled thermostable cccDNA bands appeared only on Southern blots of HBVcircle-transfected cells, but not in parental HBVcircle-transfected cells. When EcoRI was linearized, the cccDNA band disappeared ( Figure 4 A, RC: relaxed loop; DSL: double-stranded linear; CCC: cccDNA). CHIP analysis was performed using HBVcircle transfected cells. Consistent with previous publications, epigenetic modifications including trimethylated lysine 9 (H3K9me3) and acetylated lysine 27 (H3K27ac) are associated with cccDNA (Liu et al., 2013, PLoS Pathog, 9:e1003613 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com