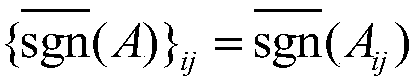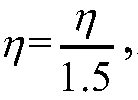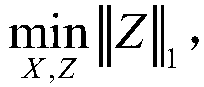High resolution SAR image classification method based on co-sparse model
A classification method and sparse model technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, computer components, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient utilization of learned analytic operators, limited accuracy of image classification, etc., and achieve fast speed and classification efficiency Improve the effect of accurate and detailed information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The present invention is a kind of high-resolution SAR image classification method based on co-sparse model, see figure 1 , including the following steps:
[0027] Step 1. Input the image to obtain the initial pixel value matrix: select a high-resolution SAR image to be classified, such as figure 2 For the image shown in (a), read the image with Matlab software. If the input image is a three-channel RGB image, it needs to be converted into a grayscale image. If it is a single-channel grayscale image, the image can be obtained directly. Gray value matrix, each element in the matrix corresponds to a pixel in the image.
[0028] Take all pixels as the center to intercept M 1 × M 1 For the convenience of subsequent data processing, each pixel block is expanded into a column. Traverse all pixels in the image to get the experimental sample X∈R M×LL , M is the number of pixels in a pixel block, LL is the number of pixels in the high-resolution SAR image to be classified,...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The method for classifying high-resolution SAR images based on the co-sparse model is the same as that in Embodiment 1, wherein in step 3, the method for combining the projected subgradient and the unified row norm compact frame is used to construct the analytical operator and includes the following steps:
[0043] 3.1. Construct the initial analytical operator Ω 0
[0044] Randomly generate an overcomplete matrix D=[d of size M×N 1 , d 2 ,...,d i ,...,d N ], where d i is a column vector, 1≤i≤N, N is the dimension of the analytical operator, the size of N is manually selected according to the needs but must be greater than M, and the initial analytical operator Ω is obtained 0 ,Ω 0 is the transpose matrix of the overcomplete matrix D, that is, Ω 0 =D T .
[0045] 3.2, by the subgradient projection formula Calculation parameter Ω G , 0≤i≤K max1 , K max1 In order to find the maximum number of iterations of the analytical operator, Ω i is the i-th analytical...
Embodiment 3
[0056] The method for classifying high-resolution SAR images based on the co-sparse model is the same as in Embodiment 1-2, wherein in step 4, the augmented Lagrangian method is used to solve the co-sparse coefficient Z problem: s.t.Z=ΩX, including the following steps:
[0057] 4.1. Given the initial pixel value matrix X 0 =X, analytical operator Ω, initial co-sparse coefficient Z 0 =ΩX 0 , the initial parameter matrix B 0 for size with Z 0 Equal zero matrix, constant parameter λ<1, constant coefficient γ<1.
[0058] 4.2. Calculate the pixel value matrix X according to the following formula i+1 , co-sparse coefficient Z i+1 and parameter matrix B i+1 , 0≤i≤K max2 , K max2 is the maximum number of iterations to find the co-sparse coefficients.
[0059]
[0060]
[0061] in
[0062] B i+1 =B i -(Z i+1 -ΩX i+1 )
[0063] 4.3. Repeat step 4.2 until ||Z i+1 -ΩX i+1 || 2 ≥ε or i>K max2 When the iterative process ends, ε is a constant error coefficient mu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com