Quantitative detection method of resistance genes of intestinal bacterial antibiotics
A quantitative detection method and technology of antibiotic resistance, applied in the field of quantitative detection of antibiotic resistance genes of intestinal bacteria, can solve the problems of underestimating the number of intestinal microorganisms and the deviation of the carrying amount of intestinal bacteria resistance genes, and achieve high theoretical research. Significance and practical value, stable and reliable results, accurate test results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1 Screening and identification of antibiotic-resistant strains
[0039] 1. Sample collection was carried out at Guanli Marine Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Maoming City. The specification of Litopenaeus vannamei is 50-60 tails / catties, the body length is about 13-15cm, and the weight is about 10g. After the prawns were temporarily raised in the aquarium for 2 days, they were randomly divided into 5 groups, with 80 prawns in each group. According to the weight of the shrimp body, different concentrations of antibiotics were added, as shown in Table 1. After the antibiotics were dissolved and mixed with the feed, they were fed into the aquarium, and the feed dosage was 1% of the body weight of the shrimp.
[0040] Table 1 Group design situation
[0041] Group
Types of
antibiotic type
Antibiotic Concentration
Cont
control group
Do not use
CipH
High concentration ciprofloxacin group
40mg / kg shrim...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Example 2 Real-time quantitative detection of intestinal bacterial resistance genes of Litopenaeus vannamei
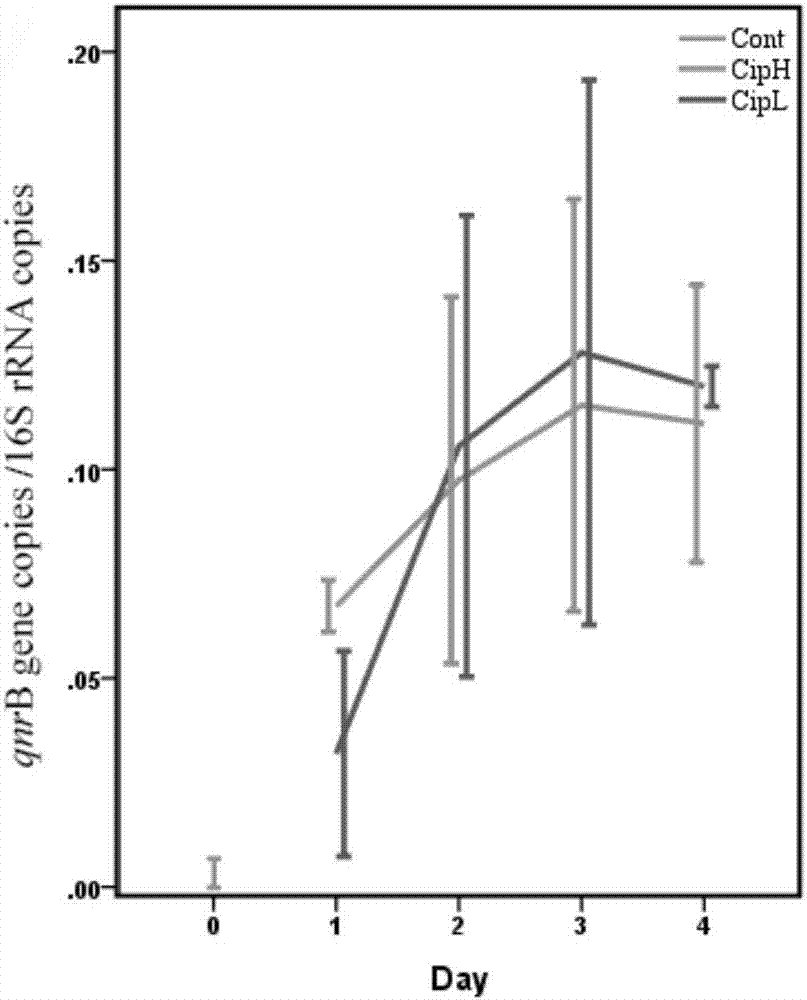
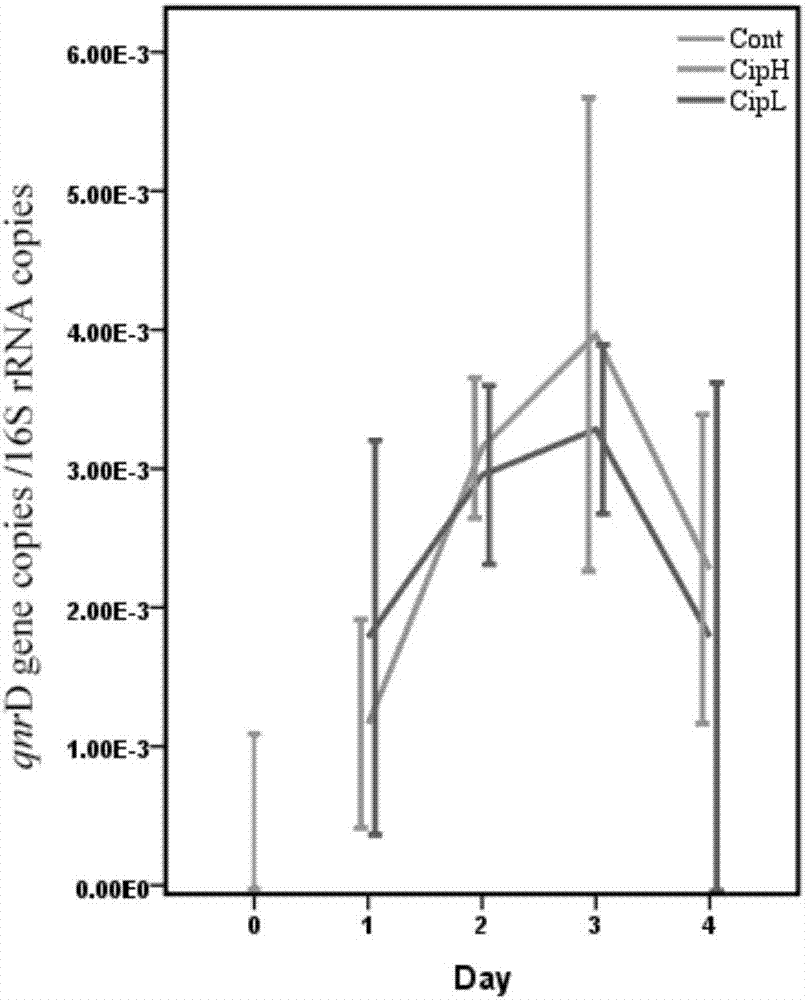
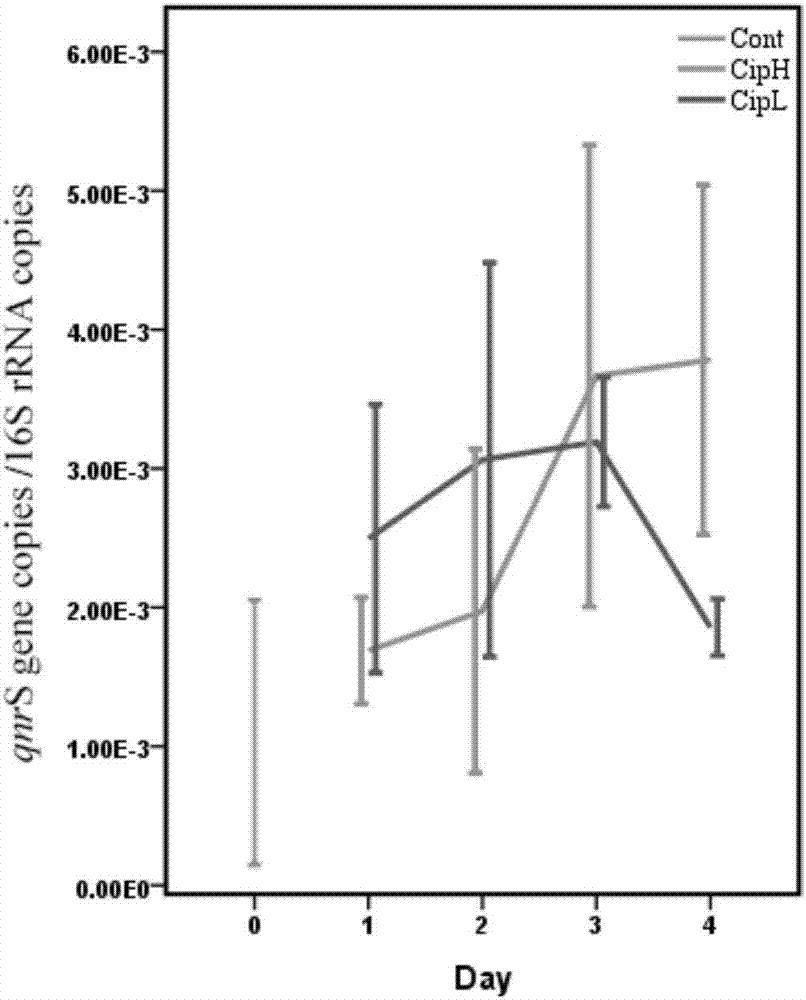
[0064] 1. Using the method established in Example 1, carry out the antibiotic resistance gene before feeding antibiotics, the 1st day after feeding, the 2nd day after feeding, the 3rd day after feeding, and the 4th day after feeding Quantitative PCR detection.
[0065] Before administration of ciprofloxacin, intestinal qnr B copies / 16s copies is 3.37×10 -3 , qnr D copies / 16s copies are 5.34×10 -4 , qnr S copies / 16s copies is 3.30×10 -3 .
[0066] Before feeding sulfamethazine, sul 1 copies / 16s copies is 2.53×10 -3 , sul 2 copies / 16scopes is 2.21×10 -2 , sul 3 copies / 16s copies is 5.55×10 -4 .
[0067] 2. Changes in antibiotic resistance genes
[0068] (1) For qnr B gene, in the CipH group, qnr B copies / 16 copies were 6.73×10 from the first day to the fourth day after feeding -2 , 9.74×10 -2 , 1.15×10 -1 , 1.11×10 -1 . In the CipL group, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com