Programmable multi-site specificity transcription inhibition system and application thereof
A site-specific and specific technology, applied in genetic engineering, using vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as sgRNA expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
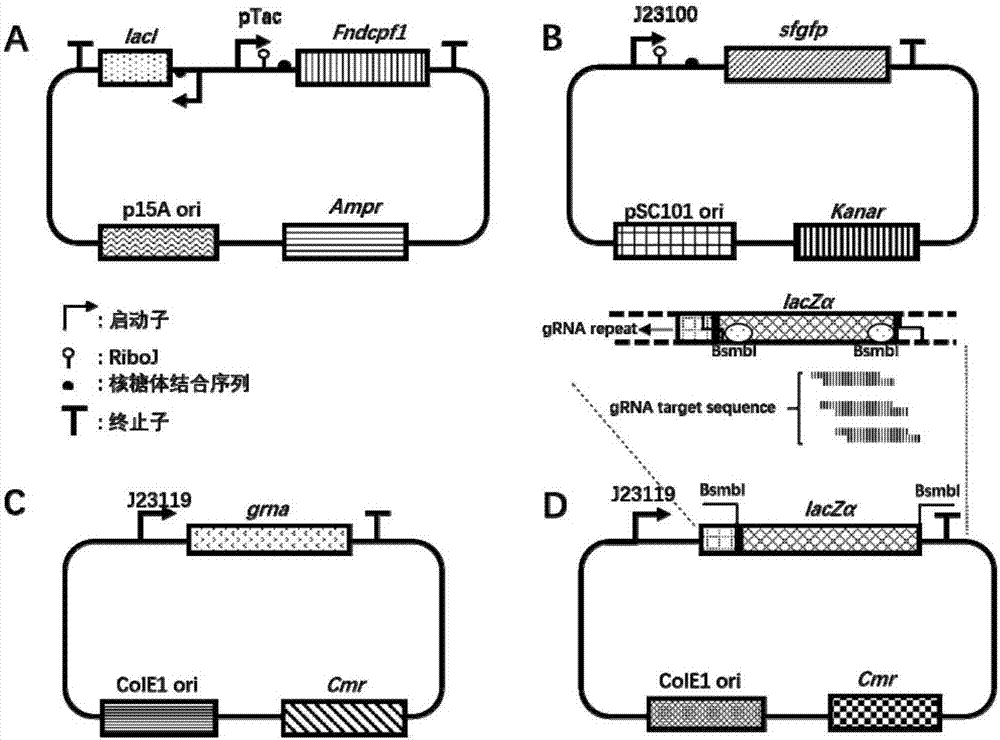
[0045] Embodiment 1, the construction of transcription inhibition test system
[0046] In the present invention, in Escherichia coli DH5α (TransGen Biotech), different plasmids are selected to express FndCpf1, sgRNA and fluorescent reporter protein respectively. The lower the intensity, the stronger the transcriptional repression, so as to study the transcriptional repression of FndCpf1 under different designs.
[0047] Among them, the FndCpf1 expression plasmid (full sequence is shown in sequence 3 in the sequence table), the promoter is a pTac inducible promoter, and isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG) is used as an inducer to induce expression, Ampicillin resistance, p15A replicon. sgRNA expression plasmid, the promoter is J23119 constitutive promoter, chloramphenicol resistance, ColE1 replicon. The reporter plasmid (full sequence shown in sequence 5 in the sequence listing) uses sfgfp as the reporter gene, the promoter is the constitutive promoter of J23100, kanamycin r...
Embodiment 2
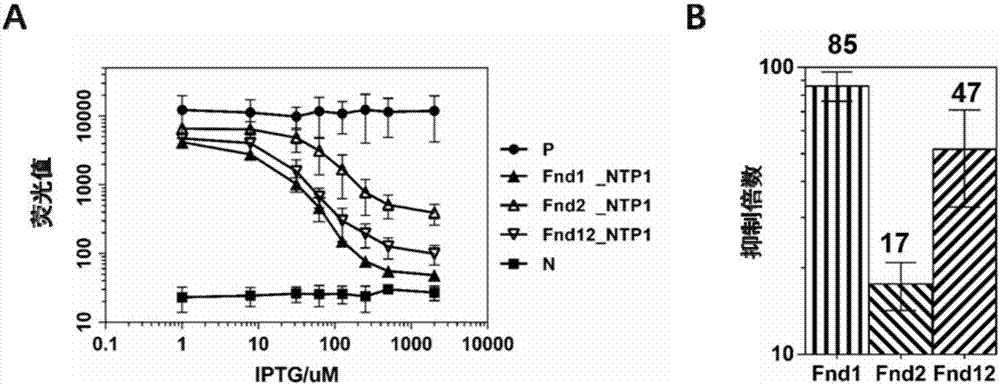
[0053] Example 2, Comparison of the transcriptional inhibition effects of different DNase mutants of FnCpf1
[0054] According to the genetic mutation studies of FnCpf1, the mutation of a single amino acid site in FnCpf1 (D917A) and FnCpf1 (E1006A) can make FnCpf1 lose its DNA-cleaving activity completely. Therefore, the present invention designs three FnCpf1 mutant forms, respectively FnCpf1 (D917A), FnCpf1 (E1006A), FnCpf1 (D917A, E1006A), the target site selects the non-template strand of the promoter region of the reporter gene, that is, NT strand, sgRNA Named as NTP1, the expression plasmids and sgRNA NTP1 expression plasmids of the three FndCpf1 mutants (constructed according to the method of Example 1, wherein the NTP1 primer containing the target sequence is F: agatgcactgtacctaggactgagctag; R: cttcctagctcagtcctagtacagtgc) and reporter plasmid (ie, Example The reporter plasmid in 1) was co-transfected into Escherichia coli DH5α, and the concentration of the inducer IPTG...
Embodiment 3
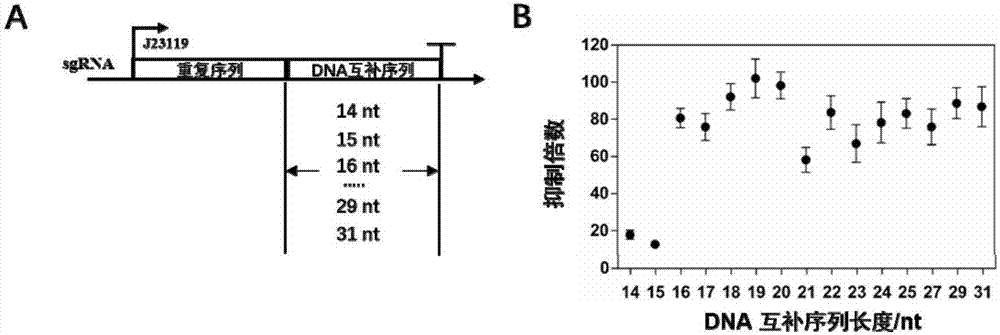
[0063] Example 3, Influence of repeat sequence length and spacer sequence length on transcription inhibition in the construction of sgRNA
[0064] 1. Changes in the length of the sgRNA target sequence
[0065] The inventors of the present invention selected a site on the coding region of the sfgfp gene in the reporter plasmid (ie, the reporter plasmid in Example 1), changed the length of the target sequence in the sgRNA, and explored its shortest target sequence length. In this experiment, the sequence length Set to 14-25nt (base-by-base increase) and 27nt, 29nt, 31nt ( image 3 Middle A).
[0066] The specific operation is as follows: the construction method of each sgRNA-related plasmid is shown in Example 1 ( figure 1 Middle D), the sequence information is shown in Table 3.
[0067] Table 3 Target sequence information of different lengths in sgRNA
[0068]
[0069] The expression plasmid of the FndCpf1 mutant was co-transfected with each sgRNA-related plasmid and rep...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com