In-vivo enrichment device of circulating free DNA
An enrichment and bulk technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of low efficiency and low quality in vitro capture, and achieve excellent biocompatibility, reduce phlebitis, and excellent mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
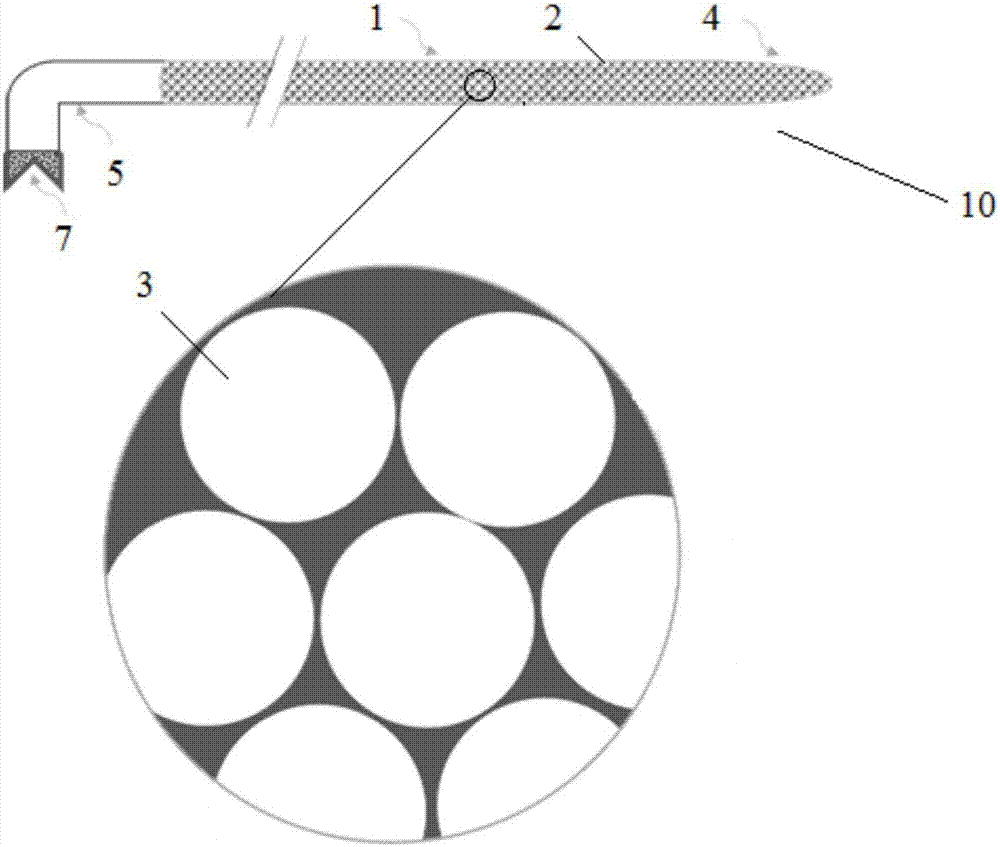
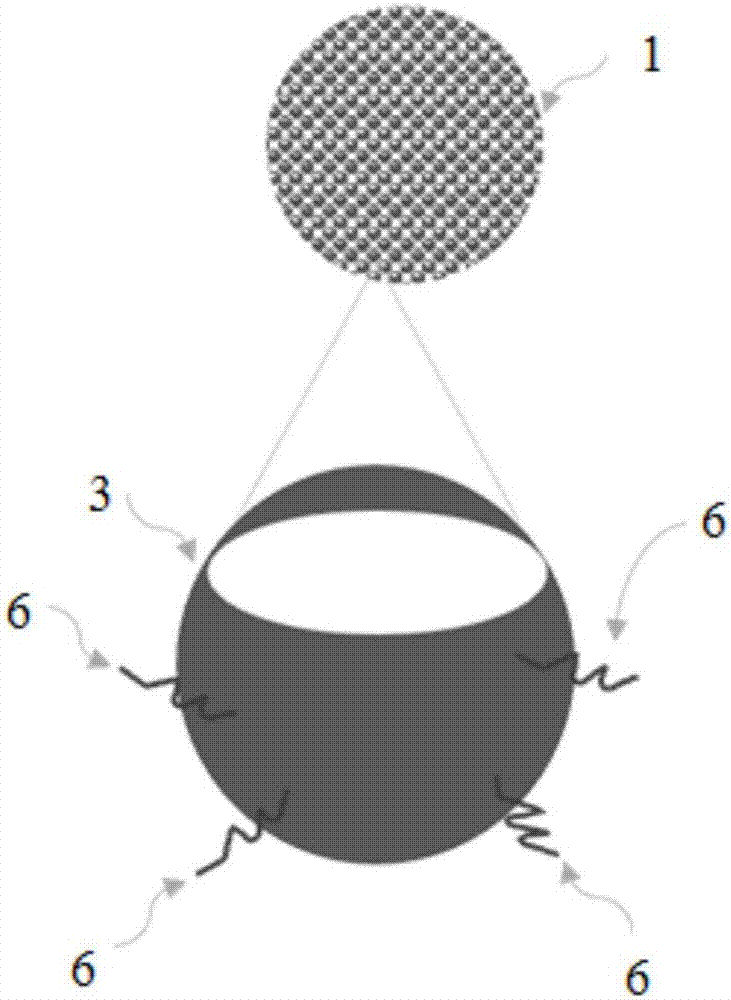
[0037] Such as figure 1 Shown is an in vivo enrichment device 10 according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. The device includes: a catheter body 1 that can reach the central vein through peripheral venous puncture, a plurality of sieve holes 2 are distributed on the tube wall of the catheter body 1 , and magnetic beads 3 that specifically bind ccfDNA are filled in the catheter body 1 . The magnetic beads 3 can be commercially available magnetic beads for nucleic acid extraction. The aperture of the mesh 2 is smaller than that of the magnetic beads 3 to prevent the magnetic beads 3 from leaking out of the catheter body 1 . From figure 1 It can be seen from the figure that the catheter body 1 has a uniform diameter along its length. The front end 4 of the catheter body 1 is a blind end to prevent the magnetic beads from leaking out.
[0038] Preferably, about 10 mm of the front end of the catheter body 1 is passivated to reduce damage to blood vessels and ...
Embodiment 2
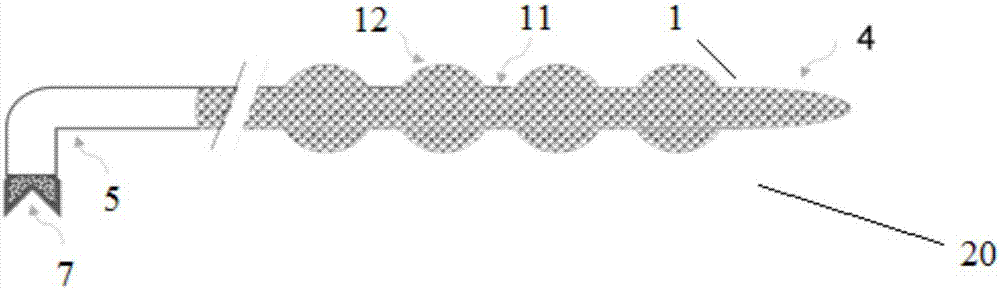
[0044] Such as figure 2 Shown is an in vivo enrichment device 20 according to another preferred embodiment of the present invention. The structure of the device 20 is substantially similar to that of the device 10 of the previous embodiment, the only difference is that the catheter body 1 has an uneven diameter along its length. According to this particularly preferred embodiment, the catheter body 1 has along its length a plurality of bulbous projections 12 spaced apart from each other by a cylindrical section 11 , the tube diameter of which is always greater than that of the cylindrical section 11 . This structure is also called "spherical expansion type". The advantage of this "spherical expansion type" is that it can increase the volume of blood in contact with the magnetic beads 3. If the clinical stage is earlier and the vessel diameter is appropriate, this "spherical expansion type" is theoretically preferred for high efficiency and high efficiency. Texture collectio...
Embodiment 3
[0047] According to this embodiment, the present invention also provides an optional operating procedure for the above-mentioned in vivo enrichment device 10, specifically as follows:
[0048] 1) The device should be used by medically professionally trained personnel, always observing routine hygienic requirements.
[0049] 2) Position the patient so that the patient's limb is at 90 degrees to the body.
[0050] 3) Place a waterproof pad or a disposable pad under the punctured limb, and place a tourniquet.
[0051] 4) Select the puncture site. The principle of vein selection is as follows: the basilic vein is the first choice, followed by the median vein, and then the cephalic vein.
[0052] 5) From the pre-puncture point along the vein to the right sternoclavicular joint, subtract 2-5cm from the measured value to get the catheter insertion length.
[0053] 6) Wear a sterile isolation gown (assisted by an assistant) and sterile gloves.
[0054] 7) Lay out the sterile table:...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com