Full depth remote scanning Raman spectrometer
A Raman spectrometer and a Raman spectroscopic technology, which are applied in the field of Raman spectrometers, can solve the problems of unfavorable endoscopy imaging field application, reduction of mechanical scanning mechanism, complicated optical design and mechanical design, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0045] The present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings, so that those skilled in the art can implement it with reference to the description.
[0046] It should be understood that terms such as "having", "comprising" and "including" as used herein do not assign the presence or addition of one or more other elements or combinations thereof.
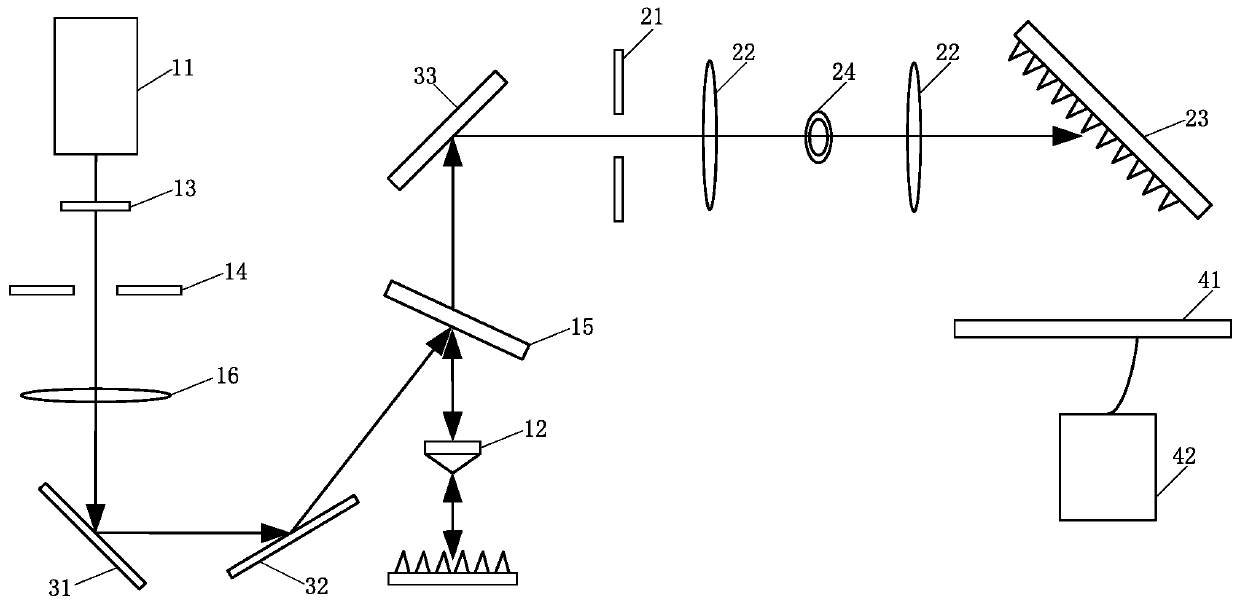
[0047] like figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a full-depth remote scanning Raman spectrometer, which includes an illumination unit, a spatial light modulation unit and a spectrum collection unit. The illumination unit is used for outputting near-infrared light to illuminate the sample, so as to realize near-infrared light illumination for the sample. The spatial light modulation unit is located at the output end of the illumination unit, and selects the spot size of the Raman light scattered on the sample to output Raman spectra of different depths. The spectrum c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com