Artificially-synthetic Bt insecticidal gene mcrylF for transgenic insect-resistant plant
A technology of transgenic plants and transgenic cell lines, applied in the field of biological control, can solve the problem of no commercialization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] Embodiment 1, transformation of Cry1F gene and acquisition of mcry1F gene
[0080] The amino acid sequence of Cry1F protein is shown as sequence 4 in the sequence listing. The nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding Cry1F protein (hereinafter referred to as Cry1F gene for short) is shown as sequence 3 in the sequence listing.
[0081] The inventors of the present invention carefully analyzed the active region of the Cry1F protein, and under the premise of ensuring further improvement of its expression level, modified the gene coding frame and codons of the Cry1F protein according to the coding characteristics of monocotyledonous plants. The modified Cry1F protein was named mcry1F protein. The amino acid sequence of mcry1F protein is shown as sequence 2 in the sequence listing. The nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding mcry1F protein (that is, the modified Cry1F gene, hereinafter referred to as mcry1F gene) is shown in sequence 1 in the sequence listing.
[0082] ...
Embodiment 2
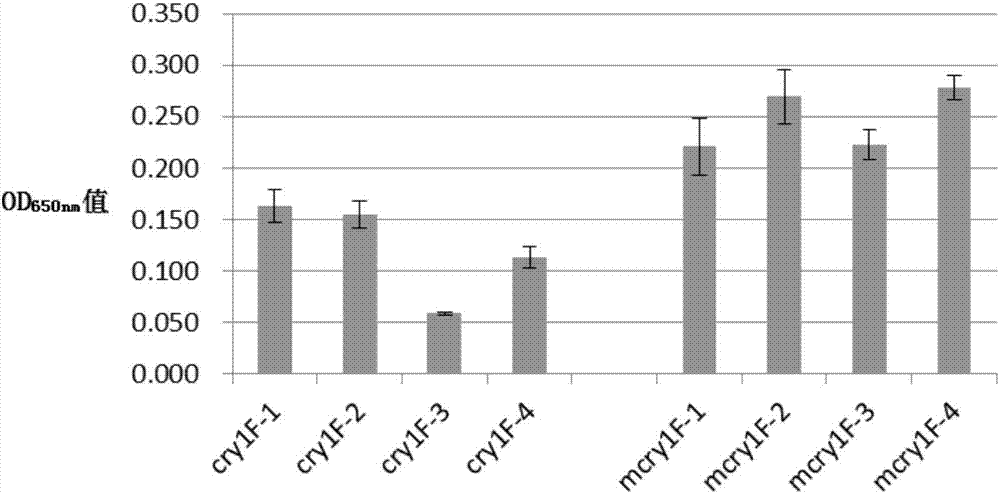
[0086] Example 2, bioassay of mcry1F protein on Lepidoptera insects
[0087] 1. In vitro expression and purification of mcry1F protein
[0088] The in vitro expression and purification steps of mcry1F protein are as follows:
[0089] 1. Artificially synthesize the double-stranded DNA molecule shown in sequence 1 in the sequence listing.
[0090] 2. Ligate the double-stranded DNA molecule synthesized in step 1 with the prokaryotic expression vector pEASY-E1 to obtain the recombinant plasmid pEASY-mcry1F.
[0091] The recombinant plasmid pEASY-mcry1F was sequenced. Sequencing results show that the recombinant plasmid pEASY-mcry1F contains the DNA molecule shown in sequence 1 in the sequence listing and expresses the mcry1F protein shown in sequence 2 in the sequence listing.
[0092] 3. The recombinant plasmid pEASY-mcry1F was introduced into Escherichia coli transetta to obtain a recombinant bacterium, which was named transetta-mcry1F.
[0093] 4. Take a single clone of tra...
Embodiment 3
[0104] Example 3. Obtaining and identification of insect resistance of transgenic mcry1F maize
[0105] 1. Construction of recombinant vector
[0106] The recombinant plasmid pCAMBIA3301+mcry1F was constructed and sequenced. According to the sequencing results, the structure of the recombinant plasmid pCAMBIA3301+mcry1F is described as follows: replace the small fragment between the recognition sequences of the restriction endonucleases HindIII and BstEII of the vector pCAMBIA3301 with the sequence 5 in the sequence listing from 1 to 2392 from the 5' end Double-stranded DNA molecules are shown. The recombinant plasmid pCAMBIA3301+mcry1F expresses the mcry1F protein shown in Sequence 2 in the Sequence Listing.
[0107] The expression cassette is contained in the recombinant plasmid pCAMBIA3301+mcry1F, and the nucleotide sequence of the expression cassette is shown in sequence 5 in the sequence list. In sequence 5 in the sequence listing, the 1st to 583rd from the 5' end is t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com