Process for producing calcium D-pantothenate
A technology of calcium pantothenate and pantothenic acid, applied in organic chemistry, fermentation, etc., can solve problems such as lower crystallization yield, inability to remove monosaccharides or oligosaccharides, and high viscosity of D-calcium pantothenate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
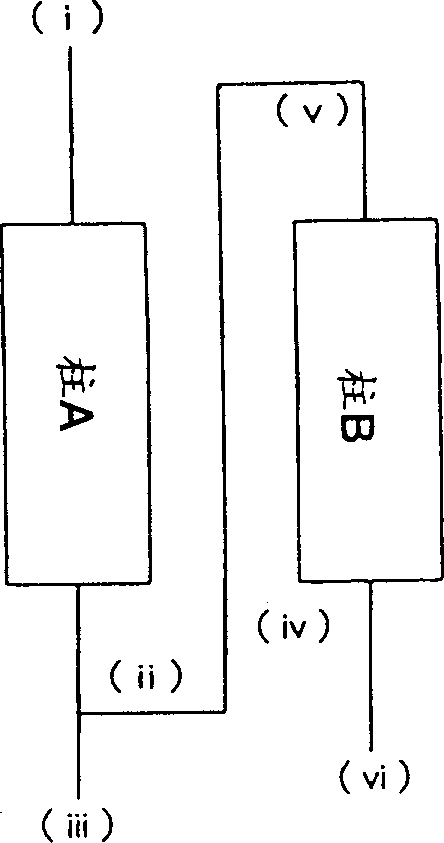
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
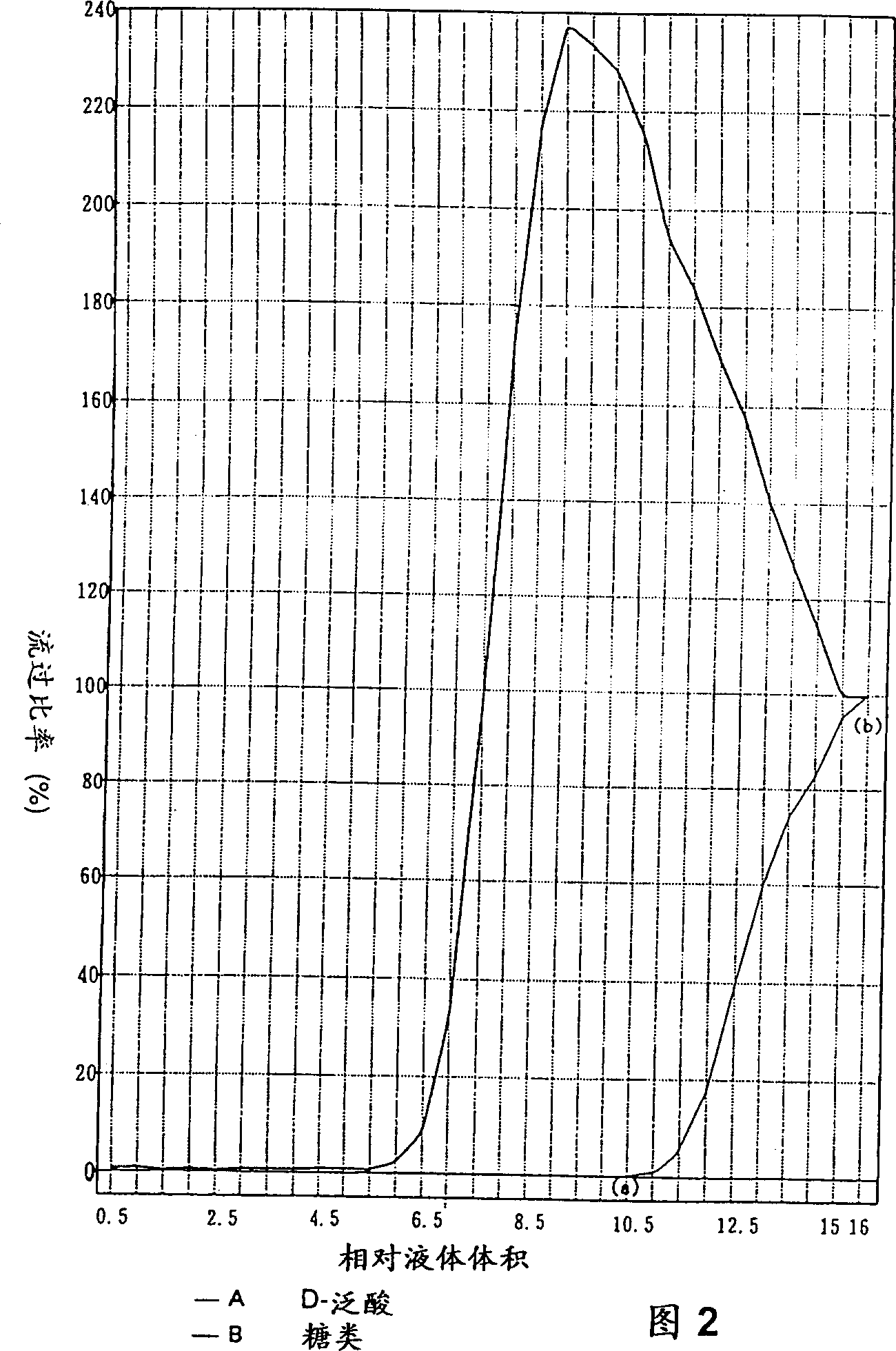
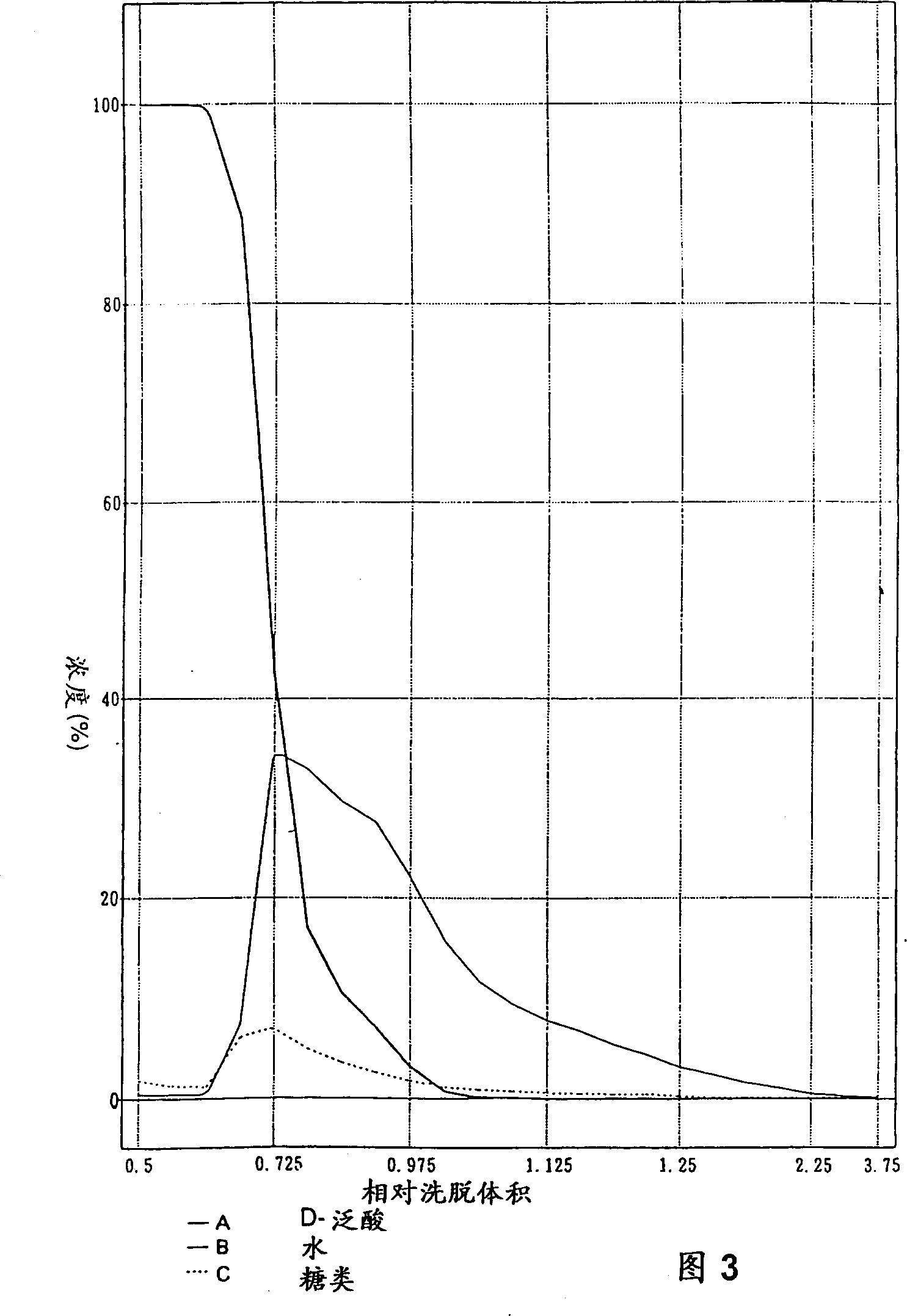
[0028] The Escherichia coli IFO 814 / pEV 31 strain was cultured in a 5-liter fermenter according to a conventional method. The medium contained glucose as a sugar source, and the direct fermentation medium (2.5 liters) containing D-pantothenic acid was obtained through fermentation. The liquid fermentation broth was filtered through a ceramic filter (manufactured by Toshiba Ceramics Co., Ltd.) having a mesh diameter of 0.1 µ at 40°C to remove insoluble matter such as bacterial cells to obtain a filtrate (1.67 liters). The filtrate contained D-pantothenic acid (38.5 mg / ml (64.3 g)), sugars (total amount determined by the phenol-sulfuric acid method: 10.3 mg / ml (about 27% based on D-pantothenic acid)). The filtrate was passed through an activated carbon column (inner diameter: 70 mm, height: 130 mm, packing volume: 500 ml) packed with activated carbon K1 for decolorization (manufactured by Takeda Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., sieve volume: 1.12 cc / g, average sieve diameter: 32A). ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com