Intelligent formation method of lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery and battery technology, applied in the direction of secondary batteries, electrochemical generators, non-aqueous electrolyte batteries, etc., can solve the problems of not considering the difference between batteries, difficulty in reducing production costs, poor battery consistency, etc., and achieve consistency High, reduce the production rate of inferior products, improve the effect of performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
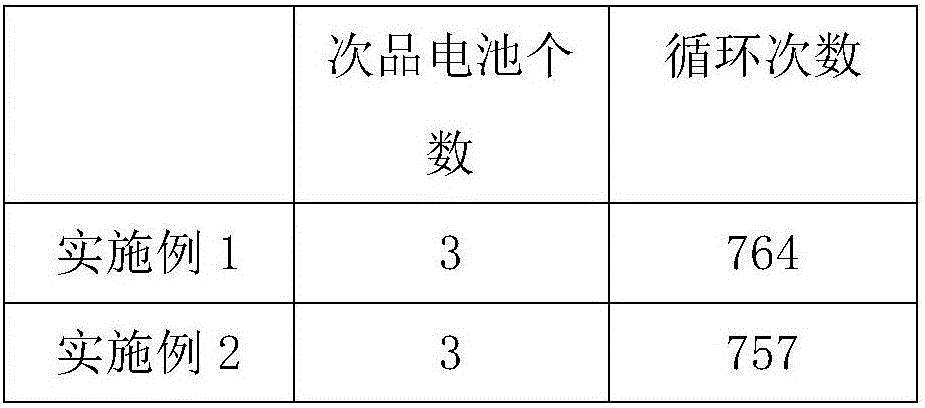
Embodiment 1
[0028] 1) Charge the lithium-ion battery to 3.6V at 0.05C;
[0029] 2) Charge to 4.2V at 0.1C;
[0030] 3) Discharge at 1C to 2.7V;
[0031] 4) Measure the temperature of each single battery and calculate the average temperature;
[0032] 5) Continue to over-discharge the battery whose temperature is higher than the average value to the cut-off voltage:
[0033] Cut-off voltage=2.7-0.1*(single battery temperature / average temperature-1);
[0034] 6) Perform positive and negative alternating pulse current cycles on all batteries near their voltage for 3 times, the magnitude of the positive pulse current and the negative pulse current are the same as 0.1C, the pulse action time is the same as 10s, and the interval is 0s;
[0035] 7) Charge the battery to 4.2V with 1C, then cycle the battery twice between 4.2-2.7V with the same current, check the battery capacity, and classify the battery according to the battery capacity.
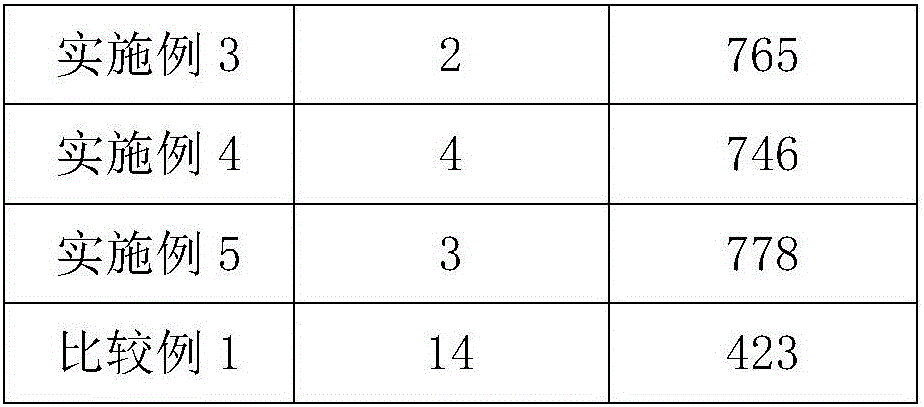
Embodiment 2
[0037] 1) Charge the lithium-ion battery to 3.7V at 0.1C;
[0038] 2) Charge to 4.3V at 0.5C;
[0039] 3) Discharge at 2C to 2.8V;
[0040] 4) Measure the temperature of each single battery and calculate the average temperature;
[0041] 5) Continue to over-discharge the battery whose temperature is higher than the average value to the cut-off voltage:
[0042] Cut-off voltage=2.8-0.8*(single battery temperature / average temperature-1);
[0043] 6) Perform positive and negative alternating pulse current cycles on all batteries near their voltage for 20 times, the magnitude of the positive pulse current and the negative pulse current are the same as 0.2C, the same pulse action time is 60s, and the interval is 20s;
[0044] 7) Charge the battery to 4.3V at 2C, then cycle the battery 5 times between 4.3-2.8V with the same current, check the battery capacity, and classify the battery according to the battery capacity.
Embodiment 3
[0046] 1) Charge the lithium-ion battery to 3.6V at 0.08C;
[0047] 2) Charge to 4.2V at 0.2C;
[0048] 3) Discharge at 1.5C to 2.7V;
[0049] 4) Measure the temperature of each single battery and calculate the average temperature;
[0050] 5) Continue to over-discharge the battery whose temperature is higher than the average value to the cut-off voltage, and the cut-off voltage satisfies the following formula:
[0051] Cut-off voltage=2.7-0.5*(single battery temperature / average temperature-1);
[0052] 6) Perform positive and negative alternating pulse current cycles on all batteries near their voltage for 10 times, the magnitude of the positive pulse current and the negative pulse current are the same as 0.2C, the same pulse action time is 30s, and the interval is 10s;
[0053] 7) Charge the battery to 4.2V at 1.5C, then cycle the battery 4 times between 4.2-2.7V with the same current, check the battery capacity, and classify the battery according to the battery capacity....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com