Quantum cryptography implementation method based on quantum light source
A technology of quantum cryptography and implementation method, applied in the application field, can solve the problems of low coincidence rate, unreachable signal state of optimal strength, poor performance, etc., and achieve the effect of eliminating intensity modulation error, excellent practical performance and huge development potential.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
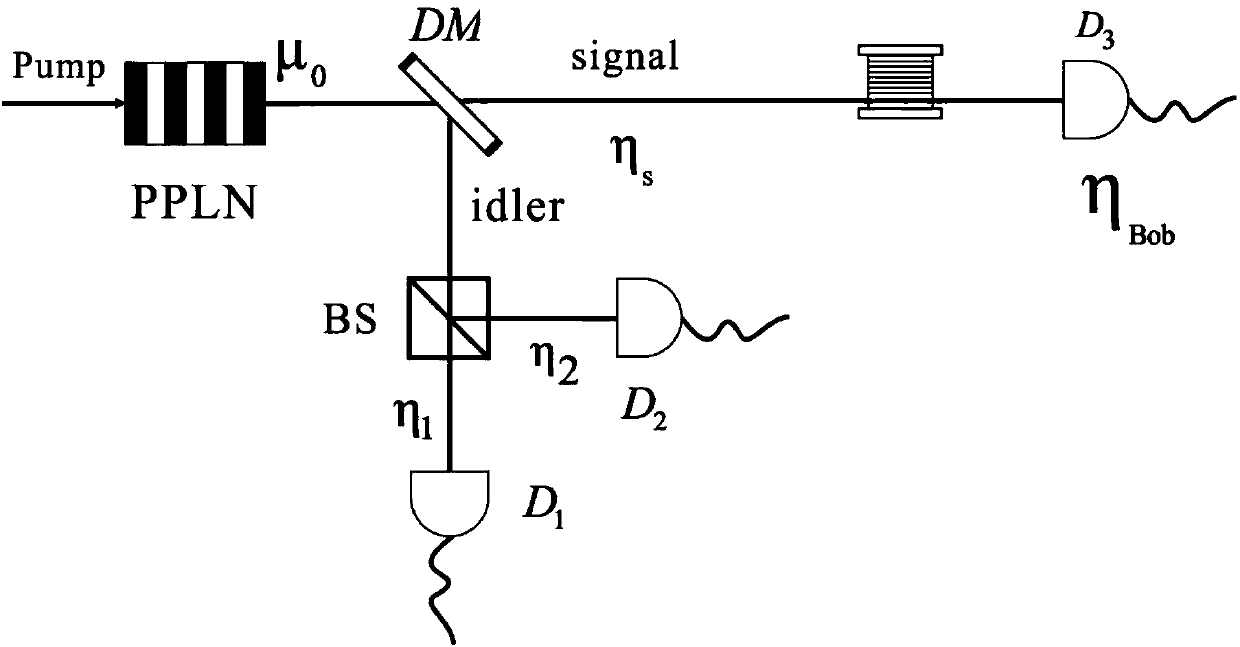
[0020] In the scheme of the present invention, a decoy state method and a novel low-loss unequal-arm MZ interferometer are adopted.
[0021] In the QKD system conventionally using HSPS light sources of the present invention, the dual-mode light field state obtained from the parametric down-conversion process can be described as:
[0022]
[0023] where |n> represents an n photon state, P n is the corresponding photon number distribution, in the present invention P n It obeys the Poisson distribution; I and S represent leisure light and signal light respectively. Usually leisure light (mode I) is detected locally by Alice at the transmitting end, while signal light (mode S) is sent to Bob at the receiving end.
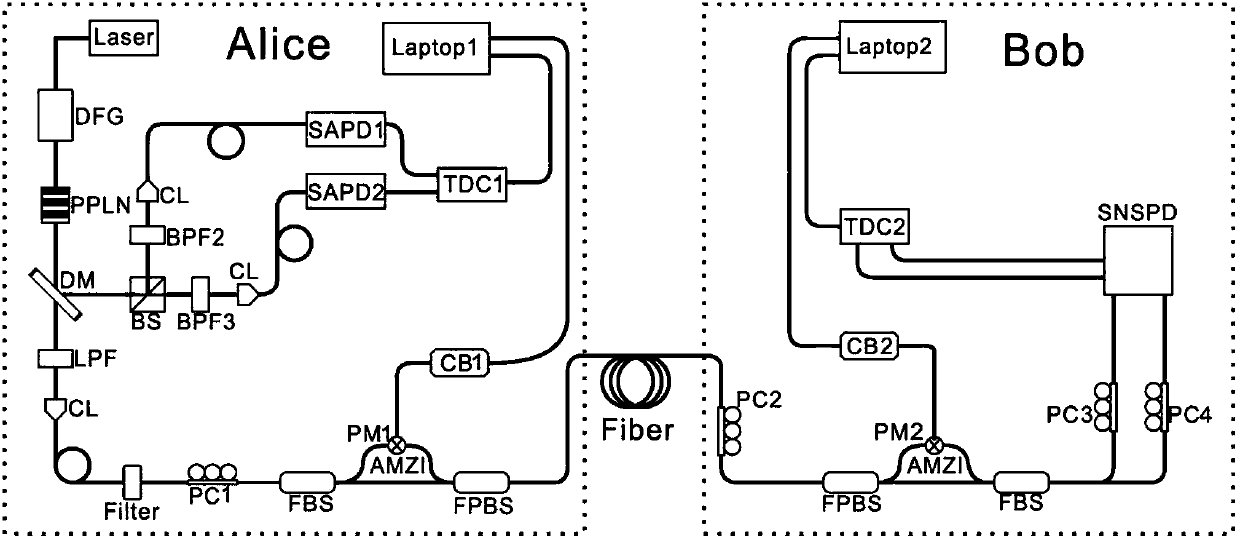
[0024] The scheme for generating passive HSPS of the present invention is explained below. The main process can be divided into the following steps: the first step, after the parametric down-conversion process, the leisure light is divided into two parts after pass...
Embodiment 2
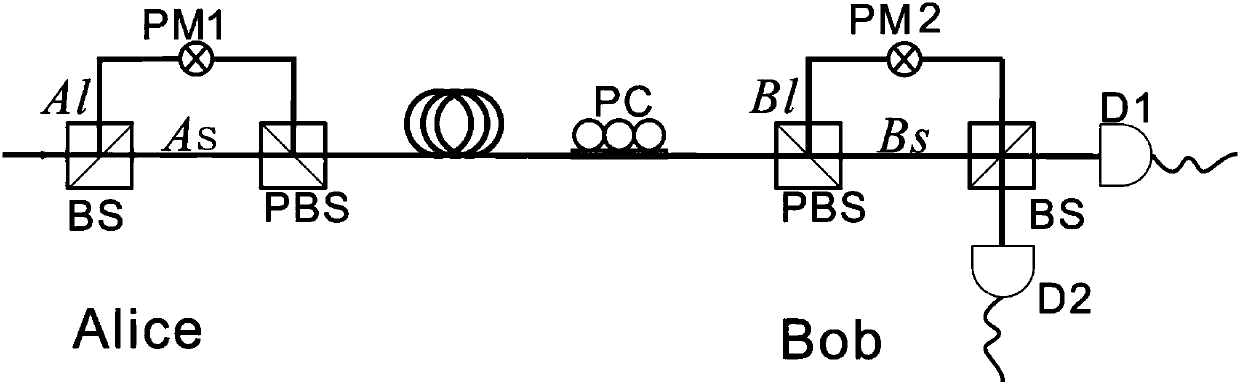
[0041] For the sake of simplicity in the experiment, only three events such as x, y, z are used to estimate the key extraction rate. The parameters used in the experiment satisfy 010 20 0 1 =tη 10 , η 2 =(1-t)η 20 , with η 1 >0,1-η 2 >0,1-η 1 -η 2 >0. due to d 1 >>1, for any n≥2, we can get:
[0042]
[0043] So for any n≥2 the following inequalities hold:
[0044]
[0045] Using the above formula and considering statistical fluctuations, the lower bound Y of the single photon responsivity can be obtained 1 L and an upper bound on the single-photon bit error rate
[0046]
[0047] where e 0 (=0.5) and Y 0 Respectively represent the qubit bit error rate and dark count at Bob's end in the vacuum state. Q ξ and E ξ (ξ=x, y, z) represent the total response rate and qubit error in any ξ state, respectively;
[0048]
[0049] γ is the standard deviation of statistical fluctuation analysis, which is assumed to be a constant γ=5.3, and the correspondin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com