Manufacturing process for polysaccharide beads
A technology for polysaccharide beads and polysaccharide, which is applied in the field of preparing polysaccharide beads, cross-linked polysaccharide beads, and preparing polysaccharide beads by reversed-phase suspension technology, can solve problems such as elimination, and achieve the effect of good pore structure and mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0043] Emulsification method (reference example uses 1,2-dichloroethane)
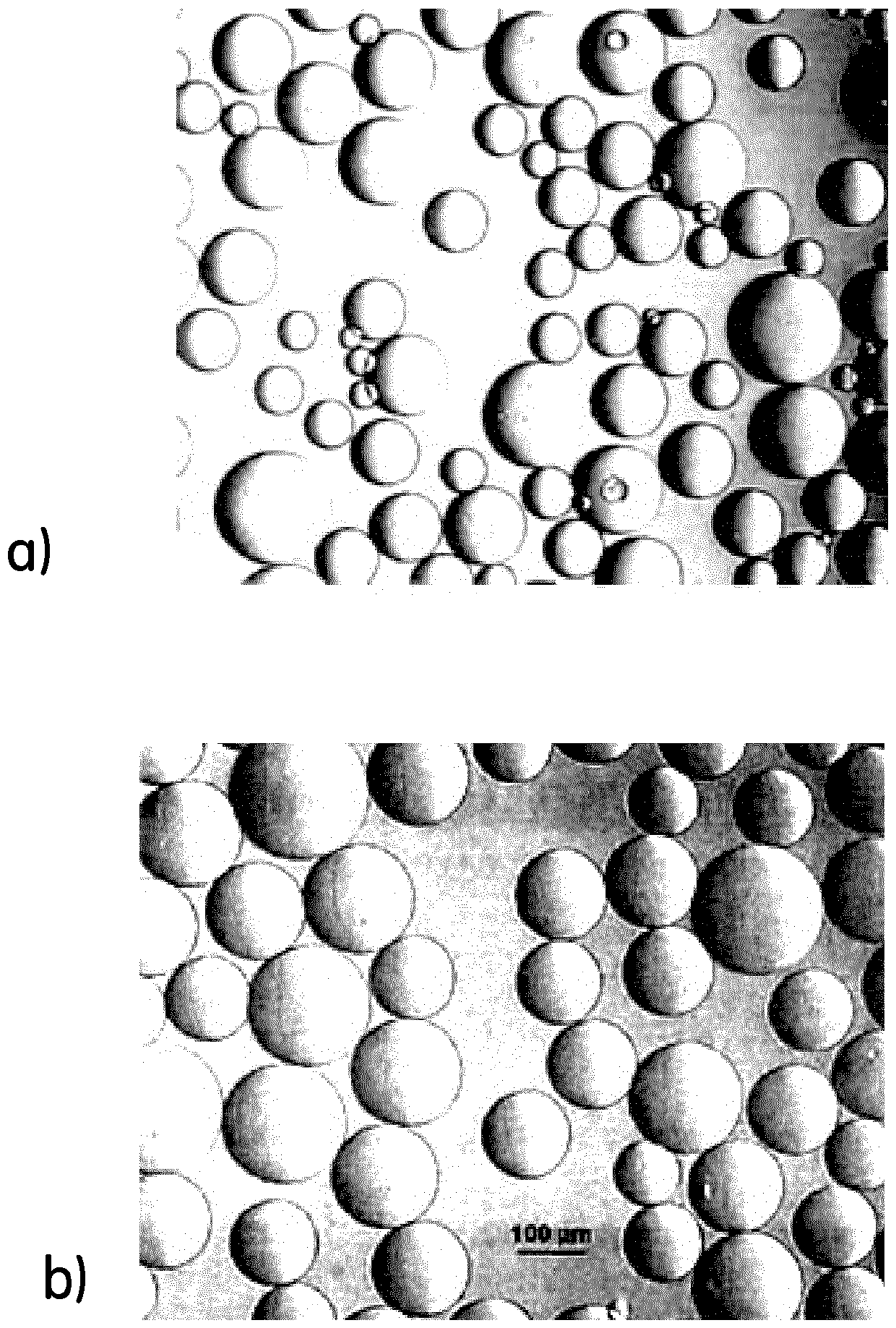
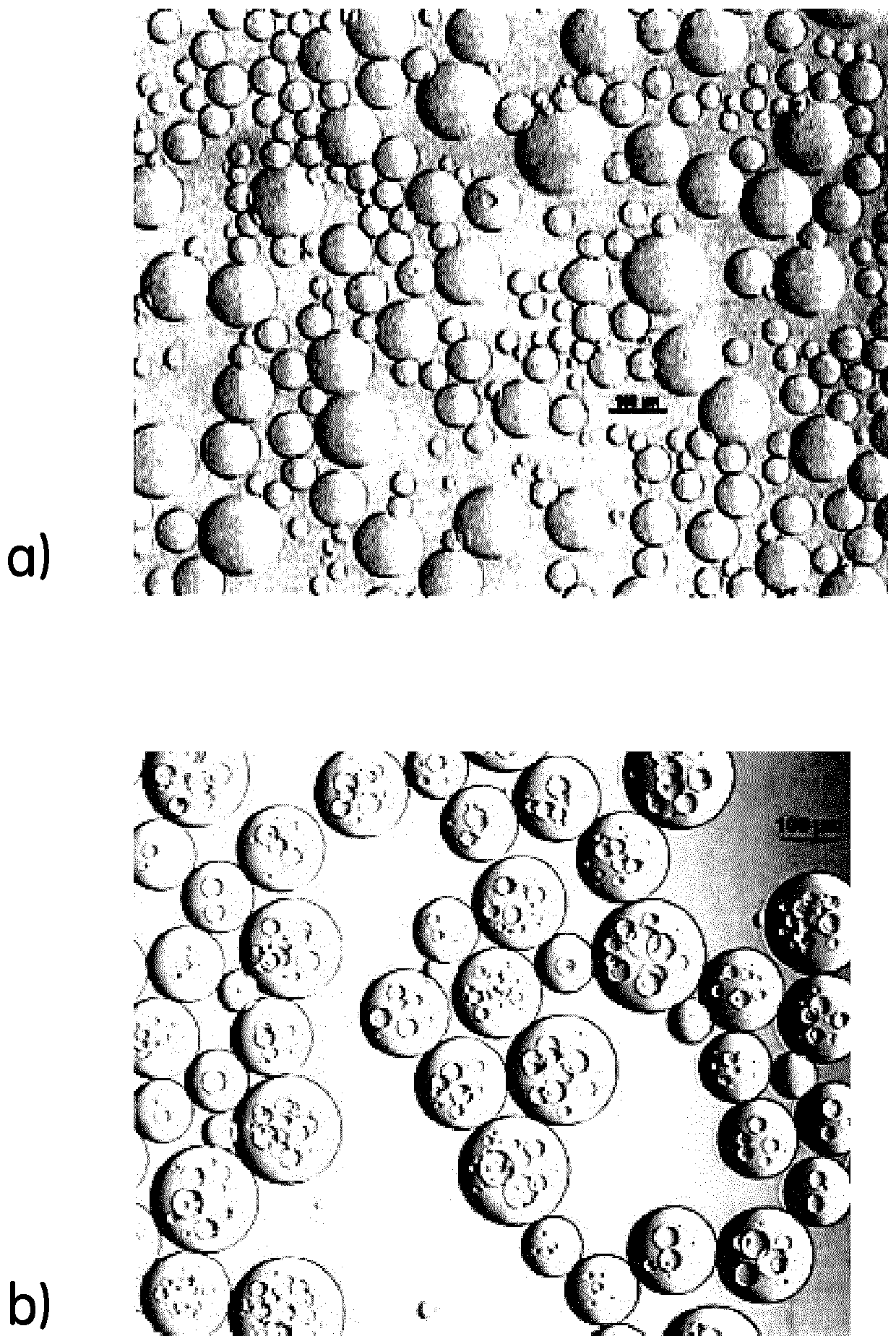
[0044] 165 g of dextran (Mw 150-250 kD) was dissolved in 390 ml of distilled water while 22 ml of 50% sodium hydroxide (NaOH) was added under stirring. 0.8 g sodium borohydride (NaBH 4 ) was added to the solution.
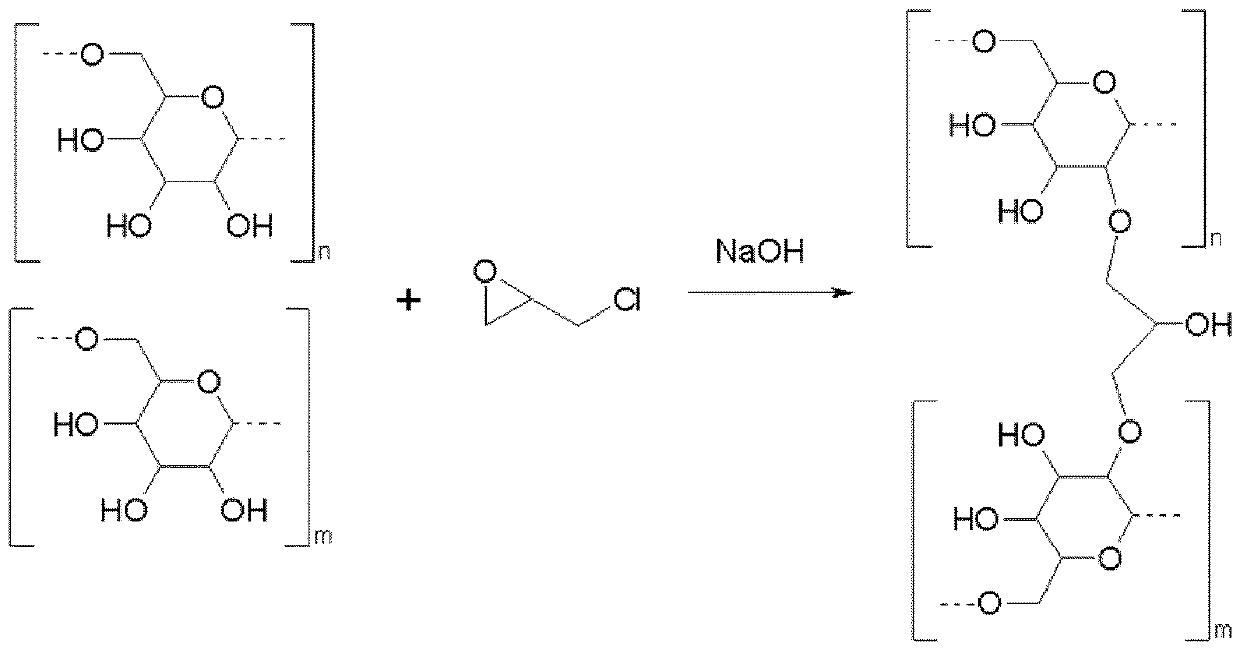
[0045] 21 g of cellulose acetate butyrate (CAB) were added to a 1000 ml glass reactor with an overhead stirrer. Start the stirrer and add 350 ml 1,2-dichloroethane (EDC) (so the CAB concentration is 0.060 g / ml EDC). The solution was stirred until the CAB was dissolved. The aqueous phase was then added to the oil phase with stirring at 50°C, and stirring continued until a suitable droplet size was achieved, as judged from microscopic examination of a small sample drawn. When the proper size was obtained, the emulsion was immediately stabilized by adding 22.4 ml of epichlorohydrin (ECH) to cross-link the dextran and thus solidify the droplets. 20 minutes after the addition of ECH, 50 ml o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com