Method for detecting single-base mutation
A single-base mutation, gene technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of λ exonuclease degradation rate and other problems, and achieve easy preparation, low detection cost, and simple operation. Effect
Active Publication Date: 2018-02-23
BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
View PDF0 Cites 0 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
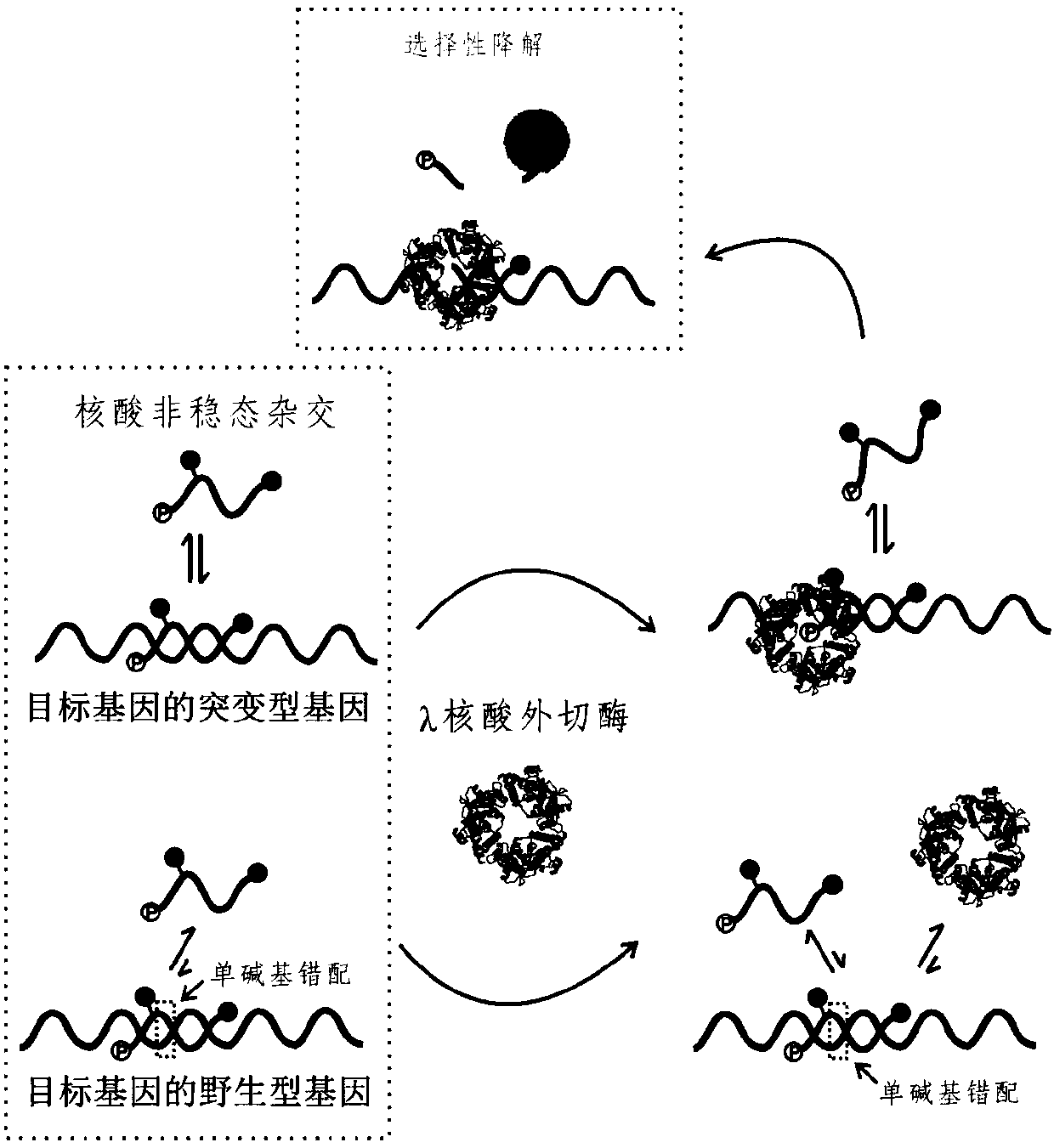
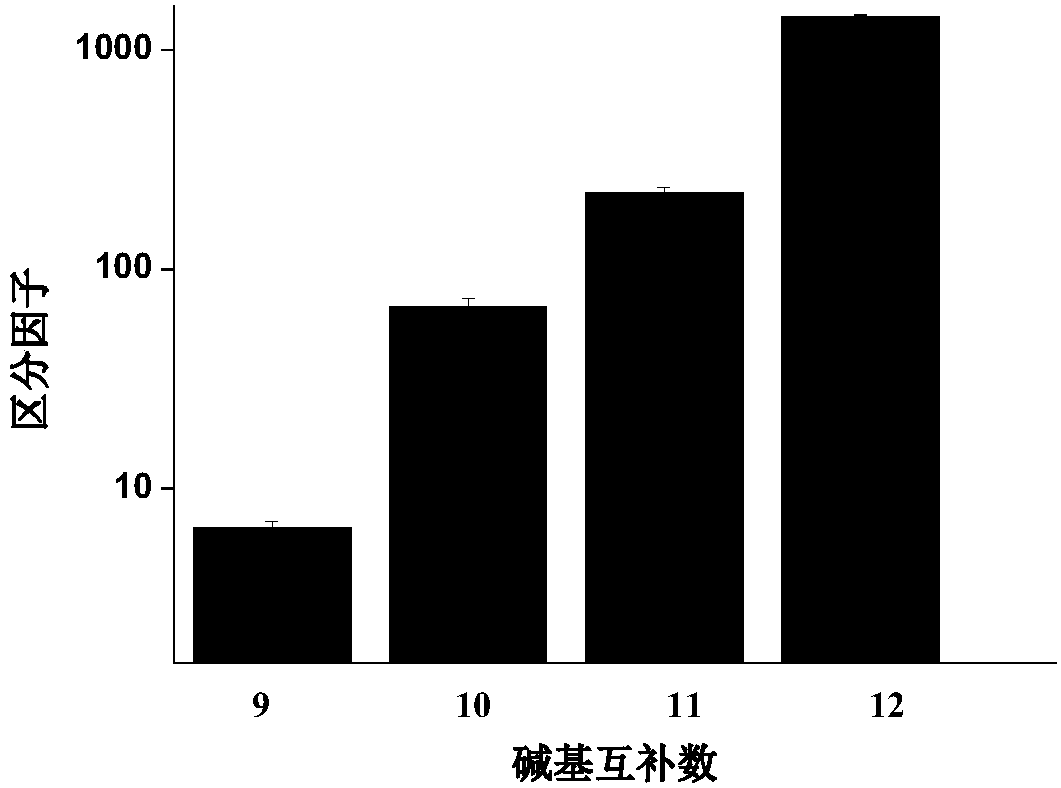
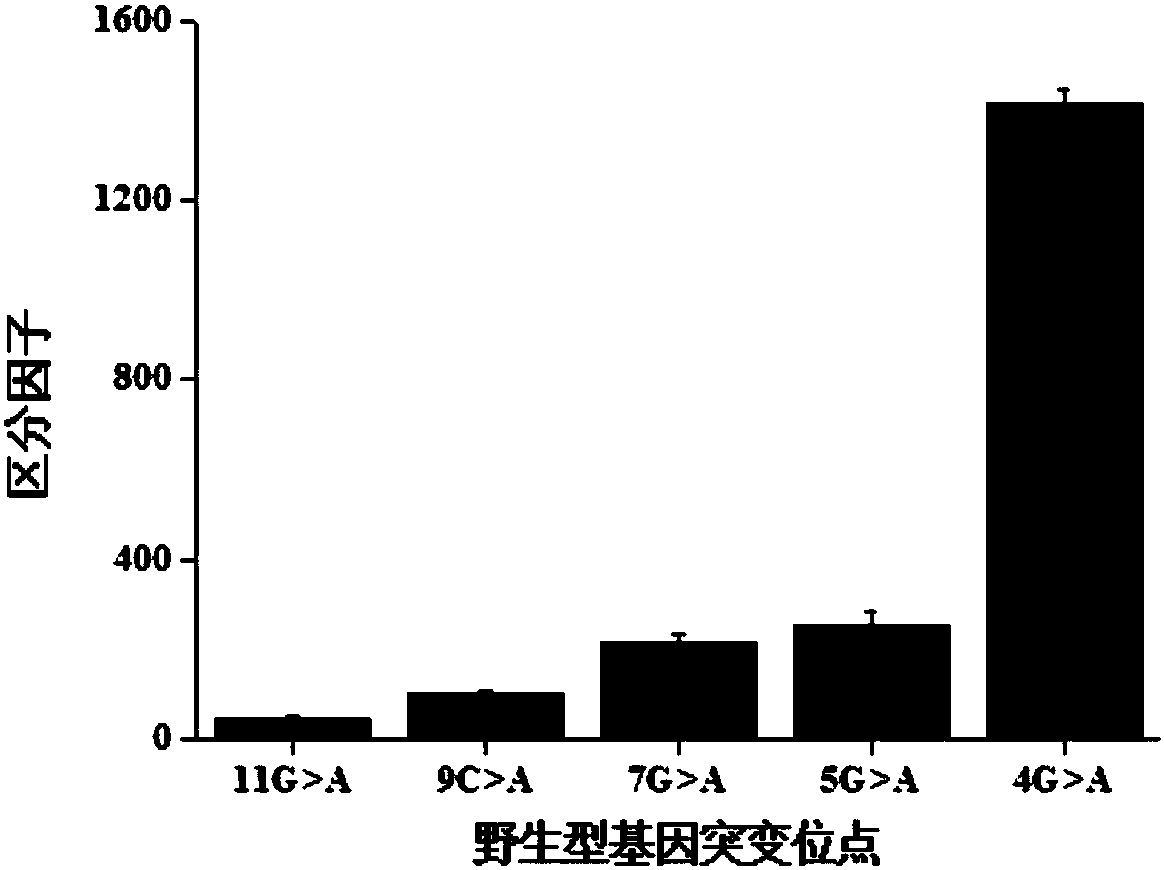
The rate at which the lambda exonuclease degrades the double strand is sensitive to base pairing, and the presence of mismatches usually leads to a decrease in the degradation rate of the lambda exonuclease
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment 1
[0047] Embodiment 1: Using the method of the present invention to detect single base mutations in target genes
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
The invention relates to a method for detecting single-base mutation in the field of gene mutation detection. The method comprises the following steps: S1, designing a fluorescent signal probe according to a target gene, wherein the fluorescent signal probe is completely complementary to a mutant gene of the target gene and forms a single-base mismatch with a wild-type gene of the target gene; S2,adding a target gene sample to be detected and lambda exonuclease into a fluorescent signal probe-containing solution to form a reaction system; S3, acquiring a real-time fluorescence curve of the reaction system during the reaction, and judging whether the single-base mutation exists in the target gene sample to be detected. By the method, a single-base mutant gene sequence can be rapidly and accurately detected, and the selectivity to the single-base mutant gene sequence is high, so that the method can be applied to low-abundance mutation detection; in addition, by the method, the detectioncost is low, the preparation is easy, the operation is simple and the repeatability is high, and the method is easily popularized among non-professionals.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention belongs to the technical field of gene mutation detection, and in particular relates to a method for detecting single base mutation. Background technique [0002] Gene sequencing technology has shown that base changes in the human genome are closely related to the formation and development of tumors. In a large number of isolated tumor patient tissue samples, single-base point mutations were found in the genomes of many tumor cells. However, in the early stage of tumor onset, the content of tumor cells is low, and the percentage of mutated genes in tumor cells is also relatively low. [0003] Gene mutation detection technology can be divided into sequencing type and non-sequencing type. Sequencing technology has high accuracy and can do repetitive sequences, but the cost of sample preparation is high, the concentration of nucleic acid required is high and the analysis time is long, and low-abundance detection cannot be performed, making...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): C12Q1/6827
CPCC12Q1/6827C12Q2563/107C12Q2521/319
Inventor 苏昕郝丹丹喻长远蔡爽张怡
Owner BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com