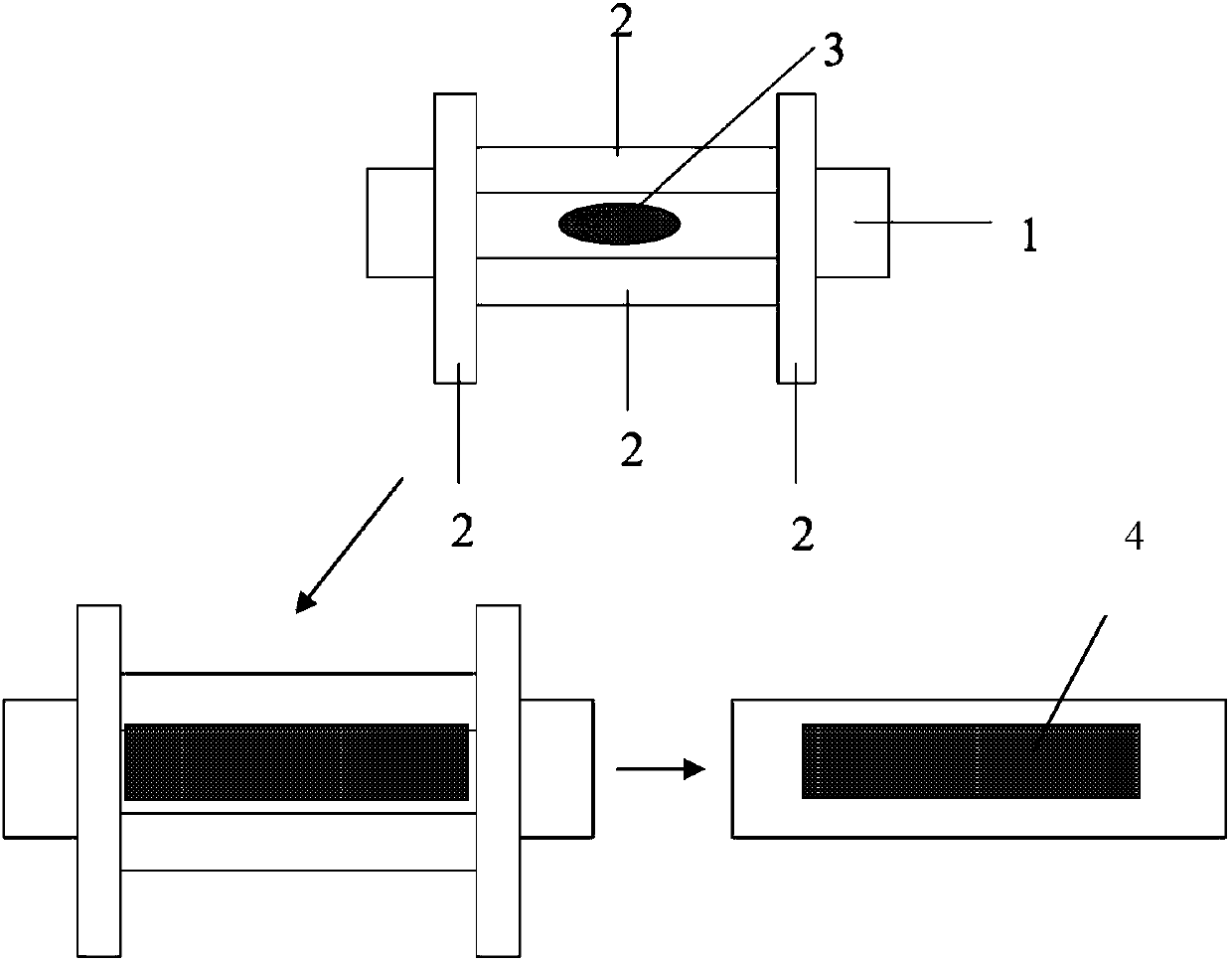
Preparing method of remote fluorescent sheet based on low-melting-point borosilicate glass powder
A borosilicate glass, low melting point technology, applied in the field of materials science, can solve the problems of uneven coating of phosphor powder, organic glue aging, yellowing, etc., and achieve the effects of high practical value, not easy to fall off, and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] 1) The SiO that will be weighed 2 , B 2 o 3 , ZnO, Na 2 CO 3 The mass percentages of the raw materials are: 15%, 44%, 21%, and 20%, and they are mixed evenly, and the glass block is prepared by melting method, and ground into a powder with a particle size of 5-13 μm;
[0024] 2) Weigh glass powder and fluorescent powder with a mass fraction ratio of 20 and 5 parts, disperse the powder in an organic matter with a mass fraction ratio of 45 parts, and uniformly mix to form a fluorescent glass slurry;
[0025] 3) The fluorescent glass slurry obtained in 2) is coated on an ultra-clear glass plate with a scraper coating technique;
[0026] 4) Fully sinter the fluorescent glass layer prepared in 3) at 180°C-300°C to completely volatilize organic matter, and then sinter at 600°C-700°C for 5-30 minutes at a low temperature to obtain the remote fluorescent glass sheet.
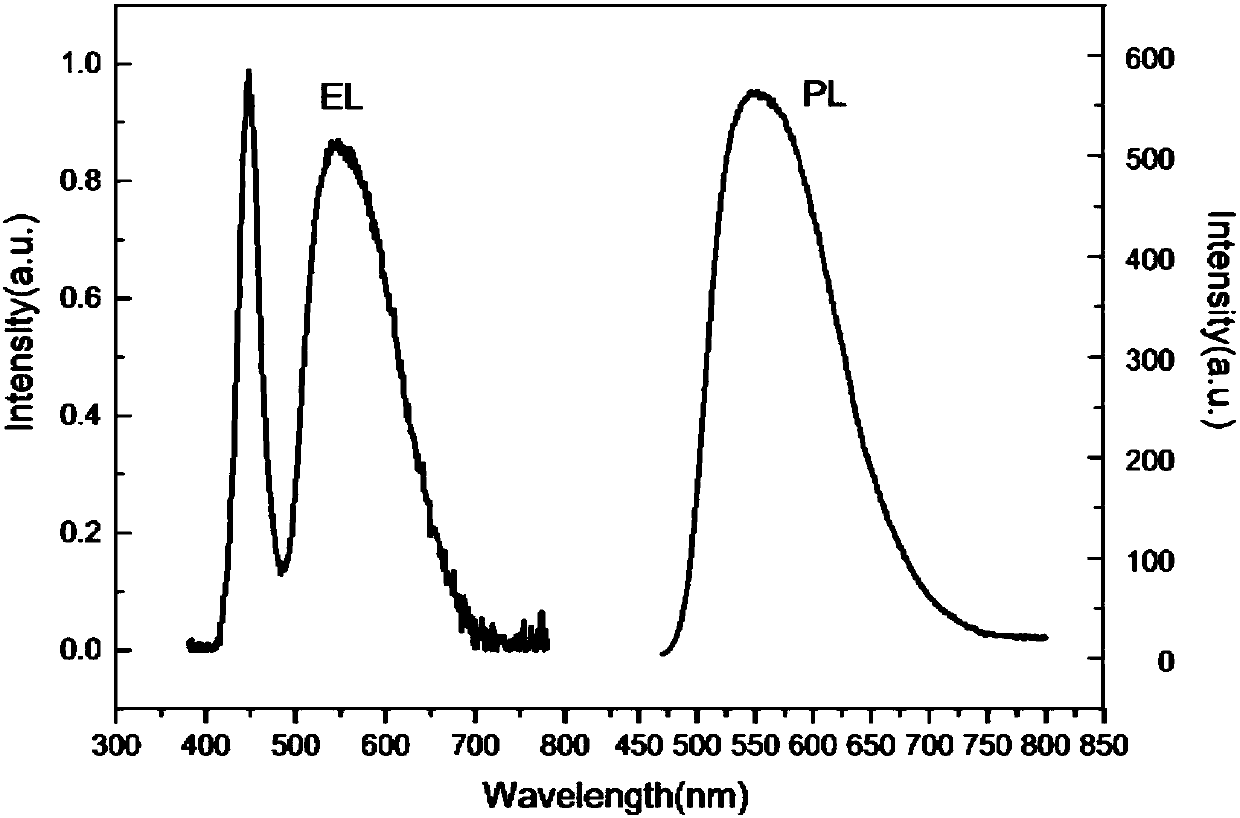
[0027] Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that under the excitation wavelength of 460nm, the fluorescent...
Embodiment 2
[0029] 1) The SiO that will be weighed 2 , B 2 o 3 , ZnO, Na 2 CO 3 The mass percentages of the raw materials are respectively: 18.5%, 45%, 20.5%, 16%, mixed uniformly, prepared glass blocks by melting method, and ground into powders with a particle size of 5-13 μm;
[0030] 2) Weighing 32 parts by mass and 6 parts by mass of glass powder and fluorescent powder, dispersing the powder in organic matter with 52 parts by mass, and uniformly mixing them to form a fluorescent glass slurry;
[0031] 3) The fluorescent glass slurry obtained in 2) is coated on an ultra-clear glass plate with a spin-coating technique;
[0032] 4) Fully sinter the fluorescent glass layer prepared in 3) at 180°C-300°C to completely volatilize organic matter, and then sinter at 600°C-700°C for 5-30 minutes at a low temperature to obtain the remote fluorescent glass sheet.
Embodiment 3
[0034] 1) The SiO that will be weighed 2 , B 2 o 3 , ZnO, Na 2 CO 3 The mass percentages of the raw materials are respectively: 20.5%, 44.8%, 21.2%, 13.5%, mixed uniformly, prepared glass blocks by melting method, and ground into powders with a particle size of 5-13 μm;
[0035] 2) Weighing 48 parts by mass and 9 parts by mass of glass powder and fluorescent powder, dispersing the powders in 67 parts by mass of organic matter, and uniformly mixing them to form a fluorescent glass slurry;
[0036] 3) The fluorescent glass paste obtained in 2) is coated on an ultra-clear glass plate with a screen printing technique;
[0037] 4) Fully sinter the fluorescent glass layer prepared in 3) at 180°C to 300°C to completely volatilize the organic matter, and then sinter at 600°C to 700°C for 5 to 30 minutes at a low temperature to obtain the remote fluorescent glass sheet
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com