Flower fresh-keeping agent
A technology of preservatives and fresh flowers, applied in the field of food additives, can solve the problems of increased long-distance transportation and long-term storage, preservatives and fresh-keeping methods that cannot meet the needs, and achieve good fresh-keeping effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
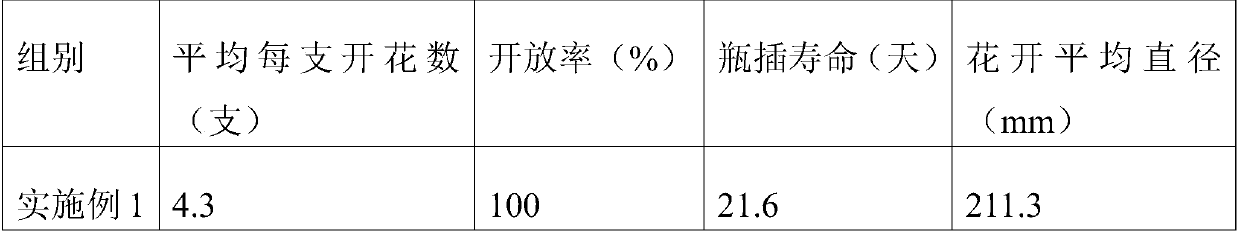
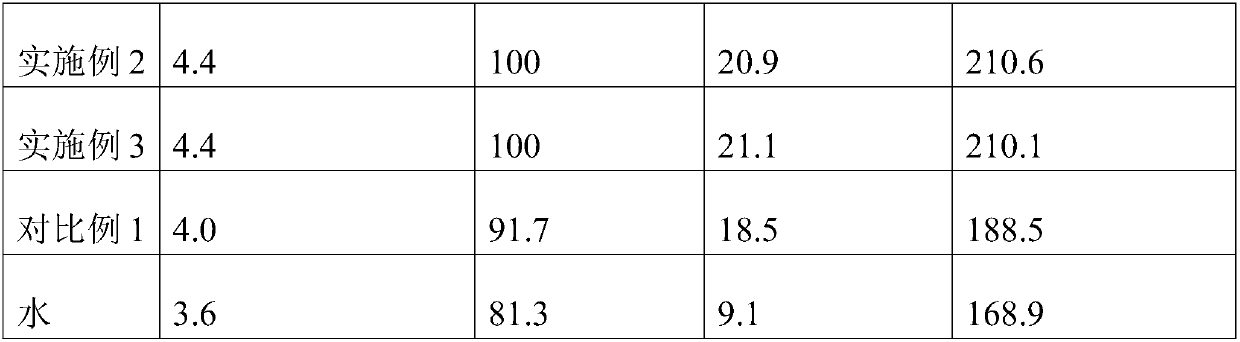
[0013] A fresh-keeping agent for flowers, which is mainly made of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 6 parts of glucose, 4 parts of tea polyphenols, 5 parts of phytic acid, 4 parts of chitosan, 6 parts of potassium sorbate, and ethanol extract of Gynostemma pentaphyllum 4 parts, nisin 3 parts, borax 6 parts, thiourea 4 parts, gibberellin 6 parts, olive leaf extract 2 parts, seaweed extract 2 parts, tea saponin 1 part and salicylic acid 2 parts.
[0014] The gibberellin is beeswax. The preparation of the above-mentioned antistaling agent is to prepare the suspension by mixing the above-mentioned raw materials.
[0015] The usage method of the fresh-flower preservative is as follows: after diluting the fresh-flower preservative with water 250 times, soak the root of the fresh flower in the preservative solution.
Embodiment 2
[0017] A fresh-keeping agent for fresh flowers, which is mainly made of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 5 parts of glucose, 8 parts of tea polyphenols, 4 parts of phytic acid, 7 parts of chitosan, 4 parts of potassium sorbate, and ethanol extract of Gynostemma pentaphyllum 2 parts, nisin 1 part, borax 7 parts, thiourea 2 parts, gibberellin 3 parts, olive leaf extract 3 parts, seaweed extract 1 part, tea saponin 0.5 part and salicylic acid 1 part.
[0018] The gibberellin is food-grade shellac. The above preservative is prepared by mixing the above raw materials to prepare a wettable powder.
[0019] The usage method of the fresh-flower preservative is as follows: after diluting the fresh-flower preservative with water 150 times, soak the root of the fresh flower in the preservative solution.
Embodiment 3
[0021] A fresh-keeping agent for fresh flowers, which is mainly made of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 10 parts of glucose, 3 parts of tea polyphenols, 9 parts of phytic acid, 3 parts of chitosan, 9 parts of potassium sorbate, alcohol extract of Gynostemma pentaphyllum 6 parts, nisin 4 parts, borax 3 parts, thiourea 6 parts, gibberellin 7 parts, olive leaf extract 1 part, seaweed extract 3 parts, tea saponin 2 parts and salicylic acid 3 parts.
[0022] The gibberellin is polyvinyl acetate. The preparation of the above-mentioned antistaling agent is to prepare the suspension by mixing the above-mentioned raw materials.
[0023] Preferably, the method of using the fresh flower preservative is: after diluting the fresh flower preservative with water 300 times, soak the root of the fresh flower in the preservative solution.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com