Process for the preparation of glycols
A diol and catalyst technology, applied in the field of diol preparation, can solve problems such as the difficulty in separating catalysts from reactants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
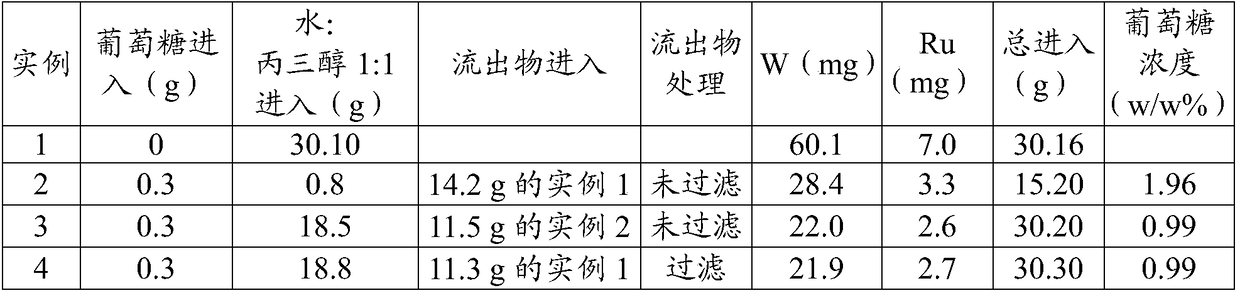
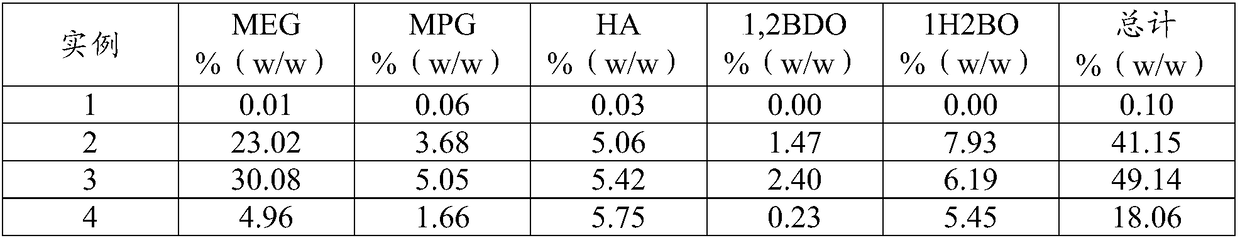
[0054] Summary of the examples: In Example 1, the catalyst precursor was converted into an unsupported hydrogenation catalyst in the presence of hydrogen in a reactor vessel, and in the presence of a catalyst component with retroaldol catalytic capability (sodium phosphotungstate ), but the activity was assessed in the absence of sugar-containing starting material (glucose). In Example 2, the activity of an unsupported hydrogenation catalyst was evaluated in the presence of a sugar feedstock (glucose) and a catalyst component with retroaldol catalytic capability. In Example 3, when additional sugar-containing feedstock (glucose) was added to the reactor vessel, more diol product (eg, MEG) was produced. In Example 4, a sample was taken from the Example 1 reactor vessel contents and filtered through a 0.45 μm pore size filter, and when mixed with the sugar-containing feedstock and the catalyst component with retro-aldol catalytic capability, two The content of alcohol products ...
example 1
[0055] Example 1 : Formation of unsupported hydrogenation catalyst and its background activity:
[0056] A 60 ml Hastelloy C22 autoclave (Medimex) equipped with a hollow shaft gas stirrer was charged with 15 g of water and 15 g of glycerol pre-dissolved in a water / glycerol mixture, 60.1 mg of sodium phosphotungstate (Aldrich (Aldrich)) and 7.0 mg ruthenium(III) acetylacetonate (catalyst precursor; Merck) (Table 1). The reactor vessel was pressurized to 5 bar with nitrogen and depressurized to atmospheric pressure three times at room temperature to remove oxygen, then pressurized to 40 bar with hydrogen. The temperature was raised to 195°C, the total pressure was raised to 80 bar with hydrogen and a stirring rate of 1450 rpm was applied. After 60 minutes, the reactor vessel was allowed to cool to room temperature, opened and a sample was taken for analysis (Table 2). Glycerol appeared to be stable as only a trace of product was formed, indicating that glycerol could be appl...
example 2
[0057] Example 2 : Activity of the unsupported hydrogenation catalyst from Example 1 in the presence of both the sugar feedstock and the catalyst component with retroaldol catalytic capability:
[0058] A 60 ml Hastelloy C22 autoclave (Medimex) equipped with a hollow shaft gas stirrer was charged with 14.2 g of the reactor vessel effluent of Example 1 . Water and glycerol were added in equal weight amounts to a total of 15.2 g of the reactor vessel contents along with 0.3 g of glucose (Millipore). The reactor vessel was pressurized to 5 bar with nitrogen and depressurized to atmospheric pressure three times at room temperature to remove oxygen, then pressurized to 40 bar with hydrogen. The temperature was raised to 195°C, the total pressure was raised to 80 bar and a stirring rate of 1450 rpm was applied. After 60 minutes, the reactor vessel was allowed to cool to room temperature, opened and a sample was taken for analysis (Table 2). This example demonstrates the catalyti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com