Method for arranging arbor to multi-layer stratified solid waste
A technology of solid waste and plant waste, applied in the direction of solid waste removal, botany equipment and methods, and fertilizer made from biological waste, can solve the problem of insufficient improvement depth of key arbor areas, unfavorable subsequent growth of arbor plants, large Deal with the cost and transportation cost and other issues, achieve the effects of recycling with significant environmental protection effect, conducive to survival and growth, and reduce secondary pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] A method for planting arbors to absorb solid waste in multiple layers,
[0036] (1) Crushing of coarse solid waste and terrain construction of buildings on site:
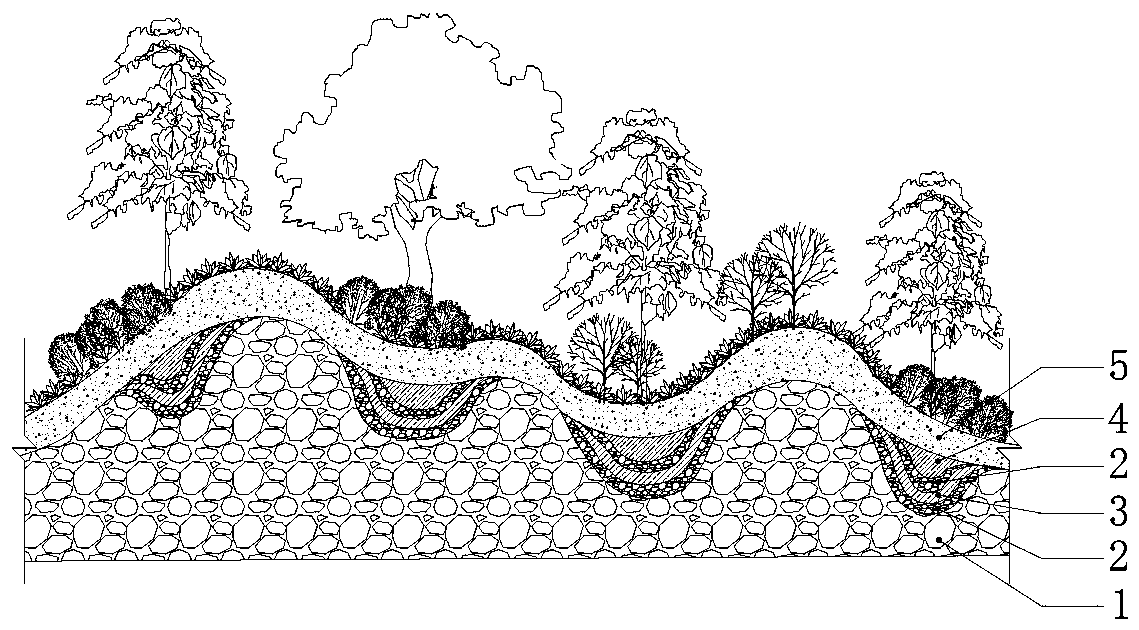
[0037] Crushing and screening the solid waste of the site and buildings according to the coarse solid waste, and at the same time sorting out the materials that will rot for a long time and cause the volume to change and cause the foundation to deform; the coarse solid waste is used as the foundation to form 15 groups including concave and convex The foundation formed continuously and alternately, the concave surface is the arbor planting hole;
[0038]The coarse solid waste: refers to the solid waste formed after the demolition of buildings and floors, after sorting and crushing, the solid waste with a particle size of 16cm-20cm; the coarse solid waste formed The height of the concave part of the foundation is 10-20cm; the height of the convex part is 80-100cm. At the same time, the solid waste is piled up ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] A method for planting arbors to absorb solid waste in multiple layers,
[0053] (1) Crushing of coarse solid waste and terrain construction of buildings on site:
[0054] Crushing and screening the solid waste of the site and buildings according to the coarse solid waste, and at the same time sorting out the materials that will rot for a long time and cause the volume to change and cause the foundation to deform; the coarse solid waste is used as the foundation to form 20 groups including concave and convex The foundation is formed continuously and alternately, the concave surface is the arbor planting hole, the coarse solid waste: refers to the solid waste formed after the demolition of buildings and floors, after sorting and crushing, the particle size is between 16cm- 30cm solid waste; the height of the concave part of the foundation formed by the coarse solid waste is 25-40cm; the height of the convex part is 90-100cm. At the same time, the solid waste is piled up ...
Embodiment 3
[0067] A method for planting arbors to absorb solid waste in multiple layers,
[0068] (1) Crushing of coarse solid waste and terrain construction of buildings on site:
[0069] Crushing and screening the solid waste of the site and buildings according to the coarse solid waste, and at the same time sorting out the materials that will rot for a long time and cause the volume variable to cause the foundation to deform; the coarse solid waste is used as the foundation to form 28 groups including concave and convex The foundation formed continuously and alternately, the concave surface is the arbor planting hole;
[0070] The coarse solid waste: refers to the solid waste formed after the demolition of buildings and floors, after sorting and crushing, the solid waste with a particle size of 16cm-20cm; the coarse solid waste formed The height of the concave part of the foundation is 10-15cm; the height of the convex part is 70-90cm. At the same time, the solid waste is piled up ac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com