Zero-speed correcting and locating method based on difference statistics
A positioning method and zero-speed correction technology, applied in the field of indoor positioning and signal processing, can solve problems such as lack of gait characteristics, achieve the effect of improving positioning accuracy, wide application range, and good development prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
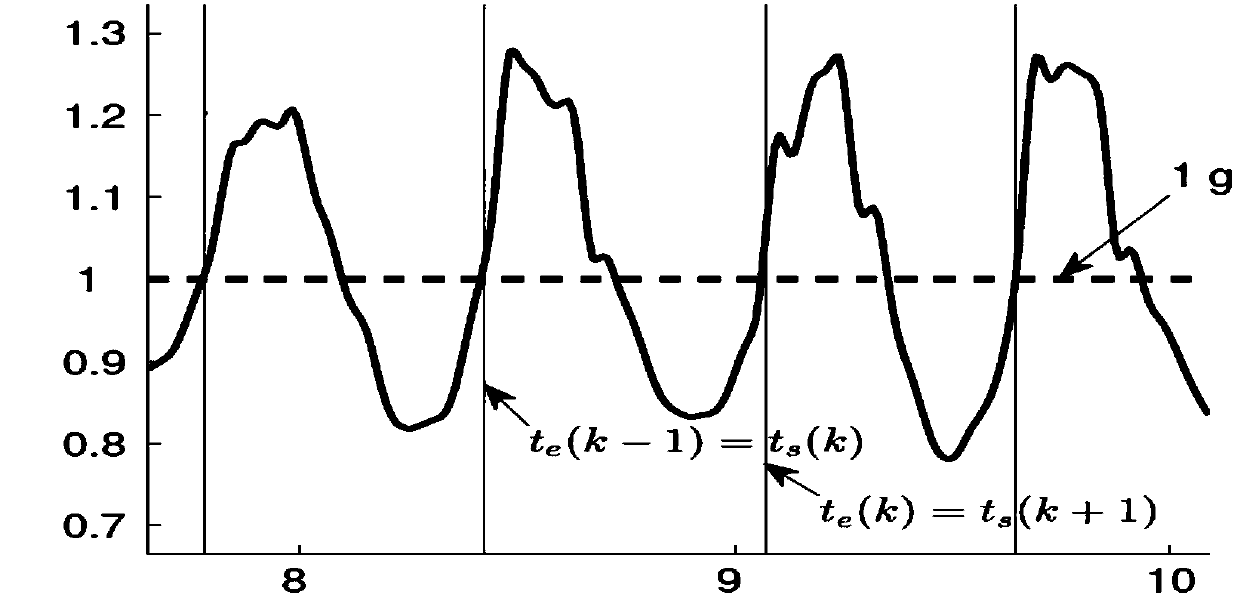
[0058] At present, the traditional ZUPT method widely used in PDR is to use the intersection of acceleration norm and gravity to complete step detection, but this method relies heavily on the motion mode and has a limited application range. Therefore, the embodiment of the present invention proposes a position-based service robot without gait characteristics, such as a sweeping robot, that does not depend on the motion mode by performing differential statistical analysis on the characteristics of the acceleration measurement in the motion state and the static state. ZUPT positioning method is also applicable to dining trolleys.
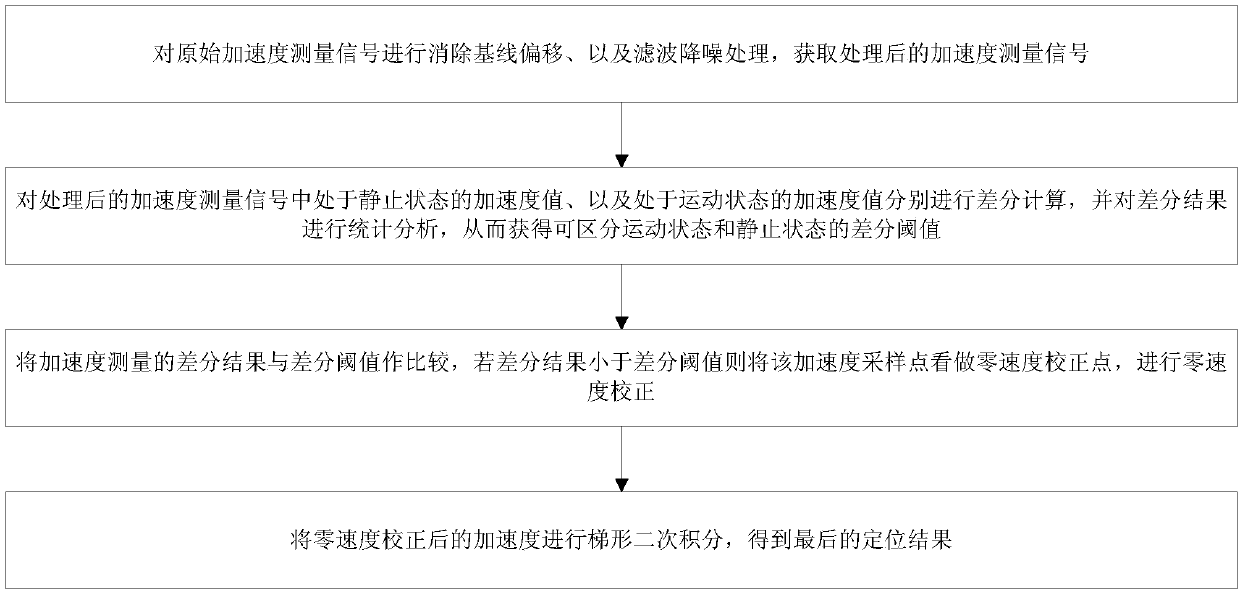
[0059] A zero-speed correction positioning method based on difference statistics, see Figure 2-Figure 3 , The zero-speed correction positioning method includes the following steps:
[0060] 101: Perform baseline offset removal and filter noise reduction processing on the original acceleration measurement signal, and obtain the processed acceleration measu...
Embodiment 2
[0067] The following combines specific examples, calculation formulas, Figure 4-Figure 5 The solution in Example 1 is further introduced, as detailed in the following description:
[0068] 1. The steps of the zero-speed correction positioning algorithm based on difference statistics are as follows:
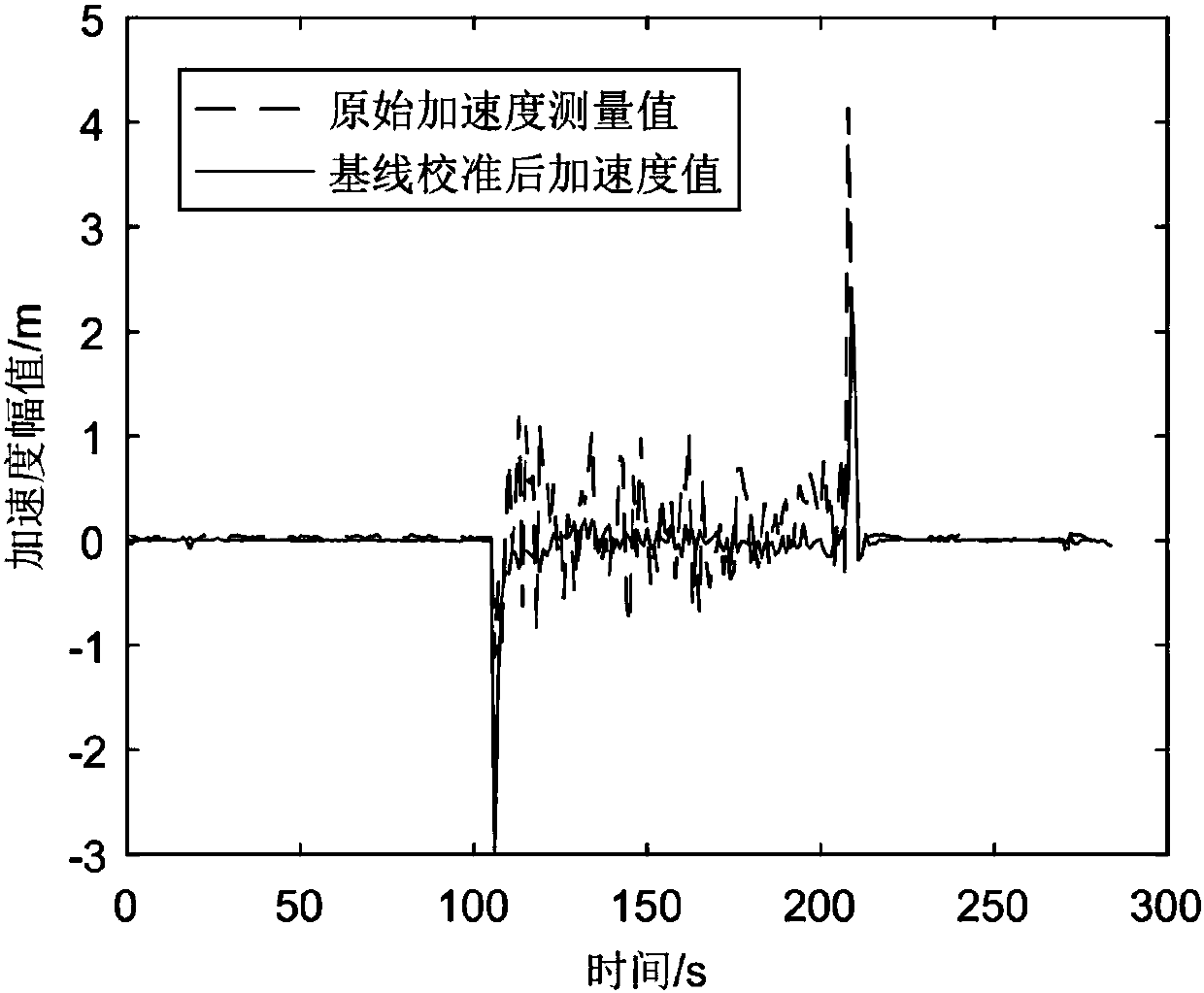
[0069] Baseline correction on the original acceleration signal: After removing the average value of the acceleration signal during the stationary period, subtract the average value from all acceleration measurements to obtain the baseline corrected signal. The processing process is as follows:
[0070]
[0071]
[0072] among them, Is the mean value of acceleration at rest, acc k Is the acceleration value with index k, K is the total number of stationary acceleration signals, Is the nth acceleration signal of baseline correction, acc n Is the acceleration value with index n, Is the average value of acceleration in a stationary state, N is the total number of acceleration signals, i...
Embodiment 3
[0092] Below in conjunction with Table 1 to Table 2, Figure 4-Figure 5 , To verify the feasibility of the schemes in Examples 1 and 2, see the following description for details:
[0093] In order to verify the effect of this method, the steps in the above Examples 1 and 2 were used to perform positioning analysis on three sets of experiments with displacement lengths of 12.25m, 4m, 4m and durations of 64 seconds, 54 seconds, and 65 seconds, respectively. In the positioning process, the integration algorithm used in the embodiment of the present invention is a trapezoidal integration algorithm.
[0094] Qualitative perspective, Figure 4 Shows a static state (see Figure 4 (a)) and the state of motion (see Figure 4 (b)) The acceleration difference value distribution range is obviously different. The acceleration difference value in the static state is small and the fluctuation range is small, while the acceleration difference value in the motion state is larger and the fluctuation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com