Method for cultivating Lactarius akahatsu mycorrhizal seedling
A technology of lactobacillus and orange, applied in the field of plant seedlings, can solve the problems of seedling decay, reduce mycorrhizal infection rate, insufficient light, etc., achieve the effect of reducing water loss, increasing mycorrhizal infection rate, and increasing photosynthesis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
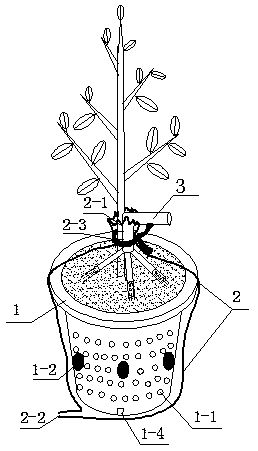
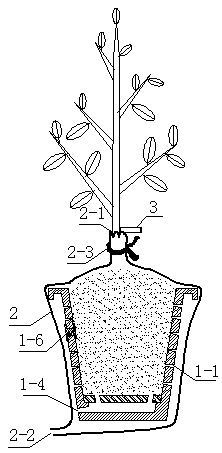
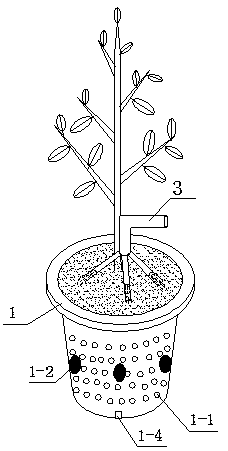
[0040] A device suitable for cultivating mycorrhizal seedlings under open-air conditions designed by the present invention is mainly composed of the following three parts: a container body 1 for cultivating sterile seedlings and mycorrhizal seedlings, and a shading, rainproof and dustproof for covering the container body Cover 2, and a water guiding device 3 for injecting water to the mycorrhizal shoots.
[0041] The designed container body 1 of the present invention sees Figure 4 Air vents 1-1 are set on the side wall of the container body 1 to achieve better air permeability of the root system of the seedling substrate plant and meet the respiration needs of mycorrhizal fungi and roots; the side wall of the container body 1 is also provided with an inoculation hole 1-2 It is convenient to punch holes and inoculate with the target bacteria. In order to avoid direct contact between the bottom of the seedling container and the nursery ground, and to prevent the native mycorrh...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Adopt the device in the embodiment 1 to inoculate and cultivate the Pinus massoniana symbiosis seedling of orange milk mushroom, method is as follows:
[0053] 1. Aseptic vaccine cultivation
[0054] Masson pine ( Pinus massoniana Lamb.) seeds are fully soaked in tap water and drained to remove inferior seeds, soaked in 0.1% potassium permanganate for 1 hour for surface disinfection, rinsed with sterile water three times, and then sowed in the container body with seedling substrate , cultivated at a substrate humidity of 60-70%, and watered with deep well water; the seedling substrate needs to be sterilized at 121°C and 0.1MPa for 1 hour. The breeding season for sterile seedlings is from May to June. Grow in a greenhouse or greenhouse. The seedling substrate formula is vermiculite: sandy loam = 1:1 (volume ratio), natural PH value.
[0055] 2. Bacteria preparation, the method is as follows
[0056] 1) Separation of strains and tissues: Orange milk mushrooms were ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com