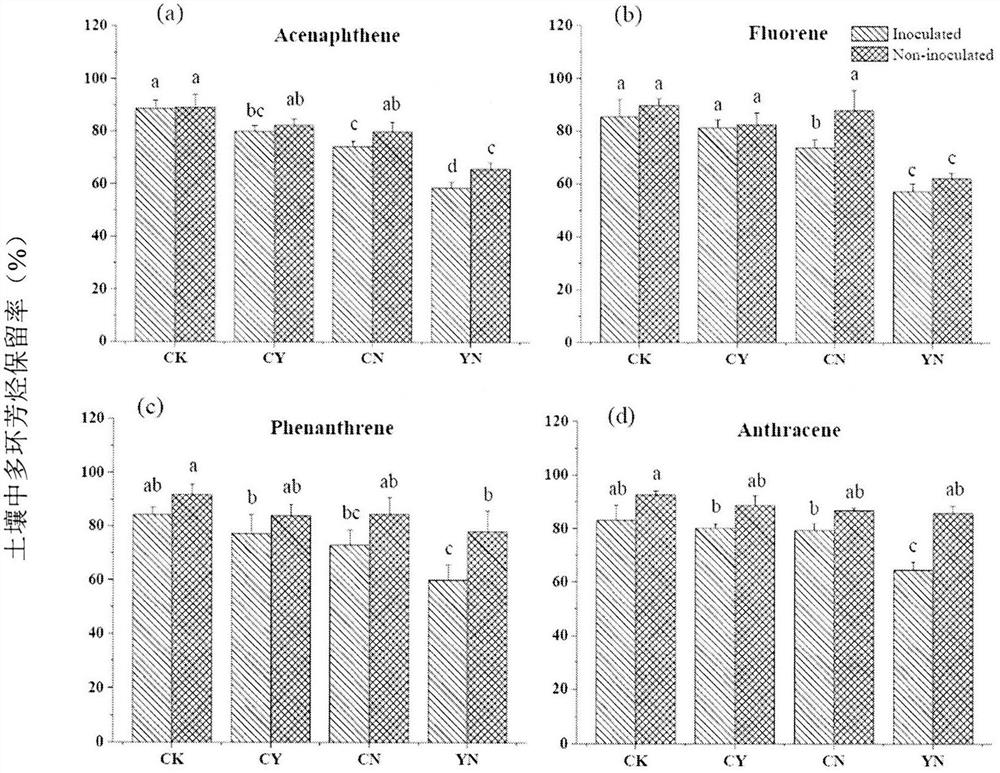
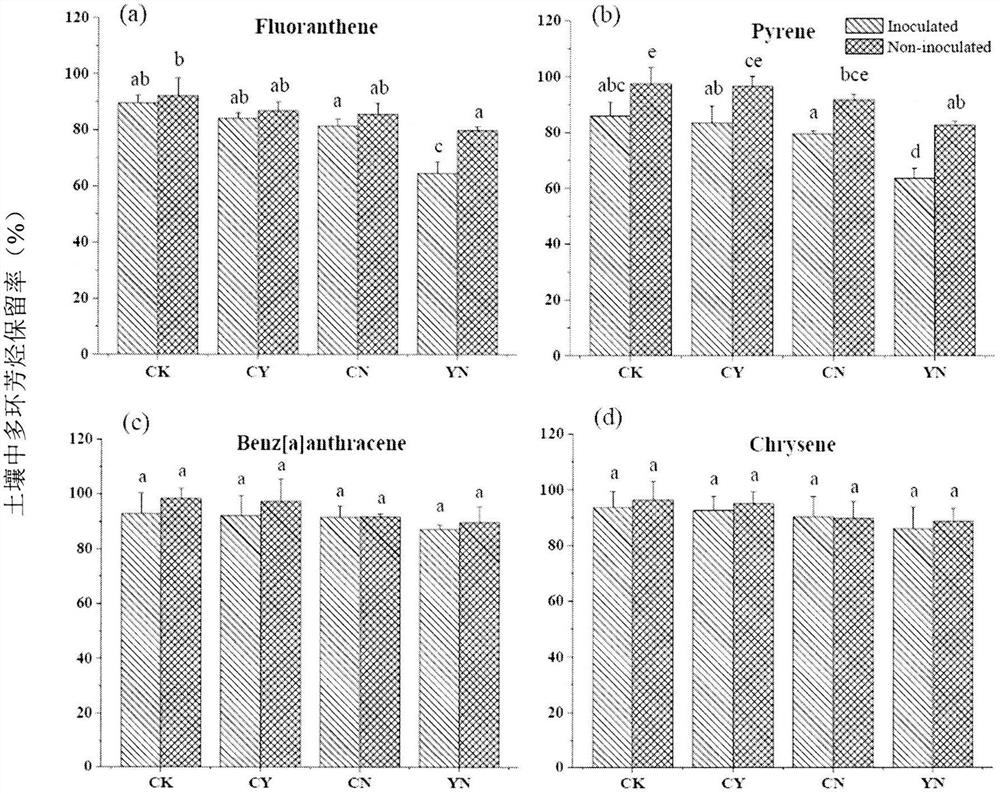
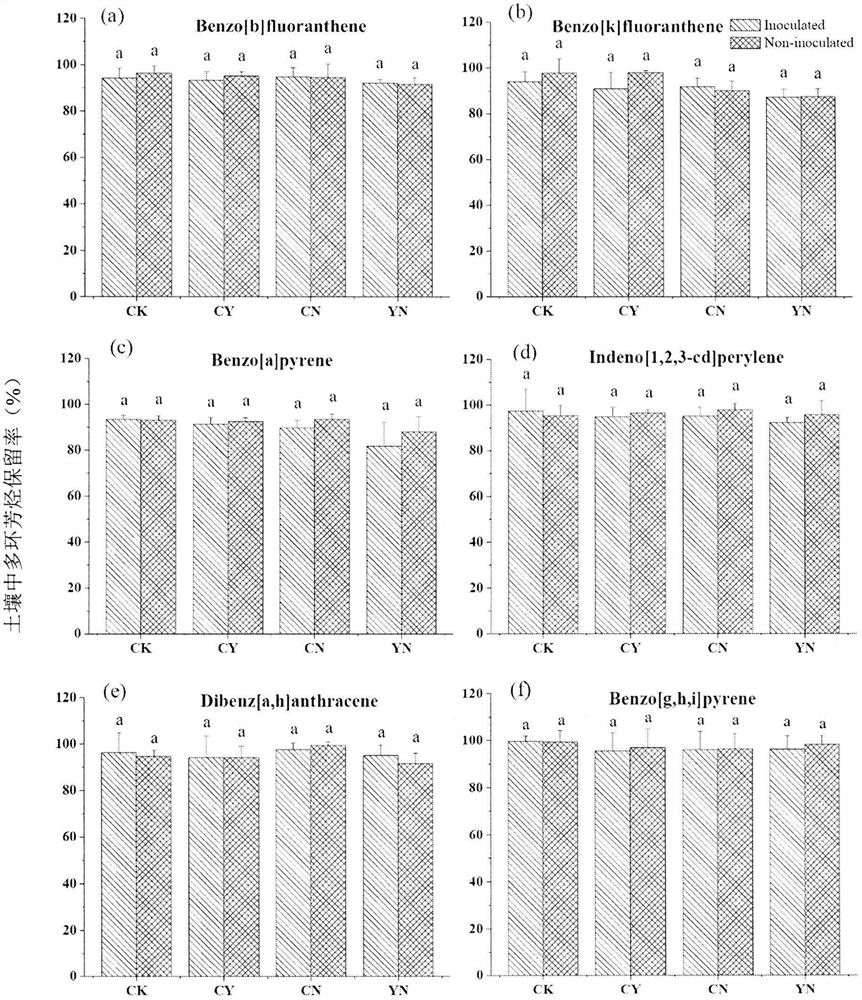
A method for the combined degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollutants in soil by chemical oxidation and anaerobic microorganisms
An anaerobic microorganism and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon technology, which is applied in the field of PAHs-contaminated soil remediation, can solve problems such as uneven transport of reactants, and achieve the effects of reducing remediation costs, good application prospects and high remediation efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0020] A specific technical implementation scheme that the present invention adopts comprises the following steps:
[0021] 1) Collection and preparation of experimental soil: Select a typical coking site, collect soil 3-4 meters underground, pass through a 2mm sieve, seal and store at 4°C for later use.
[0022] 2) Oxidation of soil samples with hydrogen peroxide: 100 g of soil and 150 mL (10%, w / w) of hydrogen peroxide were placed in a 1L beaker, and stirred with a magnetic stirrer to fully oxidize the soil to obtain an oxidized soil sample.
[0023] 3) Inoculation of microorganisms: 10% (w / w) of unoxidized soil was added to the oxidized soil sample and mixed evenly to obtain an inoculated soil sample.
[0024] 4) Soil anaerobic loading: In a nitrogen-filled glove box (anaerobic environment), transfer the oxidized soil and the inoculated soil to a 50 mL container equipped with a Teflon-lined butyl rubber stopper and an aluminum sealing cap. In the serum bottle, press the ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com