Motor imagery electrocorticogram (EEG) signal classification method based on independent component analysis
A technology of independent component analysis and motor imagery, applied in the field of brain-computer interface, it can solve the problems of difficult data model matching, unable to provide nerve source, short duration, etc., and achieve high classification recognition rate and high spatial model matching effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
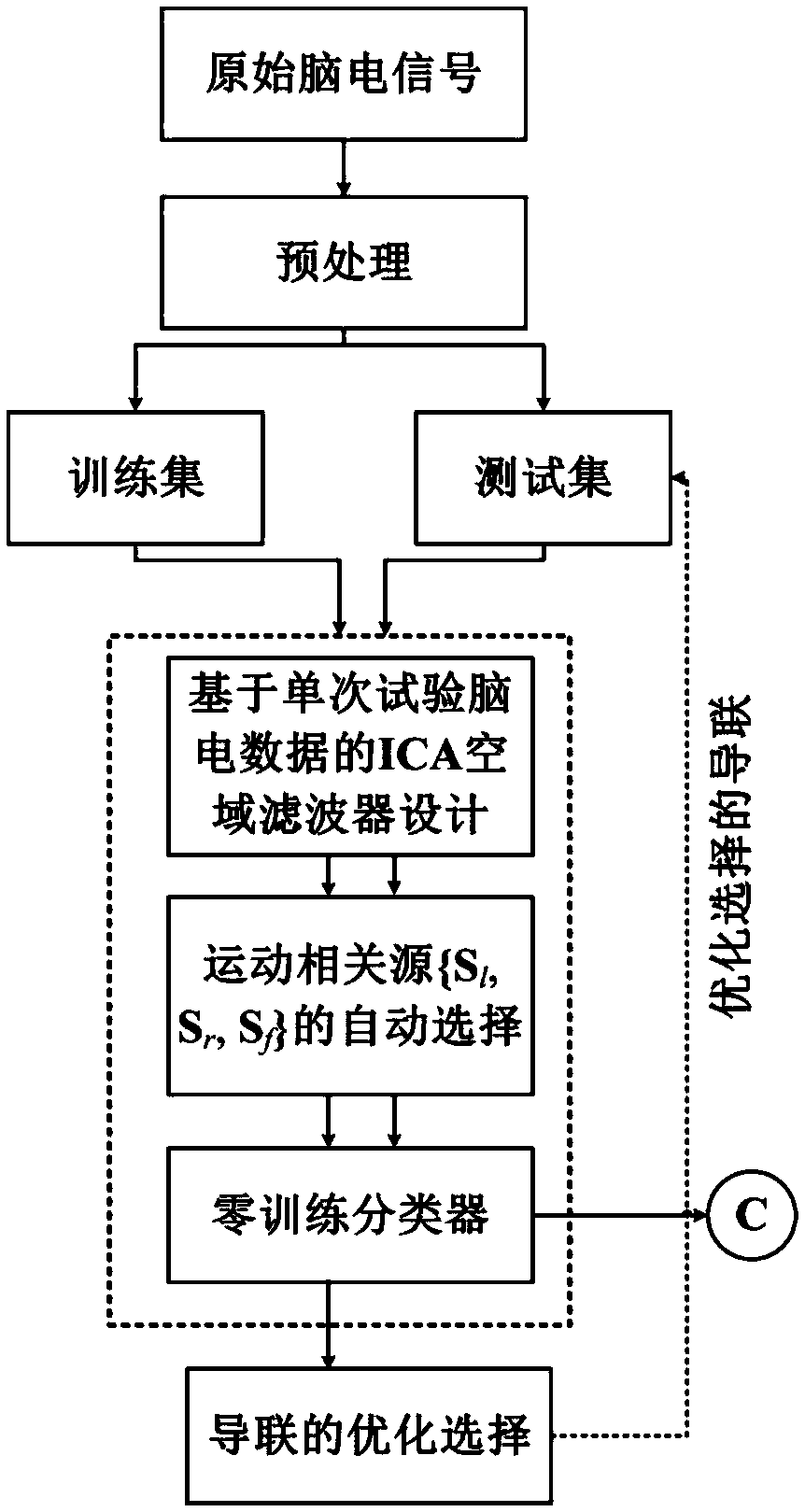
[0057] The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, so that the advantages and features of the present invention can be more easily understood by those skilled in the art, so as to define the protection scope of the present invention more clearly.
[0058] see figure 1 , the embodiment of the present invention includes:
[0059] A motor imagery EEG signal classification method based on independent component analysis, comprising the following steps:
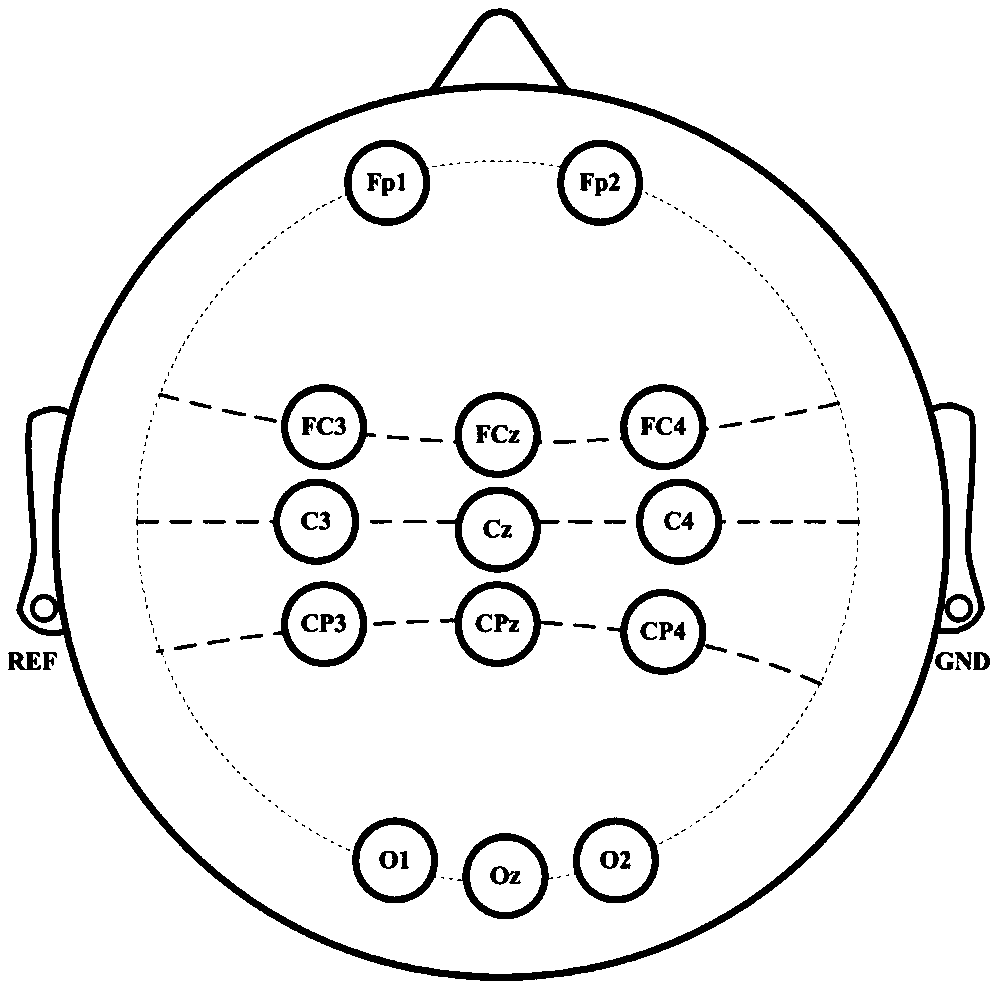
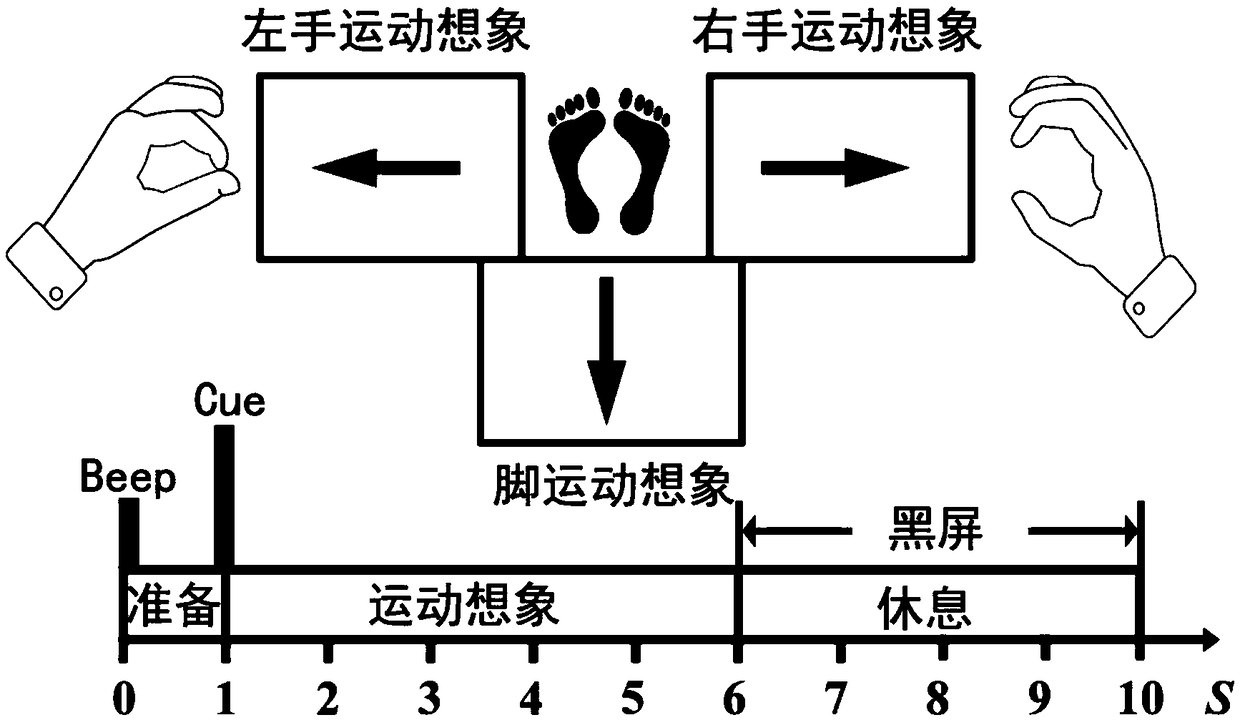
[0060] S1: Collection of experimental data: The subject wears an electrode cap, and the electrode distribution is as follows: figure 2 As shown, according to the standard 10-20 system, using 14 scalp electrodes {Fp1, Fp2, FC3, FCz, FC4, C3, Cz, C4, CP3, CPz, CP4, O1, Oz, O2} to record the left hand, right hand and foot Three types of motor imagery data X=[x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x N ] T (N=1,2...,14). Subjects sat in front of a computer, according...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com