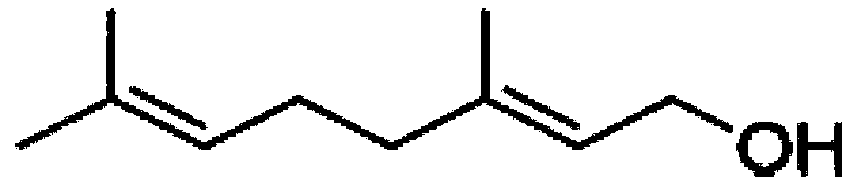
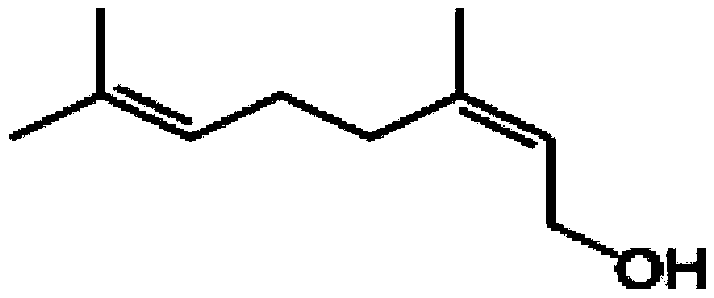
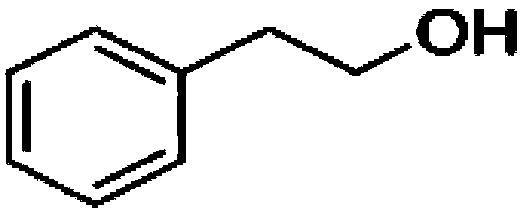
Pollination bee attractant as well as use method and application thereof
An attractant and dimethyl technology, applied in the field of bee pollination, can solve the problem that no one knows the characteristics of flower volatiles, etc., and achieve the effects of improving the rate of high-quality fruit, improving activity, and improving quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The controlled-release device is a low-density polyethylene zipper pouch with a wall thickness of 0.5mm and a size of 2.5*1cm. Each sachet contains 500mg of pollinator bee attractant and these sachets are closed with a zipper which is further heat sealed. Weighed weekly for 42 days, the release rates of individual components and combinations were measured at room temperature (18°C to 23°C).
[0038] Table 1 Release Rate mg / sachet / week
[0039]
[0040] The results showed that the system could simultaneously release geraniol and 2-phenylethanol. Those skilled in the art will appreciate that there are other methods of achieving controlled release of these compounds and mixtures, such as wax matrices, squeeze-sealed polyethylene tubing, and bottles made of other suitable polymers such as plasticized polyvinyl chloride, which Can also be used as a controlled release system.
Embodiment 2
[0042] Aiming at different attractant combinations, compare their ability to attract wall bees on fruit trees (apple).
[0043] With the attractant described in the embodiment 1 of 500mg, every tree hangs a pouch, and the pouch is with embodiment 1, and the pouch of every kind of mixture hangs 10 trees. Trees chosen for experiments should be equidistant from the wasp nests placed by fruit growers. The apple orchards used for the experiment had negligible numbers of bees as well as artificially released wall bees.
[0044] The observer selected 5 trees among the trees treated with five volatile compounds (50 minutes for each treatment), marked 10 clusters of flowers on the north and south sides respectively, and recorded the number of flower visits by the wall bees within 1 minute. No attractants were hung on the trees of the control group.
[0045] The results are shown in Table 2.
[0046] Table 2
[0047]
[0048] It can be seen from Table 2 that all the experimental ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] To compare the fruit set rate of apple trees in orchards releasing the wall bee for different attractant combinations. The apple orchards used for the experiment had negligible numbers of bees as well as artificially released wall bees. The observer selects 10 clusters of flowers on the branches of the north side and the south side of 5 trees in the trees treated by five kinds of volatiles described in embodiment 2, and counts the high-quality fruit quantity (the diameter is greater than 20mm and counts as high-quality fruit).
[0051] The results are shown in Table 3.
[0052] Table 3 The number of high-quality fruit per 10 flower clusters of apples pollinated by wall bees
[0053]
[0054]
[0055] The percentage of good fruit was significantly higher in the treated trees, especially in the trees treated with the 50:50 mixture.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com