Method for catalytically synthesizing 4-chlorotetrahydrofuran compound by using titanocene dichloride as lewis acid and chloride ion source
A technology of chlorinated tetrahydropyran and dichlorotitanocene, which is applied in the field of synthesis of chlorinated tetrahydropyran compounds, can solve the problems of harsh reaction conditions, high toxicity, strong corrosion, etc., and achieve short reaction time , low toxicity, and mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
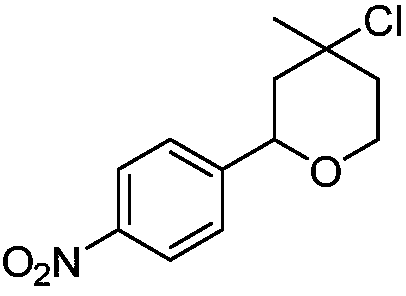
[0012] Synthesis of 4-chloro-4-methyl-2-(4-nitrophenyl)-tetrahydropyran with the following structural formula
[0013]
[0014] 0.1511g (1.0mmol) p-nitrobenzaldehyde, 151μL (1.5mmol) 3-methyl-3-buten-1-alcohol, 0.248g (1.2mmol) titanocene dichloride, 0.2281g (1.0mmol) Add 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid and 3 mL of dry dichloromethane into a Shrek tube, stir and react at room temperature for 5 hours, stop the reaction, and separate by column chromatography to obtain solid 4-chloro-4-methyl-2 -(4-nitrophenyl)-tetrahydropyran, its yield is 88%, and the structural characterization data is: 1 H NMR (600MHz, CDCl 3 )δ8.17(d, J=8.6Hz, 2H), 7.50(d, J=8.6Hz, 2H), 4.87(d, J=10.0Hz, 1H), 4.07(s, 2H), 2.14(d, J=14.2Hz, 1H), 1.90(dd, J=9.3, 4.4Hz, 2H), 1.67(s, 3H), 1.64(dd, J=14.1, 11.2Hz, 1H); 13 C NMR (151MHz, CDCl 3 )δ147.16(s), 64.83-64.70(m), 40.15(s), 33.94(s).
Embodiment 2
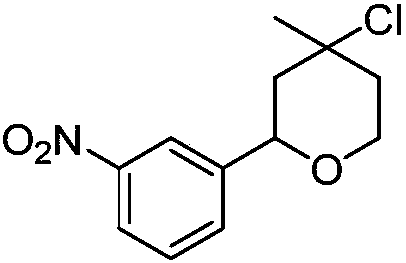
[0016] Synthesis of 2-(3-nitrophenyl)-4-chloro-4-methyl-tetrahydropyran with the following structural formula
[0017]
[0018] In this example, the p-nitrobenzaldehyde in Example 1 is replaced with equimolar 3-nitrobenzaldehyde, and other steps are the same as in Example 1 to obtain solid 2-(3-nitrophenyl)-4-chloro -4-Methyltetrahydropyran, its yield is 83%, and the structural characterization data is: 1 H NMR (600MHz, CDCl 3 )δ8.22(s,1H),8.09(dd,J=8.1,1.4Hz,1H),7.65(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),7.49(t,J=7.9Hz,1H),4.86( dd,J=11.1,1.6Hz,1H),4.05(ddd,J=13.5,8.6,4.1Hz,2H),2.16(d,J=14.1Hz,1H),1.90(dd,J=8.2,4.0Hz ,2H),1.68(d,J=3.3Hz,3H); 13 C NMR (151MHz, CDCl 3 )δ144.27(s), 120.83(s), 68.69(s), 63.99(s), 48.23(s).
Embodiment 3
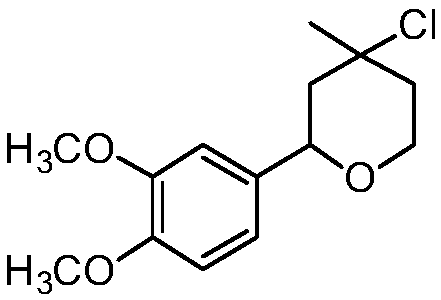
[0020] Synthesis of 4-chloro-4-methyl-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-tetrahydropyran with the following structural formula
[0021]
[0022] In this example, the p-nitrobenzaldehyde in Example 1 was replaced with equimolar 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde, and the other steps were the same as in Example 1 to obtain solid 4-chloro-4-methyl-2 -(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-tetrahydropyran, the yield is 78%, and the structural characterization data are: 1 H NMR (600MHz, CDCl 3 )δ6.91-6.82(m,3H),4.72(dd,J=11.0,1.7Hz,1H),4.07-4.02(m,2H),3.89(s,3H),3.86(d,J=2.9Hz ,3H),2.10(d,J=14.2Hz,1H),1.90(dd,J=7.5,4.3Hz,2H),1.79-1.74(m,1H),1.68(s,3H); 13 C NMR (151MHz, CDCl 3 )δ147.92(s), 108.31(s), 63.54(s), 54.86(s), 38.96(s), 33.05(s).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com