Micro-displayer pixel circuit
A micro-display and pixel circuit technology, applied in the field of pixel circuits, can solve problems such as complex peripheral circuits, slow charging speed, and difficult control of the working range of sub-threshold regions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0057] This embodiment illustrates different schemes of the pixel circuit of the microdisplay according to the present invention.
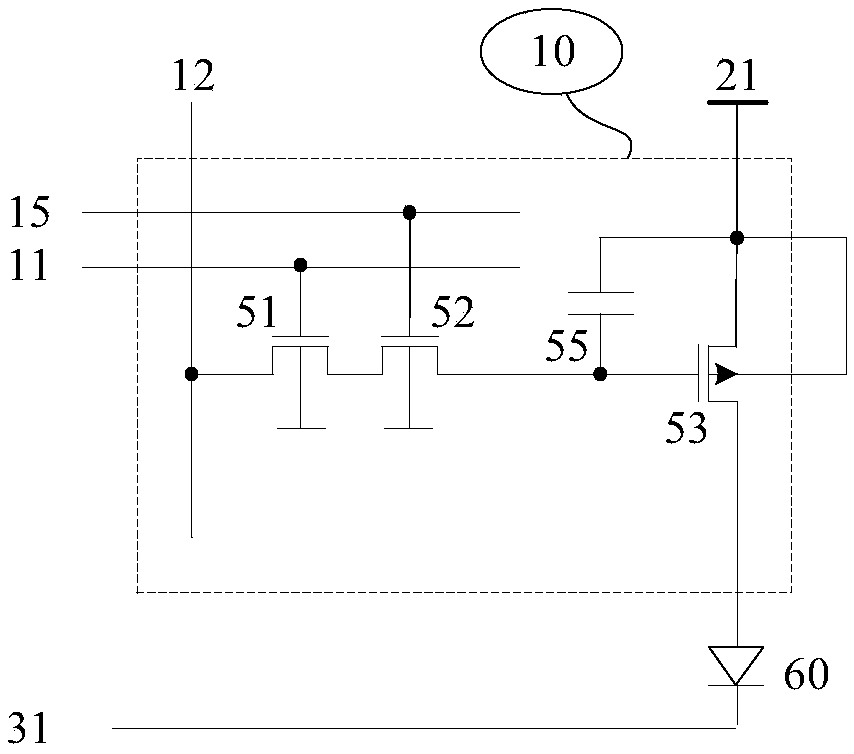
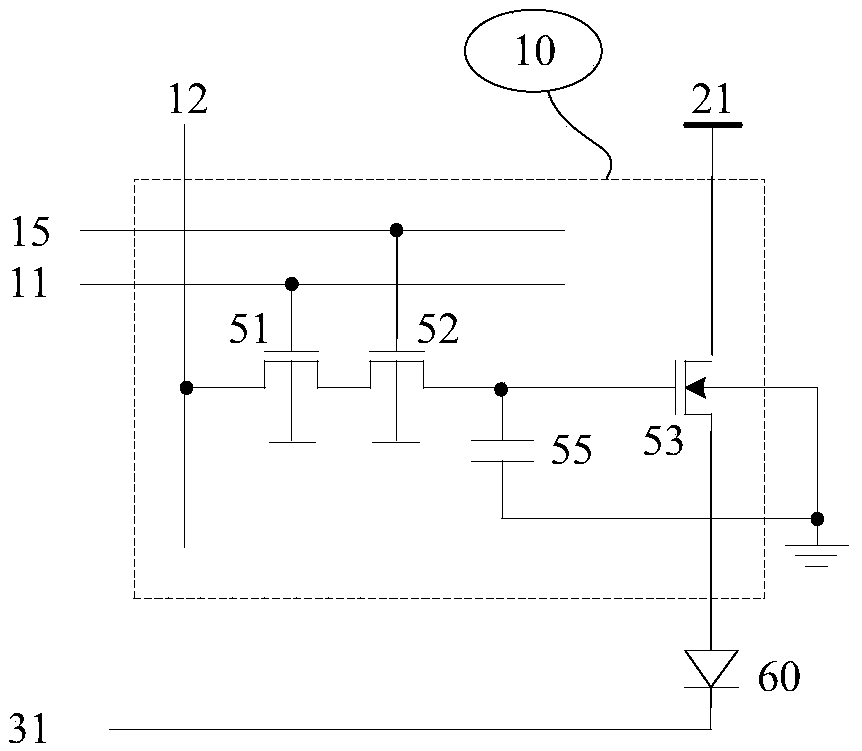
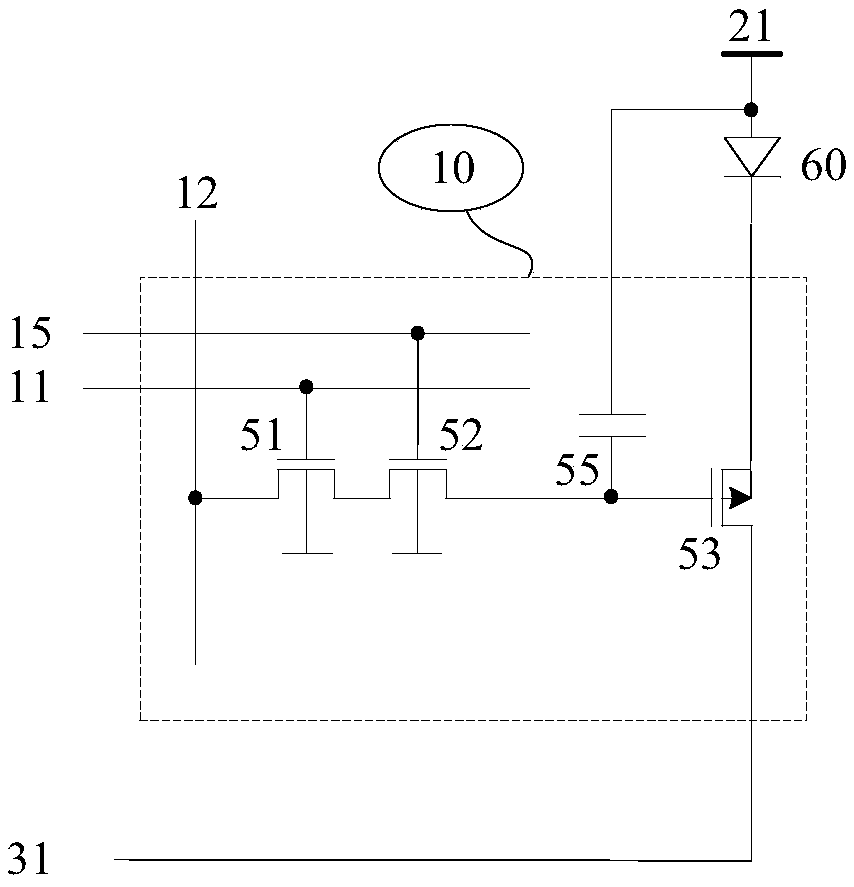
[0058]In the first solution, as shown in Figure 1(a), the pixel circuit 10 includes a series transistor 51, a series transistor 52, a first drive transistor 53, and a capacitor 55; the gate of the series transistor 51 is connected to the first gate Line 11, the gate of the series transistor 52 is connected to the second gate line 15; the source (or drain) of the series transistor 51 is connected to the data line 12, and the drain (or source) of the series transistor 51 is connected to the series transistor 52 source (or drain), the drain (or source) of the series transistor 52 is connected to the gate of the first driving transistor 53; the first driving transistor 53 is a P-type transistor, and the source is connected to the pixel power supply 21. The drain is connected to one end of the light emitting device 60 (anode in the figure), and the sub...
no. 2 example
[0070] In the first solution, as shown in Figure 3(a), the pixel circuit 10 includes a series transistor 51, a series transistor 52, a series transistor 56, a first drive transistor 53, a first control transistor 54, and a capacitor 55; the series transistor The gate of the series transistor 51 is connected to the first gate line 11, the gate of the series transistor 52 is connected to the second gate line 15, and the gate of the series transistor 56 is connected to the third gate line 16; the source of the series transistor 51 ( or drain) is connected to the data line 12, the drain (or source) of the series transistor 51 is connected to the source (or drain) of the series transistor 52, and the drain (or source) of the series transistor 52 is connected to the series transistor 56 source (or drain), the drain (or source) of the series transistor 56 is connected to the gate of the first driving transistor 53; the first driving transistor 53 is a P-type transistor, and its source...
no. 3 example
[0086] This embodiment illustrates different schemes of the pixel circuit of the microdisplay according to the present invention.
[0087] In the first solution, as shown in Figure 4(a), the pixel circuit 10 includes a first transistor 57, a second transistor 59, a first drive transistor 53, and a capacitor 55; the first transistor 57 is a P-type transistor, and its The gate is connected to the gate line 17, and the substrate is connected to the pixel power supply 21; the second transistor 59 is an N-type transistor, and its gate is connected to the gate line 19, and the substrate is connected to the ground; the source of the first transistor 57 pole (or drain) is connected to the drain (or source) of the second transistor 59 and the data line 12, and the drain (or source) of the first transistor 57 is connected to the source (or drain) of the second transistor 59 ) and the gate of the first drive transistor 53; the first drive transistor 53 is a P-type transistor, the source ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com