Dinuclear pyrene (α-diimine) nickel olefin catalyst and its preparation method and application
An olefin catalyst, diimine technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, nickel organic compounds, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of low molecular weight and branching degree of polyethylene, and achieve high molecular weight, high polymerization activity and high branching. degree of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0029] The preparation method of dinuclear pyrene (alpha-diimine) nickel olefin catalyst comprises the steps:
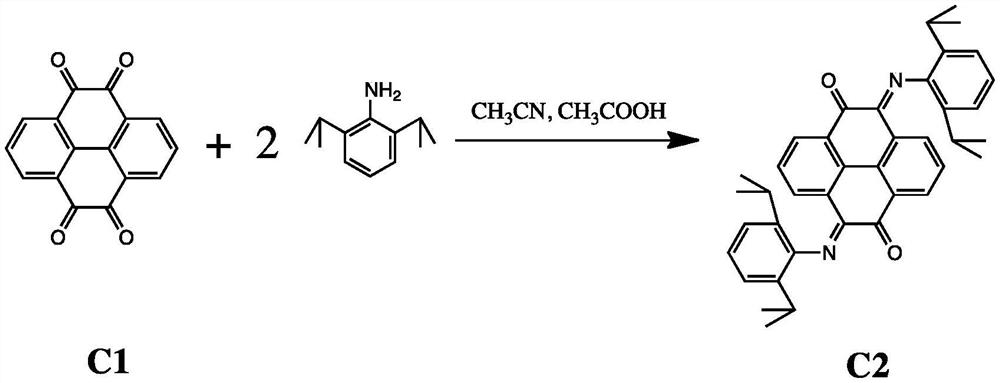
[0030] (1) Tetraketone compound C1 and 2 equivalents of 2,6-diisopropylaniline undergo ketoamine condensation reaction to obtain compound C2:
[0031]
[0032] (2) Compound C2 and 2 equivalents of 2,6-dimethylaniline undergo ketoamine condensation reaction to obtain ligand C3:
[0033]
[0034] (3) Compound C2 and 2 equivalents of 2,6-diethylaniline undergo ketoamine condensation reaction to obtain ligand C4:
[0035]
[0036] (4) Compound C2 undergoes ketoamine condensation reaction with 1 equivalent of 2,6-diethylaniline, and then performs ketoamine condensation reaction with 1 equivalent of 2,6-dimethylaniline to obtain ligand C5:
[0037]
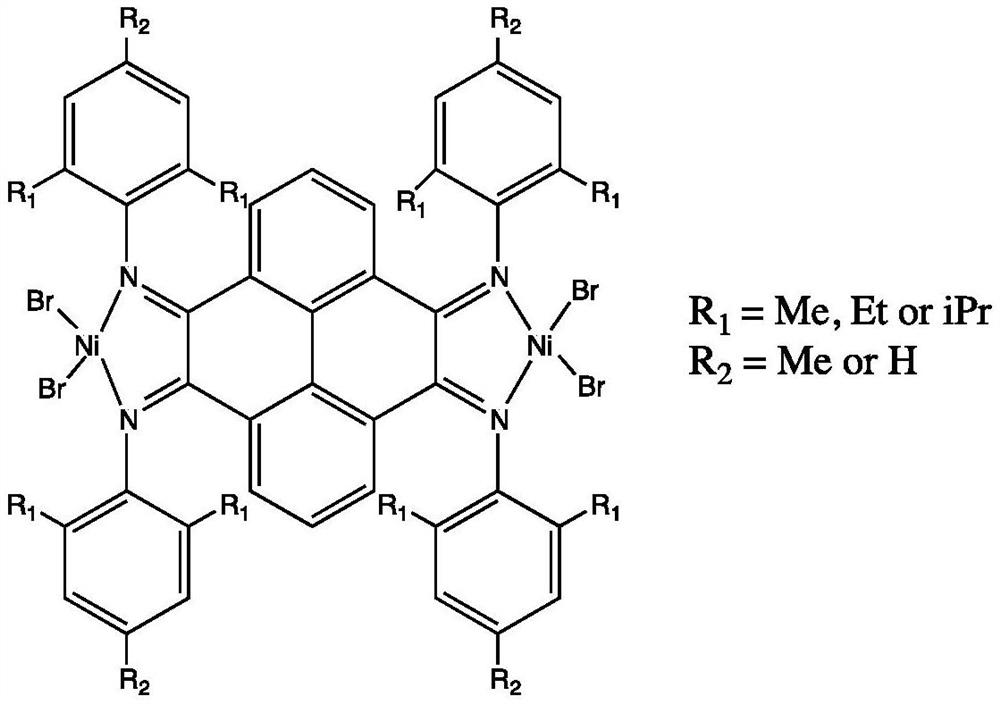
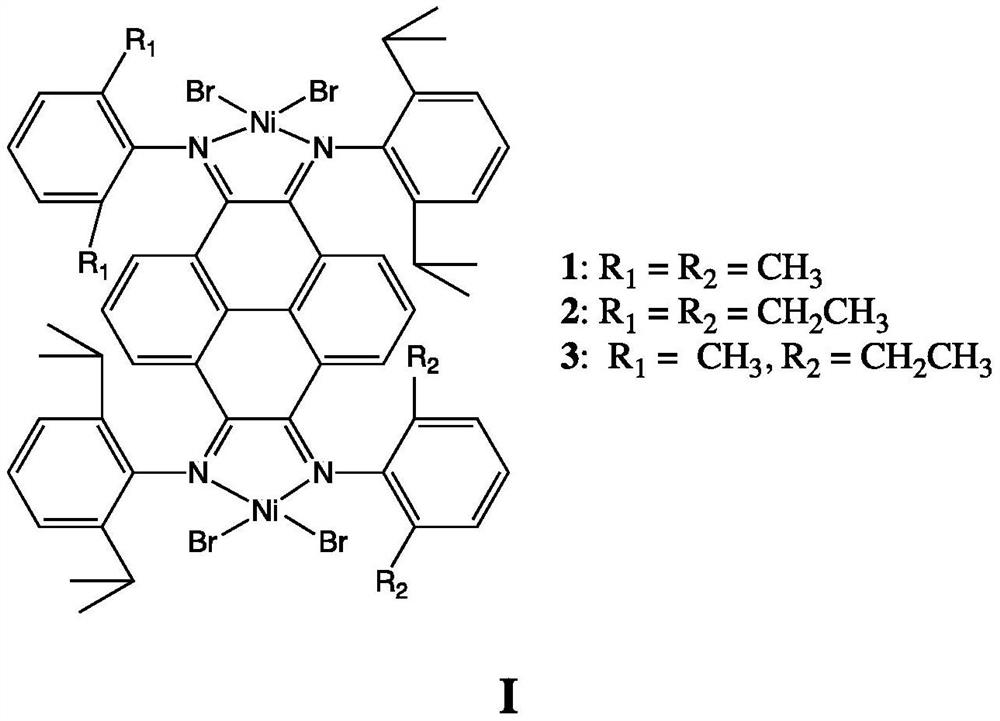
[0038] (5) Under anhydrous and oxygen-free conditions, ligands C3, C4, and C5 are mixed with 2 equivalents of (DME)NiBr 2 The complexation will obtain catalysts 1, 2, and 3 in the following formula respectively. ...
Embodiment 1
[0055] Synthesis of Ligand C3
[0056] Under nitrogen atmosphere and 85°C, compound C2 (0.58g, 1mmol) was added into a three-necked flask containing 50mL of acetonitrile, stirred mechanically, and after reflux at 85°C for half an hour, 10mL of acetic acid was added, and the reflux was continued for two and a half hours . 0.25 g (2 mmol) of 2,6-dimethylaniline were added. Stop the reaction after 24 hours, stand still, and cool naturally. The precipitate was washed with 5×50 mL of n-heptane, and then dried under vacuum at 70°C for 48 hours. 0.652 g of the product was obtained with a yield of 83%.
[0057] 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ,δin ppm): 8.16(d,4H,Py-H),7.72(d,2H,Py-H),7.43-7.51(d,4H,Ar-H),7.04-7.12(d,8H,Ar- H),2.87(sept,4H,CH(CH 3 ) 2 ),2.34(s,12H,CH 3 ), 0.86~1.20(dd,24H,CH(CH 3 ) 2 ).
[0058] Elem.Anal.Calcd.For C 56 h 58 N 4 : C, 85.50%; H, 7.38%; N, 7.12%. Found: C, 85.56%; H, 7.32%; N, 7.19%.
[0059] ESI-MS: m / z 787.50 ([M+H] + )
Embodiment 2
[0061] Synthesis of Ligand C4
[0062] Under nitrogen atmosphere and 85°C, compound C2 (0.58g, 1mmol) was added into a three-necked flask containing 50mL of acetonitrile, stirred mechanically, and after reflux at 85°C for half an hour, 10mL of acetic acid was added, and the reflux was continued for two and a half hours . 0.3 g (2 mmol) 2,6-diethylaniline was added. Stop the reaction after 24 hours, stand still, and cool naturally. The precipitate was washed with 5×50 mL of n-heptane, and then dried under vacuum at 70°C for 48 hours. 0.682 g of the product was obtained with a yield of 81%.
[0063] 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ,δin ppm): 8.16(d,4H,Py-H),7.72(d,2H,Py-H),7.51-7.57(d,4H,Ar-H),7.11-7.12(d,8H,Ar- H),2.87(sept,4H,CH(CH 3 ) 2 ),2.60(q,8H,CH 2 ),1.25(T,12H,CH 3 ),0.86~1.20(dd,24H,CH(CH 3 ) 2 ).
[0064] Elem.Anal.Calcd.For C 56 h 58 N 4 : C, 85.51%; H, 7.84%; N, 6.65%. Found: C, 85.58%; H, 7.89%; N, 6.61%.
[0065] ESI-MS: m / z 843.0 ([M+H] + )
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com