A nucleic acid aptamer targeting metastatic human breast cancer cells and its application
A technology of human breast cancer cells and metastatic breast cancer, applied in the field of biomedicine, to achieve the effect of obvious metastasis specificity, high specificity and good plasma stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
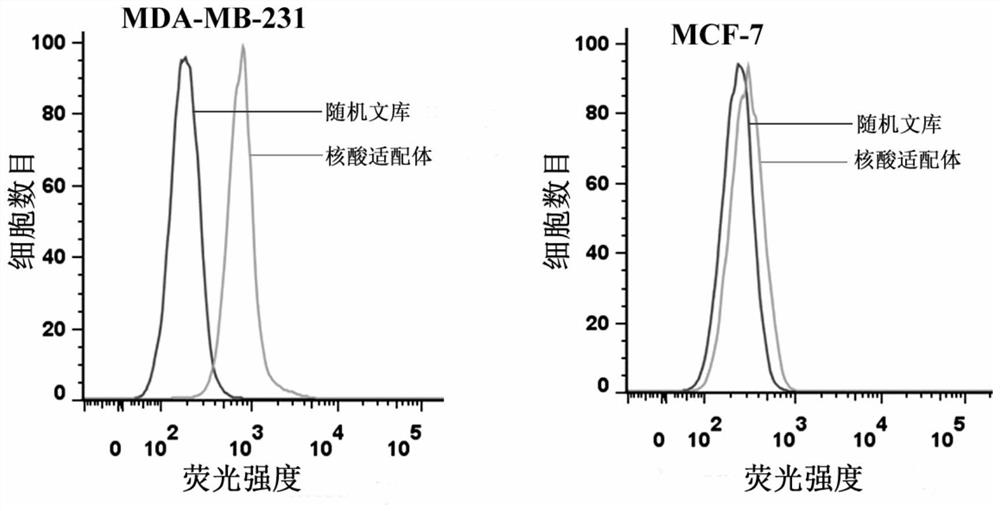
[0022] Example 1 The specific binding of the nucleic acid aptamer to the target cell MDA-MB-231 was detected by flow cytometry.
[0023] Human breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 in the logarithmic growth phase were respectively digested with enzyme-free digestion solution and blown into a single cell suspension, centrifuged at 1000rpm for 5min to remove the supernatant, and pre-cooled at 4°C Wash cells twice with Wash Buffer. Then add 200 μl of binding buffer containing 250 nM nucleic acid aptamer, incubate gently on a shaker at 4 °C for 30 min, centrifuge at 1000 rpm for 5 min, remove the supernatant, and wash the cells twice with 4 °C pre-cooled washing buffer. Finally, 300 µl PBS was added for flow cytometry detection, and the random library sequence was used as a control.
[0024] The flow cytometry detection results of the nucleic acid aptamer and the target cell MDA-MB-231 and the counter-screened cell MCF-7 are as follows: figure 1 As shown, the nucleic acid apt...
Embodiment 2
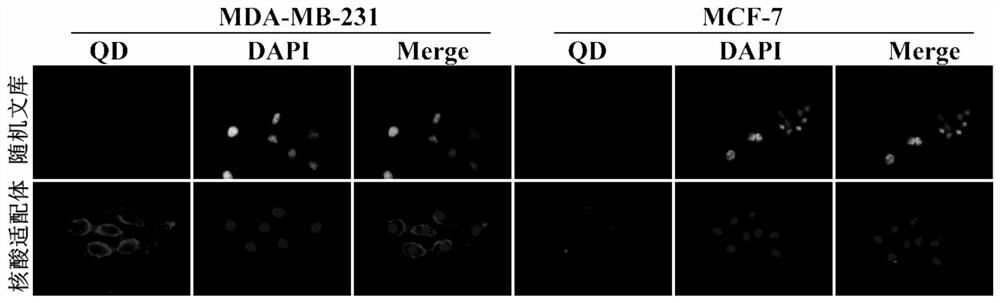
[0025] Example 2 Fluorescence microscopy was used to analyze the specific binding of the nucleic acid aptamer to the target cell MDA-MB-231.
[0026] Human breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 were cultured in confocal culture dishes respectively. After culturing for 24 hours, aspirate all the liquid in the culture dish, wash twice with 4°C pre-cooled washing buffer, and then combine the binding buffer containing 250nM biotin-labeled nucleic acid aptamer with the above two kinds of cells at 4°C Incubate with gentle shaking for 30min. After incubation, aspirate all the liquid in the culture dish, wash twice with 4°C pre-cooled washing buffer, then add quantum dot-labeled streptavidin QD-SA, and incubate at room temperature for 15 min. After incubation, aspirate all the liquid in the culture dish, wash twice with 4°C pre-cooled washing buffer, and finally add 300 µl PBS for detection, random library sequence as a control, the results are as follows figure 2 shown.
[002...
Embodiment 3
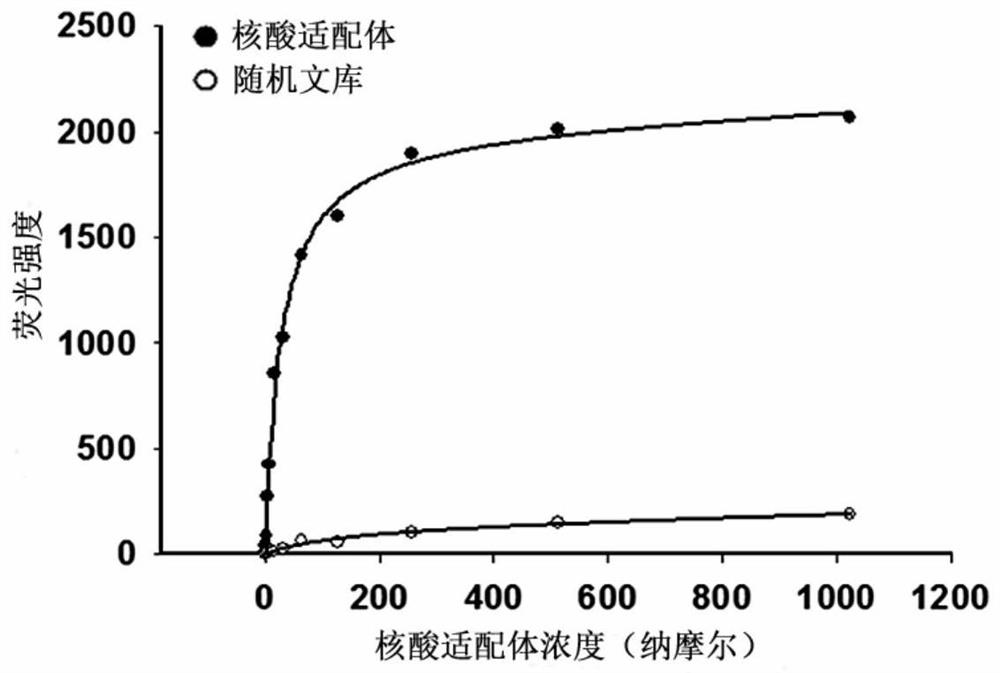
[0028] Example 3 The dissociation constant of the nucleic acid aptamer to the target cell MDA-MB-231 was determined by flow cytometry.
[0029] The nucleic acid aptamers of different concentrations were synthesized and prepared, incubated with the same amount of target cells respectively, and flow cytometry detection was performed according to the operation of Example 1, and the fluorescence intensity of the target cells under different nucleic acid aptamer concentrations was measured. Take the concentration of the nucleic acid aptamer as the abscissa, and the corresponding fluorescence intensity value as the ordinate, and fit the curve according to the formula Y=BmaxX / (Kd+X) to obtain the dissociation curve of the nucleic acid aptamer, as image 3 shown. The dissociation constant Kd of the nucleic acid aptamer obtained from the dissociation curve was 45.6 ± 1.2 nM.
[0030] The results show that: the nucleic acid aptamer has high affinity binding property to the target cell ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com