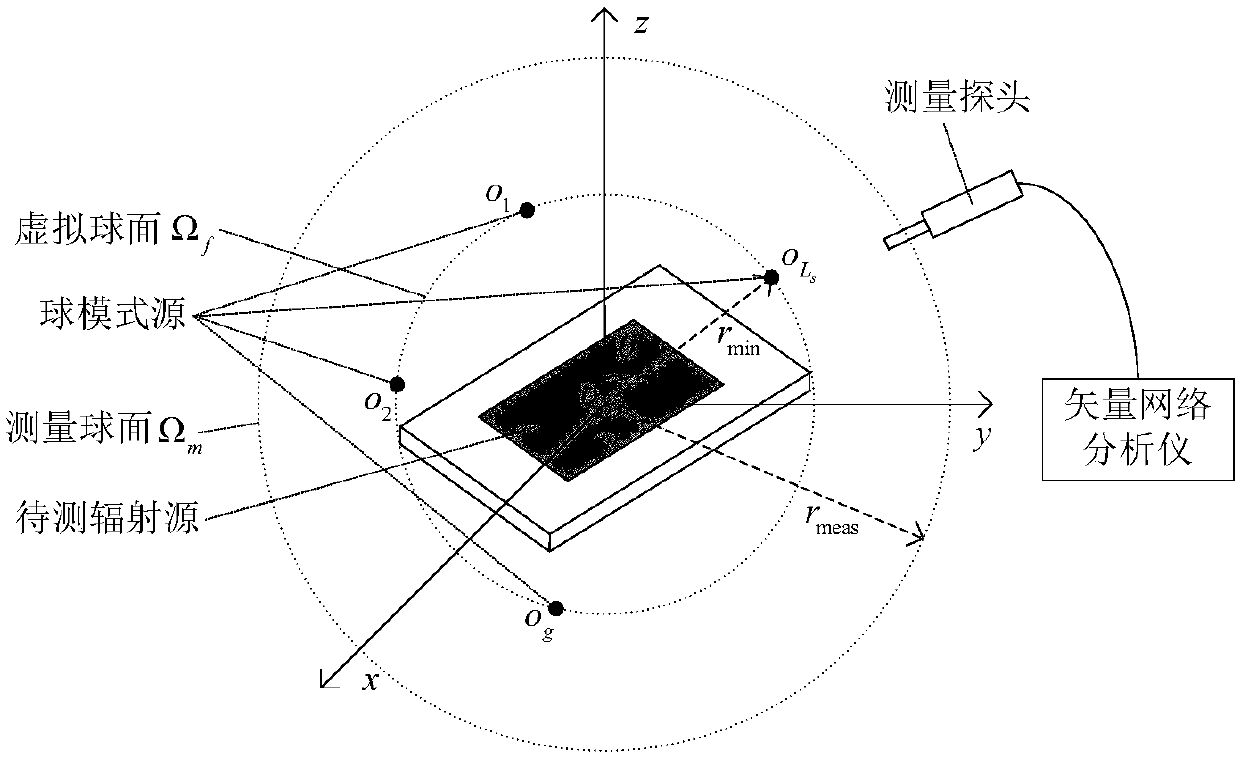
An equivalent radiation modeling method based on spherical near-field measurement and spherical mode source
A mode and near-field technology, applied in the field of effective radiation modeling, can solve problems such as inability to improve accuracy in a short period of time, low model accuracy, and lack of flexibility, achieving short modeling time, high model accuracy, and reduced calculations the effect of time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
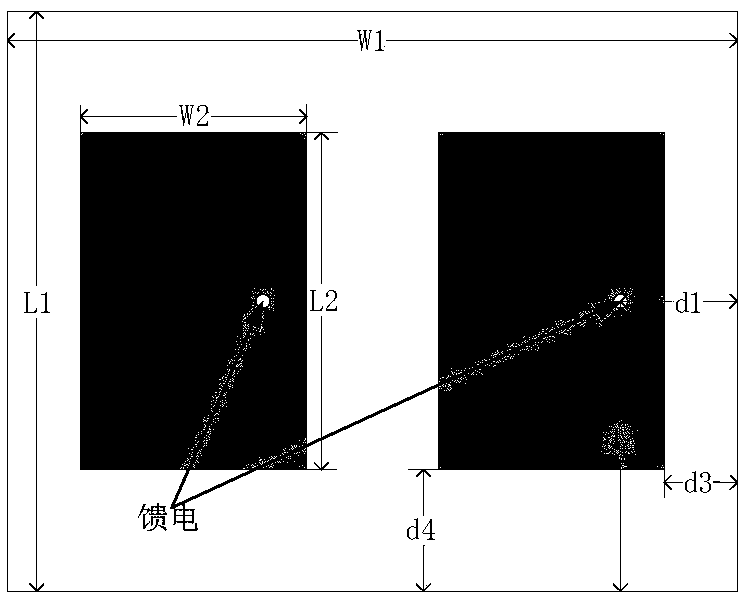
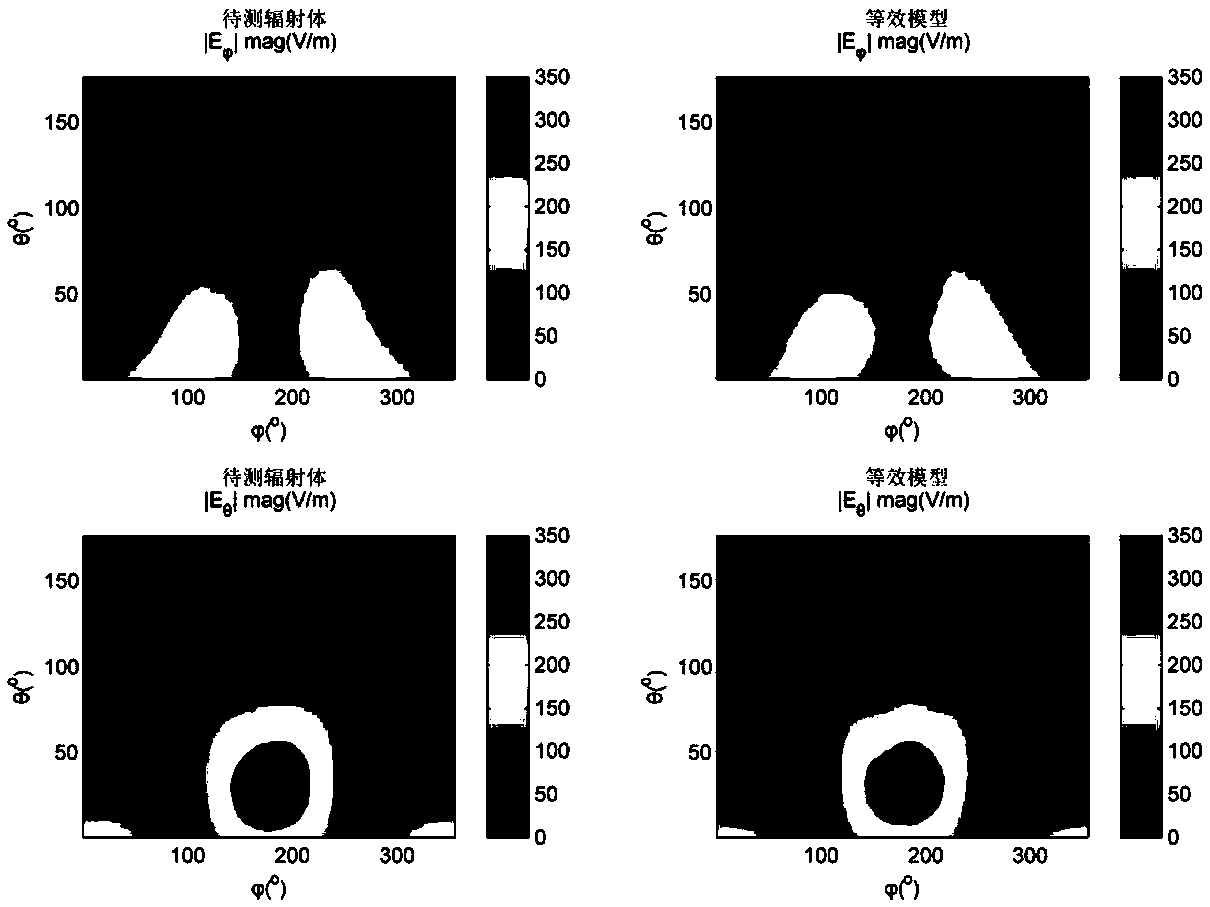
[0091] This embodiment takes the binary patch antenna array working at 3GHz as an example to model; the relative dielectric constant of the antenna dielectric substrate is 2.2, and the thickness of the dielectric substrate is 2.87mm; the antenna size is L1=80mm, L2=46.648mm , W1=100mm, W2=31.1807mm, d1=16.1mm, d2=40mm, d3=9.4096mm, d4=16.676mm; Feed phase difference is ninety degrees; Equivalent model is established by the present invention by 12 spherical patterns source composition, which can be equivalently transformed into 72 ideal dipoles, such as image 3 Shown is the radiation field comparison diagram of the antenna array and its equivalent model, the root mean square error is 6.01%, and the computer modeling time (excluding spherical near-field test time) is 303 seconds; Figure 4 Shown is the radiation field comparison diagram of the original antenna, the traditional model, and the model of the present invention; the root mean square error of the traditional model is ...
Embodiment 2
[0093] In this embodiment, a half-wave antenna placed next to the metal block is used as an example to model, and its operating frequency is 5GHz; this embodiment aims at simulating the antenna radiation characteristics affected by the environment; the equivalent model is established by the present invention by 12 The ball mode source is composed of 72 ideal dipoles, such as Image 6 Shown is the comparison diagram of the radiator and its equivalent model radiation field, the root mean square error is 5.04%, and the computer modeling time (excluding spherical near-field test time) is 263 seconds; Figure 4 Shown is the comparison diagram of the radiation field of the original antenna, the traditional model, and the model of the present invention; the root mean square error of the traditional model is 13.52%; it can be seen that the accuracy of the model of the present invention is greatly improved, and the modeling time is short.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com