Embryonic cell-based therapeutic candidate screening systems, models for huntington's disease and uses thereof
A Huntington's disease, human embryonic stem cell technology, applied in embryonic cells, drug screening, animal cells, etc., can solve problems such as heterogeneity of human systems, difficulty in explaining comparative studies, and different differentiation potentials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0346] Generation of human embryonic stem cell lines as screening and research tools
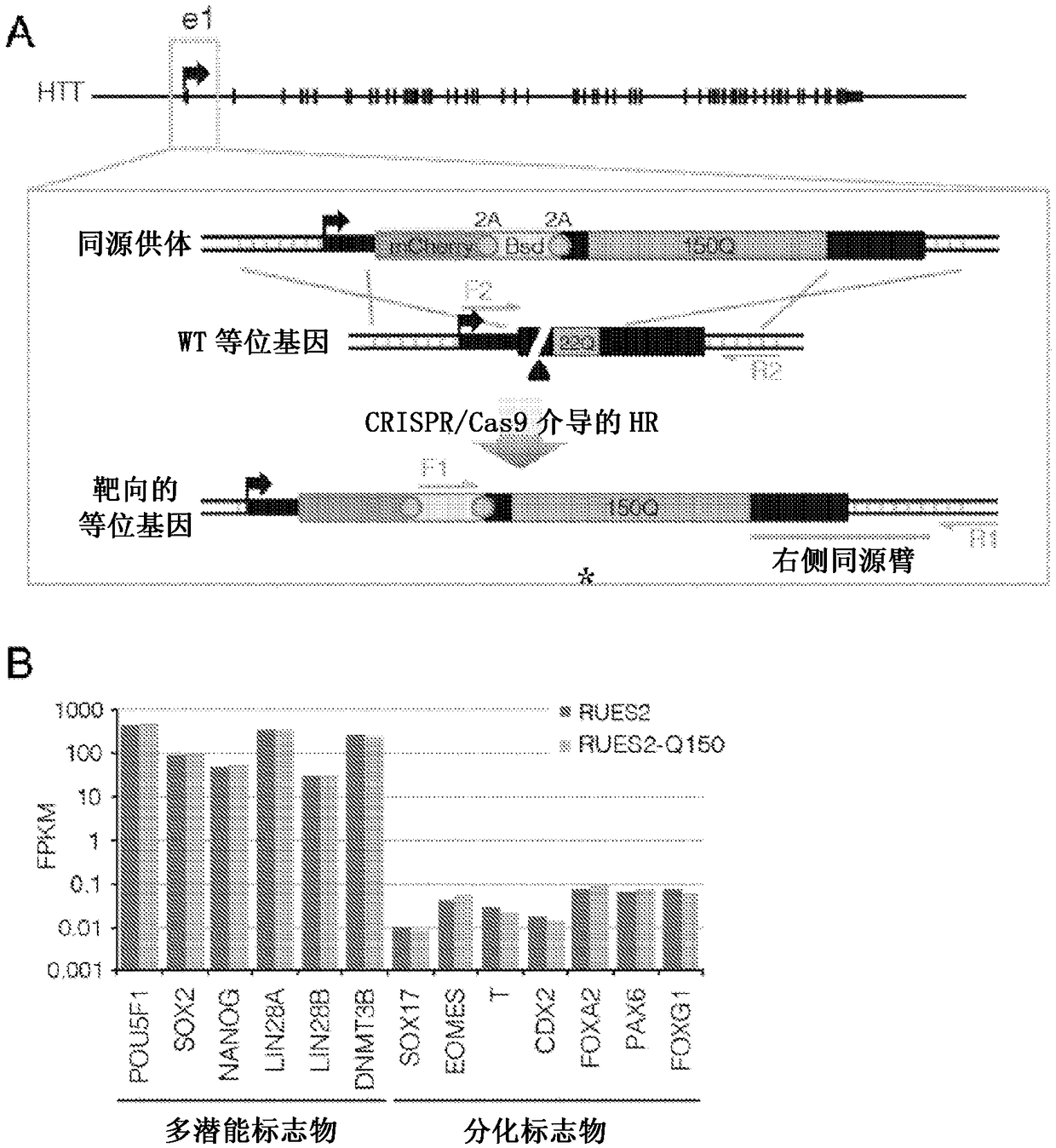
[0347] As described in the Background section, Huntington's disease (HD) is a dominant autosomal neurodegenerative disorder caused by mutations that result in the addition of polyQ repeats at the N-terminus of huntingtin (HTT). Even after years of research, current animal models do not accurately represent the pathophysiology of human HD, possibly due to species-specific differences. This has hampered progress in discovering effective candidate therapies for the disease. To provide a human platform as a drug screening and research tool to study HTT function and dysfunction in healthy and >40Q cells, this example describes the use of CRISPR / Cas9 genome editing technology in generating the first isogenic human embryonic stem cell line for HD (and isogenic wild-type controls).
[0348] In this example is described the application of a reverse editing strategy using CRISPR-Cas9 to introduce a ...
Embodiment 2
[0362] HTT extension leads to isogenic hESC transcriptome alterations
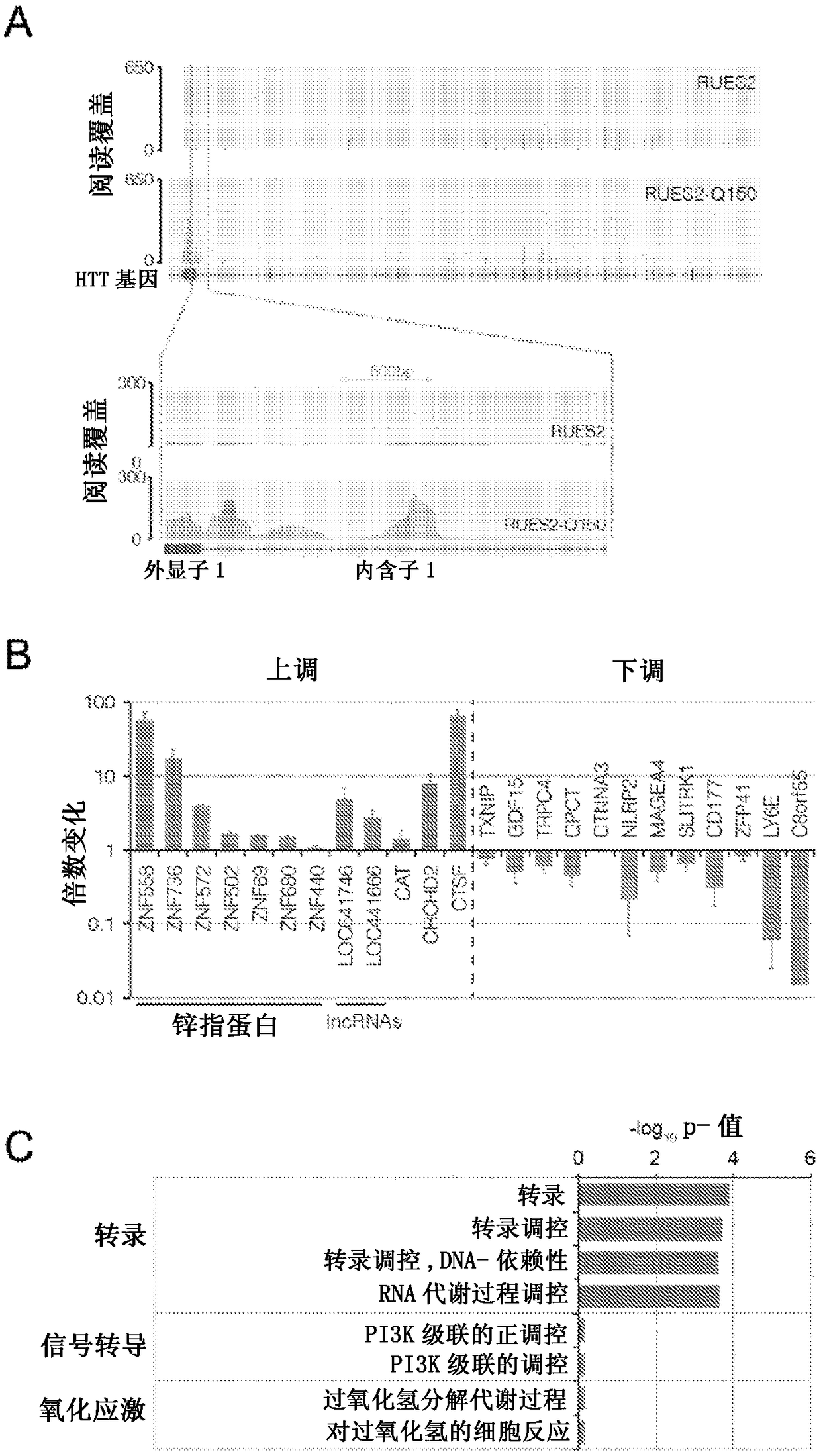
[0363] Since the HD ESC cell line is the first generation isogenic hESC modeling aspect of HD, Applicants sought to perform a comparative analysis of lines grown under exactly the same conditions and simultaneously perform transcriptome RNA-seq analysis.
[0364] Since RUES2 and RUES2-Q150 share the same genetic background, applicants had the opportunity to explore whether a simple addition of polyQ could produce transcriptional differences between the two lines. In order to solve this problem, the applicants of the present invention performed comparative RNA-seq analysis in two replicates. The presence of HTT spliced isoforms was first examined, and the question was explored whether polyQ chain addition affected HTT mRNA isoform expression. Consistent with previous observations in mice and humans, a highly enriched HTT isoform of approximately 2 kb was detected, caused solely by exon-1 to intron-1 read...
Embodiment 3
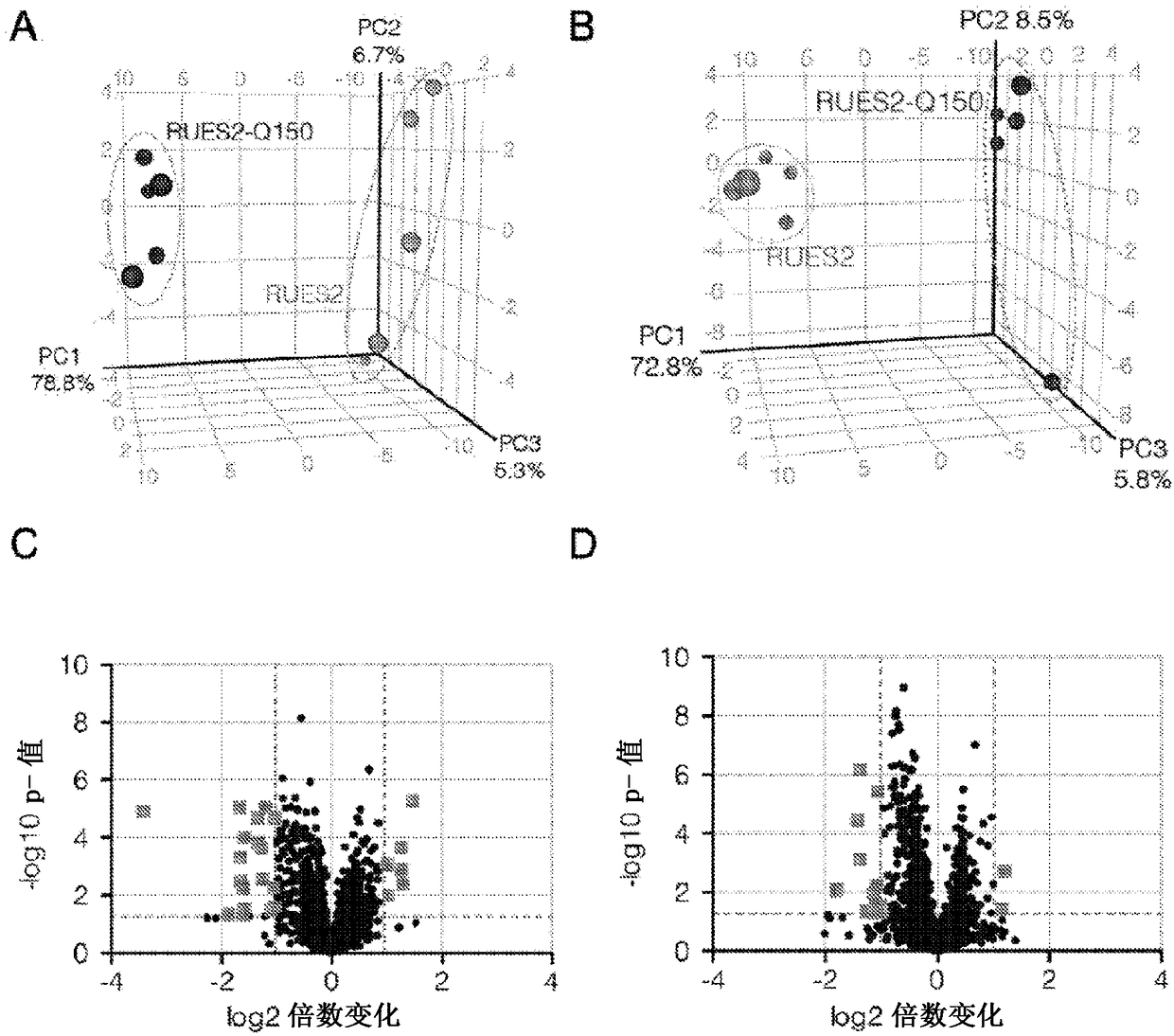
[0375] HTT expansion leads to changes in isogenic hESC metabolite profiles
[0376] Simultaneously with RNA-seq and for samples grown under the exact same pluripotency conditions, comparative non-targeted liquid chromatography / mass spectrometry (LC / MS) metabolite profiling of RUES2 and RUES2-Q150 cells was performed. Spectral data were acquired at the level of hydrophilic metabolites contributing to intermediary metabolism using aqueous normal phase LC and negative and positive ion MS detection for broad potential shift coverage. Three independent cultures of RUES2 and RUES2-Q150 were analyzed separately as 5 technical experimental replicates. Overall, this metabolomic analysis examined 2693 molecular features with 50-1000 Da / e mass / charge (m / z) ratios. Among these substances, 1196 are quantitatively negative ions ( image 3 A and image 3 C), 1497 detected as positive ions ( image 3 B and image 3 D). Principal component analysis (PCA) and unsupervised hierarchical clu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com