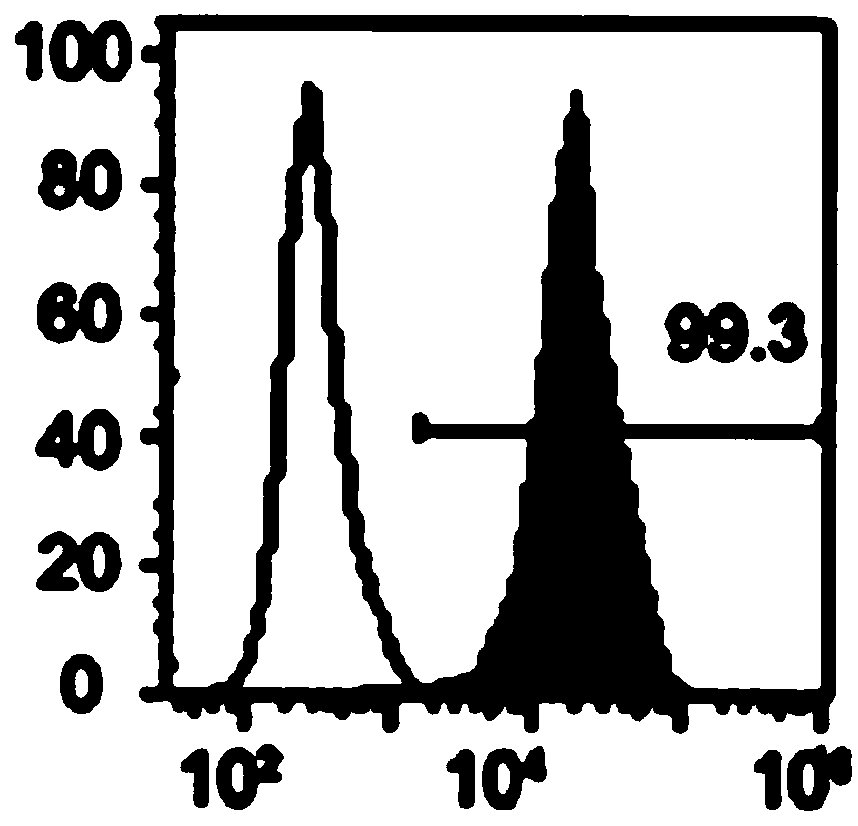
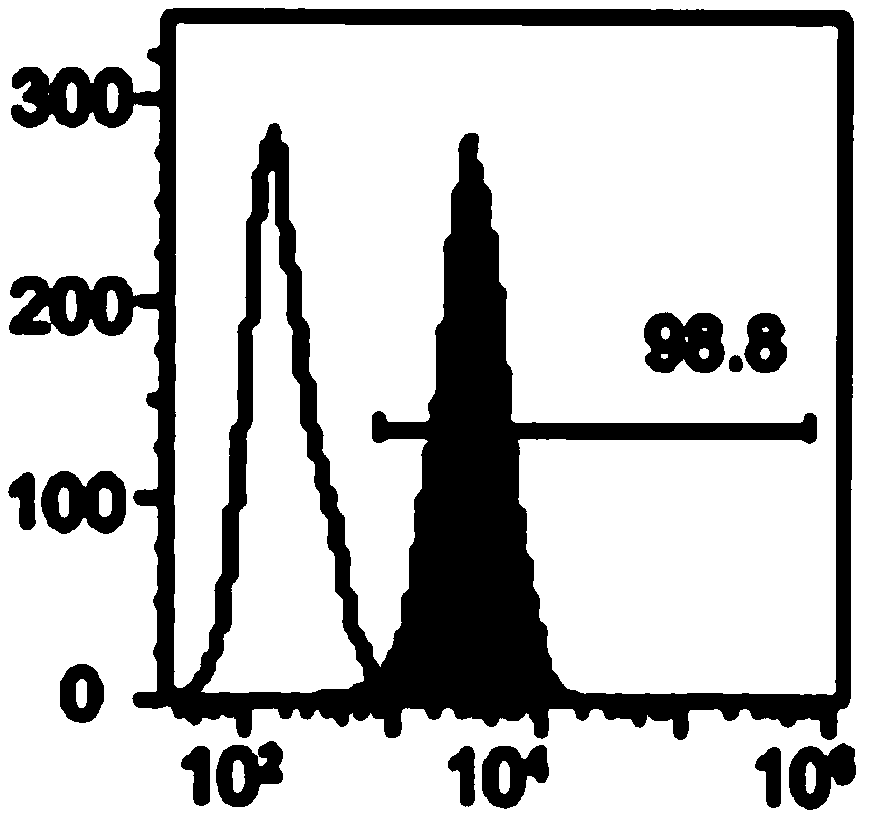
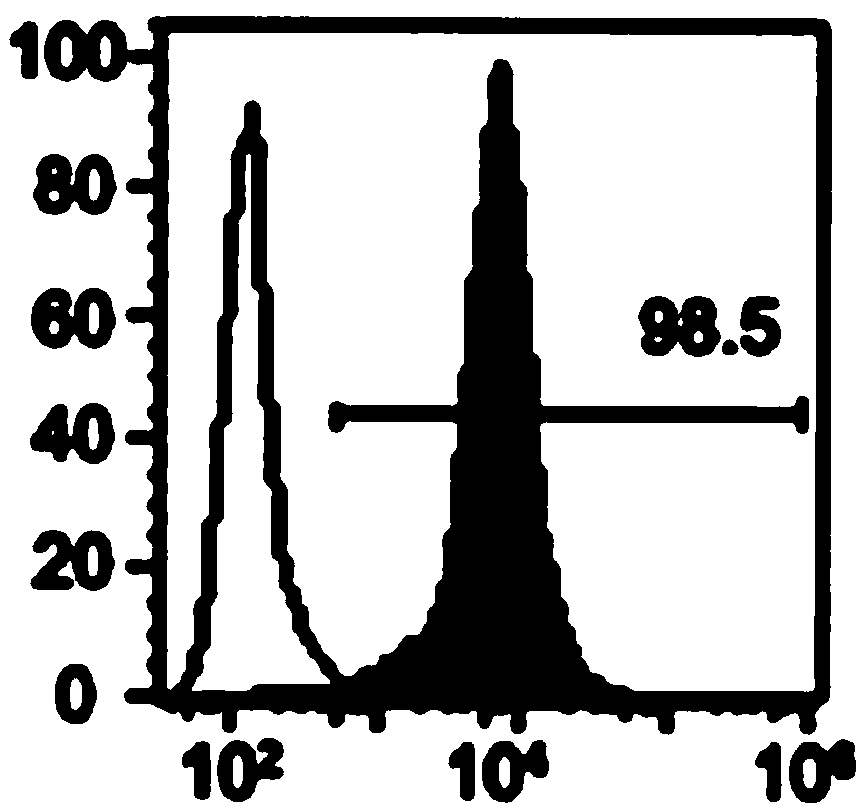
Extraction method of specific mesenchymal stem cell exosome
A technique for stromal stem cells and extraction methods, which is applied in the field of mesenchymal stem cell exosome extraction, can solve the problems of no cell specificity, the concentration of exosomes cannot reach very high, and the price is expensive, and can promote vascular repair and anti-fibrosis. Chemical, rich in active substances, reducing the effect of mechanical damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] A specific method for extracting exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells in this embodiment, the method includes the following steps:
[0063] (1) Collection of the supernatant of serum-free mesenchymal stem cells: first, culture the mesenchymal stem cells. 2 Culture in an incubator with a concentration of 5%; when the cell confluence reaches 60%, wash twice with PBS, replace with serum-free medium for culture, wait until the cells are covered with a flat bottom, collect the medium, and replace with serum-free The medium of the relevant components is ɑ-MEM, and the concentration of PLA or FBS in the replaced medium is 0, and the culture is carried out for 48 hours; centrifuged at 300g for 10min to remove cell debris and obtain the initial supernatant;
[0064](2) The initial supernatant was taken for further gradient centrifugation at 4° C. and 2000 g for 10 min to remove dead cells and large debris to obtain the supernatant after centrifugation;
[0065] (3) Transfer the...
Embodiment 2
[0070] (1) Collection of the supernatant of serum-free mesenchymal stem cells: firstly, culture the mesenchymal stem cells. 2 Culture in an incubator with a concentration of 5%; when the cell confluency reaches 65%, wash twice with PBS, replace with serum-free medium for culture, wait until the cells are covered with a flat bottom, collect the medium, and replace with serum-free The medium of the relevant components is DMEM / F12, and the concentration of PLA or FBS in the medium after replacement is 0, and the culture is carried out for 60 hours; centrifuged at 400g for 8min to remove cell debris and obtain the initial supernatant;
[0071] (2) The initial supernatant was taken for further gradient centrifugation at 4° C. and 2000 g for 10 min to remove dead cells and large debris to obtain the supernatant after centrifugation;
[0072] (3) Transfer the centrifuged supernatant to a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 10,000 g for 30 min at 4° C., and collect the supernatant containi...
Embodiment 3
[0077] (1) Collection of the supernatant of serum-free mesenchymal stem cells: firstly, culture the mesenchymal stem cells. 2 Culture in an incubator with a concentration of 5%; when the cell confluence reaches 70%, wash twice with PBS, replace with serum-free medium for culture, wait until the cells are covered with a flat bottom, collect the medium, and replace with serum-free The medium of the relevant components is ɑ-MEM, and the concentration of PLA or FBS in the replaced medium is 0, and the culture is carried out for 60 hours; centrifuged at 500g for 5min to remove cell debris and obtain the initial supernatant;
[0078] (2) The initial supernatant was taken for further gradient centrifugation at 4° C. and 2000 g for 10 min to remove dead cells and large debris to obtain the supernatant after centrifugation;
[0079] (3) Transfer the centrifuged supernatant to a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 10,000 g for 30 min at 4° C., and collect the supernatant containing microvesi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com