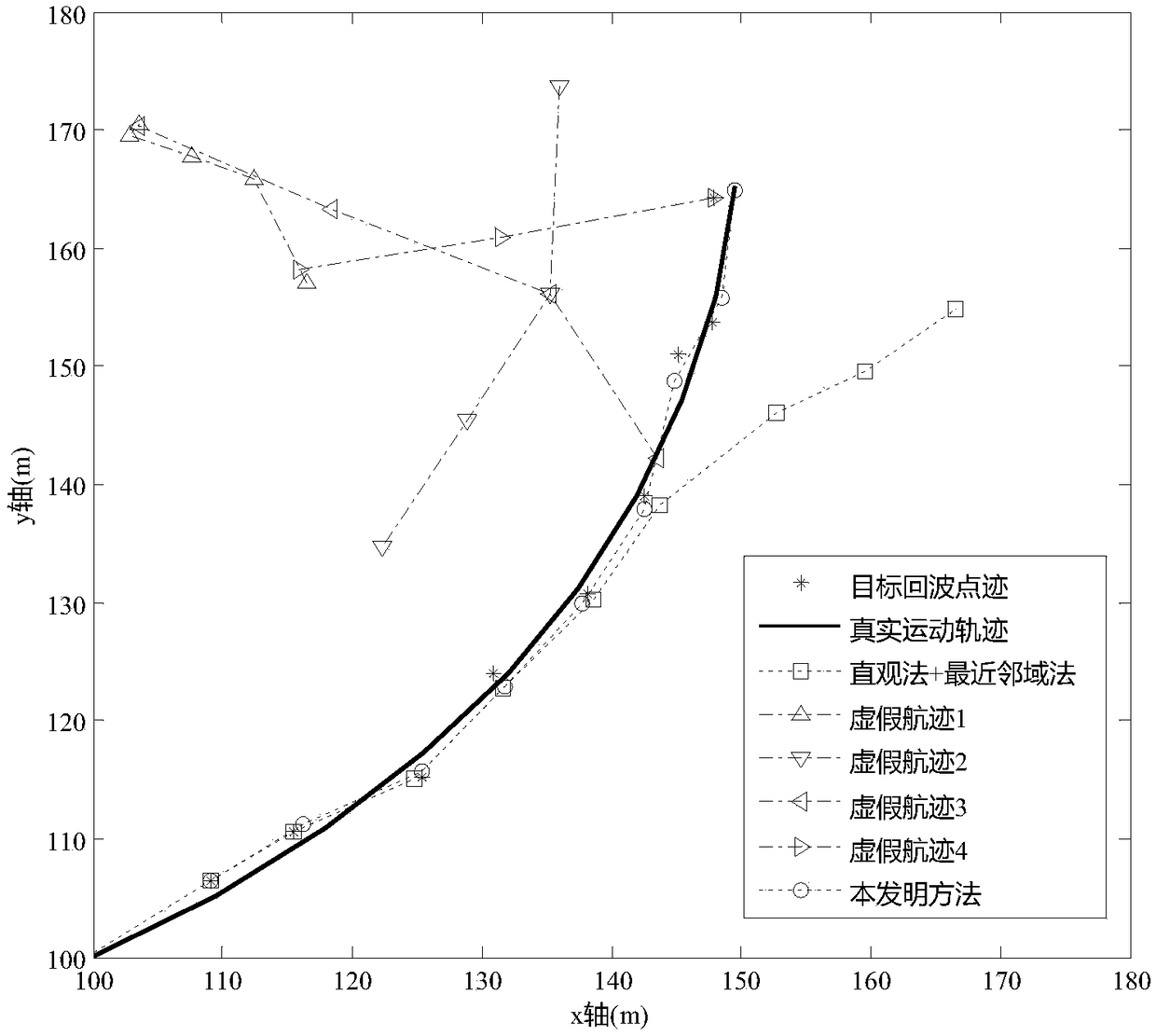
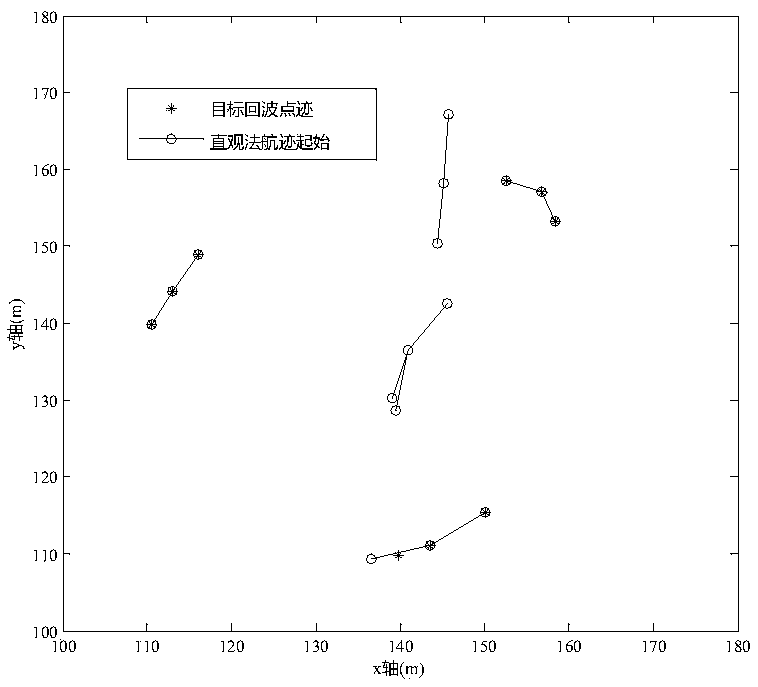
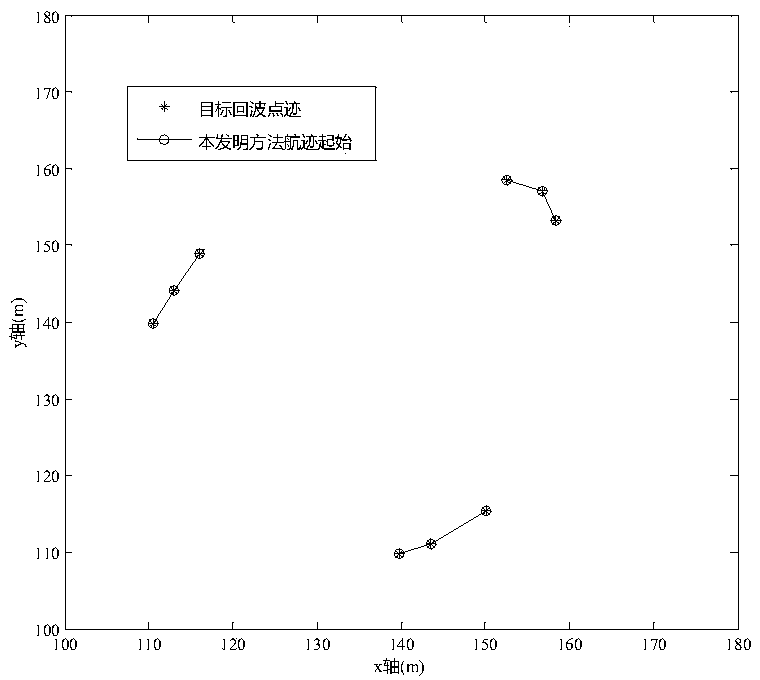
Low and slow small target tracking method based on polar coordinate system
A low-slow and small target and polar coordinate system technology, which is applied in the field of low-slow and small target tracking based on the polar coordinate system, can solve the problems of target signal concealment, high complexity, and small radar reflection area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0074] Embodiments of the present invention are described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings:
[0075] A low-slow and small-target tracking method based on a polar coordinate system, comprising the following steps:
[0076] Step 1. The radar scans the current frame of the measurement point for the first time, and starts track initiation. Use all points scanned this time as track headers to establish temporary tracks respectively, that is, all temporary tracks generated are only one dot;
[0077] After the radar system scans each frame, the signal processor will upload a trace data packet to the host computer. There may be target traces, clutter false alarm points, or no measurement traces in the trace data packet. The processing cycle of track association update is based on the radar scanning frame length, that is to say, after each frame of the host computer receives the point track data packet, it starts track processing (including initiat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com