A low-sequence-dependent high-order isothermal exponential amplification method for the detection of microRNAs
A constant-temperature exponential amplification and sequencing technology, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, and the determination/inspection of microorganisms, can solve problems such as sequence dependence, and achieve small sequence dependence, simple amplification system, and high amplification efficiency. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1 A low-sequence-dependent high-order constant temperature exponential amplification template for detecting microRNA
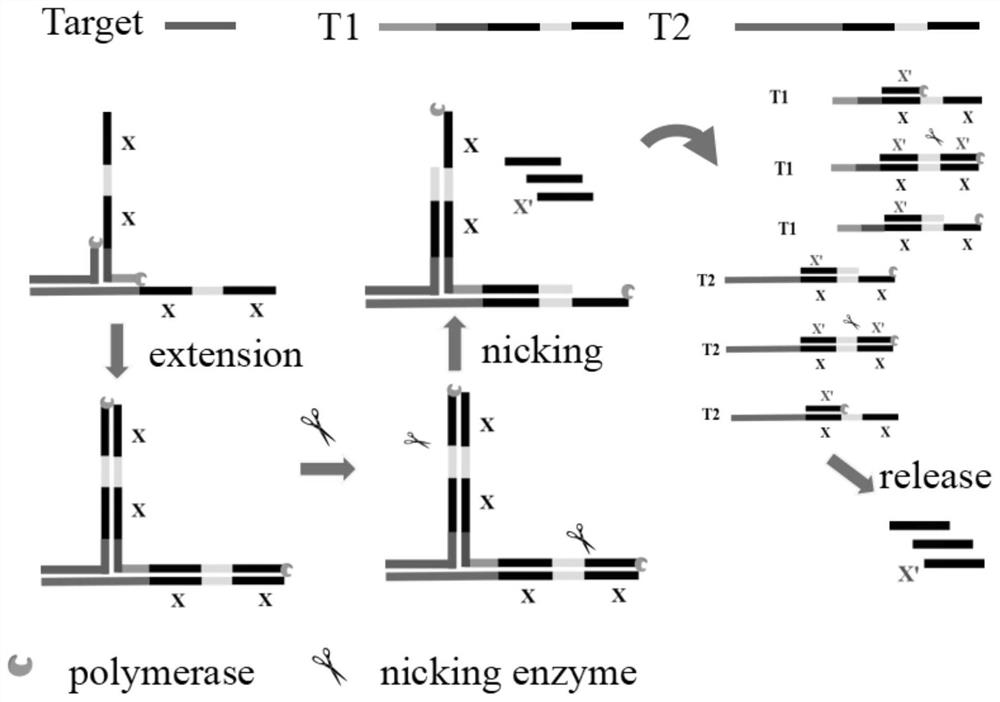
[0046] Such as figure 1 As shown, two partially complementary amplification templates T1 and T2 are designed according to the target miRNA; the 5′-terminal sequences of the templates T1 and T2 are the same, and both contain two identical sequences x (14-25 nt in length), and the two sequences There is a specific site recognized by a nicking endonuclease between x, which is denoted as x-specific site-x;
[0047] The 3' end sequence of the template T2 can be reverse complementary to the 5' end sequence of the target microRNA (the length of the 5' end sequence accounts for 8 / 21-12 / 21 of the total length of the target microRNA);
[0048] The 3' end sequence of the template T1 can be reverse complementary to the middle sequence of the template T2 (length is 8-12bp), and the middle sequence of the T2 is located between the above-mentioned 3' end sequ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2 A method for detecting microRNA by low-sequence-dependent high-order constant temperature exponential amplification
[0053] Taking the detection of let-7b in the let-7 family as an example, according to the sequence of the target let-7b to be detected, templates T1 and T2 that are partially complementary to it were designed, and the specific sequences are shown in Table 1.
[0054] Table 1 Sequences of let-7b and its template T1 and template T2
[0055]
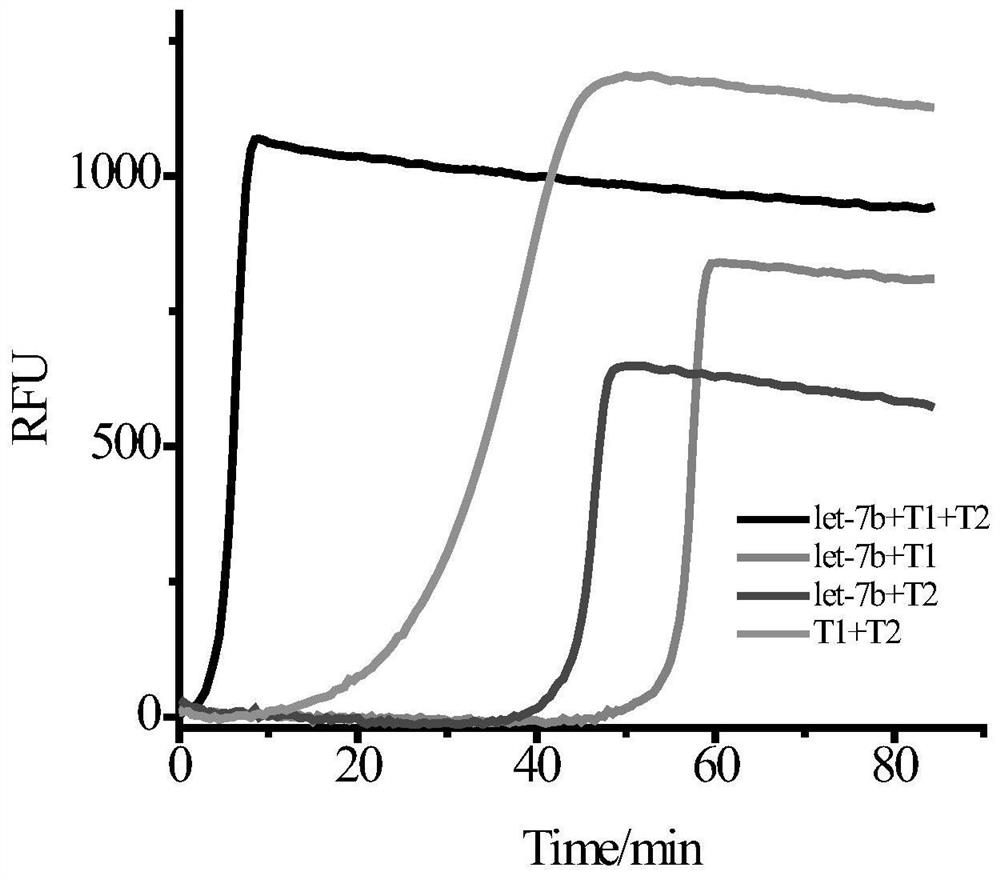
[0056] Prepare A and B reaction solutions on ice, and the A reaction solution is divided into four types: A1, A2, A3, and A4:
[0057] A1 contains endonuclease buffer, template T1, template T2, dNTP, target let-7b;
[0058] A2 contains endonuclease buffer, template T1, dNTP, target let-7b;
[0059] A3 contains endonuclease buffer, template T2, dNTP, target let-7b;
[0060] A4 contains endonuclease buffer, template T1, template T2, dNTP.
[0061] B reaction solution contains DNA polymerase buffer solut...
Embodiment 3
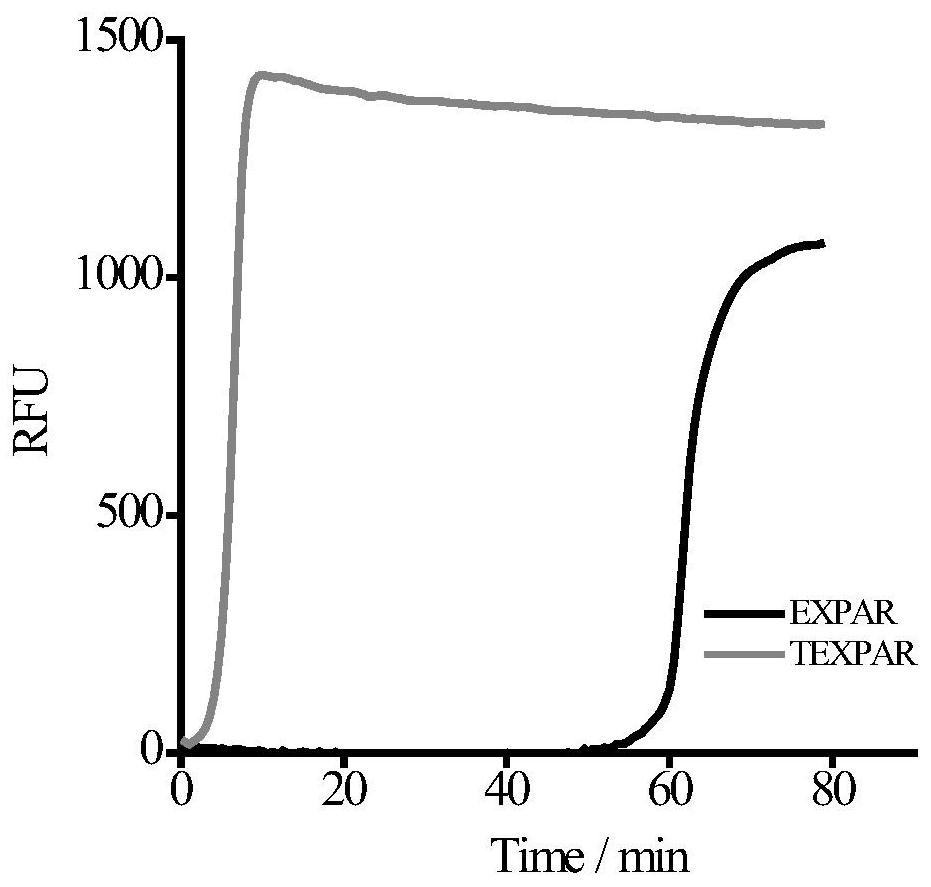
[0064] Example 3 A low sequence-dependent high-order constant temperature exponential amplification method for detecting microRNA
[0065] Taking the detection of let-7b in the let-7 family as an example, according to the sequence of the target let-7b to be detected, templates T1 and T2 that are partially complementary to it were designed, and the specific sequences are shown in Table 1.
[0066] Prepare the A and B reaction solutions of the high-order constant temperature exponential amplification technology (TEXPAR) of the present invention on ice, the A reaction solution includes endonuclease buffer, template T1, template T2, dNTP, target let-7b; the B reaction solution includes Polymerase buffer solution, Vent(exo-) polymerase, endonuclease Nt.BstNBI, SYBR Green I fluorescent dye. Mix A and B (the final concentration of T1 in the mixed system is 0.1μM, the final concentration of T2 is 0.075μM, the final concentration of endonuclease is 0.4U / μL, and the final concentration ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com