Fiber treating agent for staple fibers, and use for said agent
A fiber treatment agent and short fiber technology, applied in the field of fiber treatment agent for short fibers, can solve the problems of poor solution stability, insufficient discoloration resistance, and insufficient antistatic properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
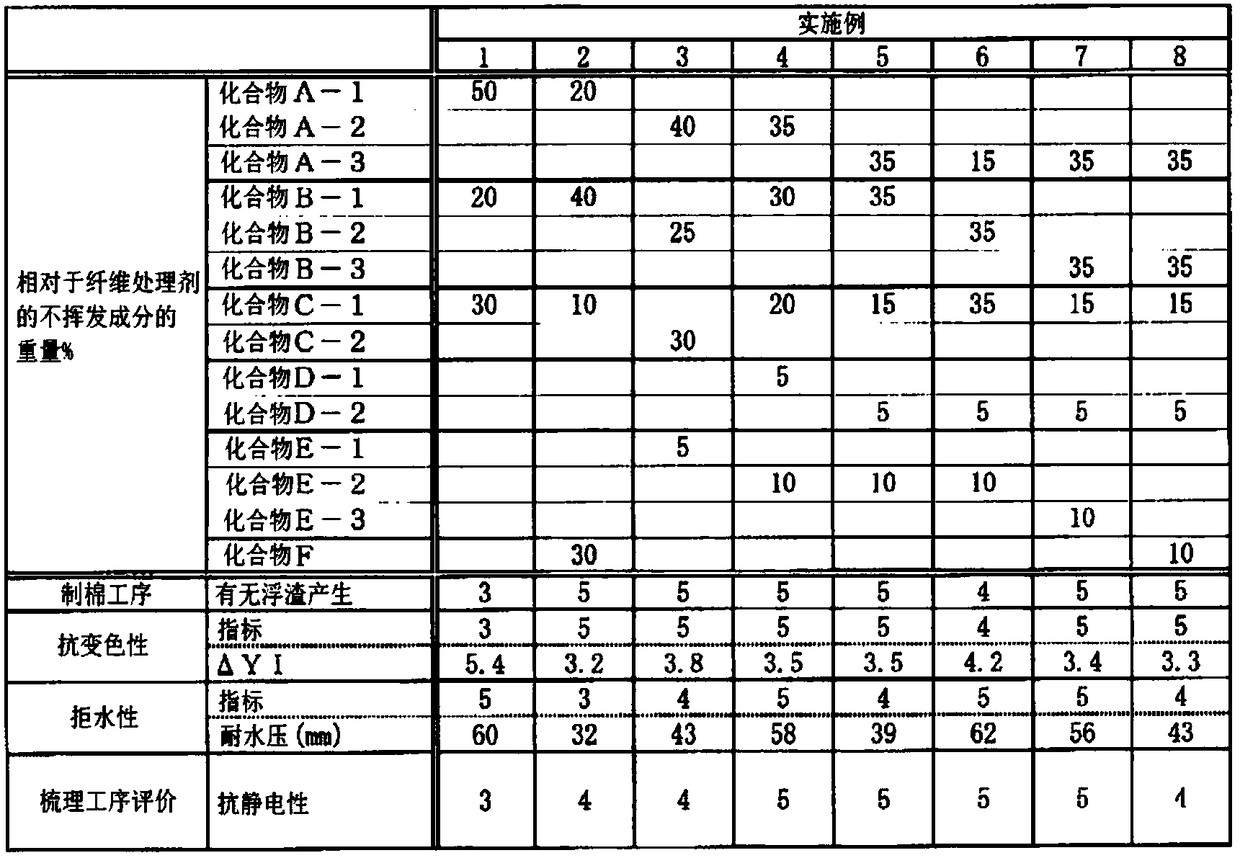
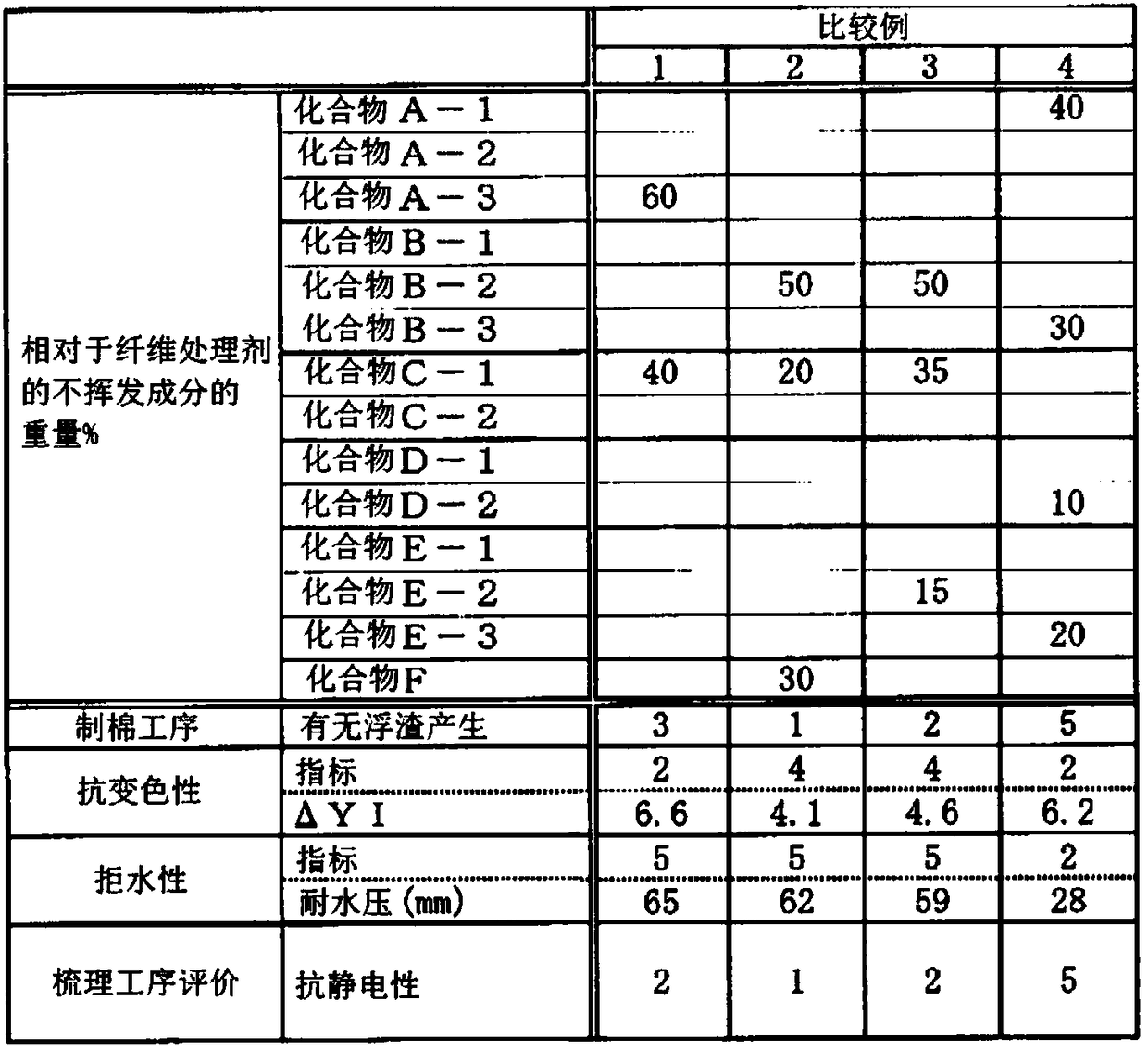
Embodiment 1~8 and comparative example 1~4
[0090] The components shown in Tables 1 to 2 were mixed with water to prepare fiber treatment agents of Examples 1 to 8 and Comparative Examples 1 to 4 in which the weight ratio of non-volatile components in the entire fiber treatment agent was 25% by weight. . The obtained fiber treating agents were diluted with warm water of about 60° C. to a concentration of 0.9% by weight of the non-volatile components, respectively, to obtain diluted solutions.
[0091] Next, 150 g of the diluted solution of each fiber treatment agent was attached to 300 g of the fiber body by dipping and oiling, and the amount of non-volatile components of the fiber treatment agent attached to the water-repellent fiber was 0.45% by weight. The fiber main body is a polypropylene (core)-polyethylene (sheath) composite fiber to which no fiber treatment agent such as a fiber treatment agent is attached. The single fiber fineness is 2.2Dtex, and the fiber length is 38mm. The fibers to which the dilutions of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com