Novel resource utilization process for waste vegetables in farmers market
A farmer's market and resource-based technology, applied in the fields of application, agriculture, and climate change adaptation, can solve problems that affect the ecological environment and endanger human health, and achieve the effect of promoting continuous proliferation and renewal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
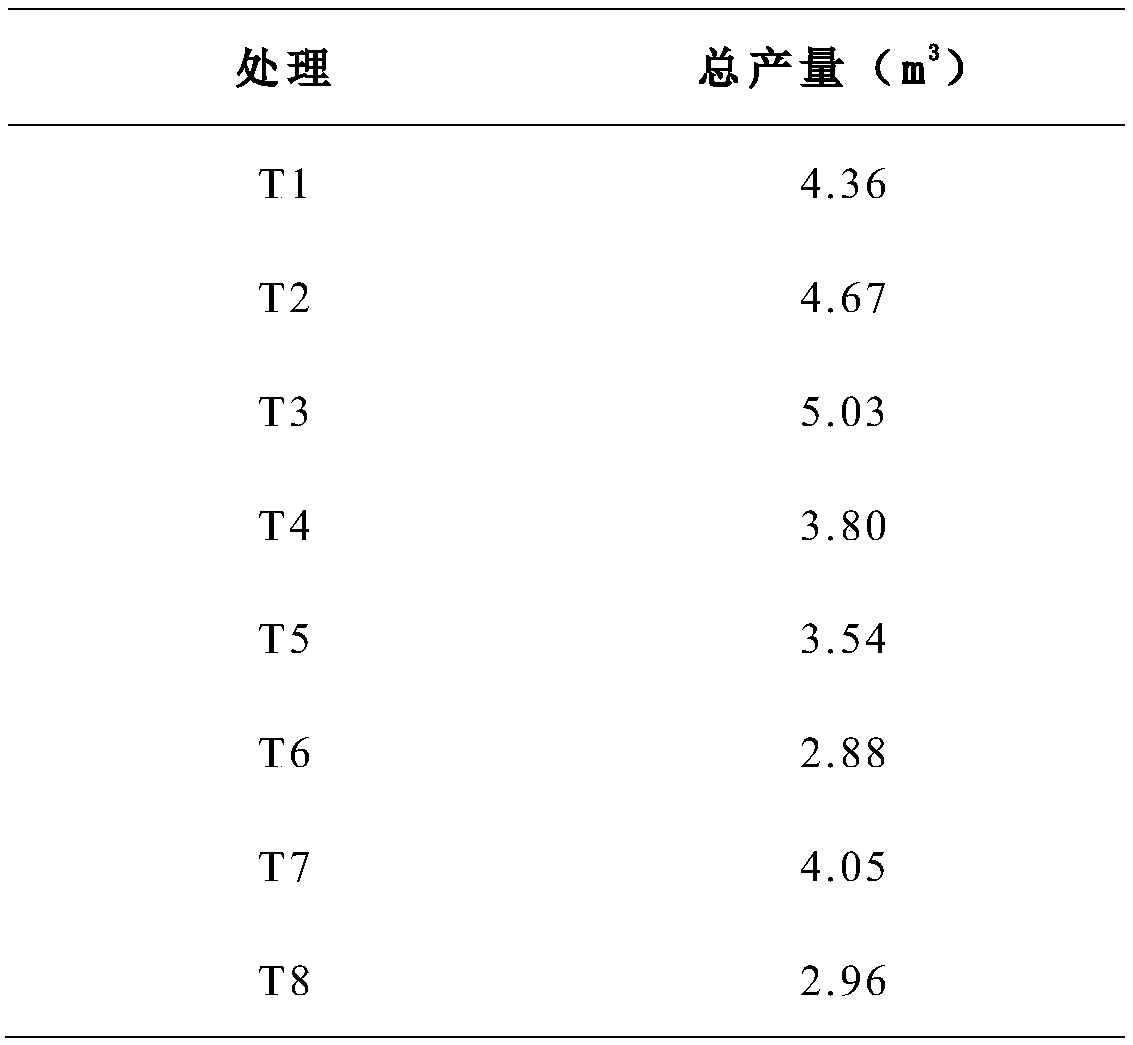
[0039] The present embodiment 1 provides a new resource utilization process of end vegetables in farmers' market, comprising the following steps:
[0040] S1: Collect the end vegetables in the farmer's market, clean them and sterilize them at high temperature;
[0041] S2: breaking the sterilized tail vegetables into fragments or paste, dehydrating, and heating and drying; grinding the dried tail vegetables into powder, and fully stirring evenly;
[0042] S3: Add the powder into the biogas fermentation tank, add water and stir to form a paste, add fermentation bacteria, and ferment to produce biogas; the fermentation process includes 1 low-aerobic fermentation and 3 to 4 anaerobic fermentations;
[0043] S4: After the fermentation is finished, the remaining biogas residue is used as the bottom material to make organic fertilizer.
Embodiment 2
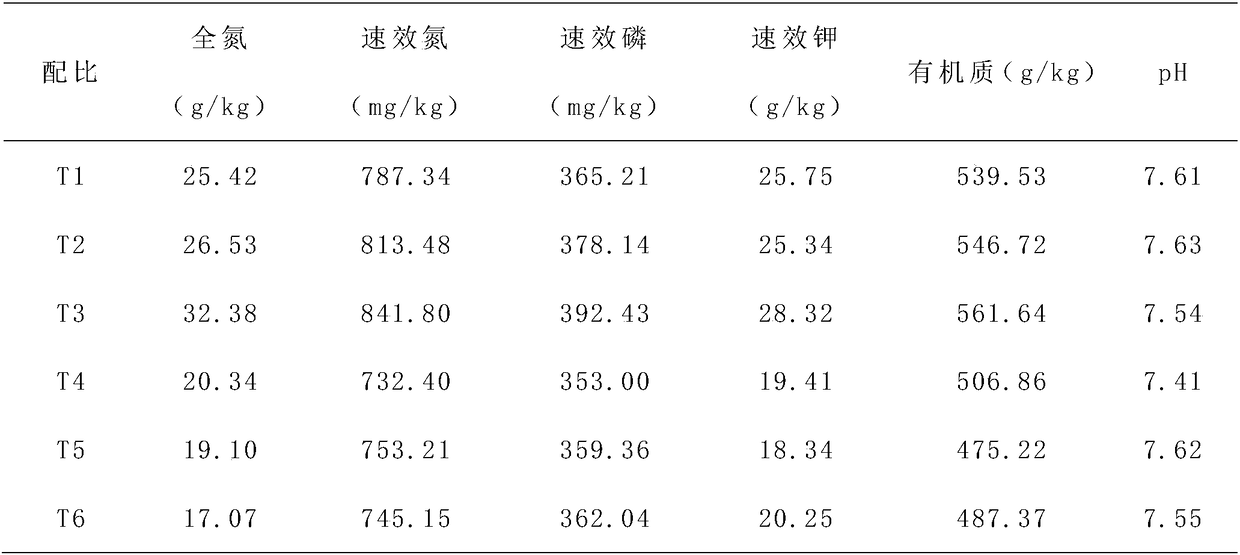
[0045] On the basis of Example 1, this Example 2 provides a new resource utilization process for end vegetables in farmers' markets. This Example 2 further defines the specific method for producing biogas from powder as follows:
[0046] S3.1: Add the powder into the biogas fermentation tank, add 25% of the powder weight in sterilized water, and fully stir it into a paste;
[0047] S3.2: Add fermented strain I suspension with 4% volume of sterilized water into the biogas fermentation tank, and stir evenly; the concentration of fermented strain I is 10 7 Individual / mL, including Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Bacteroides succinogenes with a ratio of 1:2;
[0048] S3.3: Seal the biogas fermentation tank, fill it with mixed gas I with an oxygen content lower than that of air, and discharge the original air in the biogas fermentation tank at the same time, and incubate at 28°C for 72 hours; the composition of mixed gas I is as follows: O 2Content 10%, H 2 Content 1% and N 2 Conte...
Embodiment 3
[0052] On the basis of Example 2, this Example 3 provides a new resource utilization process for end vegetables in farmers' markets. This Example 3 further defines the specific method for producing biogas with powder as follows:
[0053] S3.1: Add the powder into the biogas fermenter, add 50% of the weight of the powder in sterilized water, and fully stir it into a paste;
[0054] S3.2: Add fermented strain I suspension with sterilized water volume of 8% to the biogas fermenter, and stir evenly; the concentration of fermented strain I is 10 7 Individual / mL, including Trichoderma viridans and Butyrivibrio fibrinolyticus with a quantity ratio of 3:2;
[0055] S3.3: Seal the biogas fermentation tank, fill it with mixed gas I with an oxygen content lower than that of air, and discharge the original air in the biogas fermentation tank at the same time, and incubate at 35°C for 48 hours; the composition of mixed gas I is as follows: O 2 Content 10%, H 2 Content 1% and N 2 Content...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com