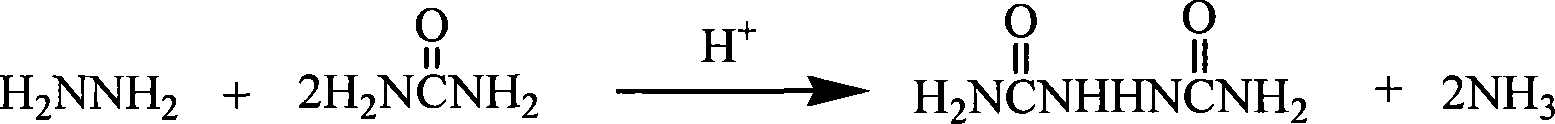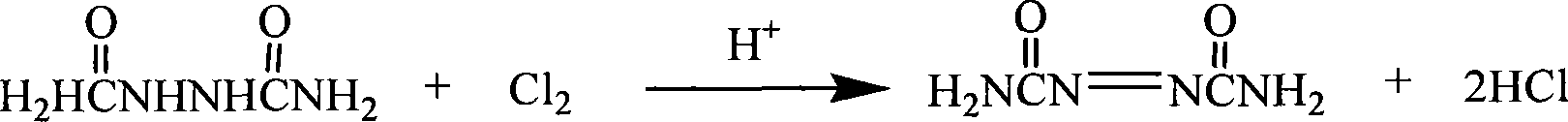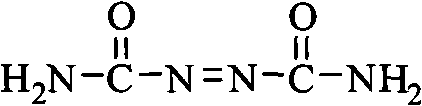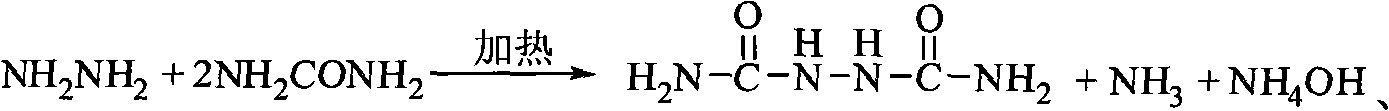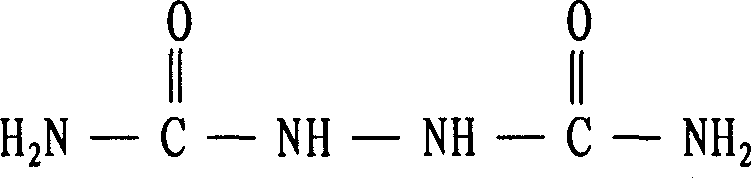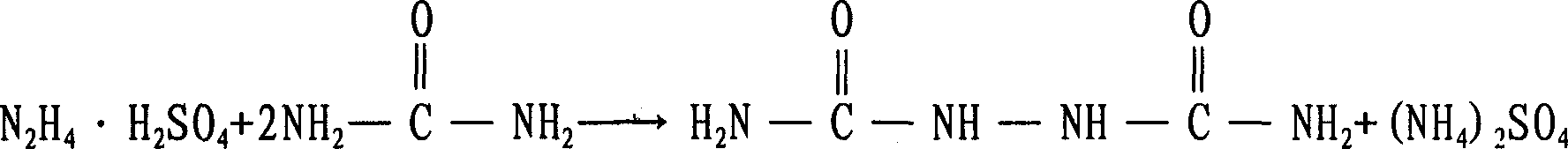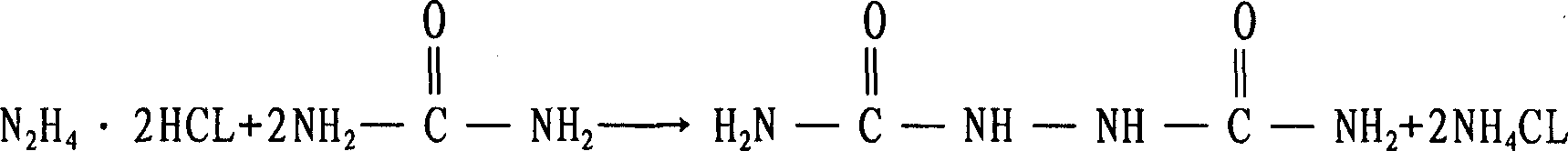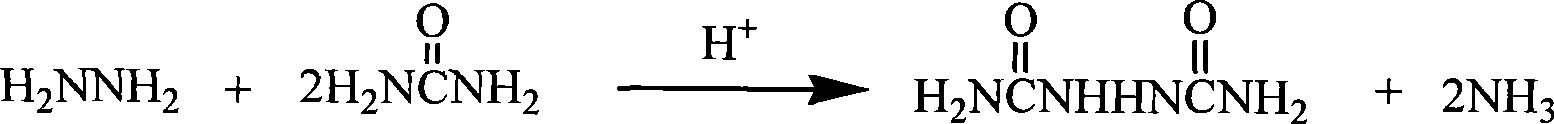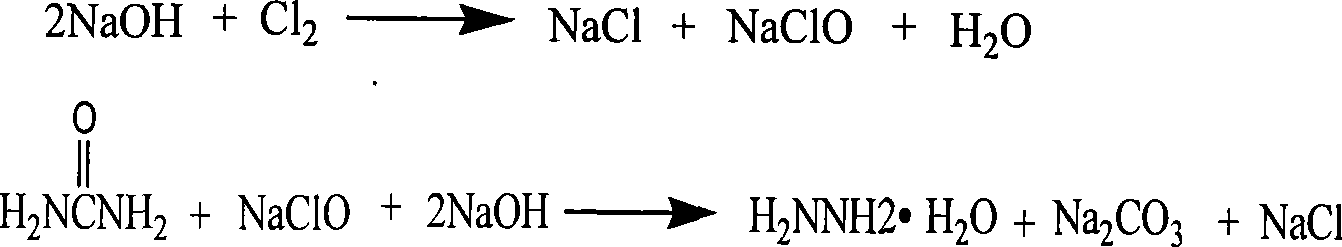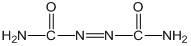Patents
Literature
84 results about "Biurea" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
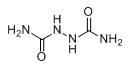
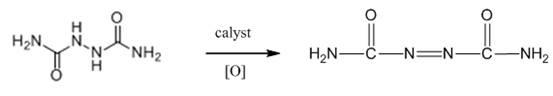
Biurea is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C₂H₆N₄O₂. It is produced in food products containing azodicarbonamide, a common ingredient in bread flour, when they are cooked. Upon exposure, biurea is rapidly eliminated from the body through excretion.
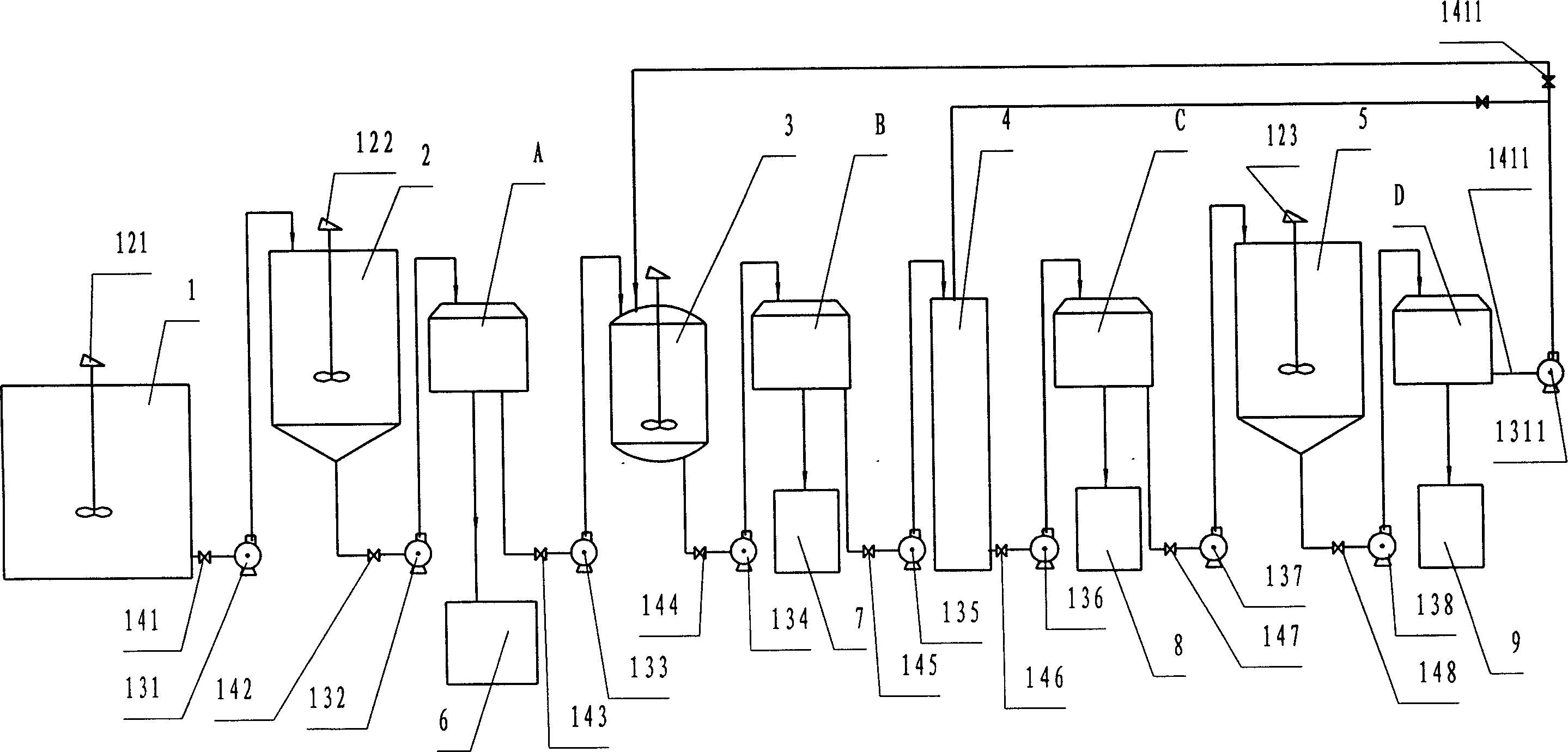
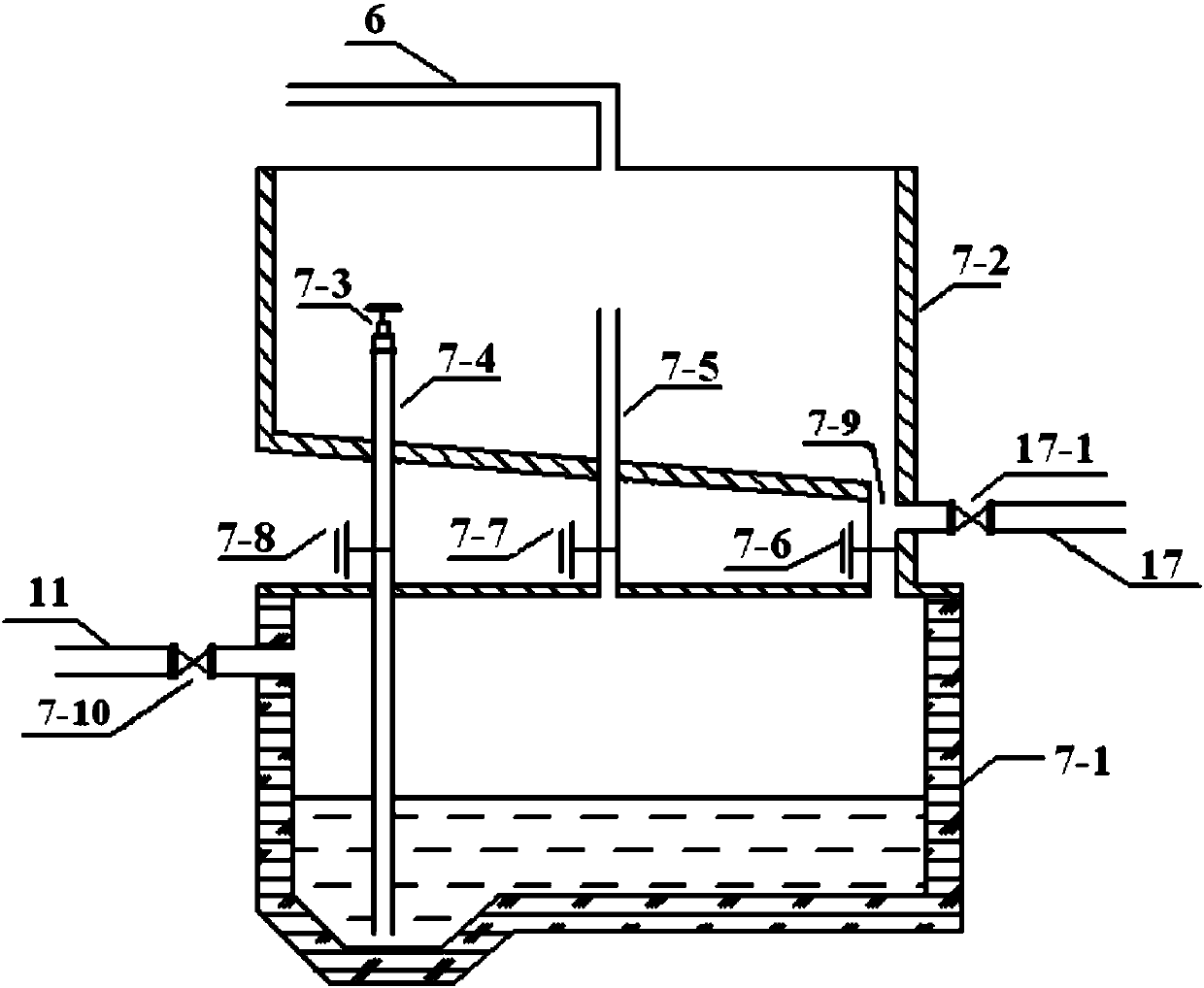
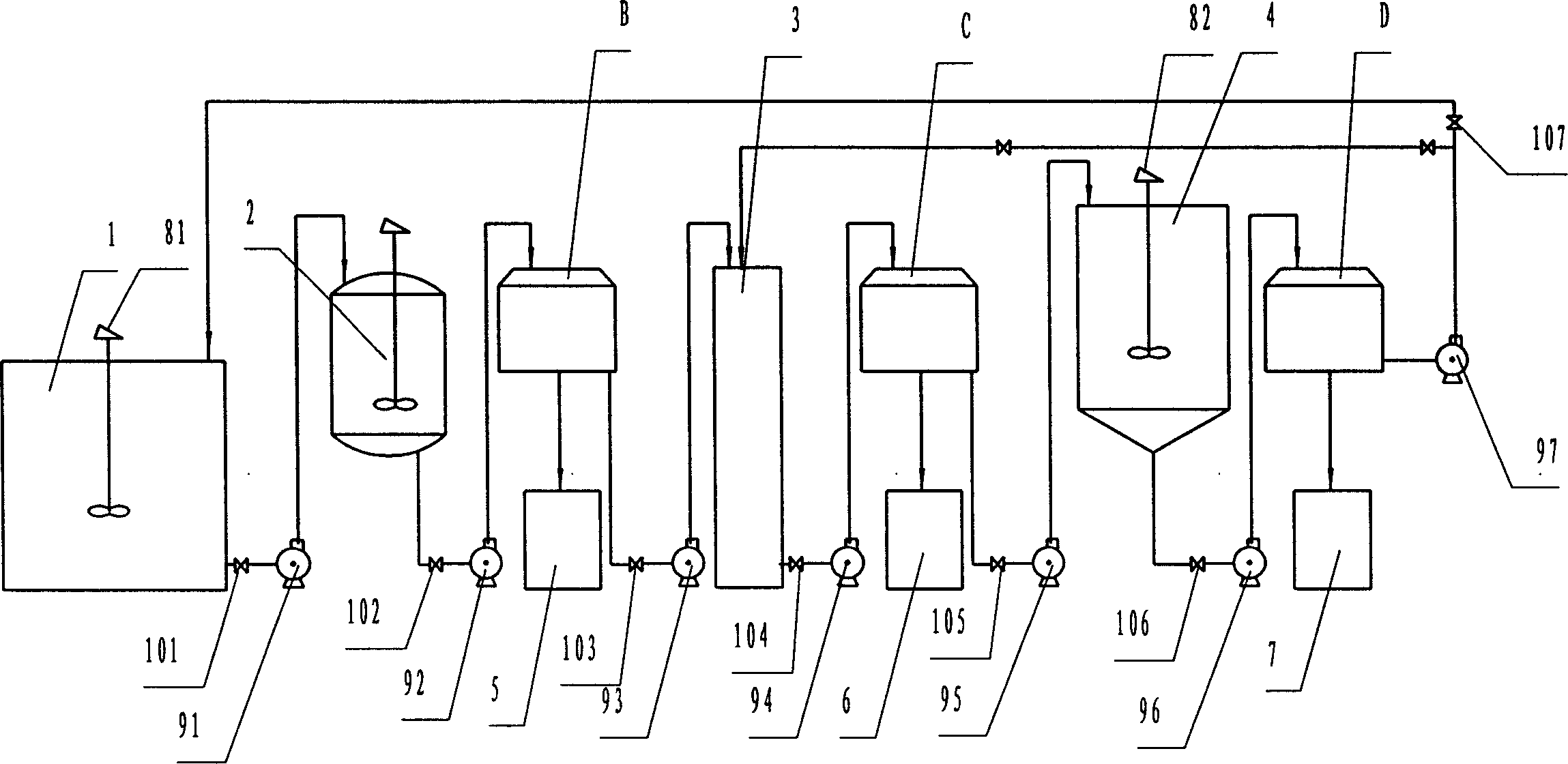
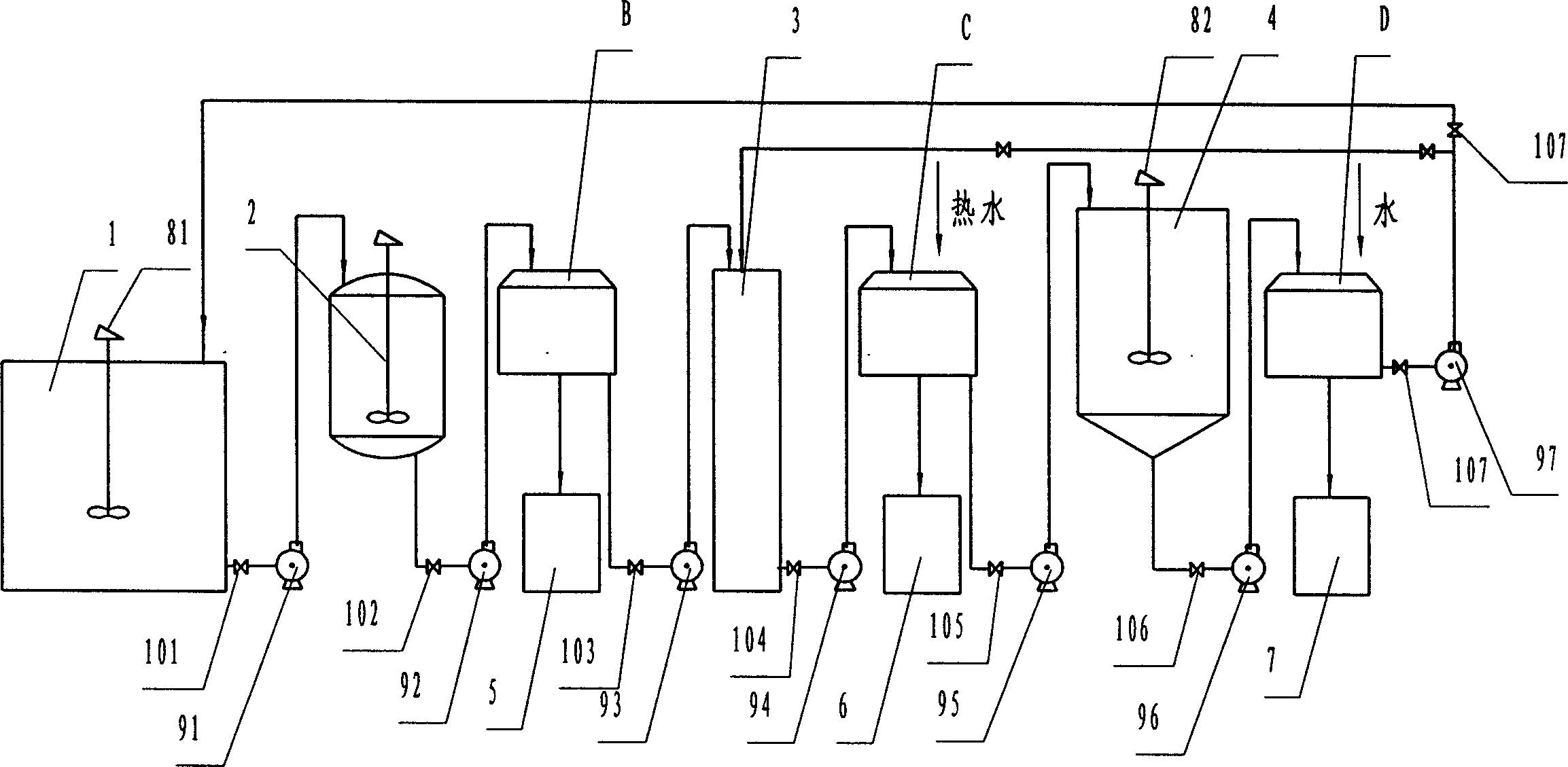
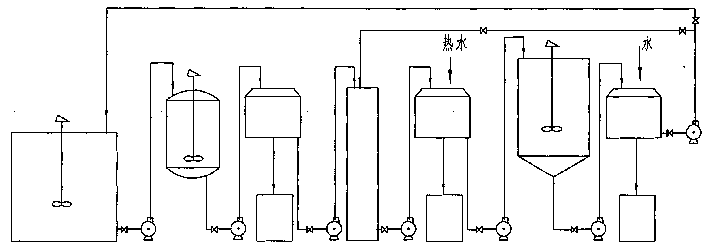
Recovery method of heavily polluted substance produced in ADC foaming agent production process and its device
InactiveCN1513834AMeet emission requirementsSimple processOrganic chemistryTransportation and packagingRecovery methodBiurea
A process for recovering the main pollutants during the production of foaming agent ADC includes freezing the neutralized hydrazine solution to 10- -5 deg.C, centrifugal separation to obtain nitrium sulfate and the first filtrate, condensating between the first filtrate and urea, filtering to obtain biurea and the second filtrate, evaporating the second filtrate, centrifugal separating to obtain sodium chloride and the third filtrate, freezing the third filtrate to 10- -5 deg.C, centrifugal separating to obtain ammonium chloride and the fourth filtrate, evaporating the fourth filtrate several times, freezing to obtain crystal of sodium chloride or ammonium chloride, and returning the residual mother liquid back to condenser.
Owner:郑守樽 +1
Method for recovery utilization of mother solution hydrochloric acid for ADC foaming agent production
ActiveCN101219974AAvoid degradationHigh yieldChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationOrganic chemistryBiureaHydrazine compound
The invention relates to a recycling and reusing method for producing an ADC foaming agent mother liquor hydrochloride, which includes the following steps: A) a hydrazine hydrate and a urea liquor carry out a concentration reaction by pumping a hydrogen chloride gas in or adding a sulfate; the hydrogen chloride gas is pumped in to control and maintain the pH value as 4 to 6 to generate a biurea and an ammonium salt; and a biurea solid and a corresponding ammonium salt mother liquor can be acquired after separation; B) the biurea is made into a suspension liquid of 10 to 40 percent and a sodium bromide which accounts for 0.2 to 1.0 percent of the amount of the biurea is added as a catalyzer to oxidize and generate the ADC foaming agent by pumping in an chlorine-oxygen, and then the ADC foaming agent and hydrochloride mother liquor can be gotten after separation; C) the separated hydrochloride mother liquor is added with an anhydrous magnesium chloride or a dihydrate magnesium chloride accounting for 20 to 40 percent of the amount of hydrochloride mother liquor feed rate, and then heated to distill a hydrogen chloride gas under the state of stirring; D) the distilled hydrogen chloride gas is returned to the biurea concentration technique to be used as the raw materials for neutralization . The beneficial effects of the invention are that the invention can save 60 percent of the amount of the acid used in the concentration process, make full use of the resources, reduce the production cost, decrease the discharging of the pollutions and has significant economic benefits.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
Method for reducing grain size of AC foaming agent
InactiveCN101838224ASmall particle sizeLower the foaming temperatureUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationN dimethylformamideLight equipment
The invention relates to a method for effectively reducing the grain size of an AC foaming agent. In the invention, hydrazine hydrate and urea are used as raw materials, an alkaline method is used for synthesizing biurea which is the intermediate of the AC foaming agent, and the biurea is oxidized to form the AC foaming agent. In the method, the biurea is formed by using the alkaline method, a mother solution is used constantly and circularly to reduce the grain size of the biurea to make the oxidation reaction more complete, and a certain amount of solution of dimethyl sulfoxide or N,N-dimethylformamide is added during the oxidation reaction to control the grain size of the AC foaming agent. Due to the circular use of the washing and filtering water and the addition of amount of the solution of the dimethyl sulfoxide or N,N-dimethylformamide during the oxidation reaction, the produced AC foaming agent has the characteristics of fine and uniform grain size, light equipment corrosion, a little amount of waste water, and environmental friendliness.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing AC blowing agent
InactiveCN1803899AIncreased acid consumptionImproving the method of freezing and removing sodium carbonate decahydrateHigh concentrationFoaming agent
The disclosed preparation method for AC foaming agent comprises: A. condensing and distilling directly the low-concentration hydrazine hydrate; B. preparing the high-concentration hydrazine hydrate; C. acidifying and condensing to prepare biurea; D. oxygenizing with Cl2 to obtain the target. This invention improves the method of freezing and removing Na2CO310H2O, decreases consumption of acid and powder, can recover the residue as byproduct to increase economic benefit, and reduces sewage discharge and tap water consumption.
Owner:薛式华
Series production technology of biurea
ActiveCN101230022AShort reaction timeIncrease production capacityUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationBiureaWater vapor
The invention provides a continuous production process for biurea, which comprises a step that the hydrazine hydrate solution and urea serving as main reaction raw materials reacts with each other to generate the biurea by condensation reaction. The invention is characterized in that: the urea is mixed with the hydrazine hydrate solution to prepare the mixed solution continusouly going into a reaction vessel; The biurea produced in the reaction together with the mother liquor containing the hydrazine hydrate and urea that do not participate in the reaction is discharged from the bottom of reaction vessel, and continuously goes into a solid-liquid separation unit; after being subject to a separation in a solid-liquid separation unit, the biurea solid substance and mother liquid are respectively obtained, and all of the mother liquid is used in circulation. The ammonia and water vapor generated in the reaction escape from the top of reaction vessel and are separated from each other after condensation, At least part of the formed liquor condensate is discharged from reaction system directly. The method shows not only short reaction time and great production capacity but realizes full circulation utilization of mother liquid and biurea washing water. The invention has less wastewater and simple components, and is suitable for comprehensive treatment.
Owner:JIANGSU SOPO GRP
Preparing process for biurea
InactiveCN1986524AAchieve emissionsGood effectUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationPolymer scienceBiurea
The present invention is a kind of practical, economic and environment friendly biurea preparing process. Biurea is prepared with no-salt hydrazine hydrate and urea as main material and sulfuric acid as medium, and through adding catalyst, adding crystal seed and condensation reaction in heating and reflux conditions. The process has high biurea yield, high product purity, relatively low cost, short reaction period and other advantages.
Owner:JUHUA GROUP TECH CENT +1
Biurea synthesis technology
The synthesis technique for LDA comprises, using hydrazine hydrate and urea as material, using pretreated HCl gas without excessive oxidizing substance to replace strong H2SO4 in existing technique and prepare the said product. To treat the waste liquid, according ammonia nitrogen content in waste, caltulating required vaporated water quantity to prepare NaCl and NH4Cl, crystallizing the NaCl and NH4Cl both of high purity by evaporation and condensation respectively, and the obtained water can be recycled; returning the last little waste liquid to system for treatment with new waste liquid. This invention has little corrosion to device and high product purity and yield, and ensures the no-pollutant discharge.
Owner:KAIFENG DONGDA CHEM GROUP
Device for treating biurea condensation sewage generated from preparation of ADC (Azodicarbonamide) foaming agent with urea method and use method of device
ActiveCN106698561AImprove recycling rateWater contaminantsDispersed particle separationBiureaChemical oxygen demand
The invention discloses a device for treating biurea condensation sewage generated from preparation of an ADC (Azodicarbonamide) foaming agent with a urea method and a use method of the device, relates to a sewage treatment device and a use method thereof, and aims to solve the problem that COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) in effluent of the biurea condensation sewage generated when the ADC foaming agent is prepared by using the urea method is hard to meet standards. The device consists of an evaporation crystallizer, a high-temperature salt bath decomposition and gas absorption system and a pressure hydrolysis-flash evaporation system. The use method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: feeding sewage into the evaporation crystallizer, performing cooling crystallization on concentrated liquid, feeding into an ammonia distillation tower for ammonia distillation, discharging the bottom liquid of the ammonia distillation tower into the pressure hydrolysis-flash evaporation system for decomposition treatment, and feeding salt generated from evaporation crystallization into the high-temperature salt bath decomposition and gas absorption system for purification treatment. By adopting the device and the use method, urea and hydrazine hydrate of the ADC condensation sewage can be recycled, sodium chloride can be purified, the water circulation utilization rate can be increased, and standards of indexes such as COD in the effluent can be met.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Grease composition for constant velocity joint and constant velocity joint containing the composition sealed therein
ActiveUS7910526B2Inhibit temperature riseIncreased durabilityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationSulfur containingDithiocarbamate
The present invention provides a grease composition for use in constant velocity joints, which comprises the following components (a) to (g) and a constant velocity joint comprising the grease composition sealed or encapsulated therein:(a) a base oil;(b) a diurea thickener represented by the following general formula:R1NH—CO—NH—C6H4-p-CH2—C6H4-p-NH—CO—NHR2 wherein R1 and R2 each independently represents an alkyl group having 8 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 12 carbon atoms or a cycloalkyl group having 6 to 12 carbon atoms;(c) a molybdenum dialkyl dithiocarbamate insoluble in the base oil;(d) a molybdenum dialkyl dithiocarbamate soluble in the base oil;(e) molybdenum disulfide;(f) at least one member selected from the group consisting of calcium phenate and calcium sulfonate; and(g) a sulfur-containing extreme-pressure agent free of phosphorus.The grease composition can efficiently prevent a temperature rise of a constant velocity joint and can impart excellent durability to the joint.
Owner:KYODO YUSHI CO LTD +1
Process for producing biurea through optimized urea method
InactiveCN104892463AIncrease concentrationReduce yieldOrganic chemistryChemical industryBiureaHydrazine compound
The present invention discloses a process for producing biurea through an optimized urea method. The process comprises that: during the biurea preparing, the crude solution of hydrazine hydrate produced through the urea method is adopted as a raw material and is subjected to repeated evaporation concentration and freezing crystallization for a plurality of times to respectively separate out sodium chloride and sodium carbonate so as to obtain a fine hydrazine solution of the hydrazine hydrate; the sodium chloride is separated at the evaporation section and the sodium carbonate decahydrate is separated at the freezing crystallization section during each evaporation, a salt extracting pump is used to extract, and the solid sodium chloride is separated out by a salt separation centrifuge; and the liquid is subjected to freezing crystallization, is separated, and then returns to the cold hydrazine solution at the evaporation section, pre-cooling is performed, and then the obtained material is conveyed to the crystallization kettle. The process of the present invention has the following beneficial effects that: the hydrazine hydrate-containing crude solution produced through the urea method is adopted as the raw material, alkali removing through freezing is performed while the cold energy and the heat energy are recovered, the repeated circulating method is used, the hydrazine hydrate concentration is improved in the low cost manner, and the process has characteristics of less raw material consumption, less energy source consumption, low cost, and high single-kettle yield during condensation.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
Process for producing biurea
ActiveCN101219973AAvoid cloggingMake sure there is no nitrogenUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationBiureaHydrazine compound
The invention relates to a preparation method of biurea, which includes the following steps: A) a crude hydrazine hydrate liquor is evaporated through an evaporator to get a salt-free hydrazine hydrate liquor and a solid saline-alkaline; B) the ejected salt and alkali are dissolved and reacted with a magnesium chloride liquor, a sulfate of zinc and a chloride liquor to generate a precipitation of basic magnesium carbonate or a basic zinc carbonate and get the basic magnesium carbonate or the basic zinc carbonate after filtering and washing; C) an evaporated hydrazine hydrate dissolves urea, which is added with sulfate or pumped with an anhydrous hydrogen chloride to carry out a condensation reaction to generate the biurea and an ammonium sulfate or an ammonium chloride; D) the mother liquor containing the ammonium sulfate or the ammonium chloride gained through separation can acquire the ammonium sulfate or the ammonium chloride through concentration. The beneficial effects of the invention are that the invention thoroughly solves the problem of serious ammonia nitrogen pollution during the production of biurea and all the byproducts are reasonably reused and recycled; besides, the evaporation efficiency is high, which saves the amount of hydrochloride or sulfate and can avoid the overflow of raw materials caused by the large amount of bubbles in the process of neutralization.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
Method for removing sodium carbonate from hydrazine hydrate crude solution
The invention discloses a method for removing sodium carbonate from a hydrazine hydrate crude solution. The method comprises the following steps: 1, a urea solution is mixed with sodium hypochlorite, wherein a molar ratio of the urea solution to sodium hypochlorite is 1-2, such that the crude solution obtained by a reaction does not contain sodium hydroxide; 2, a chloride is added into the hydrazine hydrate crude solution; and centrifugal separation is carried out, such that poorly soluble carbonate is separated; 3, the hydrazine hydrate solution with sodium carbonate removed is subjected to membrane filtration, such that cations in the solution are removed. With the method, sodium carbonate in the hydrazine hydrate crude solution is thoroughly removed. The produced poorly soluble carbonate can be directly sold after certain treatments, and can be subjected to a reaction with hydrochloric acid recovered from an ADC process for producing chloride for recycling. When the sodium-carbonate-removed hydrazine hydrate solution is used in a biurea production process, acidic substance addition can be greatly reduced. When the sodium-carbonate-removed hydrazine hydrate solution is used in a hydrazine hydrate production process through evaporation and rectification, evaporation and rectification continuous production is facilitated.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
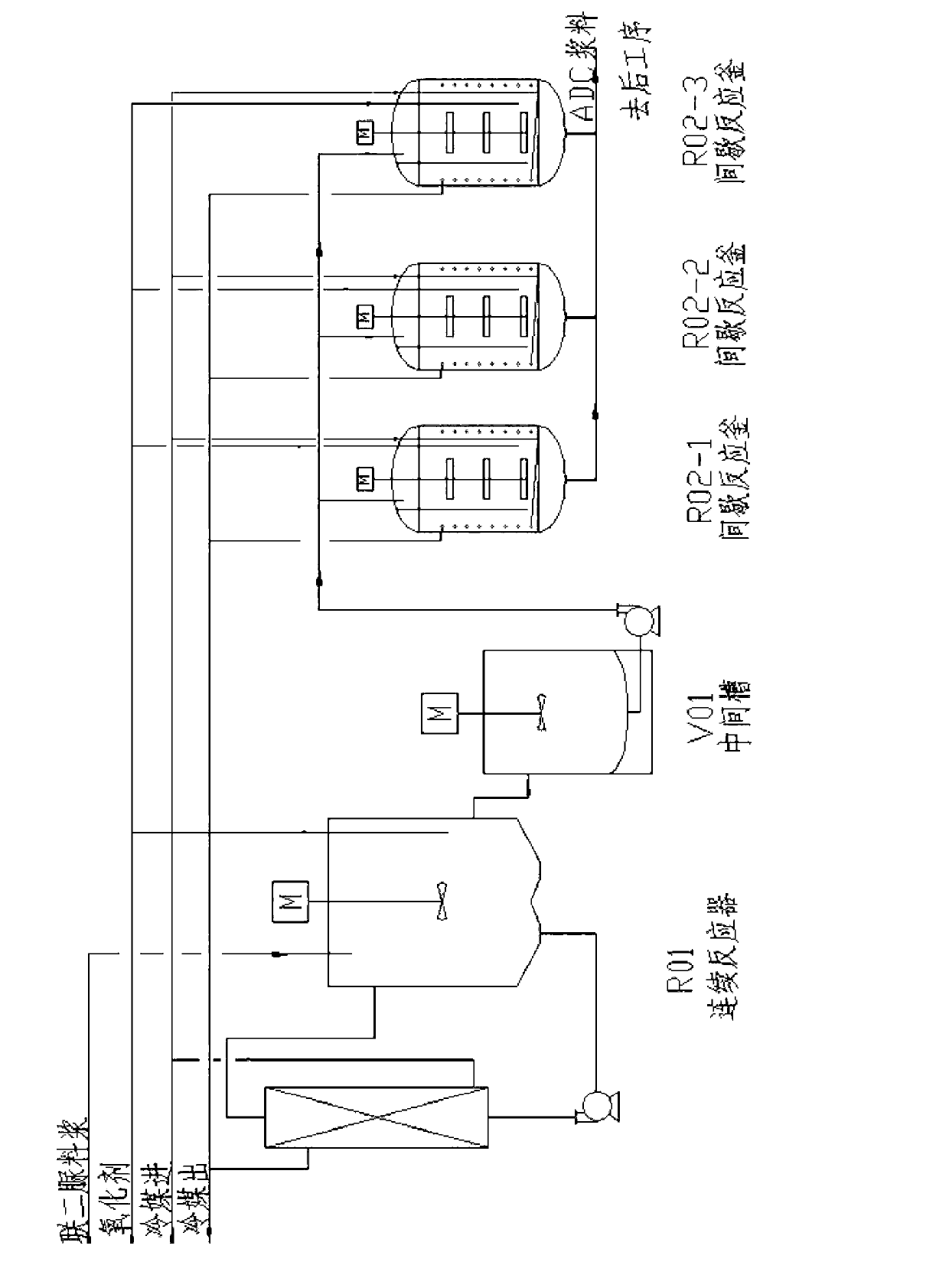
Method of semi-continuously producing particle-size-controllable ADC (azodicarbonamide) foaming agent
ActiveCN103012218AControl reaction temperatureSmall particle sizeOrganic chemistryBiureaReaction system
The invention provides a method of semi-continuously producing a particle-size-controllable ADC (azodicarbonamide) foaming agent. Staged reactions are adopted, an oxidizing agent is continuously added, a reaction system is controlled in a certain acidity range, a first stage reaction is continuous, according to the characteristics that true specific gravities of biurea and ADC are the same and particular diameters of the two are different, the particle size of the ADC generated by the reaction is controlled through using a swirl rising liquid flow to perform hierarchical control; and a second stage reaction is a discontinuous reaction, and all reactions are guaranteed to reach endpoint, so that the product quality is guaranteed. The process has the advantages that when the ADC is generated by the reactions, the particle size of the ADC foaming agent can be controlled, and a later crushing process can be reduced, so that an original crystal state is not physically damaged, and meanwhile, the particle size of the product is narrow, and because most reactions are finished in the first stage, batch differences between single kettles are also greatly reduced, and the use stability of the ADC foaming agent is more in favor of being improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
Method for comprehensively utilizing hydrazine hydrate by-product sodium carbonate decahydrate through urea method
ActiveCN103274432AIncrease concentrationHigh economic valueCarbonate preparationCooking & bakingSodium bicarbonate
The invention provides a method for comprehensively utilizing hydrazine hydrate by-product sodium carbonate decahydrate through a urea method. The method comprises the following steps: pulping sodium carbonate decahydrate subjected to freezing crystallization, heating up, forming a sodium carbonate solution with a certain concentration, filtering, removing the impurities, introducing CO2 and carbonizing in a carbonizing tower so as to generate sodium bicarbonate, centrifuging and separating the sodium bicarbonate generated in the reaction, and drying to obtain baking soda; taking a small amount of finished baking soda, adding the baking soda into a hydrazine hydrate solution prepared by the urea method, controlling the PH value, and neutralizing the excessive caustic soda solution in the crude hydrazine solution. The method has the beneficial effects that the sodium carbonate decahydrate which serves as the waste for performing low-price treatment is comprehensively utilized, and the economic value of the by-product is greatly improved; and moreover, more sodium carbonate decahydrate can be obtained in the subsequent freezing sodium carbonate removal link, the concentration of the hydrazine hydrate in the crude hydrazine is improved, and the consumption of acid in the biurea condensation reaction process is reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
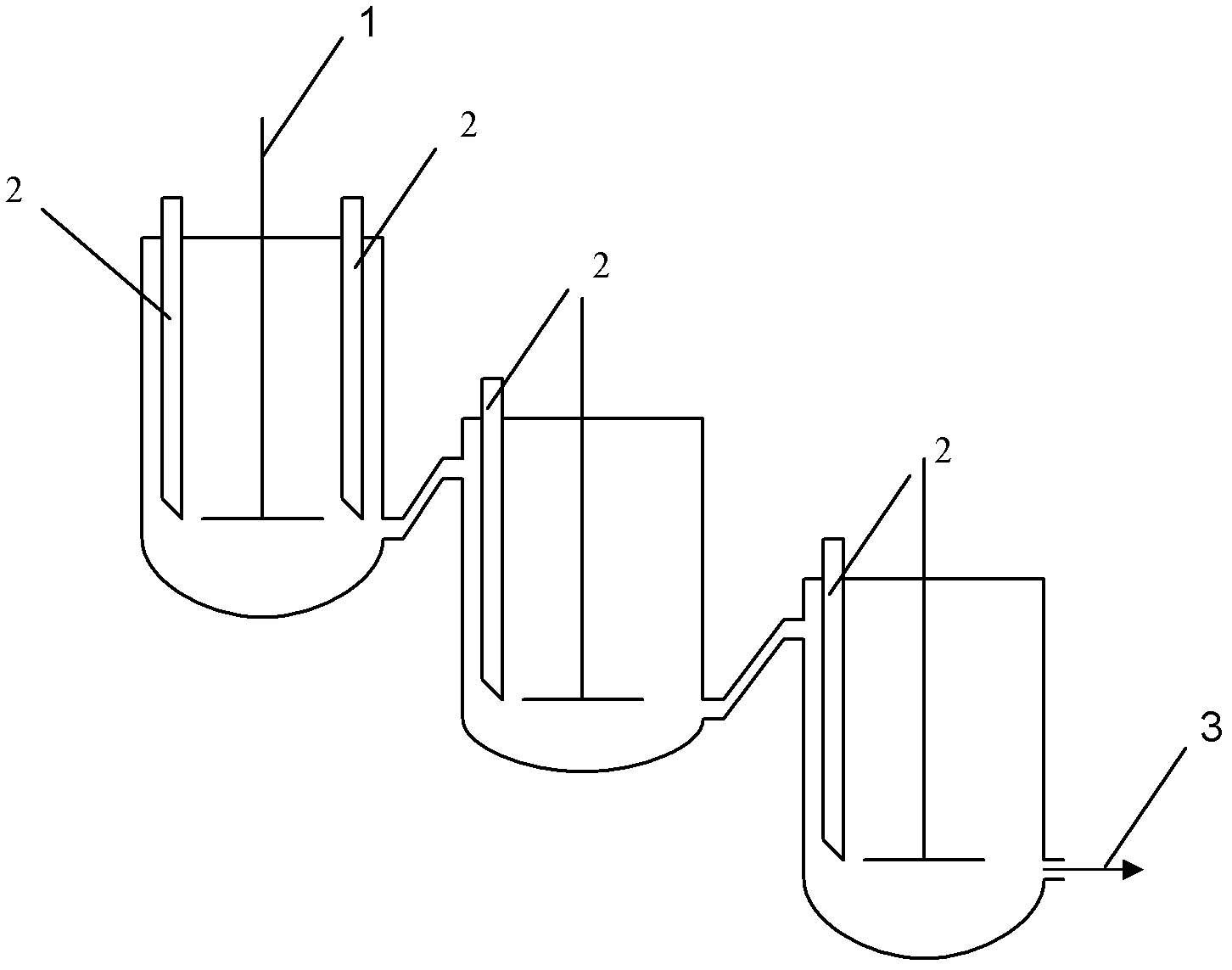
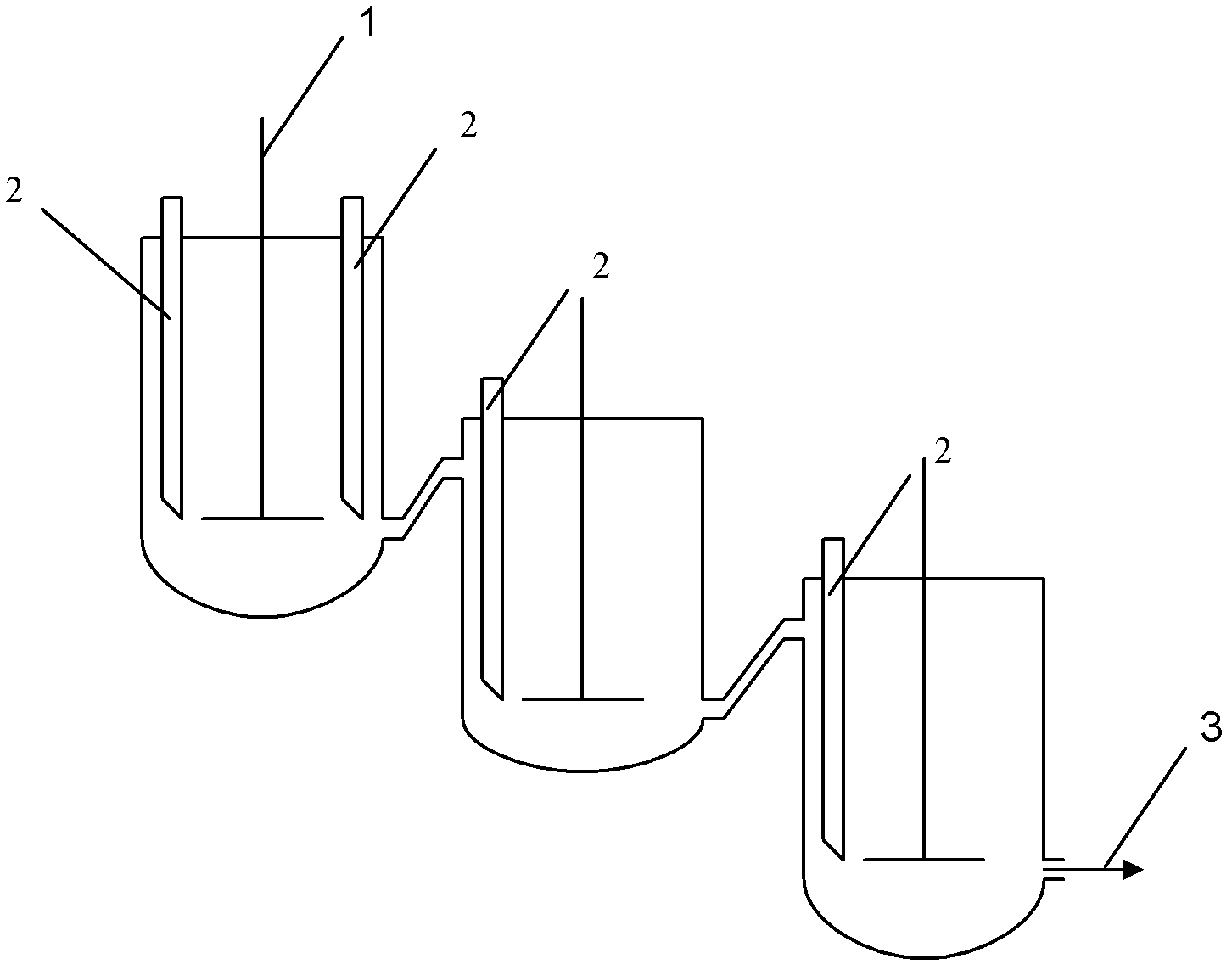
Process for continuously producing azodicarbonamide (ADC) foaming agents in multi-kettle serial-connection mode
The invention relates to a process for continuously producing azodicarbonamide (ADC) foaming agents in multi-kettle serial-connection mode, which includes a hydrazine hydrate and urea blending into biurea process and a biurea and chlorine oxidizing into ADC foaming agent process. In the biurea and chlorine oxidizing into ADC foaming agent process, two and more than two reaction kettles are adopted to be connected in series, and continuous reaction is achieved by continuously feeding and continuously stirring. Furthermore, in the hydrazine hydrate and urea blending into biurea process, two and more than two reaction kettles are adopted to be connected in series, and continuous reaction is achieved by continuously feeding and continuously stirring. The process has the advantages that by adopting the process for continuously producing ADC foaming agents in multi-kettle serial-connection mode, continuous production can be achieved, yield can be improved, uniformity of product quality can be achieved, reaction is controllable, and quality difference of products caused by multi-kettle reaction is avoided.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
Recycling method of byproduct saline during preparation of hydrazine hydrate by using urea method
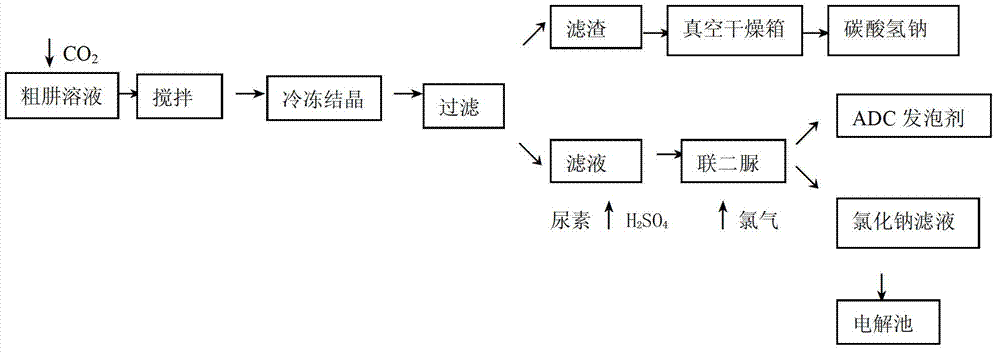
The invention discloses a recycling method of a byproduct saline during preparation of hydrazine hydrate by using a urea method. The method includes adding excess CO2 into a coarse hydrazine solution, and keeping the negative pressure of a steel cylinder containing the CO2 to be 100pa to 150pa and the flow to be 0.5-0.8mol / L; stirring the mixture continuously for 0.5 hour when the negative pressure in the steel cylinder is zero; freezing and crystallizing the solution through general freezing brine, and controlling the temperature in a range from 2 DEG C to 6 DEG C and the freezing time to be 2 hours; performing cold filtering to obtain filter residues, drying the filter residues in a vacuum drying oven for 4 hours, and keeping the temperature of the drying oven to be 35 DEG C to 45 DEG C; adding urea into the filtrate obtained through cold filtering, adding sulfuric acids to regulate the pH to be 3 to 4, controlling the temperature to be 106 DEG C to 120 DEG C, and reacting the mixture for 2 hours; and feeding chlorine into a biurea reaction still to perform oxidation to obtain the resultant ADC foaming agents, wherein the filtrate is sent to an electrolytic tank. The recycling method of byproduct saline during preparation of hydrazine hydrate by using the urea method has the advantages that the byproduct sodium salt of the hydrazine hydrate is fully recycled, the cost is reduced, and the method is a green chemical process.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
Grafting reaction-type water-retaining slow-release nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106431505AAvoid defects such as high core costShort processOrganic phosphatic fertilisersChemical reactionBiurea
The invention relates to a grafting reaction-type water-retaining slow-release nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding a potassium dihydrogen phosphate solution and industrial urea into a reactor to prepare a potassium biurea phosphate solution, adding an initiator ammonium persulfate into acrylic acid, sodium acrylate and N, N'-methylene bisacrylamide at 0 DEG C and in a nitrogen atmosphere, then adding the potassium diurea phosphate solution, and enabling reaction for 20-90 min; performing vacuum drying at 80 DEG C, and grinding to prepare the grafting reaction-type water-retaining slow-release nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer. In the grafting reaction-type water-retaining slow-release nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer, urea and potassium dihydrogen phosphate are grafted onto branched chains of a water-retaining polymer, so that the number of water-retaining groups of a water-retaining agent is increased and the water-retaining performance can be effectively improved; nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium nutrients on grafted chains can break away from a main chain of the water-retaining polymer through hydrolysis, then penetrate through a colloidal network structure and are released so as to achieve slow-release functions of the nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium nutrients.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing ADC (azodicarbonamide) foaming agent by chlorine dioxide biurea
InactiveCN103193685AQuality improvementReduced particle size distribution widthOrganic chemistryPartial oxidationChemical oxygen demand
The invention discloses a method for producing an ADC (azodicarbonamide) foaming agent by chlorine dioxide biurea. The method concretely comprises the following steps of A, adding a part of water to biurea, recovering a part of oxidized mother liquor to prepare 20-40% biurea slurry containing acid, adding an oxide additive of which the mass ratio of the biurea is 0.3-10%; B, adding the biurea slurry into an oxidizing kettle, exhausting by an exhaust fan, keeping micro-negative pressure inside the oxidizing kettle, namely -1 to -10kPa; C, opening a chlorine valve, leading chlorine, and controlling the reaction temperature at 20-60 DEG C by a refrigerant, oxidizing until the reaction is finished; keeping the micro-negative pressure inside the oxidizing kettle in an oxidizing process; D, separating, washing and drying the slurry to prepare the product ADC foaming agent after the reaction is finished; recycling a part of oxidizing mother liquor, and carrying out wastewater treatment on a part of oxidizing mother liquor. The method has the beneficial effects that the quality of the ADC product is improved by adopting these methods; the particle size distribution width is reduced; the gas forming amount is improved; a reaction terminal point is easier to control; the peroxide phenomenon is reduced; the product yield is improved; the peroxide side reaction is reduced; and the COD (chemical oxygen demand) content of the waste liquid is also reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
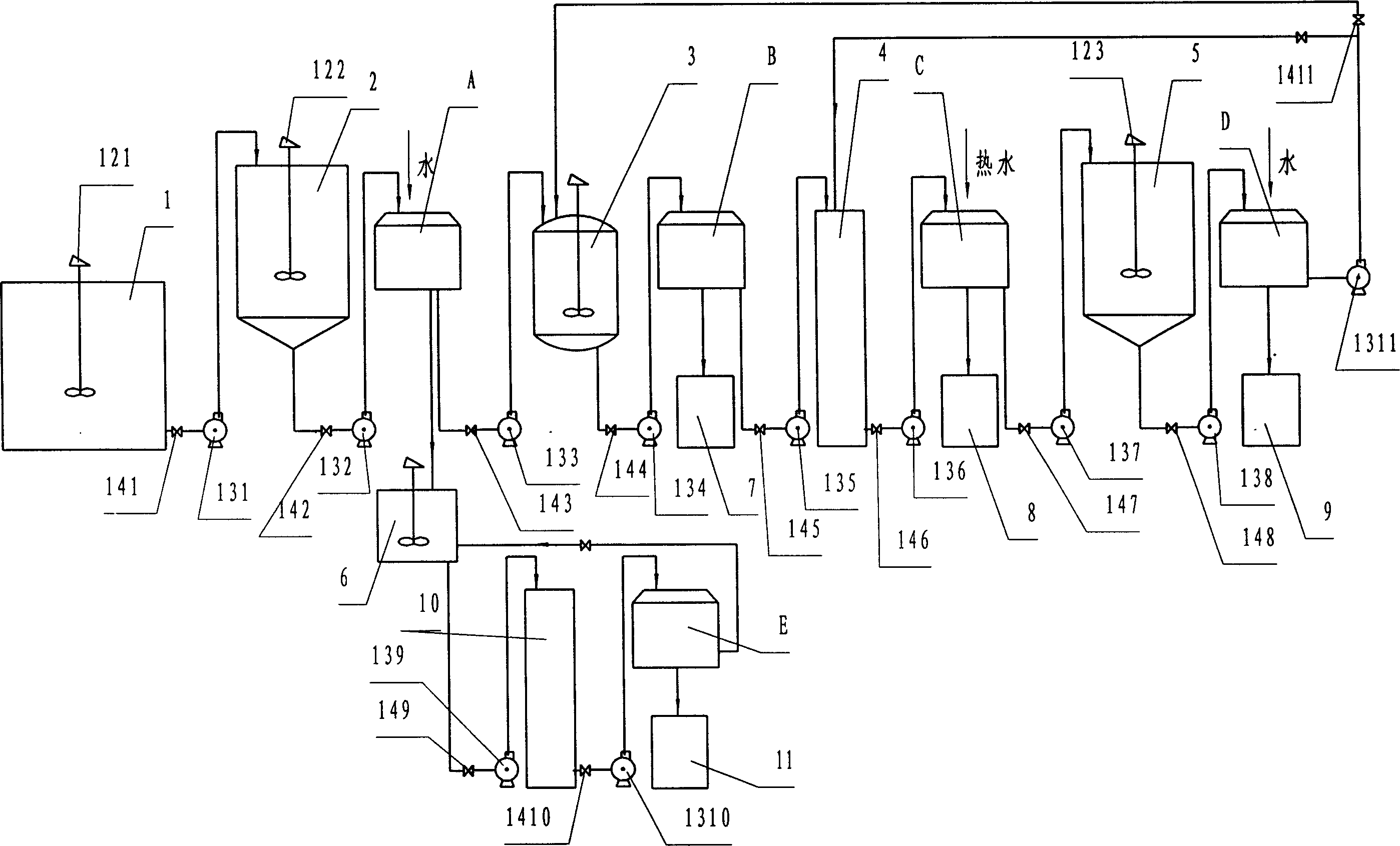
Method for comprehensively utilizing waste gas and waste liquid in production of biurea
InactiveCN101709043AHigh concentration improvement rateSolve pollutionUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationBiureaHydrazine compound
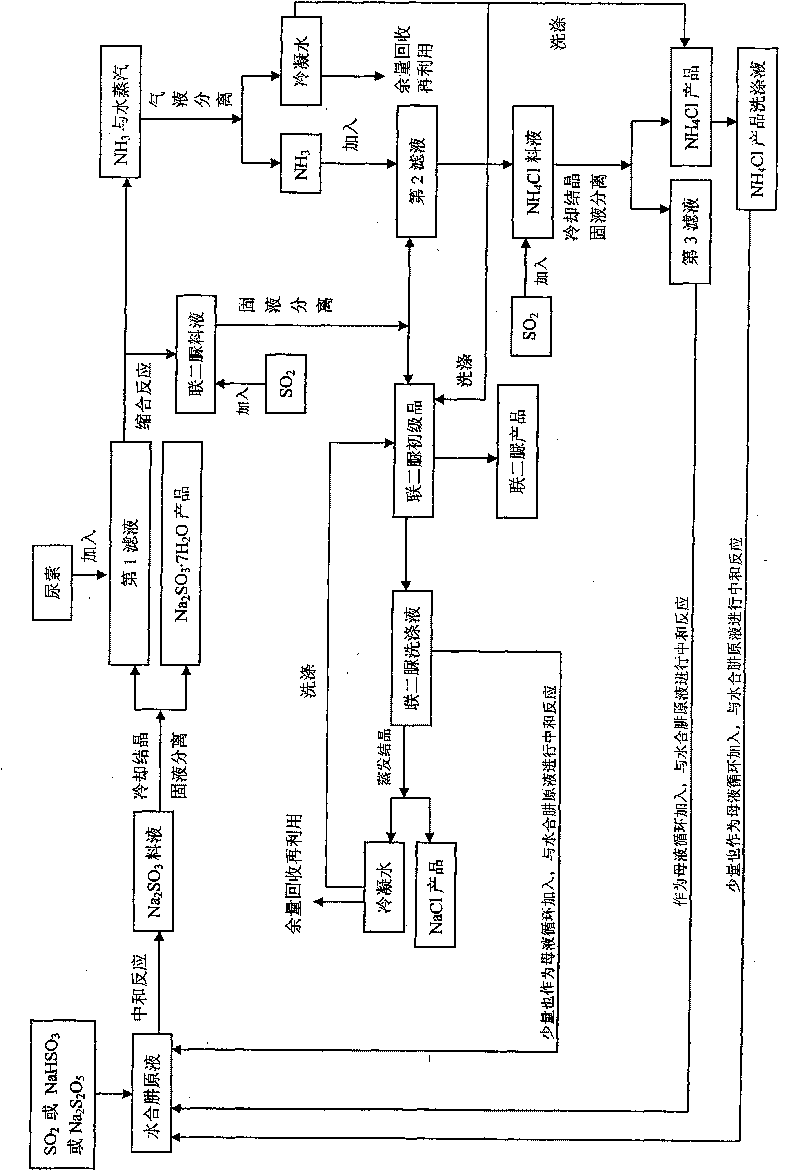
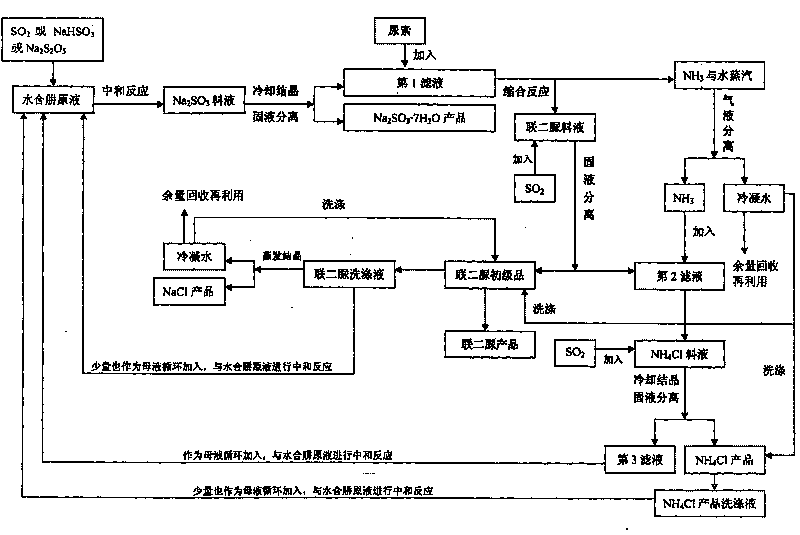
The invention provides a method for comprehensively utilizing a waste gas and waste liquid in the production of biurea, which belongs to the technical field of comprehensive utilization of the waste gas and waste liquid in the production of the biurea (ADC product midbody). Hydrazine hydrate, urea and a SO2 gas used as reaction raw materials and an intermediate product NaHSO3 used as circulating mother liquor carry out neutralization reaction, condensation reaction, SO2 gas absorption and NH3 gas absorption to generate products of Na2SO3.7H2O, biurea and NH4Cl, and biurea washing liquid is evaporated and crystallized to obtain a NaCl product. The invention obtains the products of Na2SO3 and NH4Cl with high additional values by the comprehensive utilization of the waste gas and the waste liquid in the production of the biurea and solves the problem of environmental pollution caused by the abundant discharge of secondary products which are (NH4)SO4, Na2SO4 and NaCl in the production process of a traditional process.
Owner:福建省邵武市榕丰化工有限公司
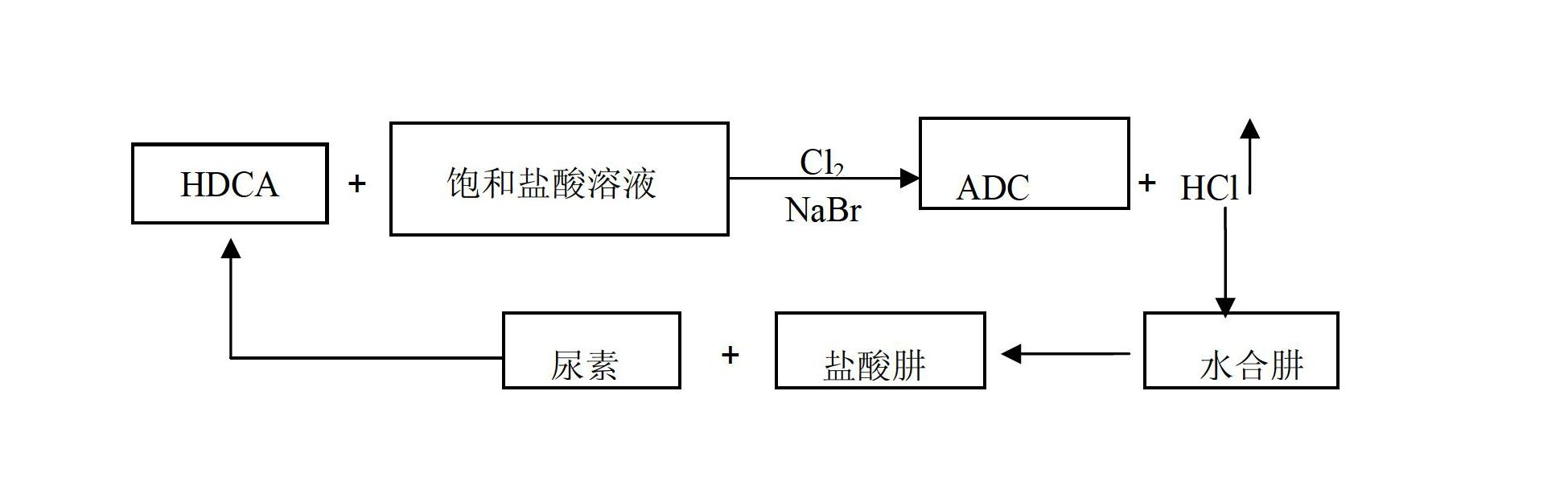
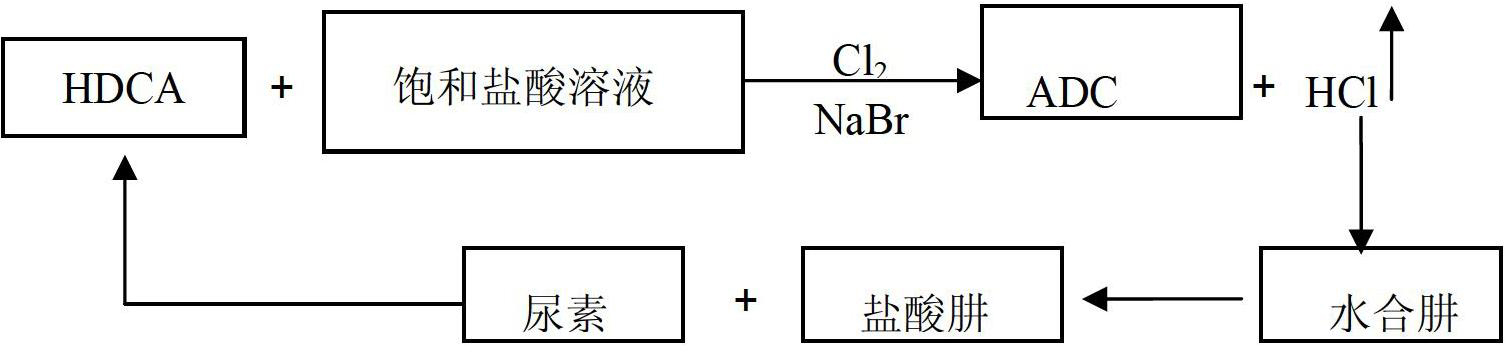
Method for producing ADC foaming agent by using chlorine gas-oxidized HDCA (biurea) in saturated hydrochloric acid solution
ActiveCN102675158AAvoid unexploitable weaknessesIncrease reaction rateOrganic chemistryBiureaHydrazine compound
The invention relates to a method for producing an ADC foaming agent by using chlorine gas-oxidized HDCA (biurea) in a saturated hydrochloric acid solution. The method comprises the following steps of: weighing a certain mass of HDCA, water and saturated hydrochloric acid solution in the mass ratio of 3:1:1, putting into a reaction kettle, and stirring uniformly to obtain slurry; weighing sodium bromide of which the amount is 3-8 percent by mass of the HDCA, adding into the reaction kettle, and connecting a chlorine gas pipeline to the reaction kettle; adding chorine gas at the flow of 0.1-0.5mol / h for oxidizing, wherein chlorine hydride gas overflows continuously in a reacting process; and controlling the reaction temperature at 25-75 DEG C till reacting completely. The method has the beneficial effects: ADCA (Azodicarbonamide) is provided by using chlorine gas-oxidized HDCA in the saturated hydrochloric acid solution, so that the defect of incapability of utilizing dilute hydrochloric acid serving as a byproduct in the conventional process can be avoided. A chlorinated hydrazine is produced by using chlorine hydride gas serving as a byproduct and a hydrazine hydrate, so that the reaction rate can be increased, and resources are saved. According to the method, circular utilization of all raw materials and side products can be realized.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
Synthesis method of food grade modified foaming agent azodicarbonamide
The invention discloses a synthesis method of food grade modified foaming agent azodicarbonamide. Biurea is used as as raw material, and under the effect of a cerium composite catalyst and a reaction solvent, the temperature of the solution is adjusted to 60-70 DEG, the pH value is 2-5, catalytic oxidation reaction is carried out for 3-5h under the oxygen condition, and then the food grade modified foaming agent azodicarbonamide can be obtained through filtering and purifying. The synthesis method disclosed by the invention has a novel process, low requirements on reaction equipment, and is environment-friendly and safe. A product obtained by the method contains fewer impurities, has good quality and high yield, and can be used in food-grade additives.
Owner:GUANGDONG FOOD IND INST
Novel foaming formula of polypropylene plastic
The present invention relates to a plastic foaming formula, particularly a novel foaming formula of polypropylene plastic. The foaming formula is characterized by including the following components: by weight, 85%-99.8% of polypropylene plastic, 0.1%-10% of an AC foaming agent, and 0.1%-10% of an N1000 foaming agent. The foaming formula is characterized by including 90% of the polypropylene plastic, 5% of the AC foaming agent, and 5% of the N1000 foaming agent. The main ingredients of the AC foaming agent include azodicarbonamide, a small amount of biurea and calcium carbonate. The AC foaming agent is a commercial product produced by Jiangsu SOPO Chemical Company. The main ingredients of the N1000 foaming agent include poly sodium bicarbonate, a small amount of sodium carbonate and sodium chloride. The N1000 foaming agent is a commercial product produced by Guangzhou Huike Chemical Co., Ltd. The foaming formula has the advantage of stable foaming, no obvious contraction in appearance, light weight, high strength, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHENGGUANG SCI & TECH
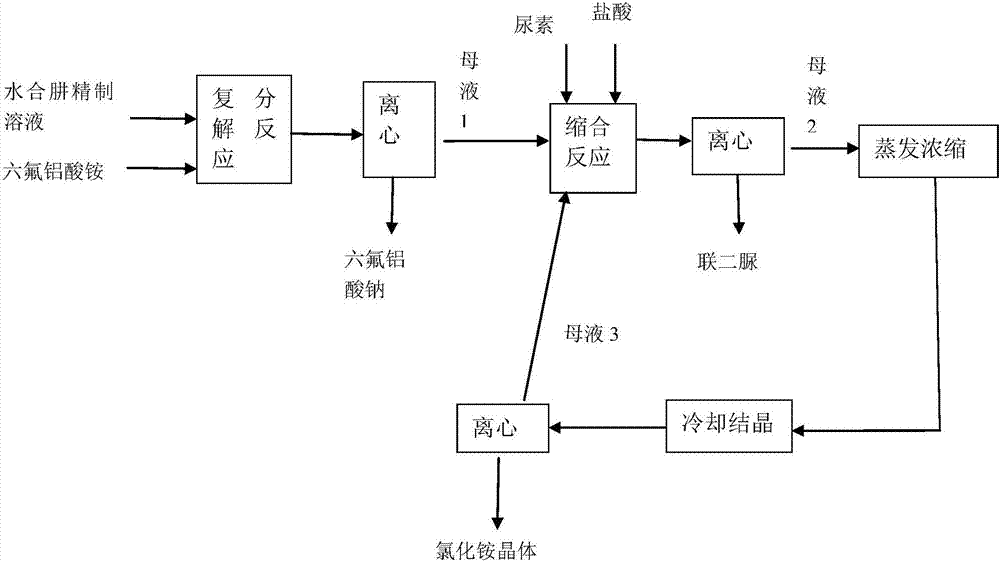
Method for co-producing sodium hexafluoroaluminate and biurea
InactiveCN107055581ANo emissionsFully producedOrganic chemistryAluminium fluoridesAmmonium hexafluoroaluminateBiurea
The invention discloses a method for co-producing sodium hexafluoroaluminate and biurea. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding ammonium hexafluoaluminate into a sodium carbonate-removed refined hydrazine hydrate solution wherein sodium chloride in the refined hydrazine hydrate solution performs double decomposition reaction with the ammonium hexafluoaluminate, thus generating the sodium hexafluoroaluminate and ammonium chloride, and separating the sodium fluoroaluminate, thus obtaining a mother solution 1; (2) adding urea and hydrochloric acid into the mother solution 1 where hydrazine hydrate and urea in the mother solution 1 performs condensation reaction with the hydrochloric acid, thus generating the biurea and ammonium chloride, and separating the biurea, thus obtaining a mother liquid 2. According to the method, the sodium hexafluoroaluminate, the biurea and the ammonium chloride which are high in yield and high in purity can be respectively produced; the yield of the sodium hexafluoroaluminate is up to 99.3 percent or above, and the contents of fluorine and aluminum in the sodium hexafluoroaluminate can meet the requirement of the national standard; the yield of the biurea is up to 97 percent or above, and the purity is 98 percent or above; the yield of the ammonium chloride is 98 percent or above, and the purity can meet the industrial standard.
Owner:衡阳市锦轩化工有限公司
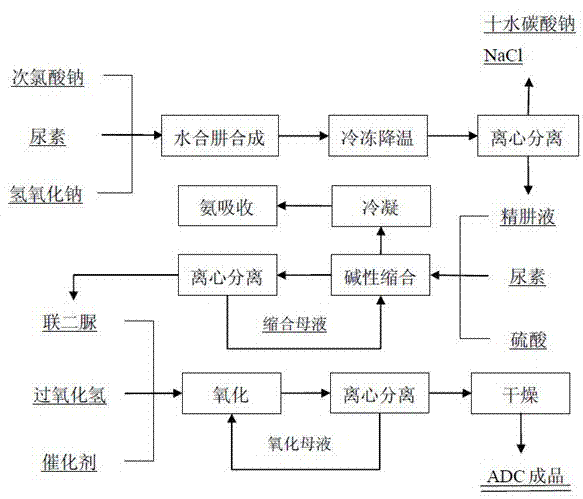
Preparation process of azodicarbonamide
The invention discloses a preparation process of azodicarbonamide. The process comprises the steps: 1) synthesizing a hydrazine hydrate crude product by a urea method; 2) refining hydrazine hydrate by a freeze separation method; 3) preparing biurea by alkaline condensation; and 4) obtaining the azodicarbonamide by a hydrogen peroxide oxidation method. According to the preparation process, different procedure production methods are analyzed and compared, the hydrazine hydrate is synthesized by selecting the urea method; refined hydrazine is obtained from crude hydrazine by the freeze separation method, biurea is prepared in a continuous condensation manner by an alkaline process, and finally, the azodicarbonamide is generated by the biurea oxidized by the hydrogen peroxide. Thus, the traditional acid condensation is changed into alkaline condensation to synthesize the biurea, consumption of raw materials and environmental pollution are reduced, hydrogen peroxide is selected as an oxidant in the oxidation process of the biurea, just by-product water is generated in the reaction, the environment is not polluted, and a green chemical pathway is taken.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Recovery method of heavily polluated substance produced during production of foaming agent and device
InactiveCN1513835ASimple processReasonable workmanshipOrganic chemistryTransportation and packagingRecovery methodFoaming agent
A process for recovering the main pollutants generated during production of foaming agent ADC includes condensation between hydrazine solution and urea, filtering to obtain biurea and the first filtrate, evaporating the first filtrate, centrifugal separating to obtain sodium chloride and the second filtrate, freezing the second filtrate to 10- -5 deg.C, centrifugal separating to obtain ammonium chloride and the third filtrate, evaporating the third filtrate several times, freezing to obtain the crystal of sodium chloride or ammonium chloride, and returning the residual mother liquid back to condensater.
Owner:郑守樽 +1
Novel method of simply controlling particle sizes of ADC (azodicarbonamide) product
The invention discloses a novel method of easily controlling the particle sizes of an ADC (azodicarbonamide) product. The novel method comprises the specific step of adjusting the particle sizes of a foaming agent by adding aldehyde compounds when an oxidizing agent is used for oxidizing biurea, wherein the additive amount of the aldehyde compounds accounts for 0.1%-0.5% of mass of the biurea. The particle sizes of the foaming agent can be effectively reduced by adding the aldehyde compounds, thus greatly saving the subsequent treatment cost and improving the dispersity of the ADC foaming agent. The novel method has the beneficial effects that the novel method is simple, has no need of changing the traditional technologies and equipment and is relatively low in cost, the usability of the foaming agent can be improved, the subsequent treatment cost of the foaming agent is reduced, and the added value of the product is increased.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
Method for preparing azodicarbonamide by oxygen oxidation
InactiveCN106008279ASolve existing problems such as corrosion equipmentSolve problems such as corrosion equipmentOrganic chemistryBiureaManganese
The invention relates to a method for preparing azodicarbonamide by oxygen oxidation. The method comprises the following steps: taking biurea as a raw material; dissolving the biurea in a solvent to form a solution; adding a cobalt manganese catalyst in the solution; feeding oxygen under joint catalysis of the cobalt manganese catalyst and under the neutrality condition that the temperature of the solution is kept at 60-100 DEG C and carrying out oxidation reaction; after reaction is conducted for 6-8 hours, purifying to obtain the azodicarbonamide with uniform grain size. By the method for preparing the azodicarbonamide by oxygen oxidation, a preparation process is simple, requirements to equipment are low, and the prepared product is high in purity and uniform in grain size.
Owner:JIANGSU SOPO CHEM +2
Method for preparing compound ADC (azodicarbonamide) foaming agents with nano-particles
The invention discloses a method for preparing compound ADC (azodicarbonamide) foaming agents with nano-particles. The method includes steps of (1), synthesizing biurea; (2), preparing ADC; (3), preparing ZnO-SiO2 nano-powder; (4), proportionally mixing the ZnO-SiO2 nano-powder and the ADC which is a foaming agent with each other to obtain mixtures, and sufficiently grinding the mixtures. The method has the advantages that excellent activation effects can be realized by the compound ADC foaming agents with the nano-particles, and accordingly the quality of products can be greatly improved.
Owner:衡阳市锦轩化工有限公司
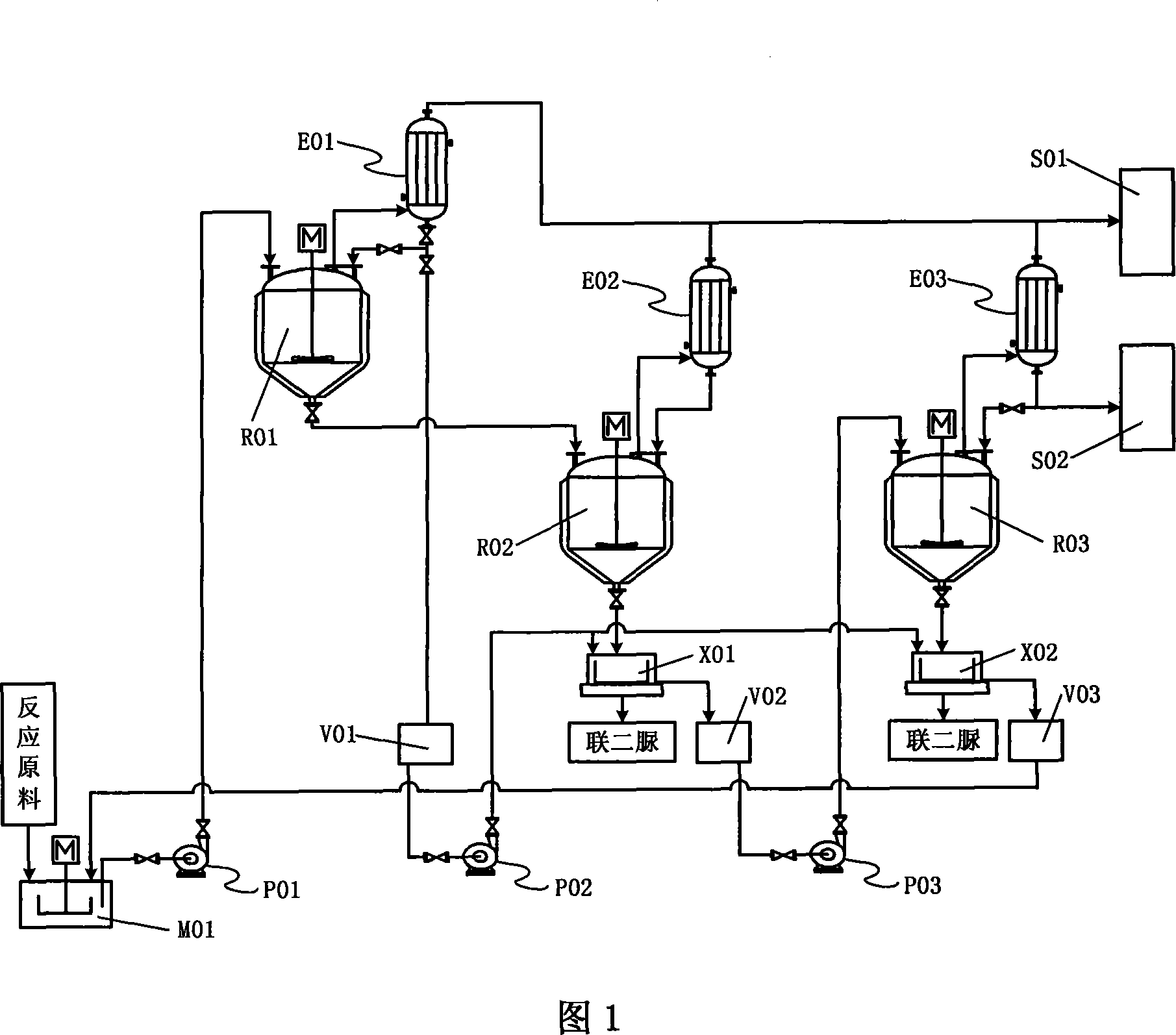
Biurea preparation device and preparation method
ActiveCN106220534AImprove conversion rateIncrease production capacityOrganic chemistryChemical industryBiureaHydrogen chloride
The invention discloses a biurea preparation device and preparation method. The biurea preparation device comprises a hydrogen chloride treatment mechanism and a condensation kettle, wherein the hydrogen chloride treatment mechanism comprises a cooler, a chlorine adsorber, a pressure pump and a flow meter which are sequentially connected in series through a first pipe. The condensation kettle comprises a kettle body, wherein a hydrogen chloride inlet, a liquid raw material inlet and a discharging outlet are formed in the kettle body, the hydrogen chloride inlet is connected with a flow meter outlet through a second pipe, and one end of the second pipe extends into the kettle body. The biurea preparation method adopting the biurea preparation device comprises the step of treated hydrogen chloride gas participates in biurea condensation reaction to prepare a biurea finished product. The biurea preparation device is combined with the biurea preparation method, and the purposes of saving energy, improving the yield of the single condensation kettle and improving the conversion rate of hydrazine hydrate are achieved in the biurea preparation process.
Owner:QINGHAI SALT LAKE IND
Method for reducing particle size of foaming agent
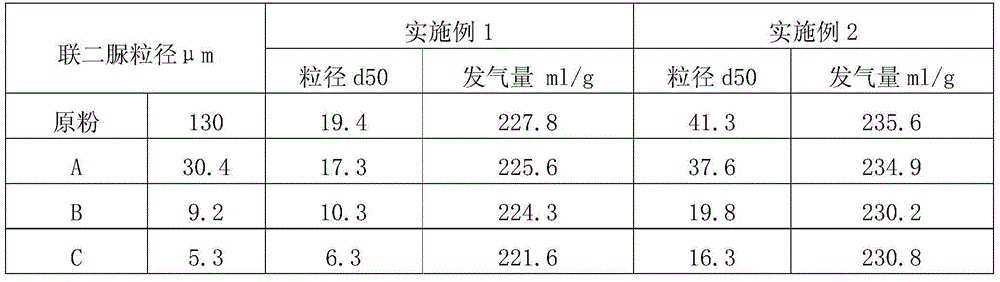
InactiveCN104478764ASolve problems that create foamSolve the problem of generating foamOrganic chemistryFoaming agentBiurea
The invention discloses a method for reducing the particle size of a foaming agent. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding water into a biurea solid to prepare a biurea suspension liquid of which the water content is 30% to 50%; (2) adding a defoaming agent of which the mass is 0.1% to 5% of the mass of the biurea into the biurea suspension liquid and adding a catalyst sodium bromide of which the mass is 1% to 5% of the mass of the biurea and a catalyst aid, namely an iron agent of which the mass is 0.5% to 2% of the mass of the biurea, and uniformly stirring; (3) continuously adding an excessive amount of an oxidant into the solution, continuously stirring at the temperature of 30 to 80 DEG C, and further stirring for 15-30 minutes after the oxidant is completely added dropwise; (4) after the reaction is ended, filtering and washing the solid, drying in an oven at the temperature of 105 DEG C until the solid is constant in weight, filtering and recycling the mother liquid. The method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the defoaming agent is taken as an additive, so that a remarkable particle size reduction effect is realized, and particles can be reduced from 40 micrometers to about 25 micrometers in particle size.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com