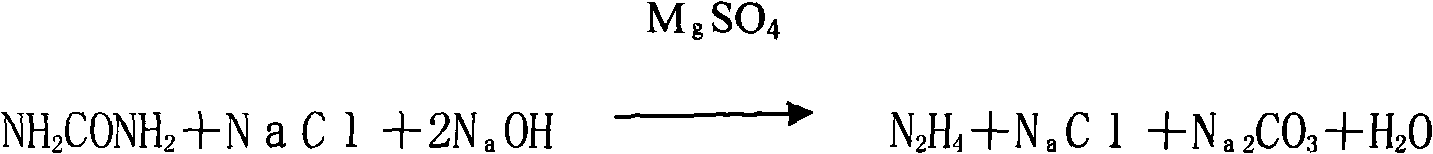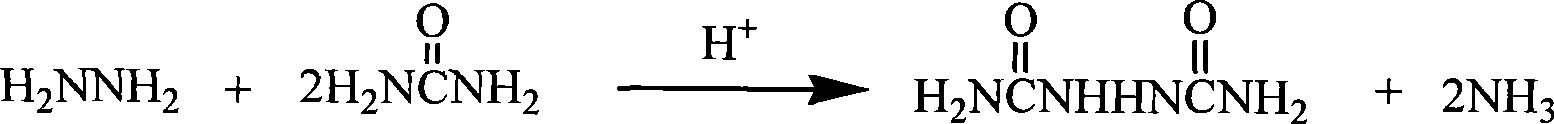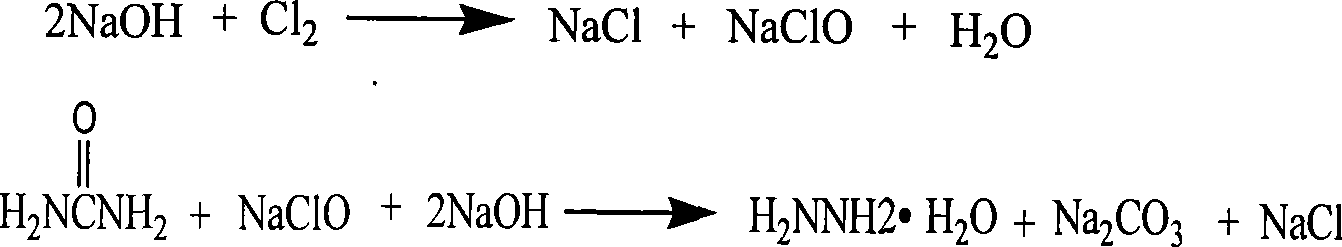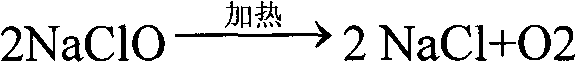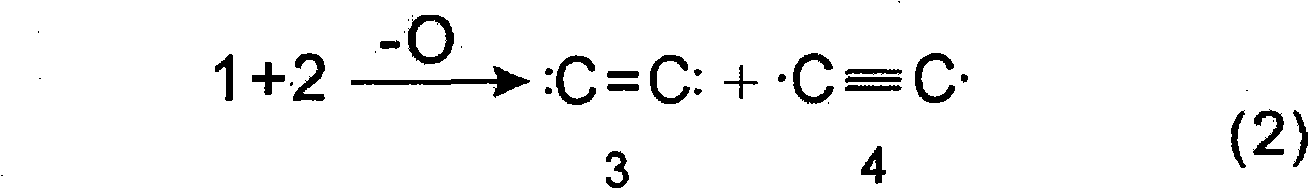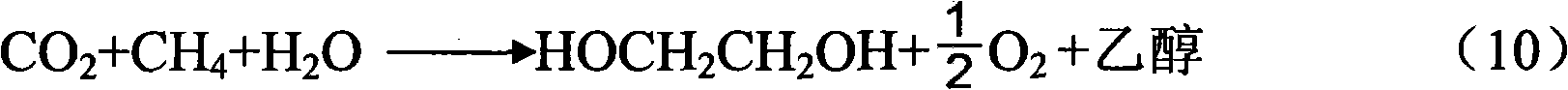Patents
Literature
123results about "Hydrazine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
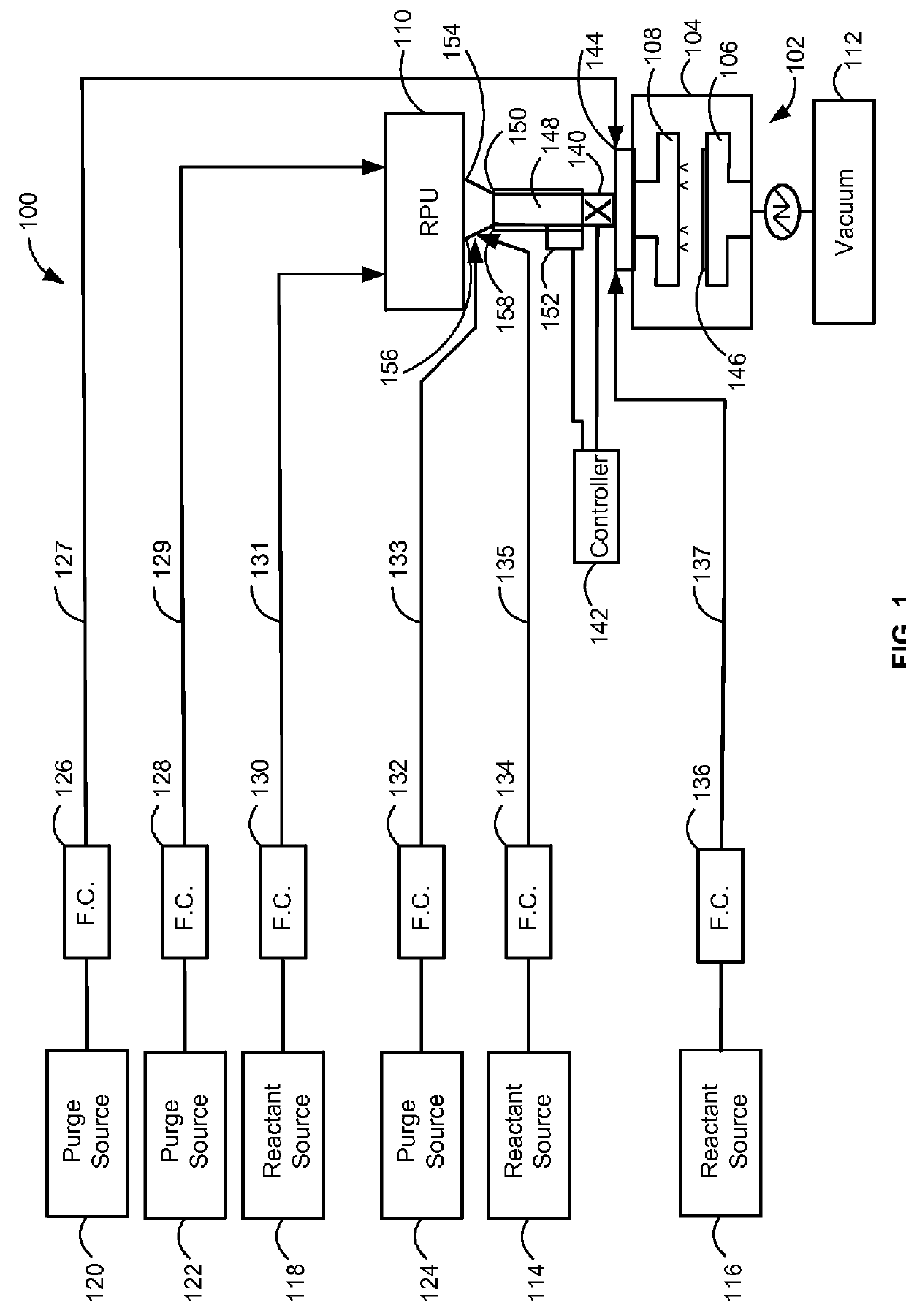
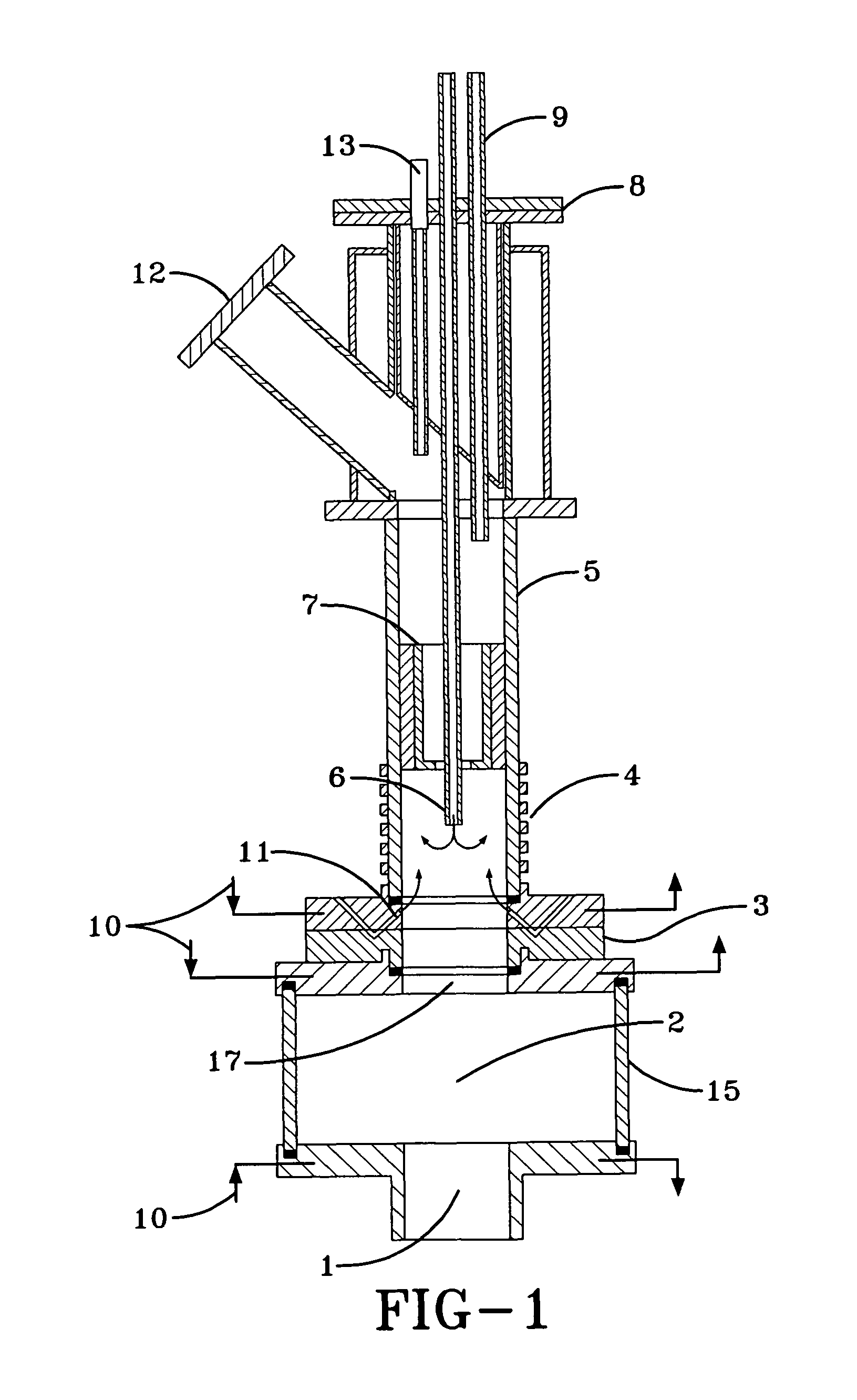
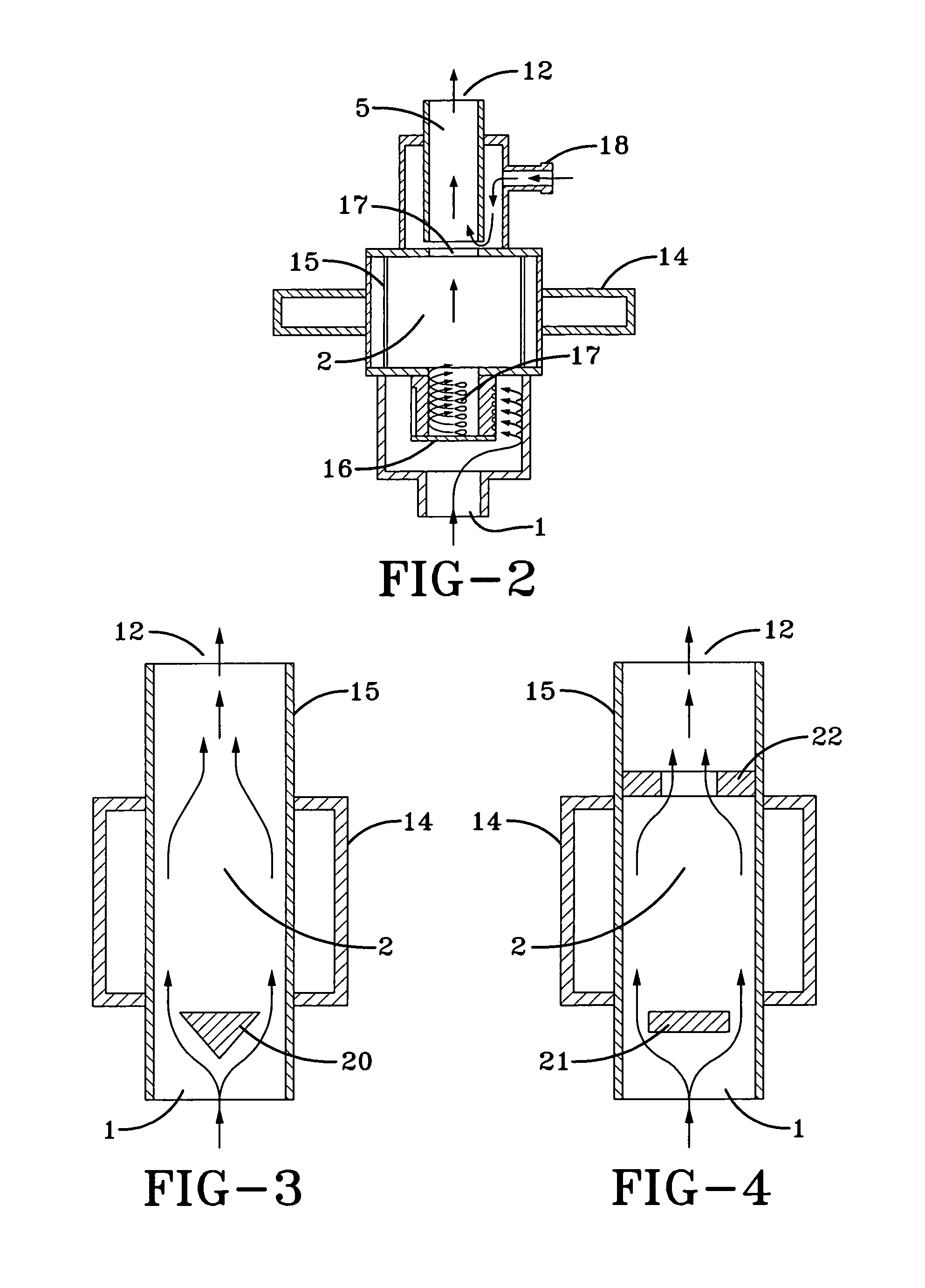
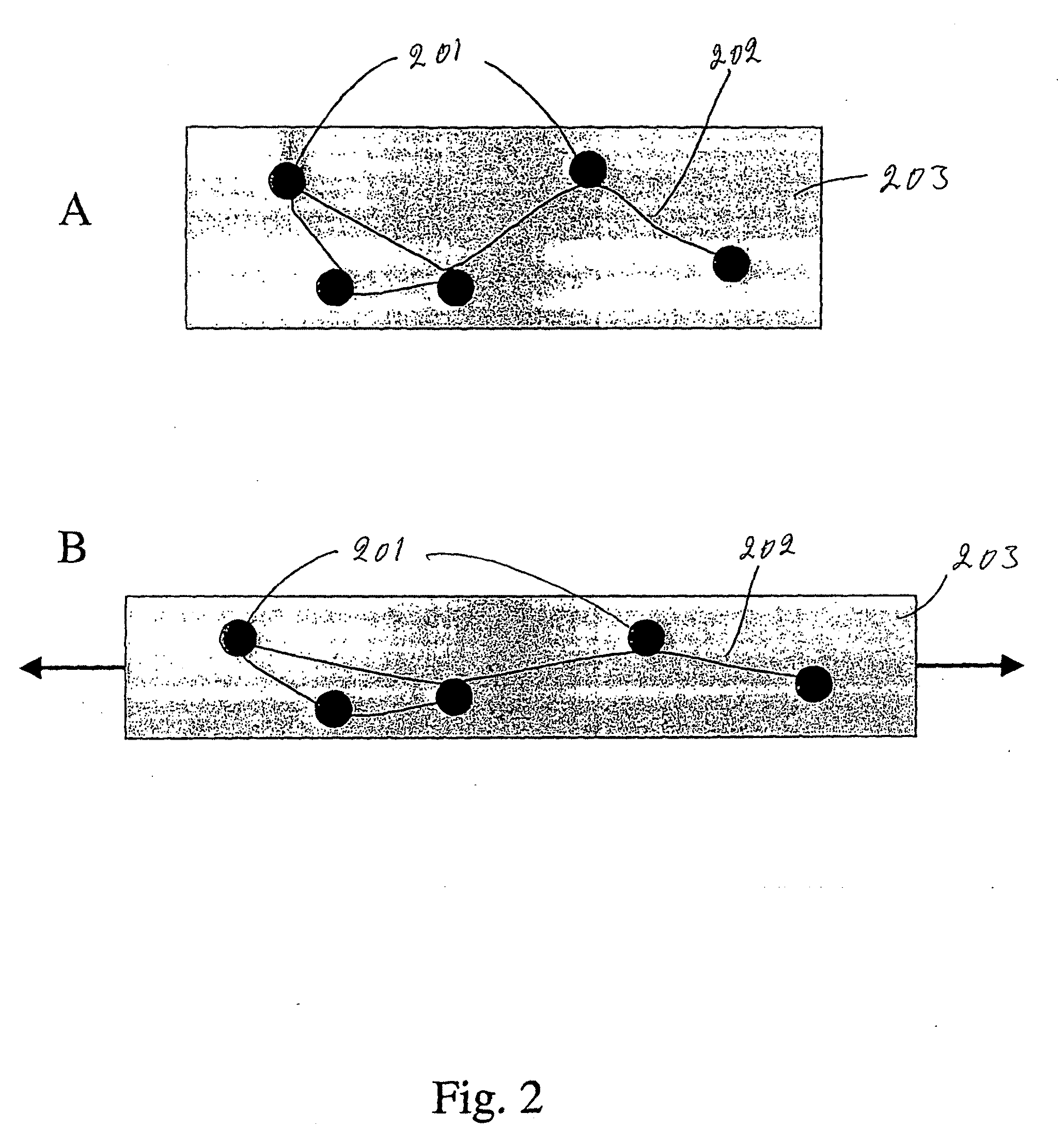
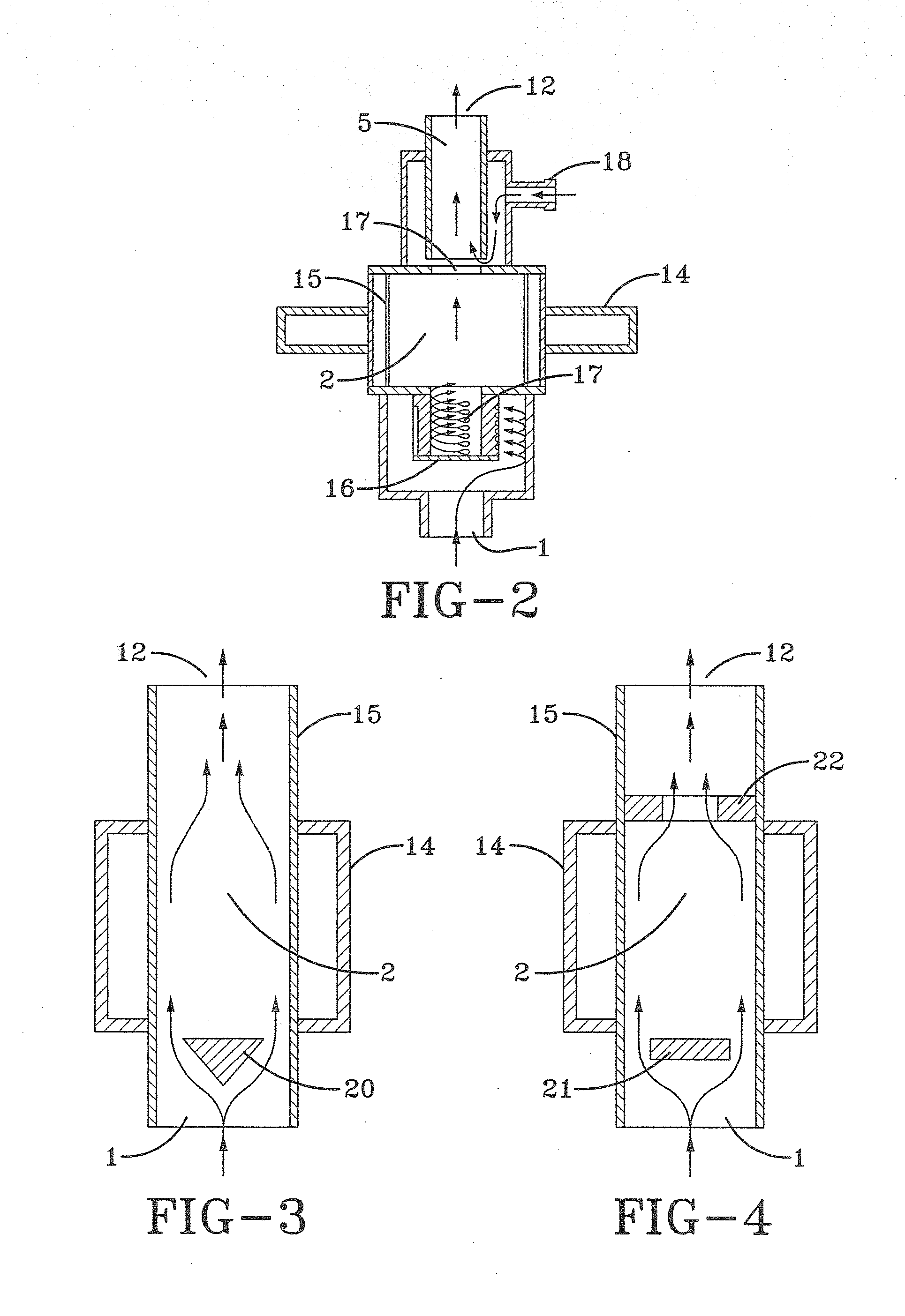
Method and system for in situ formation of gas-phase compounds
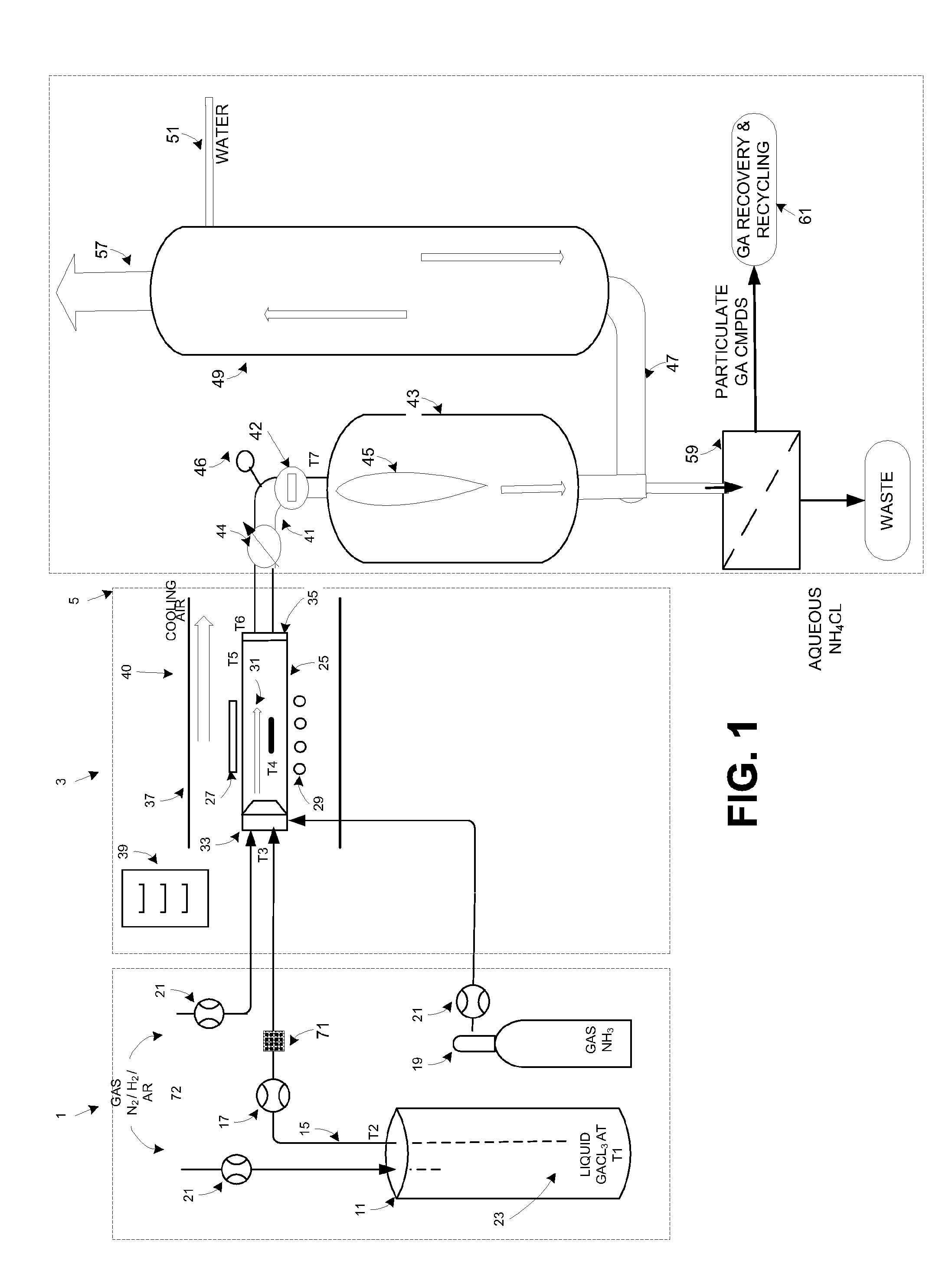
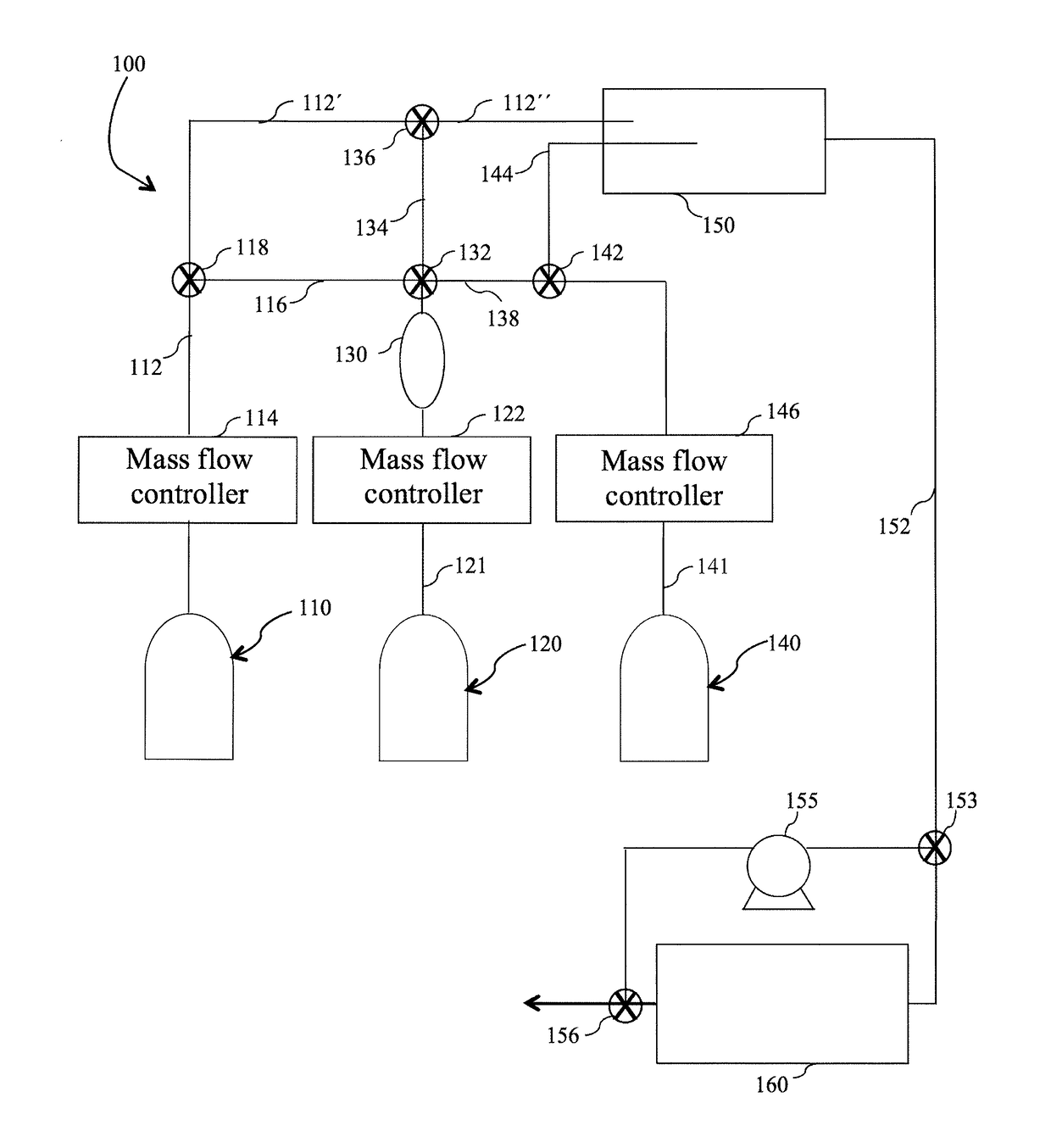
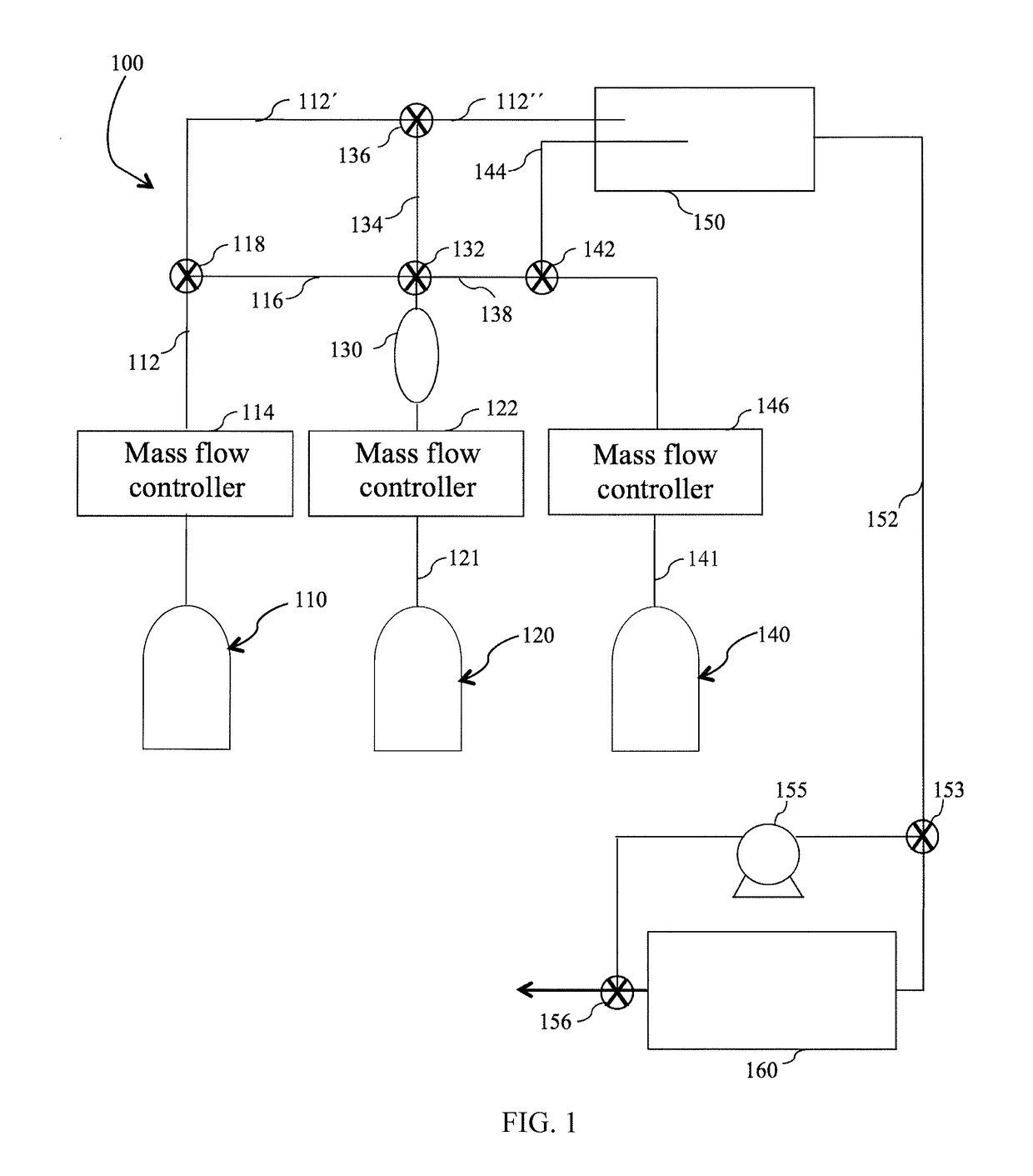
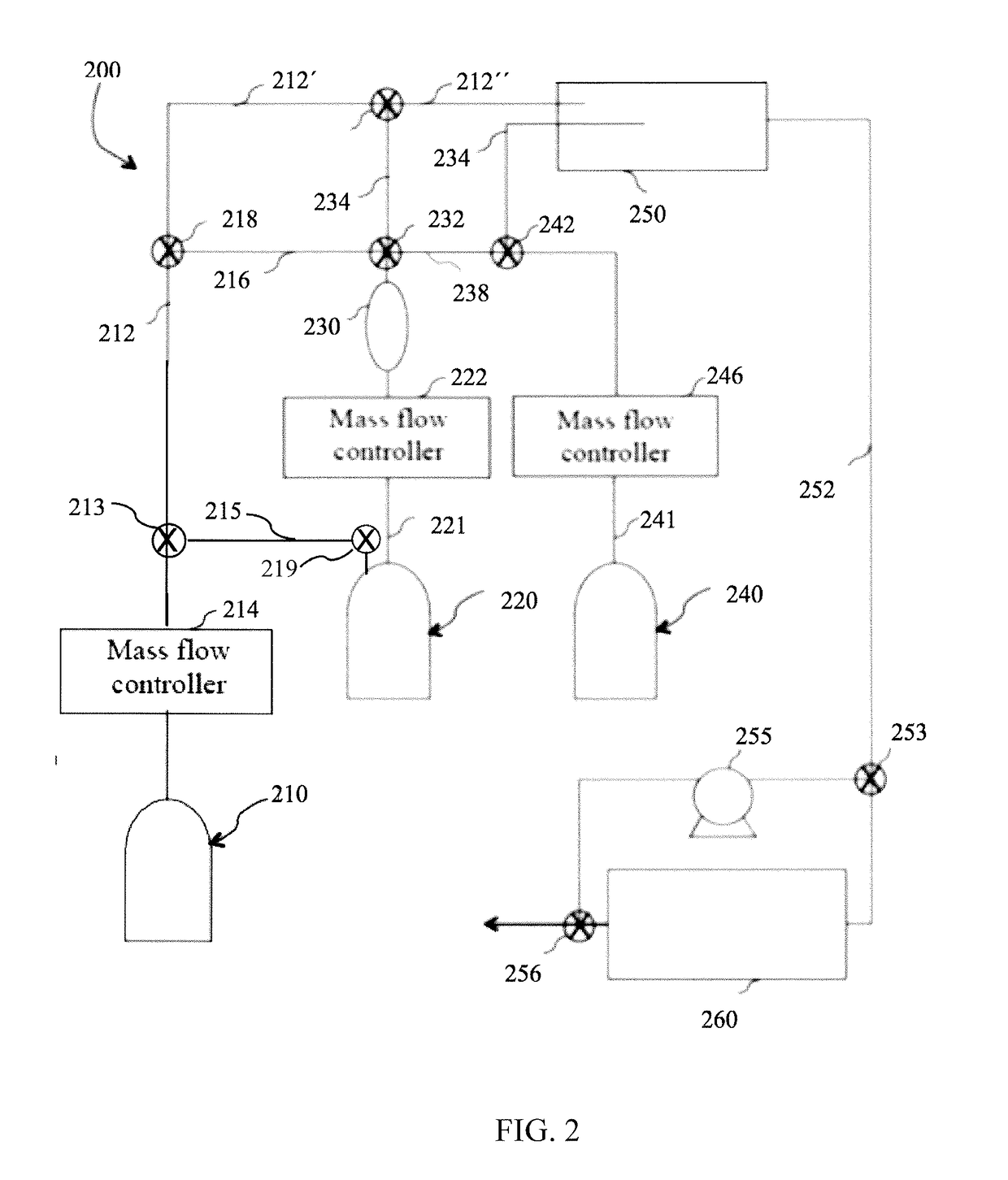
ActiveUS20160051964A1Process can be usedProcess control/regulationCell electrodesCompound aGas phase
A system and method for providing intermediate reactive species to a reaction chamber are disclosed. The system includes an intermediate reactive species formation chamber fluidly coupled to the reaction chamber to provide intermediate reactive species to the reaction chamber. A pressure control device can be used to control an operating pressure of the intermediate reactive species formation chamber, and a heater can be used to heat the intermediate reactive species formation chamber to a desired temperature.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Preparation method for propellant fuel
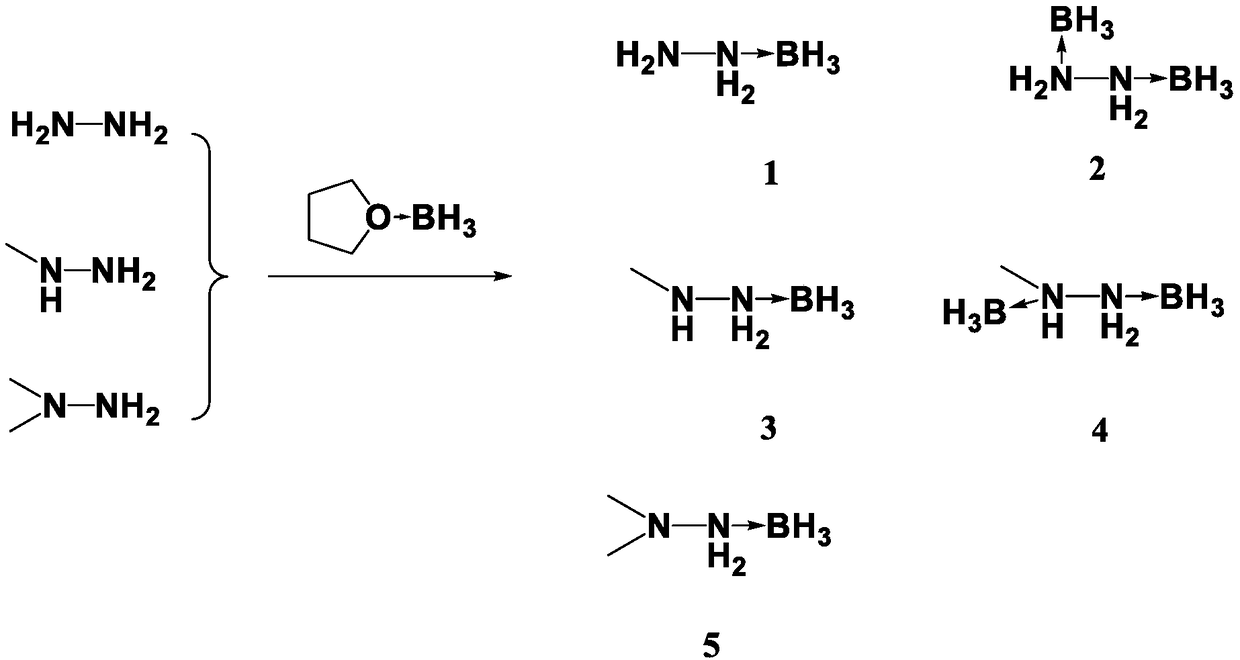
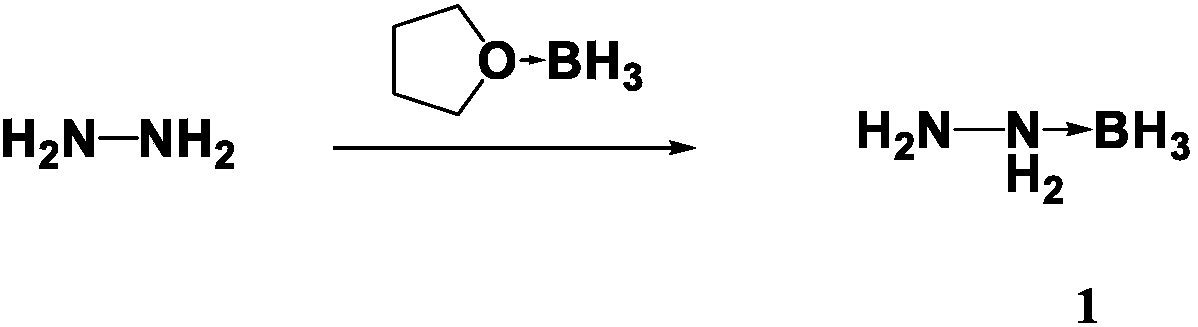
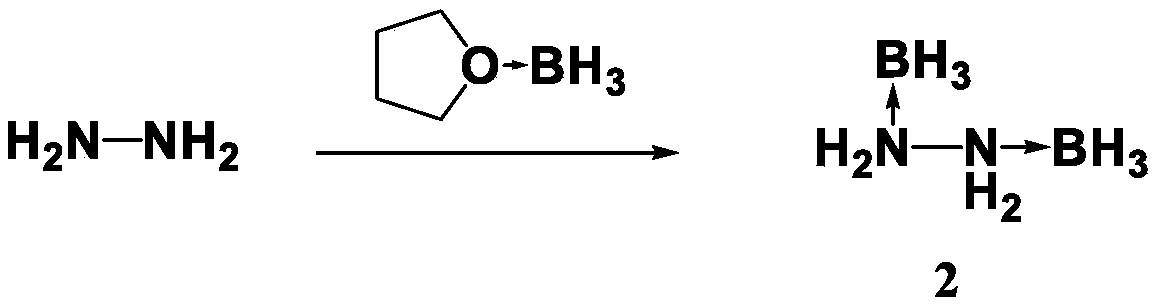
InactiveCN108910843AShorter ignition delay timeHazard reductionOrganic chemistryHydrazineEvaporationIgnition delay
The invention discloses a preparation method for propellant fuel. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing hydrazine or a methyl derivative thereof with a tetrahydrofuransolution of borane to perform a reaction, and after the reaction, performing rotary evaporation on the tetrahydrofuran solution to obtain a first product; adding a first solvent into the first product, then performing washing, and then performing rotary evaporation to remove the first solvent, so as to obtain a hydrazinoborane derivative. According to the method, hydroboration is carried out on ahighly-volatile hydrazine fuel and a methylated derivative of hydrazine, the obtained borohydride of the hydrazine is a colorless non-volatile liquid or a white solid, has no volatility and greatly reduces hazard of the hydrazine fuel, and is a novel aerospace propellant fuel since the ignition delay time of the hydrazine borofluoride is extremely short.
Owner:INST OF CHEM MATERIAL CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
Solution-based deposition process for metal chalcogenides
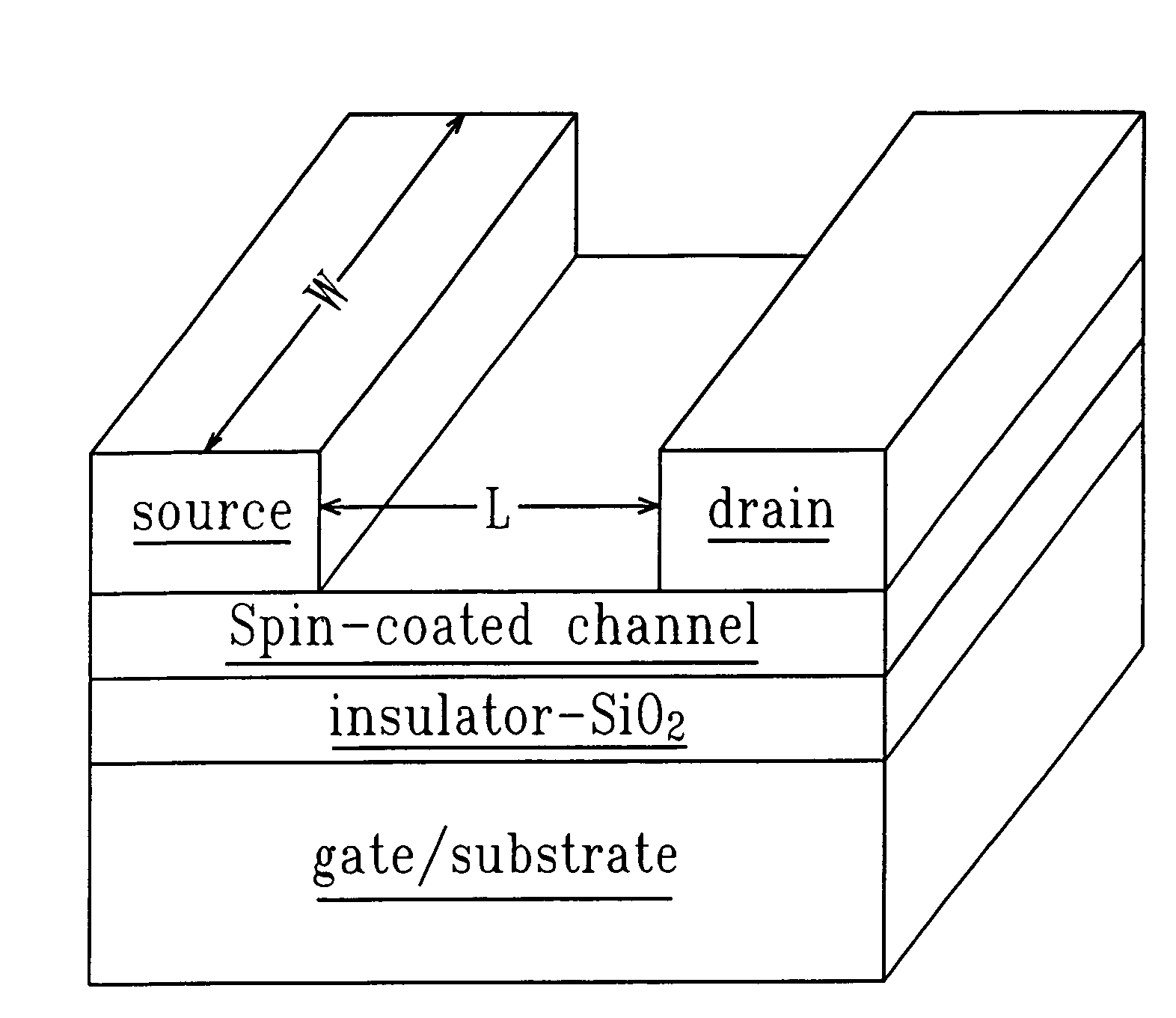
A solution of a hydrazine-based precursor of a metal chalcogenide is prepared by adding an elemental metal and an elemental chalcogen to a hydrazine compound. The precursor solution can be used to form a film. The precursor solutions can be used in preparing field-effect transistors, photovoltaic devices and phase-change memory devices.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
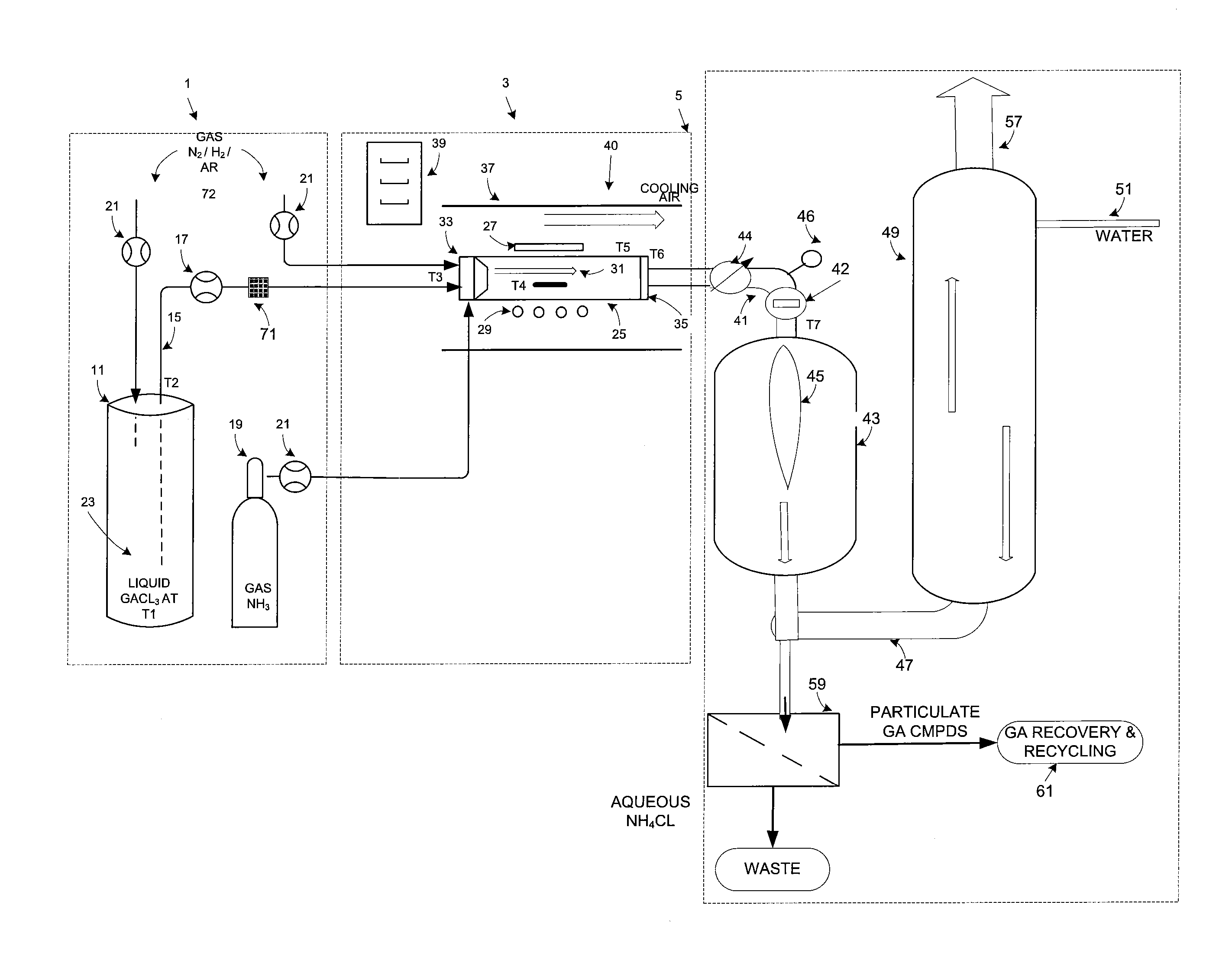
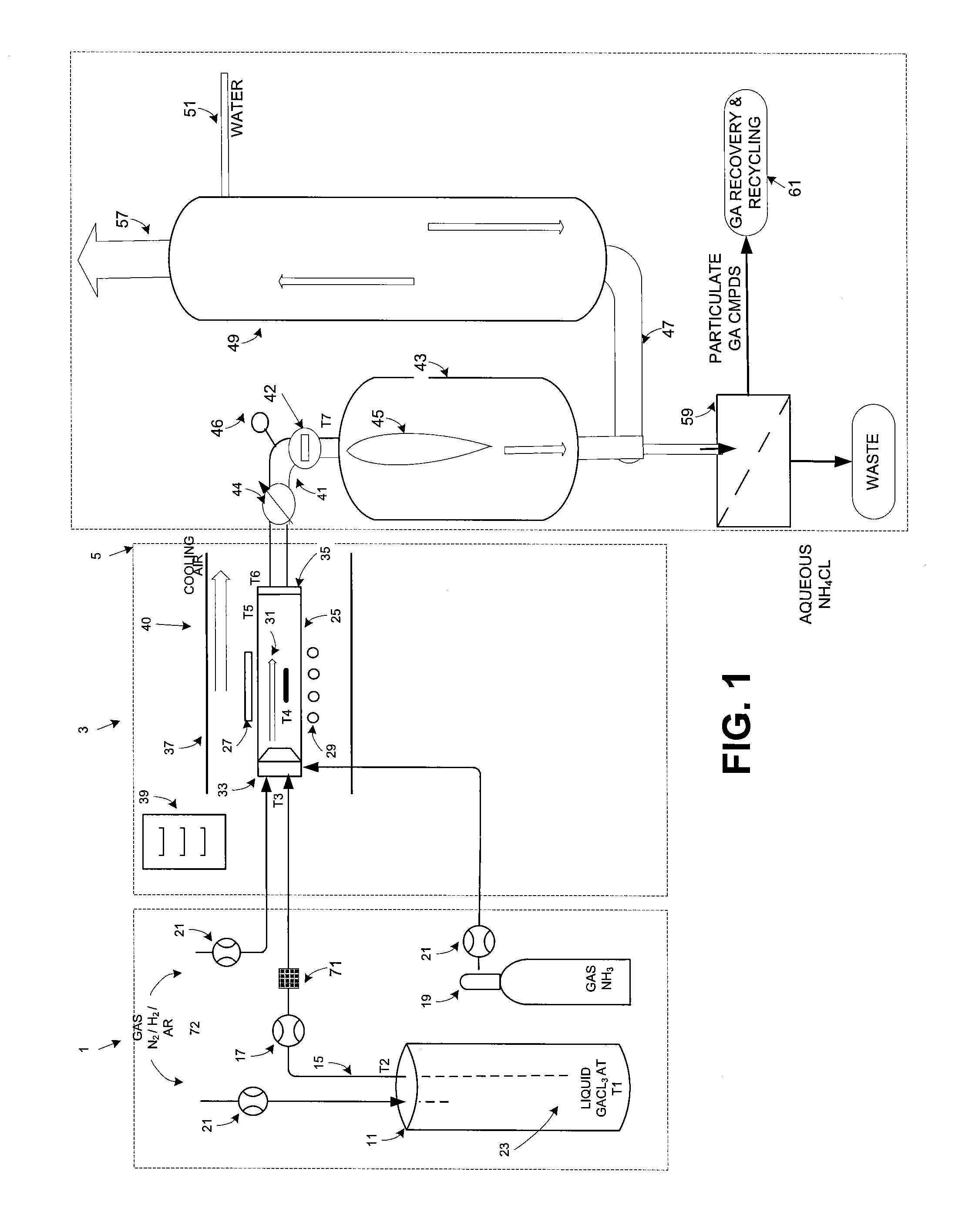
Gallium trichloride injection scheme
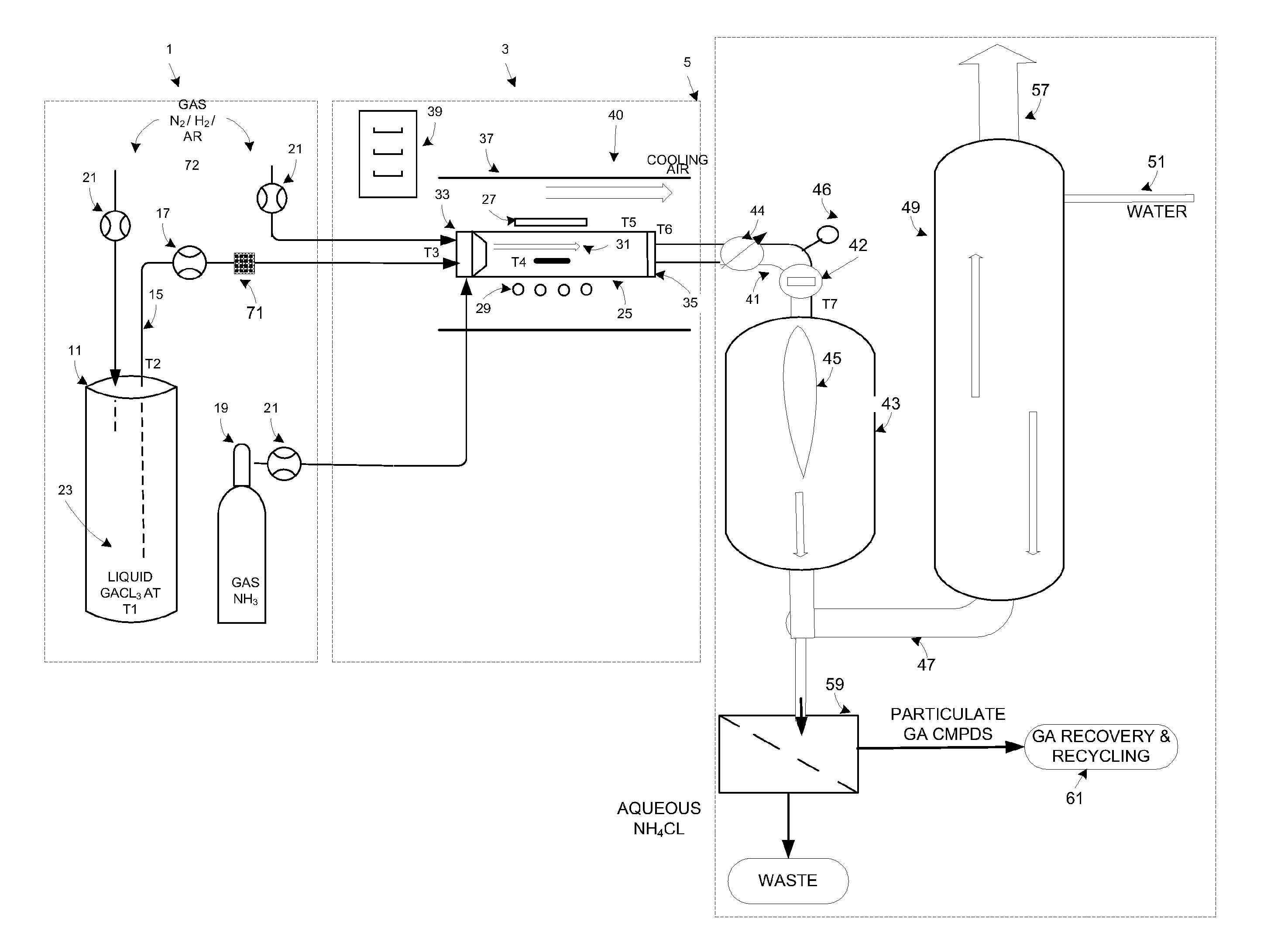
InactiveUS20090178611A1Low reaction temperatureLong operating timeLighting and heating apparatusSolid-state devicesHigh volume manufacturingSemiconductor materials
The present invention is related to the field of semiconductor processing equipment and methods and provides, in particular, methods and equipment for the sustained, high-volume production of Group III-V compound semiconductor material suitable for fabrication of optic and electronic components, for use as substrates for epitaxial deposition, for wafers and so forth. In preferred embodiments, these methods are optimized for producing Group III-N (nitrogen) compound semiconductor wafers and specifically for producing GaN wafers. Specifically, the method includes reacting an amount of a gaseous Group III precursor as one reactant with an amount of a gaseous Group V component as another reactant in a reaction chamber under conditions sufficient to provide sustained high volume manufacture of the semiconductor material on one or more substrates, with the gaseous Group III precursor continuously provided at a mass flow of 50 g Group III element / hour for at least 48 hours. A system for conducting the method is also provided.
Owner:S O I TEC SILICON ON INSULATOR THECHNOLOGIES
Solution-based deposition process for metal chalcogenides
A solution of a hydrazine-based precursor of a metal chalcogenide is prepared by adding an elemental metal and an elemental chalcogen to a hydrazine compound. The precursor solution can be used to form a film. The precursor solutions can be used in preparing field-effect transistors, photovoltaic devices and phase-change memory devices.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Inhibitors of serine protease activity of matriptase or MTSP1
InactiveUS20030050251A1Elevated proteolyticAssist in cancer invasion and metastasisCarbamic acid derivatives preparationHydrolasesPharmaceutical SubstancesOrganic chemistry
The present invention provides compounds which inhibit serine protease activity of matriptase or MTSP1. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions comprising those compounds and methods of using the compounds and pharmaceutical compositions to treat conditions ameliorated by inhibition of matriptase or MTSP1.
Owner:DENDREON PHARMA LLC
Plasma reactor for carrying out gas reactions and method for the plasma-supported reaction of gases
ActiveUS8636960B2Promote activationImprove throughputGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsMicrowave heatingPlasma reactorPlasma chamber
A device for carrying out gas reactions, comprising a plasma reactor with a through-flow of gases which has a, particularly cylindrical, plasma chamber, wherein flow-forming elements for forming a flow of gases are arranged before and / or in and / or after the plasma reactor in order to form a gas stream within the plasma chamber such that at least one, particularly central, zone in the gas flow is formed which is flow-reduced. A method for carrying out gas reactions is also provided.
Owner:IPLAS
Novel hybride materials and related methods and devices
ActiveUS20090171106A1Strong lightHigh tensile strengthMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentNanoparticleCarbon nanotube
The invention provides devices and methods for end and side derivatization of carbon nanotubes. Also facile methods to attach moieties and nanoparticles on the side walls and both ends are described. The invention provides hybide materials for analytical, and optoelectronic purposes as well as materials applications. Materials have improved properties in the areas of tensile, electrical and thermal conductivity.
Owner:AMROY EUROPE OY
Gallium trichloride injection scheme
ActiveUS20120048182A1Efficiently formedLow reaction temperatureLighting and heating apparatusSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method and system for epitaxial deposition of a Group III-V semiconductor material that includes gallium. The method includes reacting an amount of a gaseous Group III precursor having one or more gaseous gallium precursors as one reactant with an amount of a gaseous Group V component as another reactant in a reaction chamber; and supplying sufficient energy to the gaseous gallium precursor(s) prior to their reacting so that substantially all such precursors are in their monomer forms. The system includes sources of the reactants, a reaction chamber wherein the reactants combine to deposit Group III-V semiconductor material, and one or more heating structures for heating the gaseous Group III precursors prior to reacting to a temperature to decompose substantially all dimers, trimers or other molecular variations of such precursors into their component monomers.
Owner:SOITEC SA
Multiwall polymeric microcapsules from hydrophilic polymers
InactiveUS6528035B1Improve concentrationHigh removal rateLayered productsDrug compositionsPolymer dissolutionOrganic solvent
Two or more hydrophilic polymers that are not soluble in each other at a particular concentration and temperature, but which have a positive spreading coefficient in solution, are used to form multi-layered polymeric microspheres. The multi-layer microspheres produced by the method are distinguished by extremely uniform dimensioned polymer layers and actual incorporation of a substance to be delivered into the polymer layers. In the preferred embodiment of the method, two polymers are dissolved in an aqueous solvent, the substance to be incorporated is dispersed or dissolved in the polymer solution, the mixture is suspended in an organic solvent or polymer / water mixture and stirred, and the solvent is slowly evaporated, creating microspheres with an inner core formed by one polymer and an outer layer formed by the second polymer.
Owner:BROWN UNIV RES FOUND INC
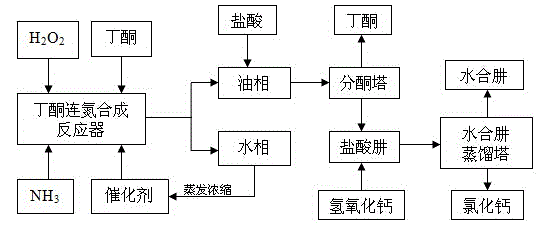
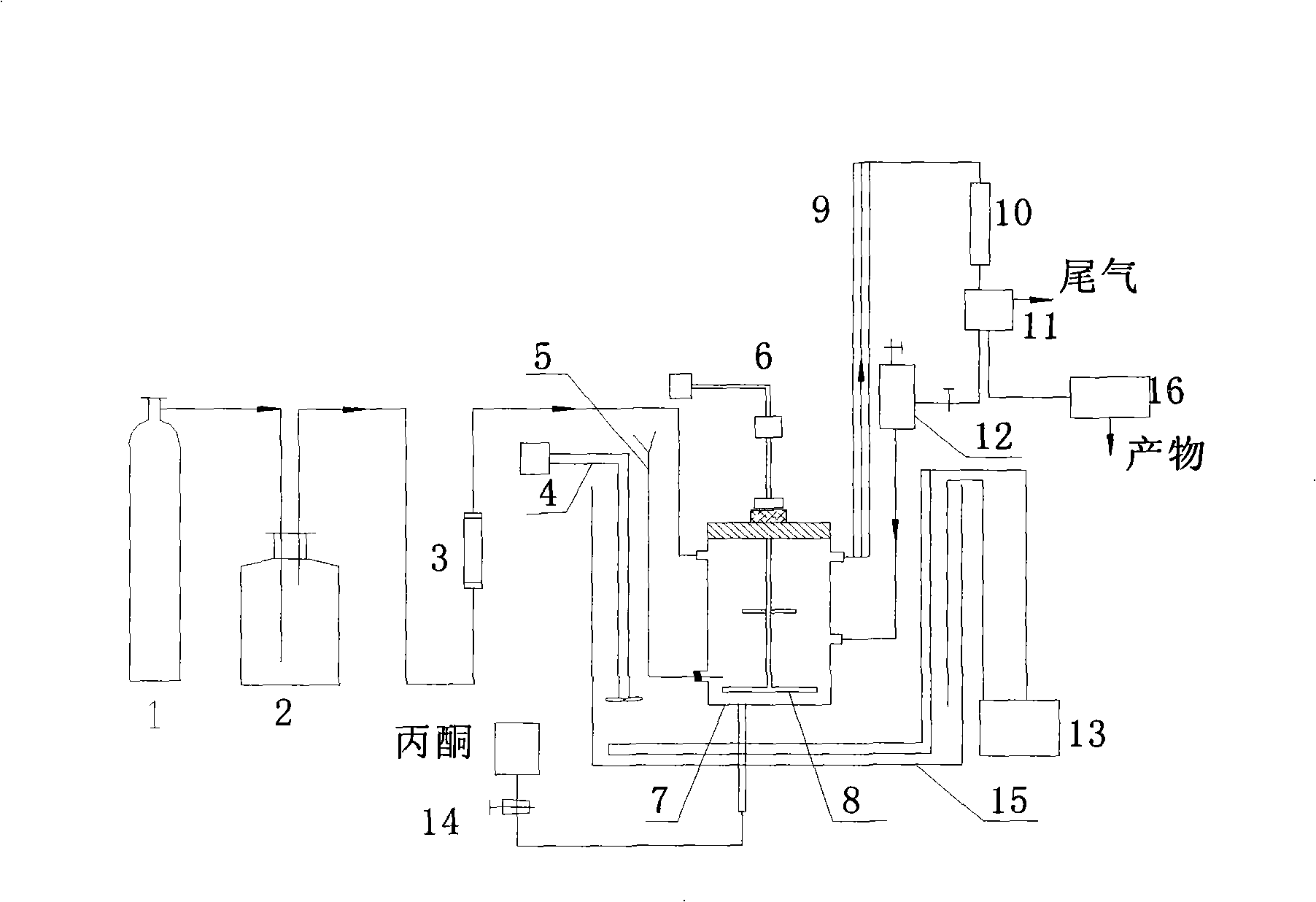
Preparation method of hydrazine hydrate
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical synthesis, particularly relates to a preparation method of hydrazine hydrate and aims at improving production process of a hydrogen peroxide method and provides a hydrazine hydrate preparation method which is low in energy consumption, high in yield and free of pollution. The hydrazine hydrate preparation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: carrying out reaction on ammonia, hydrogen peroxide and butanone in the presence of a catalyst to generate methyl ethyl azine; separating the methyl ethyl azine -containing upper oil phase from the catalyst-containing water phase; concentrating the catalyst-containing water phase to reuse; acid decomposing the methyl ethyl azine into hydrazonium salt and butanone, recycling the butanone, neutralizing the hydrazonium salt into hydrazine hydrate by alkali and distilling and recovering to obtain a hydrazine hydrate solution. The method can be used for preparing hydrazine hydrate and is high in yield and free of pollution.
Owner:重庆锦杉科技有限公司
Separation of salt and alkali from waste salt and alkali residue in production of hydrazine hydrate and technique of cyclic utilization
InactiveCN1796280ANo pollutionNo need for external dischargeHydrazineAlkali metal chloridesSodium bicarbonateHydrazine compound
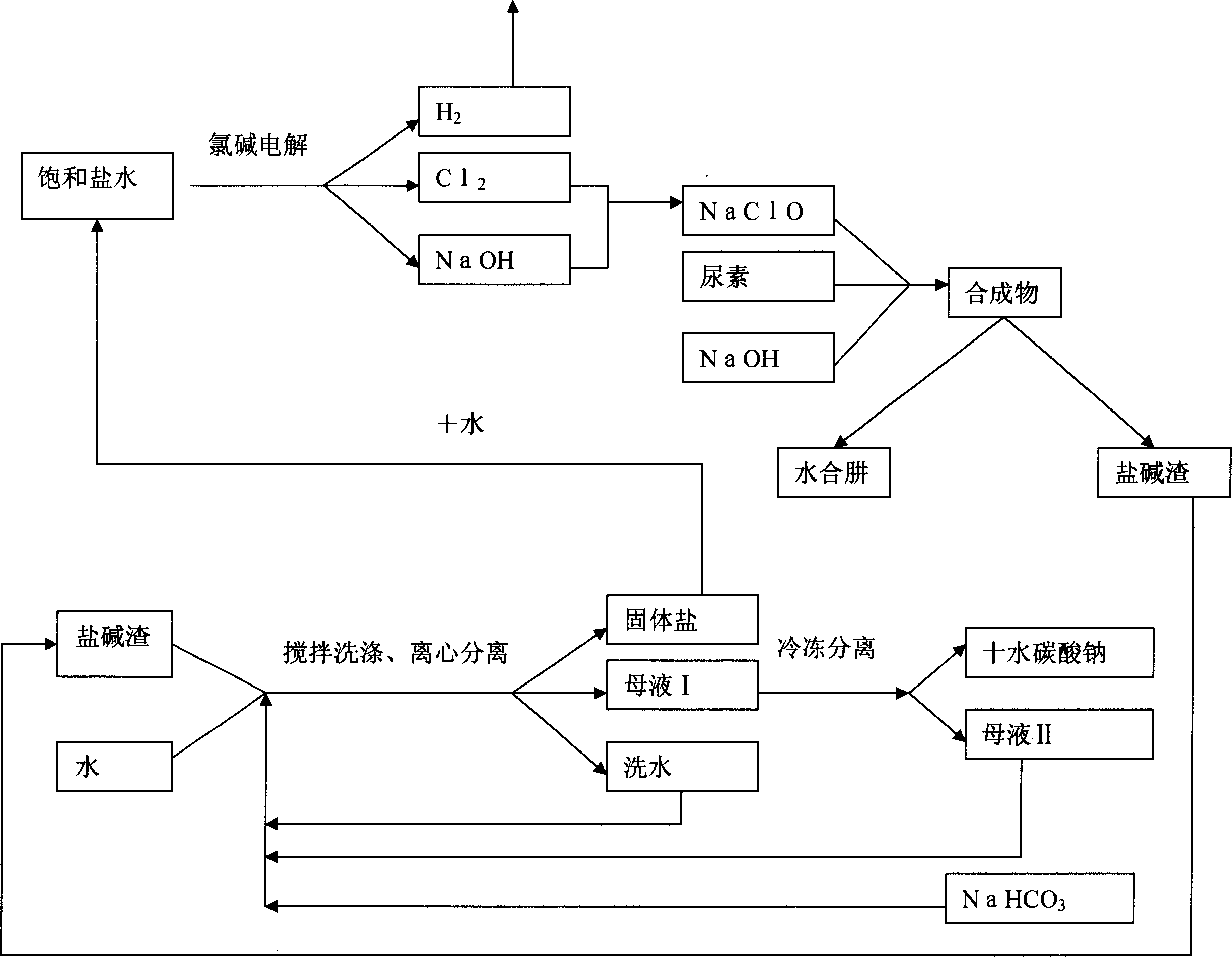
This invention describes a process for the recovery and recycle of industrial waste solids, especially the salt-alkali separation and recycle of the waste salt-alkali solids from the manufacturing of hydrated nitriles. This invention uses water, mother liquid and sodium bicarbonate to wash the waste salt-alkali solids from the manufacturing of hydrated nitriles, so that Na2CO3 and NaOH in the waste salt-alkali solids are washed into the solution. The washing solution is then cooled to 0-5deg.C, and filtrated and separated to obtain solid sodium carbonate decahydrate, which can be commercialized after washing. The mother liquid, after separating the solid alkali, is directed to the next process for washing the waste salt-alkali solids without discharge. During the circulatory washing of the waste salt-alkali solids, the table salt keeps in the solid state. After centrifugal separation, the table salt containing 3% of alkali can be obtained and used for sodium carbonate industry. The said table salt NaCl, after washing and separation to remove a small amount of hydrazine and amine, can be used for chlorine-alkali industry. Chlorine Cl2 and sodium hydroxide NaOH are raw materials for sodium hypochlorite NaClO, which is a raw material for producing hydrazine hydrate. In addition, sodium hydroxide is directly involved in the reaction for producing hydrazine hydrate N2H4íñH2O, thus constituting an internal recycling system of a manufacturing plant without discharging, which not only is environmentally friendly but also reduces transportation load and production cost. This invention describes a rational process for large-scale hydrazine hydrate manufacturing plants.
Owner:陈大元
Method for recycling organic solvents of wastewater generated in synthesis of hydrazine hydrate by ketazine method
InactiveCN104086362AReduce pollutionIncrease added valueOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds purification/separationAcetone productOrganosolv
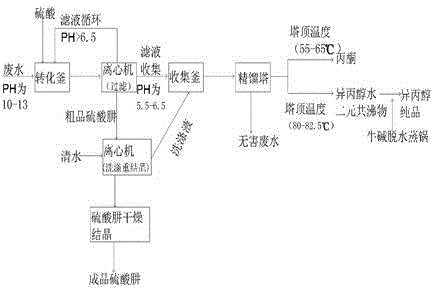
The invention relates to a method for extracting organic solvents and hydrazine sulfate from wastewater generated in synthesis of hydrazine hydrate by a ketazine method. The method comprises the following steps: converting, purifying hydrazine sulfate, rectifying and preparing isopropanol, wherein the step of conversion comprises the following steps: slowly dropping sulfuric acid into a hydrazine hydrate wastewater solution under the condition of 0-15 DEG C so as to precipitate and separate out hydrazine sulfate from the solution, and performing centrifugal filtration to obtain a crude hydrazine sulfate product; the step of purifying hydrazine sulfate comprises the following steps: filtering the crude hydrazine sulfate product, washing for 2-3 times by using cold water, and performing centrifugal filtration and drying crystallization so as to obtain a pure hydrazine sulfate product; the step of rectifying comprises the following steps: collecting filtrate and a washing liquid, feeding into a rectifying tower, rectifying when the tower top temperature is 55-56 DEG C so as to collect a pure acetone product, and rectifying when the tower top temperature is 80-82 DEG C so as to collect binary azeotrope of isopropanol-water; the step of preparing isopropanol comprises the following steps: dehydrating the binary azeotrope of isopropanol-water by using caustic soda flakes, and subsequently distilling, thereby obtaining a pure isopropanol product.
Owner:潍坊蓝海环境保护有限公司
Method for recovering hydrazine sulfate and chromium hydroxide from chromium-containing waste acid
InactiveCN102101732AReasonable useEasy to operateMultistage water/sewage treatmentHydrazineChromium(III) hydroxideSulfate
The invention discloses a method for recovering hydrazine sulfate and chromium hydroxide from chromium-containing waste acid, which comprises the following steps of: diluting hydrazine hydrate, slowly adding waste acid into the hydrazine hydrate with stirring, ensuring an acid adding end point when the pH of feed liquid is 0.8-1.2, and reacting hexavalent chromium in the waste acid with the hydrazine hydrate to reduce the hexavalent chromium into trivalent chromium and generate indissoluble hydrazine sulfate crystals; performing solid-liquid separation to obtain crude hydrazine sulfate and acidic chromium sulfate solution; adding alkali into acidic chromium sulfate solution for neutralization to obtain a chromium hydroxide precipitate, performing solid-liquid separation, washing with water, and drying to obtain an industrial product chromium hydroxide meeting quality requirement; and treating wastewater subjected to solid-liquid separation and washing in a wastewater treatment device for up-to-standard emission. The method is easy to operate, and the chromium-containing waste acid is treated for up-to-standard emission; meanwhile, the hydrazine sulfate and chromium hydroxide are recovered, so that the resources are reasonably utilized and the economic benefit is obvious.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Plasma reactor for carrying out gas reactions and method for the plasma-supported reaction of gases
InactiveUS20140183033A1Increase productionAvoid problemsMicrowave heatingHydrogen/synthetic gas productionPlasma reactorPlasma chamber
A device for carrying out gas reactions, comprising a plasma reactor with a through-flow of gases which has a, particularly cylindrical, plasma chamber, wherein flow-forming elements for forming a flow of gases are arranged before and / or in and / or after the plasma reactor in order to form a gas stream within the plasma chamber such that at least one, particularly central, zone in the gas flow is formed which is flow-reduced. A method for carrying out gas reactions is also provided.
Owner:IPLAS
Process for simultaneous preparation of nanocystalline anatase titanium dioxide powder and hydrazine monohydrochloride
InactiveUS20050106095A1Inhibition of agglomerationMaterial nanotechnologyTitanium dioxideHydrazine compoundHydrazine monohydrate
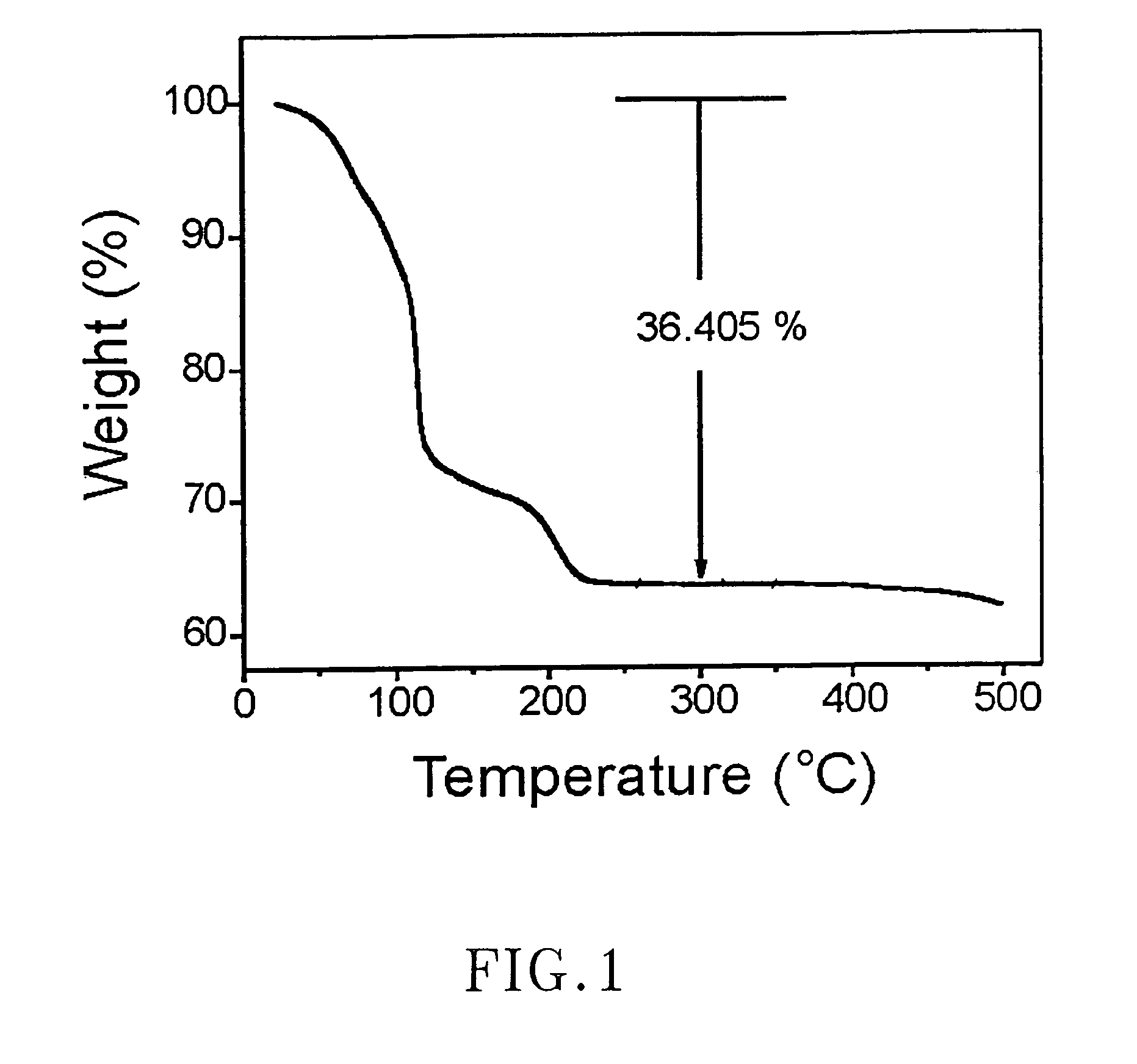
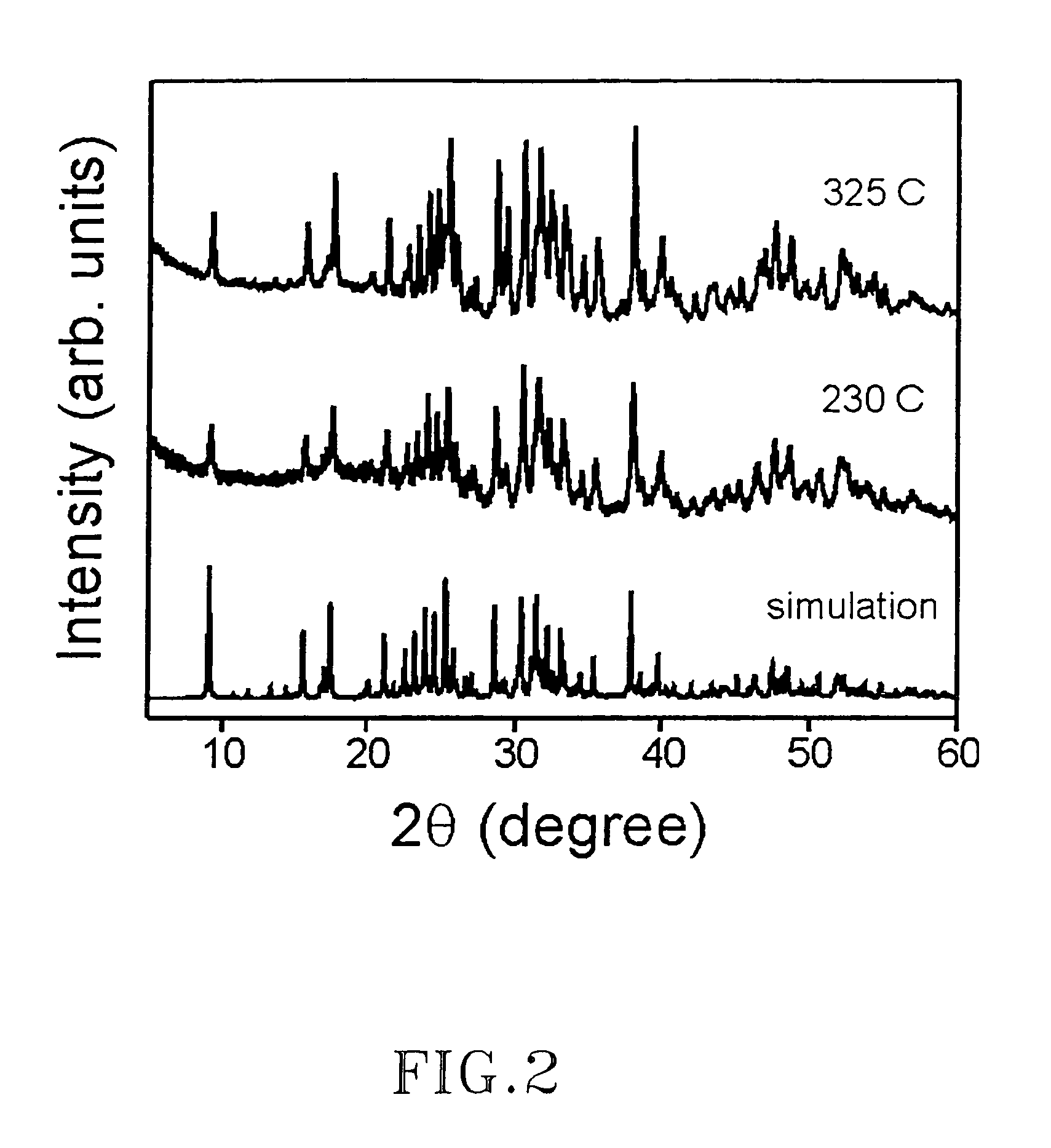
The present invention relates to an environmentally benign process for the simultaneous preparation of nanocrystalline anatase titanium dioxide and hydrazine mohydrochloride, in substantial amounts from the acidic aqueous titanium tetrachloride solution by reacting with hydrazine monohydrate at ambient conditions of temperature and pressure. The process of the present invention is simple, easy to operate, pollution free, high in product purity and homogeneous in product particle.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
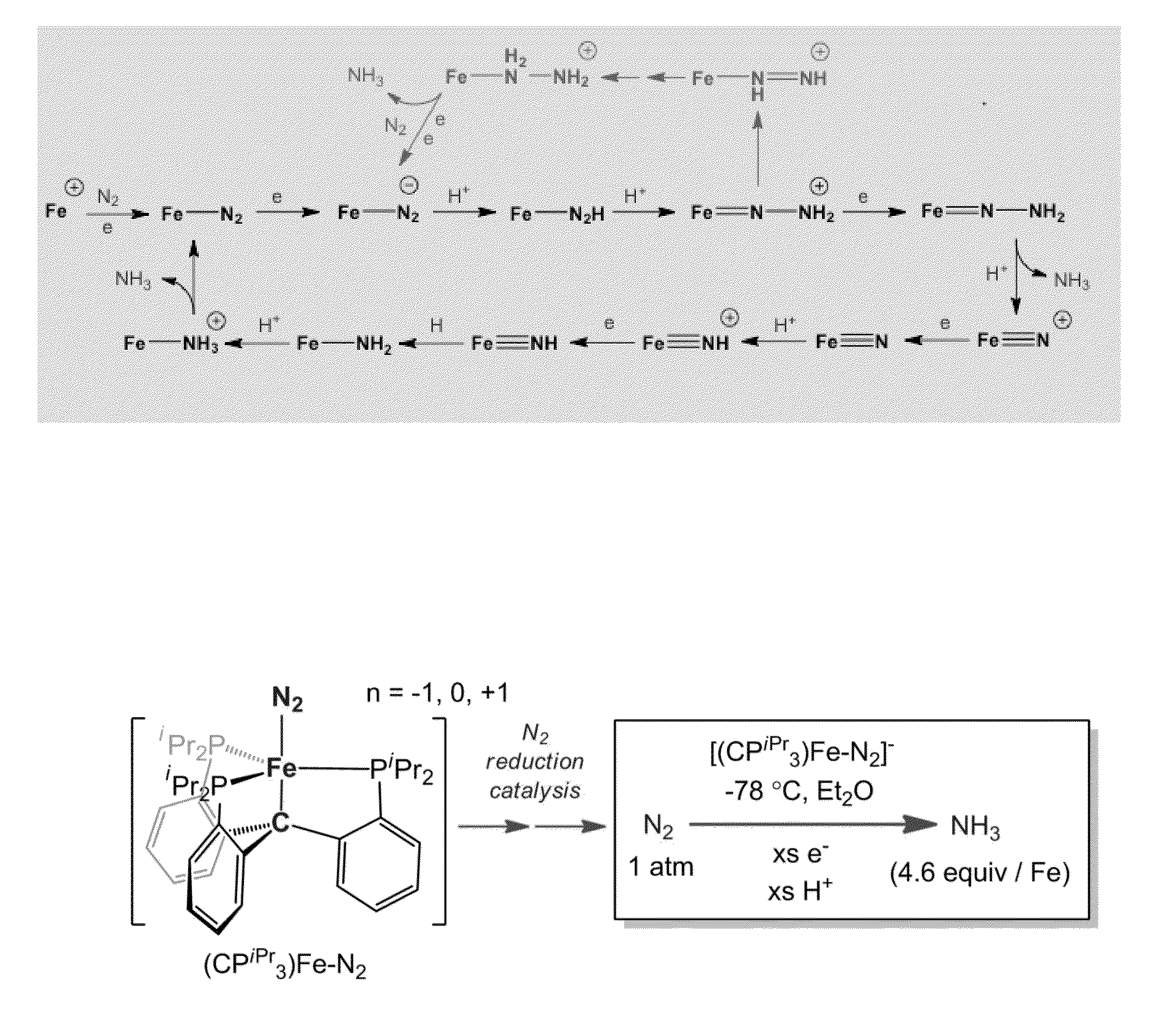
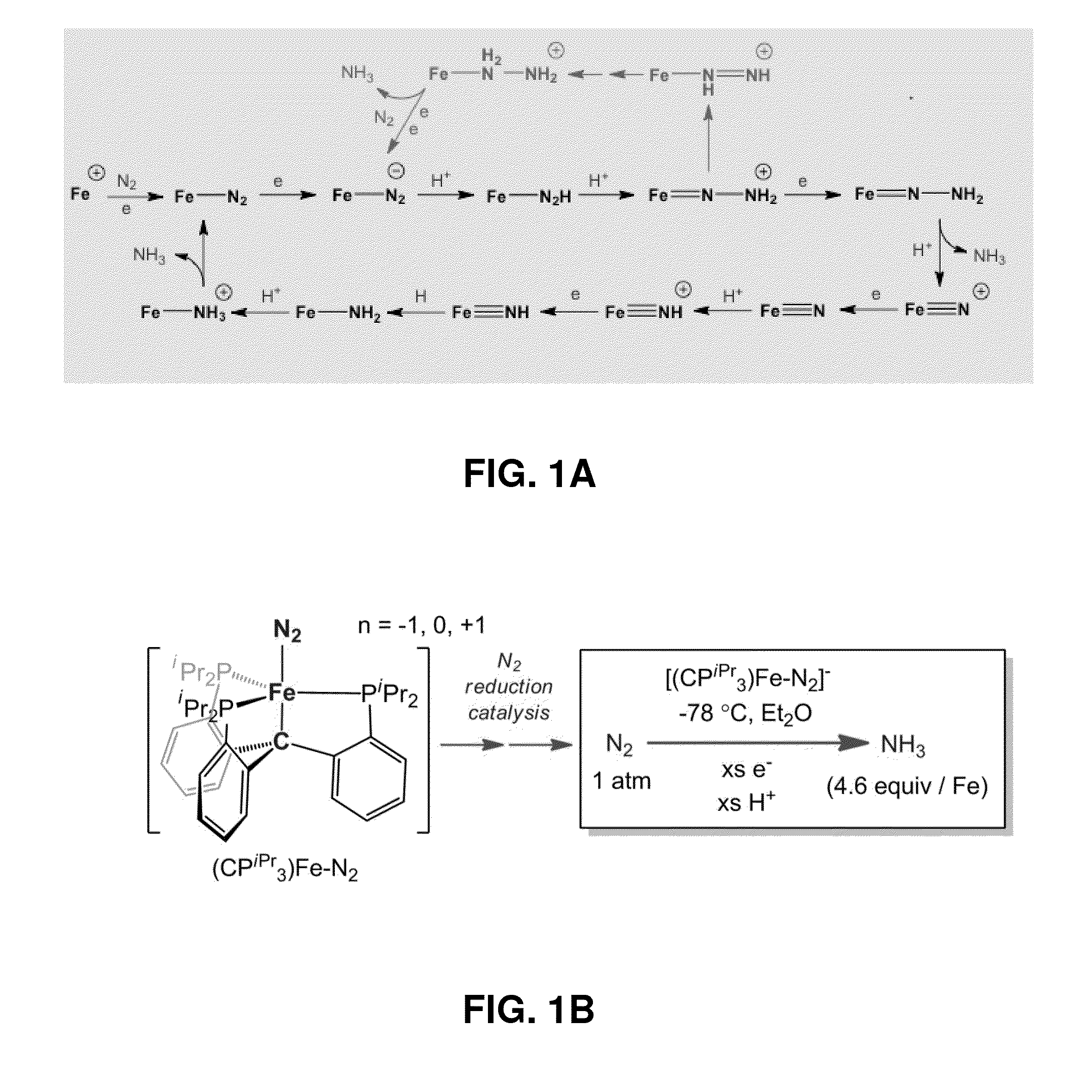
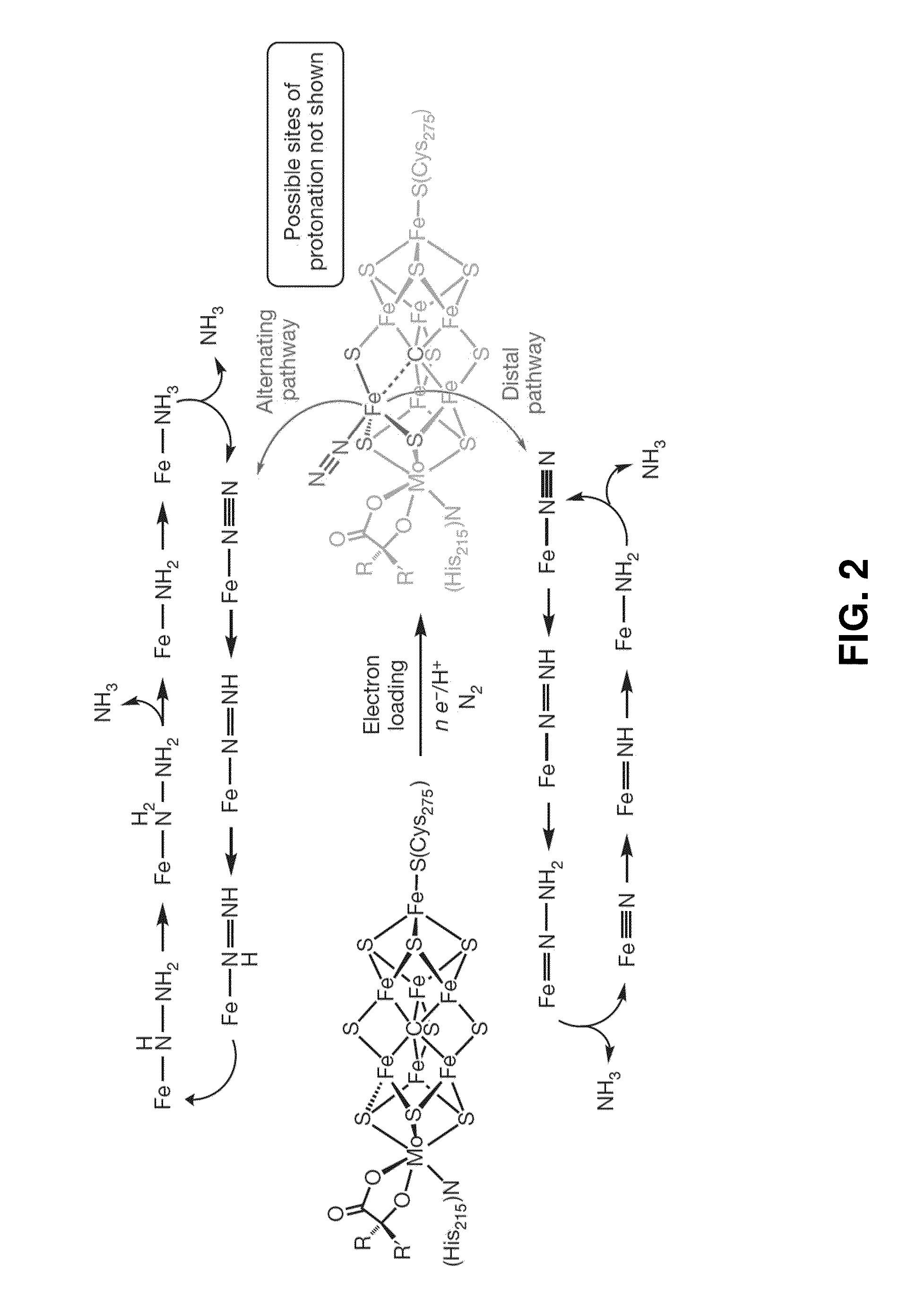
Catalytic ammonia synthesis by transition metal molecular complexes
ActiveUS20150104371A1Useful catalytic efficiencyGood turnover ratioSilicon organic compoundsOther chemical processesChemical reactionCatalytic method
This invention relates to molecular catalysts and chemical reactions utilizing the same, and particularly to catalysts and catalytic methods for reduction of molecular nitrogen. The molecular catalytic platform provided herein is capable of the facile reduction of molecular nitrogen under useful conditions such as room temperature or less and atmospheric pressure or less.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for gas stripping and separating hydrazine from hydrazine-containing solution using acetone and use thereof
ActiveCN101311107ASolving the Condensation Wastewater ProblemHydrazine preparationHydrazineGas phaseHydrazine compound
The invention relates to a method for obtaining pure hydrazine hydrate by isolating and purifying from solution containing hydrazine. The preparation method is that gas-phase acetone and the hydrazine which is contained in oxidation liquid are directly reacted and stripped under the boiling condition; or liquid-phase acetone and the solution are reacted first and then gas stripping is carried out, after the solution is hydrolyzed, the pure hydrazine hydrate is obtained; and the obtained product is sent into a general hydrolyzing tower, in which hydrolysis is carried out to produce the pure hydrazine hydrate solution, and acetone produced by the hydrolysis is sent back to a system for recycling, wherein, the mole ratio of the acetone and the hydrazine is 2 to 3.6 and the reaction temperature is 100 DEG C to 130 DEG C. By adopting the invention, the hydrazine produced by urea-chlorine method can be stripped by acetone azine (CH3)2C=N-N=C-(CH3)2, which causes the recycling of the inorganic materials such as sodium carbonate, sodium chloride, and the like, in the solution to be possible, thereby thoroughly solving the problem of waste water condensation of the ADC processing technique in the urea-chlorine method.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Process for producing biurea
ActiveCN101219973AAvoid cloggingMake sure there is no nitrogenUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationBiureaHydrazine compound
The invention relates to a preparation method of biurea, which includes the following steps: A) a crude hydrazine hydrate liquor is evaporated through an evaporator to get a salt-free hydrazine hydrate liquor and a solid saline-alkaline; B) the ejected salt and alkali are dissolved and reacted with a magnesium chloride liquor, a sulfate of zinc and a chloride liquor to generate a precipitation of basic magnesium carbonate or a basic zinc carbonate and get the basic magnesium carbonate or the basic zinc carbonate after filtering and washing; C) an evaporated hydrazine hydrate dissolves urea, which is added with sulfate or pumped with an anhydrous hydrogen chloride to carry out a condensation reaction to generate the biurea and an ammonium sulfate or an ammonium chloride; D) the mother liquor containing the ammonium sulfate or the ammonium chloride gained through separation can acquire the ammonium sulfate or the ammonium chloride through concentration. The beneficial effects of the invention are that the invention thoroughly solves the problem of serious ammonia nitrogen pollution during the production of biurea and all the byproducts are reasonably reused and recycled; besides, the evaporation efficiency is high, which saves the amount of hydrochloride or sulfate and can avoid the overflow of raw materials caused by the large amount of bubbles in the process of neutralization.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
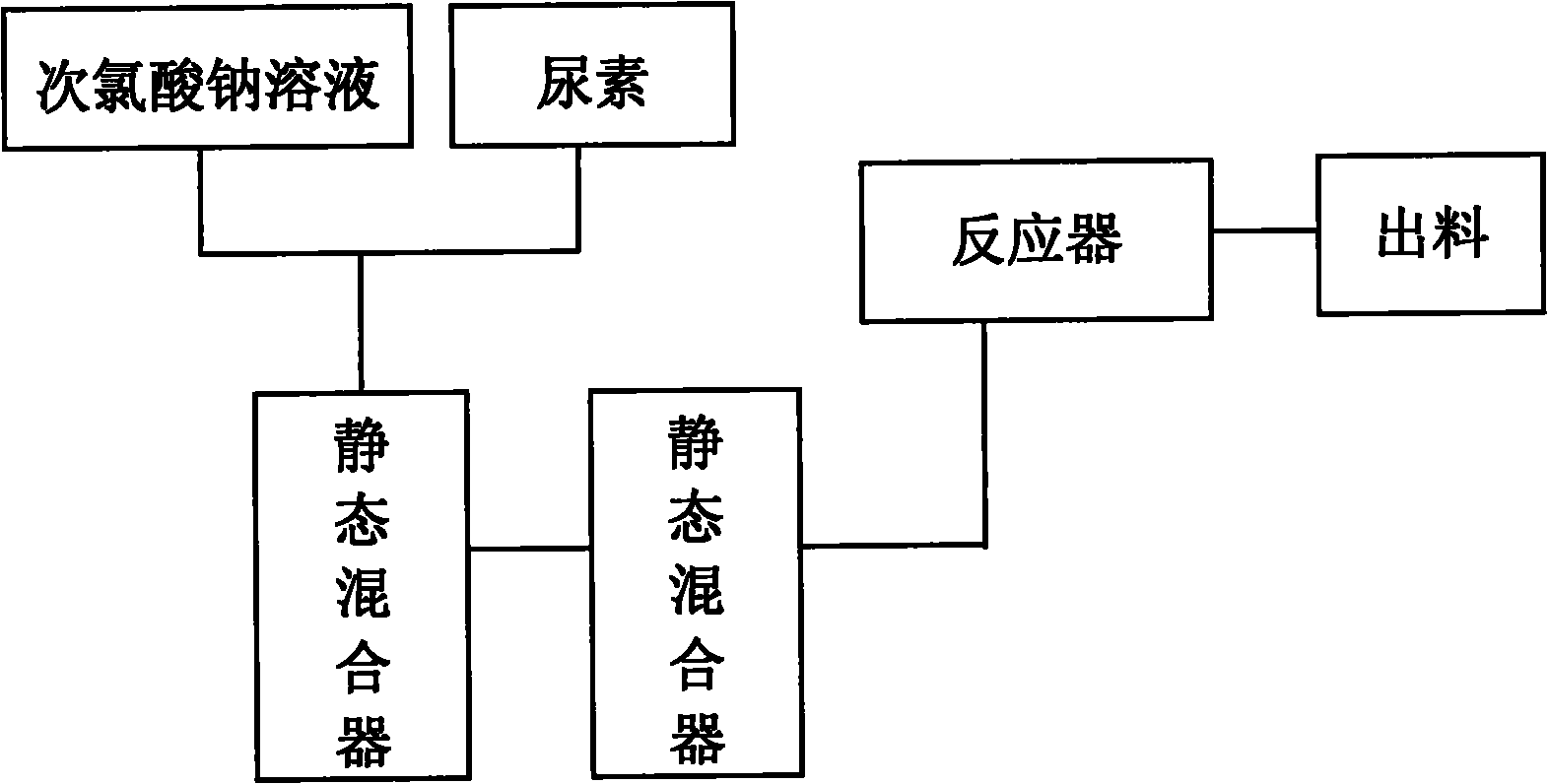
Technology for continuously producing hydrazine hydrate
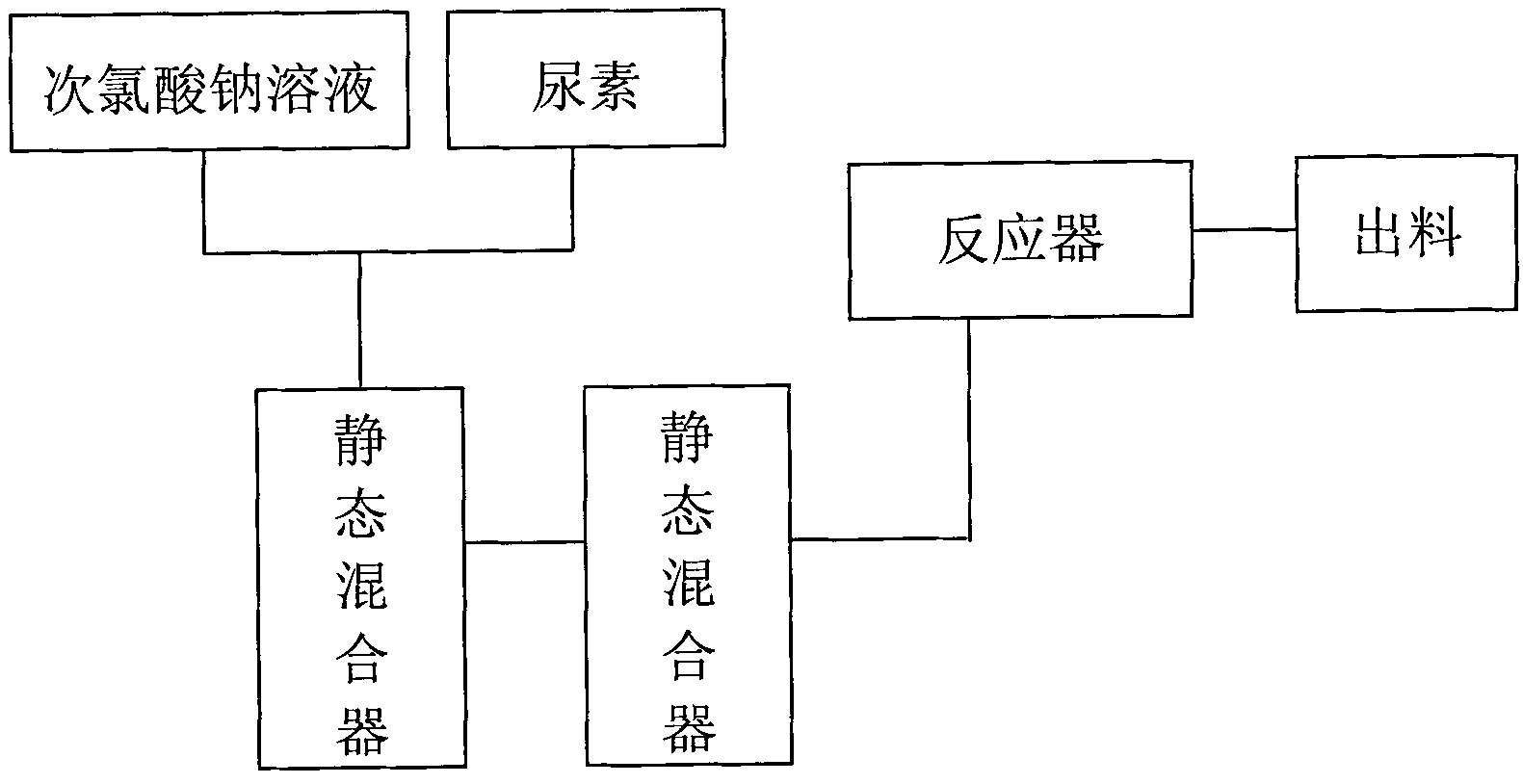
The invention relates to a technology for continuously producing hydrazine hydrate. A two-step method is adopted for reaction in the technology and the two steps is as follows: firstly, urea and sodium hypochlorite are subjected to full oxidization reaction in low temperature, concretely, two or more than two static mixers with freezing brine jackets are adopted for fully mixing materials to ensure the full performance of the oxidization reaction; and secondly, the product of the first step reacts rapidly in high temperature under the action of sodium hydroxide and is subjected to Hofmann rearrangement so as to generate the hydrazine hydrate. The benefits are as follows: the method is simple in technology and can realize continuous production; only the quantity of the static mixers needs to be increased, so that the investment is little; and the content of the obtained hydrazine hydrate is over 85%.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
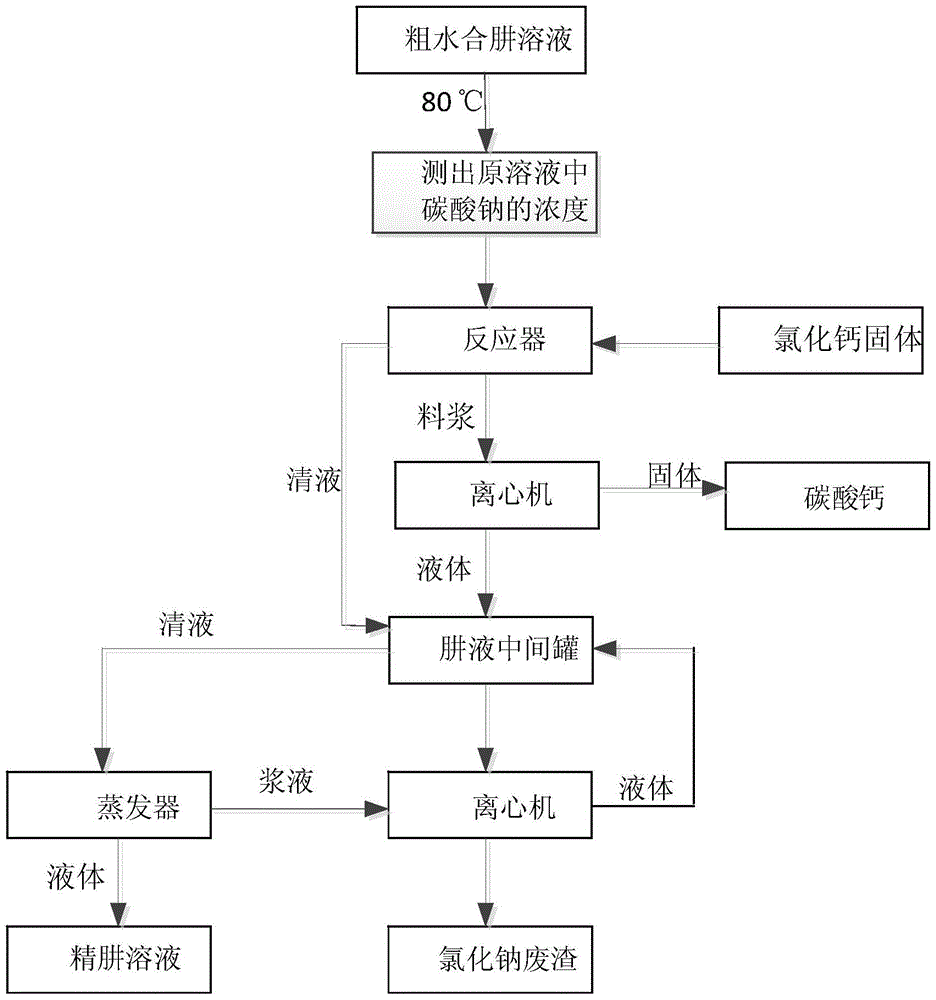
Method for removing sodium carbonate in solution
The invention discloses a method for removing sodium carbonate in a solution, and relates to the technical field of chemical impurity removal. The problem that a traditional technology for removing sodium carbonate in thick hydrazine hydrate solution is complex in process and high in economic cost is solved. The method for removing sodium carbonate in the solution comprises the steps that calcium chloride solids are added into an original solution, the calcium chloride is made to sufficiently react with sodium carbonate, and therefore the sodium carbonate in the original solution is removed. According to the method for removing sodium carbonate in the solution, the technology for removing impurities of the original solution is effectively simplified, and meanwhile the energy consumption and economic cost of the technology are lowered.
Owner:ЦИНХАЙ СОЛТ ЛЕЙК ИНДАСТРИ ГРУП КО ЛТД
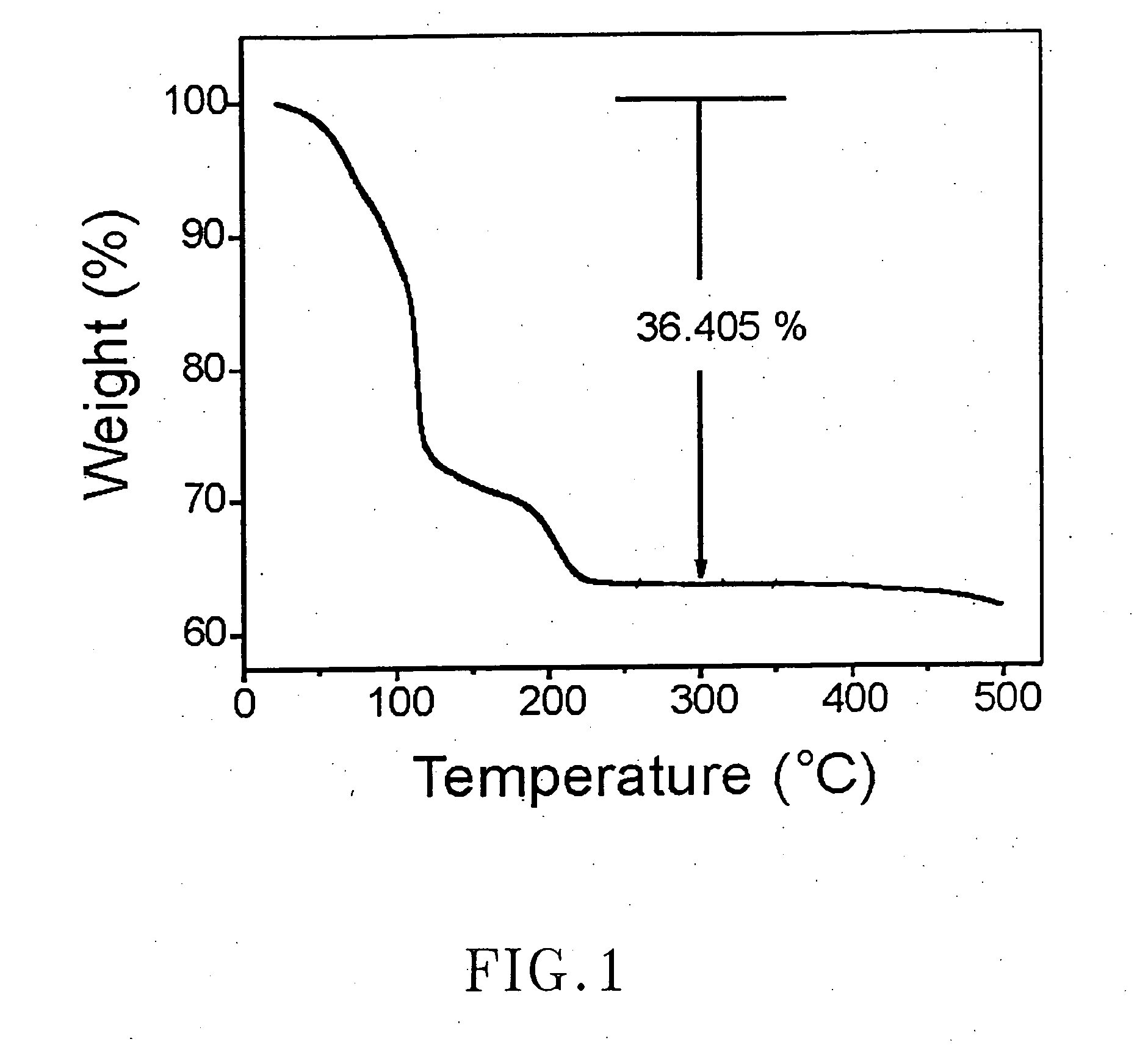
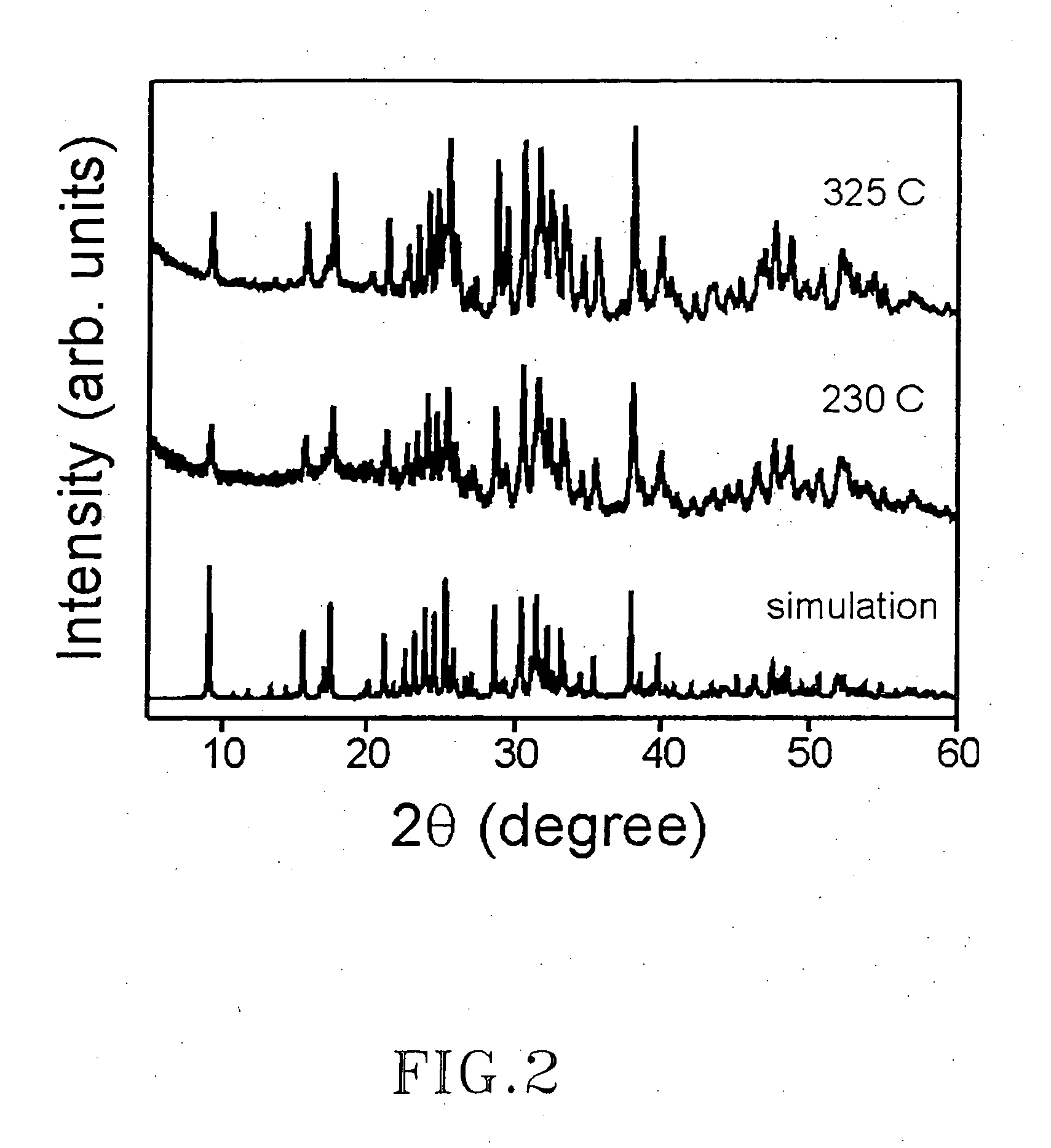
Removal of moisture from hydrazine
The present invention generally relates to the field of gas and liquid phase desiccation. In particular, the present invention relates to methods for removing moisture (and hence oxygen precursors) from hydrazine, thereby providing a high purity source gas suitable for use in vapor deposition processes, such as but not limited to, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or an atomic layer deposition (ALD).
Owner:MATHESON TRI GAS
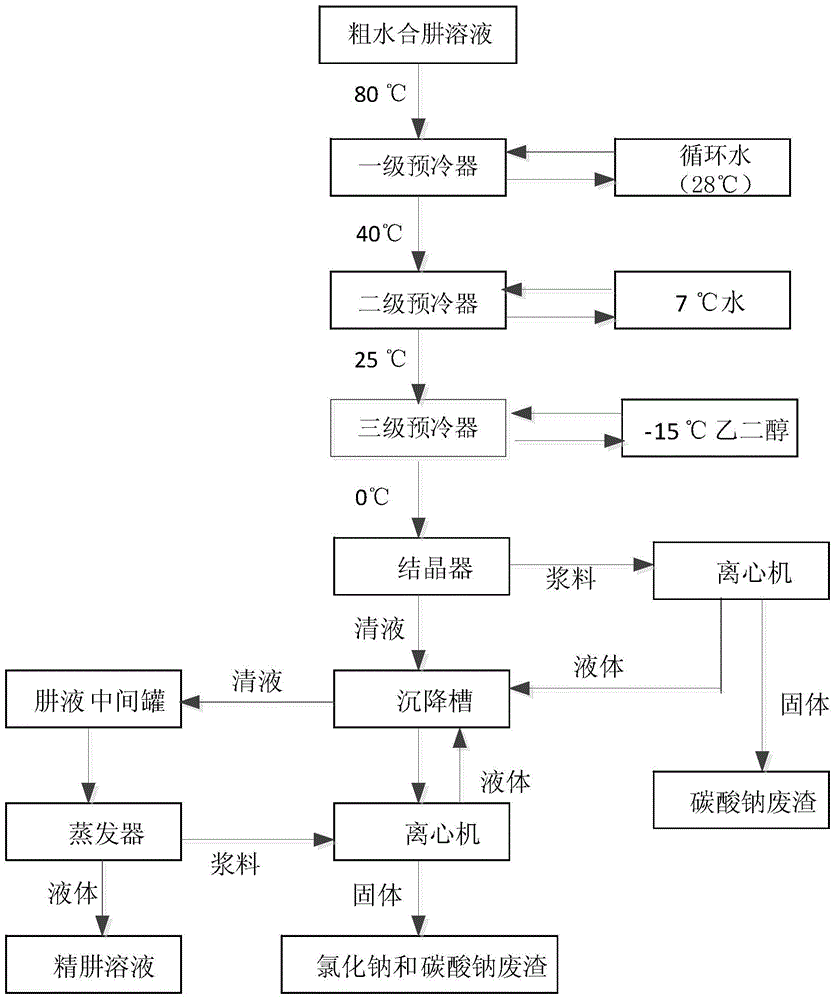
Method for removing sodium carbonate from hydrazine hydrate crude solution
The invention discloses a method for removing sodium carbonate from a hydrazine hydrate crude solution. The method comprises the following steps: 1, a urea solution is mixed with sodium hypochlorite, wherein a molar ratio of the urea solution to sodium hypochlorite is 1-2, such that the crude solution obtained by a reaction does not contain sodium hydroxide; 2, a chloride is added into the hydrazine hydrate crude solution; and centrifugal separation is carried out, such that poorly soluble carbonate is separated; 3, the hydrazine hydrate solution with sodium carbonate removed is subjected to membrane filtration, such that cations in the solution are removed. With the method, sodium carbonate in the hydrazine hydrate crude solution is thoroughly removed. The produced poorly soluble carbonate can be directly sold after certain treatments, and can be subjected to a reaction with hydrochloric acid recovered from an ADC process for producing chloride for recycling. When the sodium-carbonate-removed hydrazine hydrate solution is used in a biurea production process, acidic substance addition can be greatly reduced. When the sodium-carbonate-removed hydrazine hydrate solution is used in a hydrazine hydrate production process through evaporation and rectification, evaporation and rectification continuous production is facilitated.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
Method for reducing inorganic compound by water as hydrogen source or by molten alkali and use thereof
The invention relates to a method for reducing an inorganic compound by water as a hydrogen source to synthesize an organic compound or hydride and a use thereof. The related hydrogen acceptors comprise inorganic or organic compounds such as carbon dioxide, carbonate, acetic acid and urea containing C=O groups, and also comprise inorganic compounds such as nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, sulfate and nitrate. The method utilizing water as a hydrogen source can realize high efficiency and low cost conversion of the inorganic compounds containing C=O groups into alcohol organics or conversion of inorganic compounds containing S=O and N=O groups into corresponding hydrides. The invention also relates to a method for reducing carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide or nitrogen dioxide into carbon simple substance, sulfur simple substance or nitrogen by molten alkali catalysis and a use thereof and also relates to a method for reducing a metal hydroxide into a corresponding metal simple substance by molten alkali catalysis and a use thereof.
Owner:李坚
Fenton and Fenton-Like System Hardening Agent and Usage Thereof
InactiveUS20120305497A1Efficient use ofWide rangeWater treatment parameter controlOrganic chemistryHydrazine compoundSulfite salt
Fenton and Fenton-like system enhancing agent and the usage thereof are provided. It relates to a water treatment enhancer (enhancing agent) and the usage thereof. It widens water pH range of Fenton and Fenton-like system reaction. It reduces amount of Fe2+ required for Fenton reaction. It increases rate of Fenton-like reaction. The enhancing agent is selected from sodium sulfite, lithium sulfite, potassium sulfite, magnesium sulfite, calcium sulfite, hydroxylamine hydrochloride, hydroxylamine perchlorate, hydroxylamine sulfate, hydrazine, N,N-diethylhydroxylamine, amino ethanolamine, hydroxylamine solution or N,N,N′,N′-tetrasubstituted p-phenylenediamine. The method of use of enhancing agent comprises the steps of: adding Fenton or Fenton-like system enhancing agent, an agent for enhancement and hydrogen peroxide into water subject to treatment; and mixing and allowing reaction. The enhancing agent can increase the rate of reaction for the water treatment and reduce the dosage of the agent for enhancement.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for achieving ammonium chloride cooperative production through ADC foaming agent wastewater by means of total-hydrochloric acid pure hydrazine hydrate condensation
InactiveCN105417510AUnique methodSolve difficult governance problemsHydrazineAlkali metal carbonatesFoaming agentProcess engineering
The invention relates to ADC foaming agent production technology improvement and waste water recycling, in particular to a method for achieving ammonium chloride cooperative production through ADC foaming agent wastewater by means of total-hydrochloric acid pure hydrazine hydrate condensation. The method comprises the steps that vapor containing hydrazine is prepared from a hydrazine hydrate coarse solution at first, then the vapor containing hydrazine is rectified through a rectifying tower to obtain pure hydrazine needed for producing ADC, crystallized sodium chloride and sodium carbonate particles in the evaporation process are deposited at the bottom of an evaporator, separated through a centrifugal machine and then fed to sodium carbonate for electrolysis, urea and hydrochloric acid produced through oxidation in follow-up working procedures are added into the hydrazine hydrate obtained after rectification to be used for production of an ADC foaming agent, the obtained waste water only contains ammonium chloride, water in the ammonium chloride solution is continuously evaporated through heating, and an ammonium chloride crystal is separated out after supersaturation is reached; the method is unique, the ADC foaming agent production wastewater is converted into the water solution only containing ammonium chloride, follow-up treatment is more simple, and the obtained product is higher in value.
Owner:NINGXIA RISHNEG HIGH NEW IND CO LTD
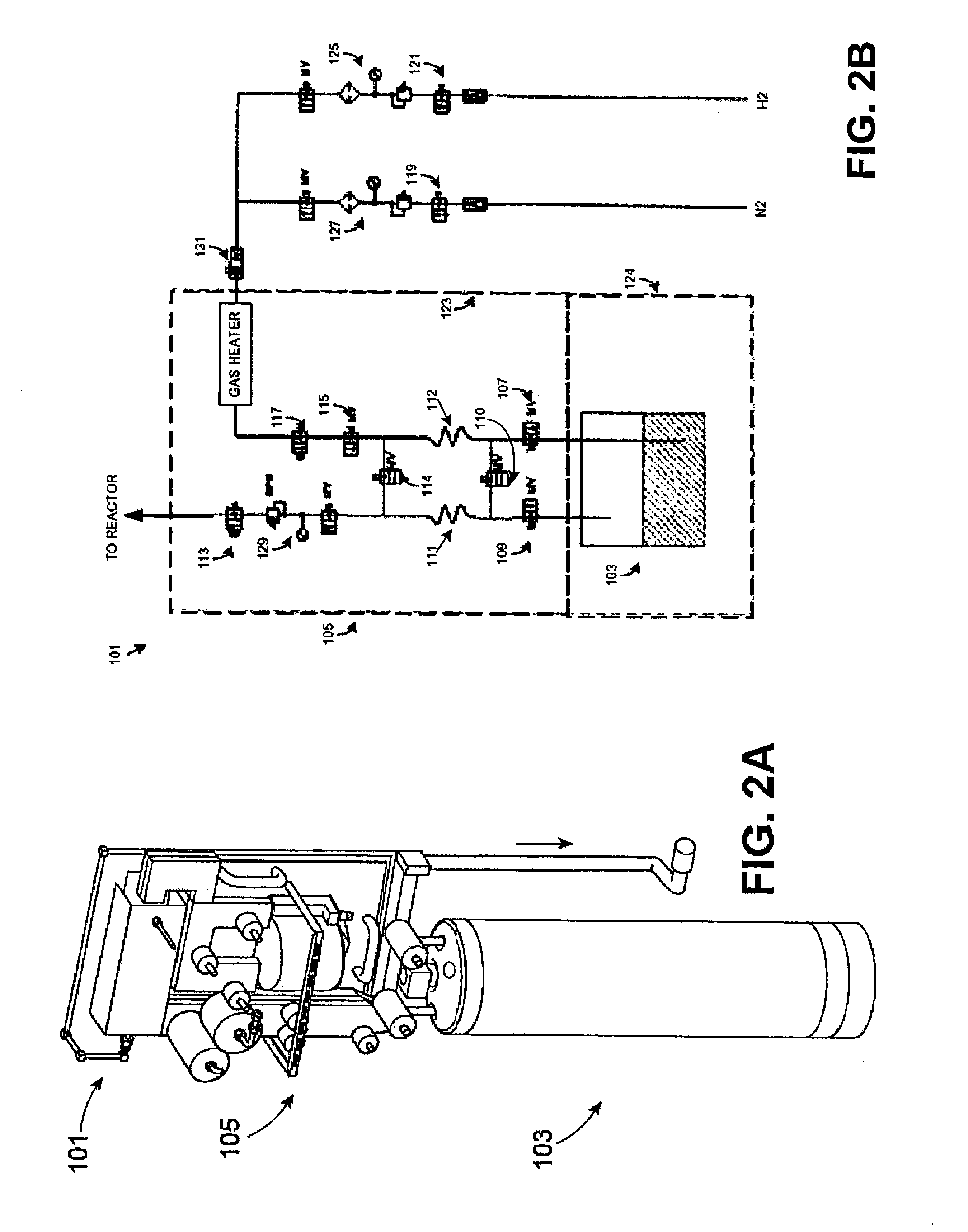
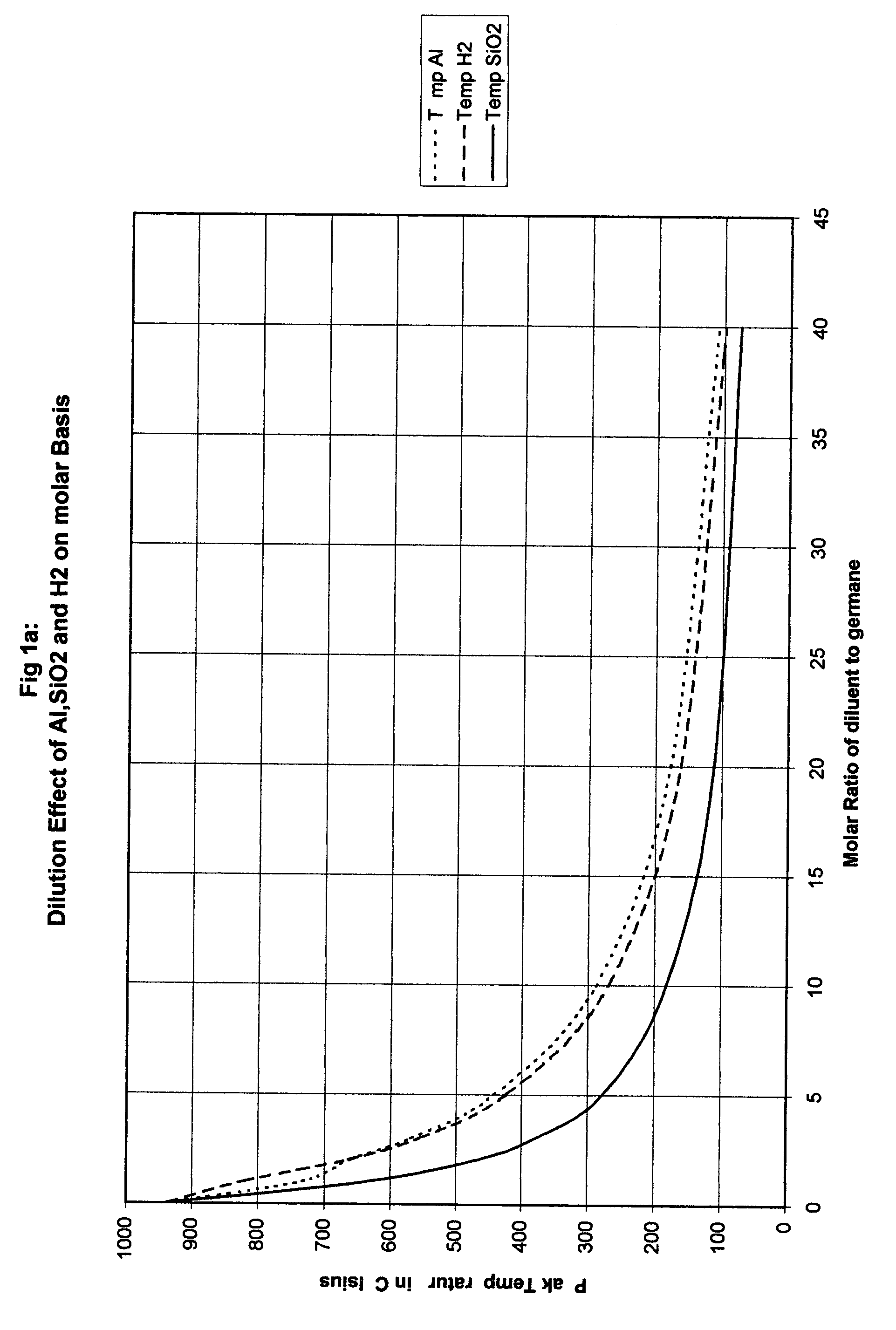
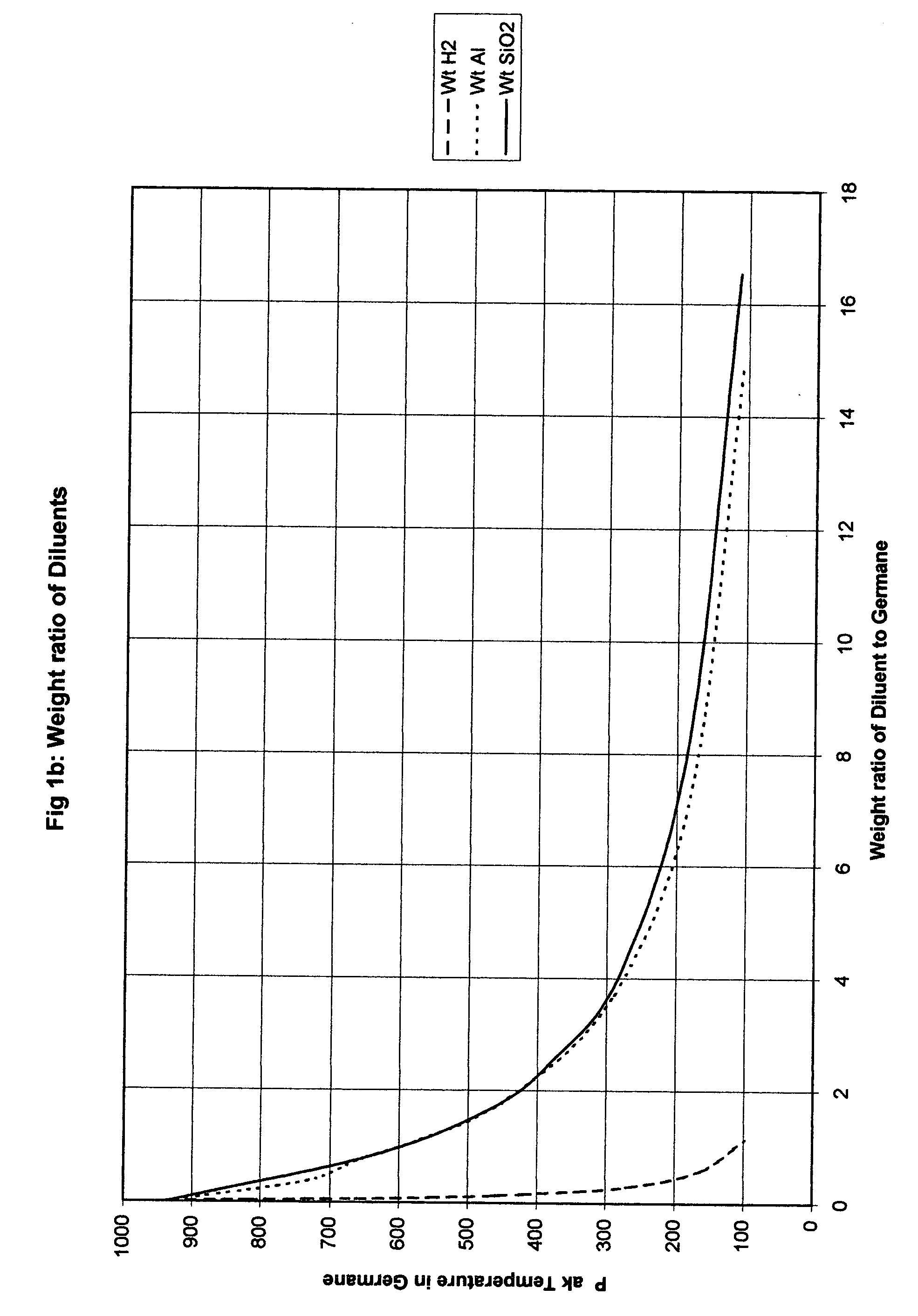
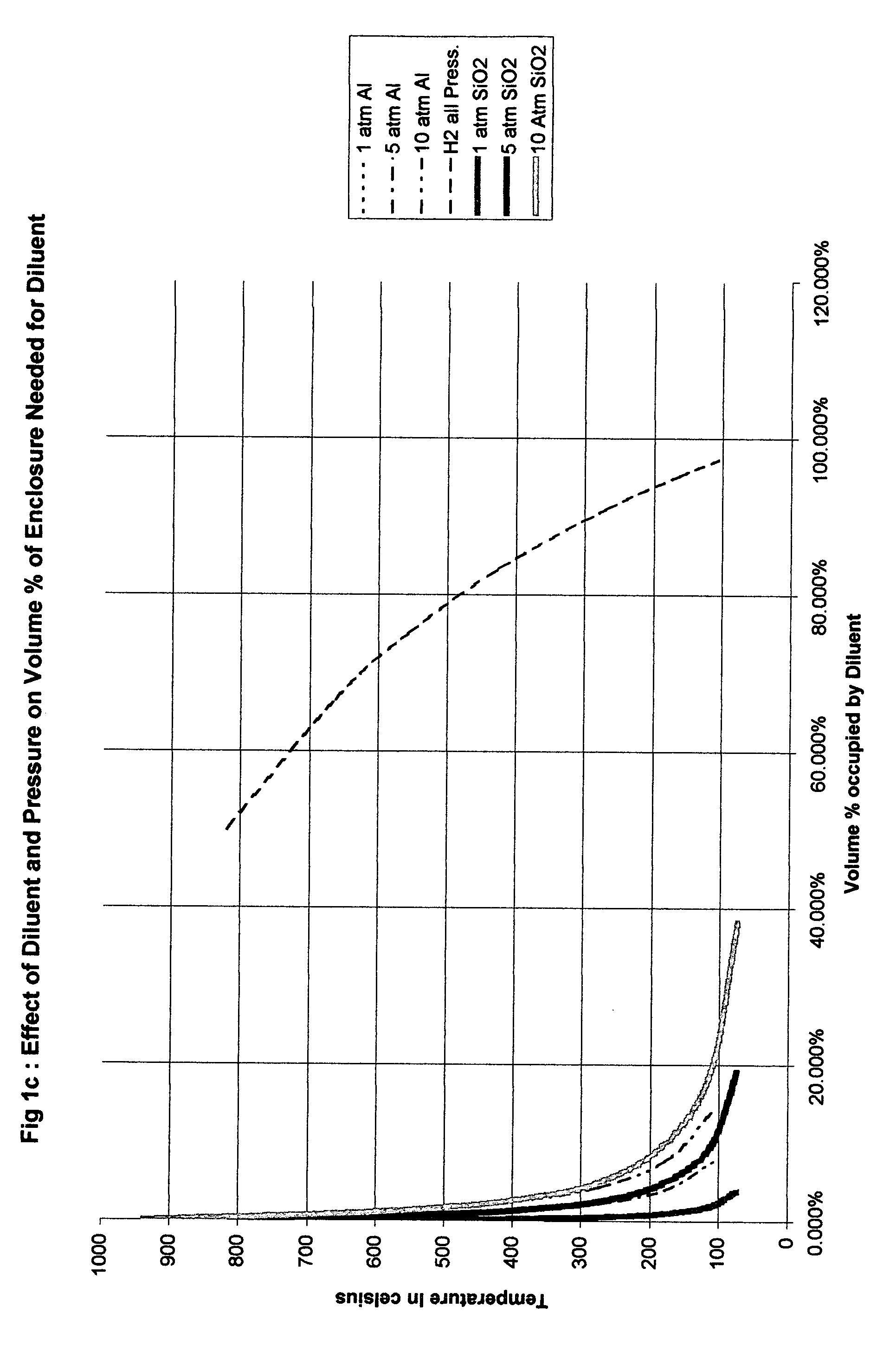
Method for safe handling of unstable hydride gases
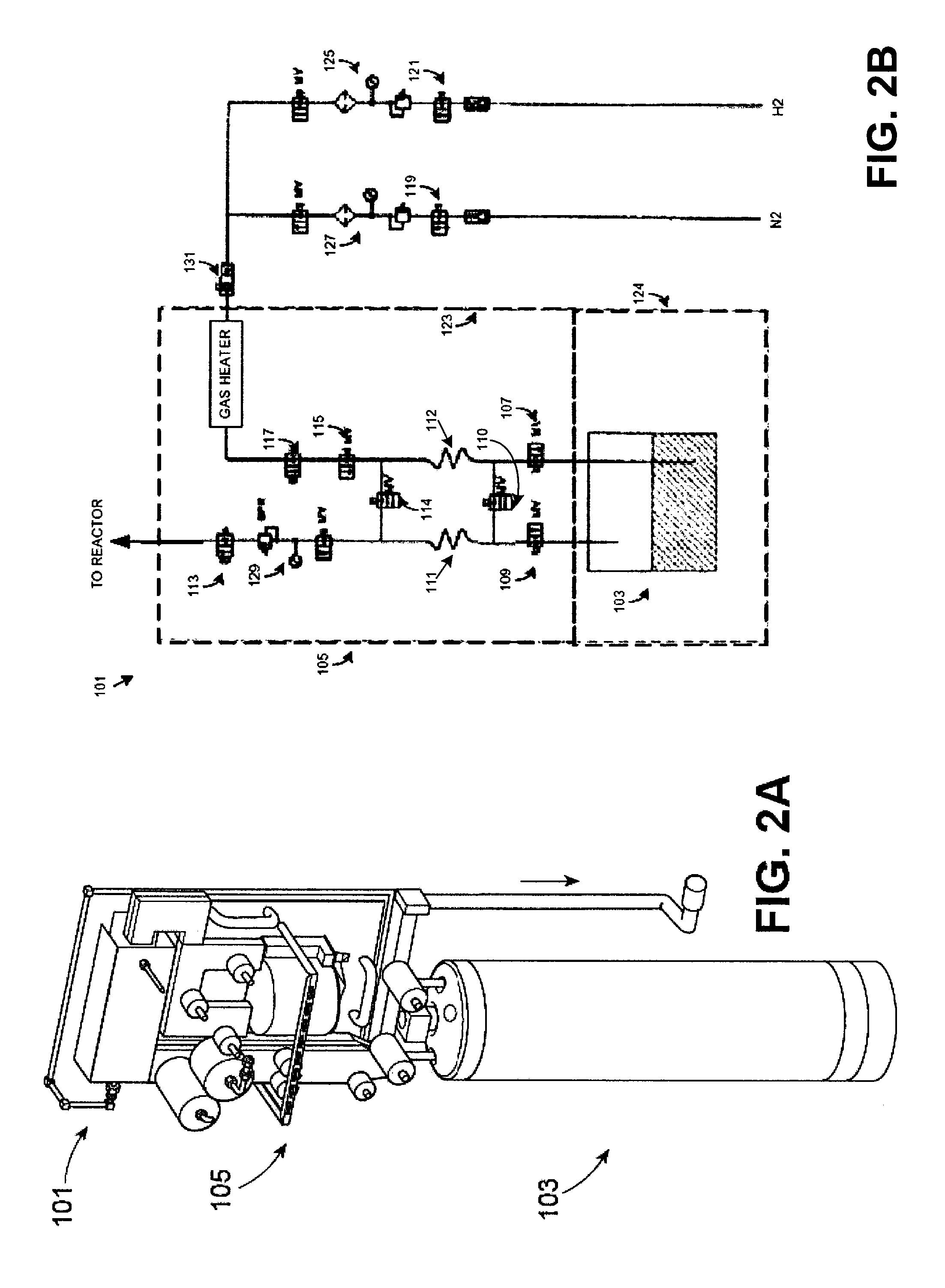
InactiveUS20050023365A1Lower peak temperatureSafe handlingLighting and heating apparatusSilicon hydridesChemical reactionSilanes
A method for safely handling unstable hydrides in an enclosure which contains a hydride and has one or more openings, by partitioning the enclosure into smaller but interconnected volumes and providing heat storage and transfer within the enclosure to rapidly remove heat from any incipient hot spot before it can reach a temperature where it could rapidly propagate to the rest of the enclosure. The minimum temperature used to size the partitions is the thermal decomposition temperature for unstable gases which can decompose without oxidation such as hydrazine, silane and germane. A preferred embodiment includes where the partitioning material comprises part or all of the means to store the heat and has a large surface area to rapidly adsorb heat from the gases in the smaller volume. An even more preferred embodiment is where the partitioning material comprises materials that can be poured into the enclosure. The use of sensible heat, phase change or chemical reactions is feasible ways to store the heat. The materials chosen for the partitioning means and the heat sink are substantially free from adsorbing the gas contained in the enclosure.
Owner:LORD LTD LP
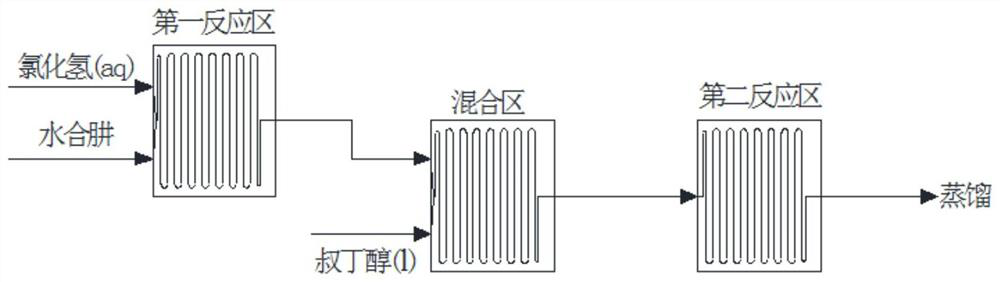
Preparation method for continuously preparing tert-butylhydrazine hydrochloride
PendingCN112028788AIncrease reaction rateHigh utilization rate of raw materialsHydrazine preparationChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsSide reactionAlkene
The invention discloses a method for continuously preparing tert-butylhydrazine hydrochloride by using a micro-channel reactor. The method comprises the steps of 1, carrying out primary reaction mixing on hydrazine hydrate with the mass concentration of 40-80% and hydrochloric acid with the concentration of 25-36% in the micro-channel reactor to obtain a hydrazine hydrochloride solution; 2, mixingthe hydrazine hydrochloride solution with a tert-butyl alcohol solution in the micro-channel reactor for later use; and 3, carrying out a secondary reaction on the material mixed in the step 2 to obtain a product aqueous solution, continuously concentrating the product aqueous solution to achieve a certain concentration, carrying out cooling crystallization, filtering, and drying to obtain the tert-butylhydrazine hydrochloride. According to the method, the reaction rate and the raw material utilization rate are increased, the side reaction for producing the olefin compounds through tert-butylalcohol dehydration is avoided, the reaction is easy to control, the production period is short, emission of three wastes is little, the total yield can reach 85% or above, and the automation degreeof the reaction process is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI NO 4 REAGENT & H V CHEM
Method for implementing co-production of ammonium sulfate from ADC foaming agent wastewater by extracting hydrazine hydrate
The invention relates to a method for coproducing ammonium sulfate from wastewater, in particular to a method for implementing co-production of ammonium sulfate from ADC foaming agent wastewater by extracting hydrazine hydrate. The method comprises the following steps that after being preheated step by step by condensate water with each effect, hydrazine hydrate coarse solution enters evaporator with each effect in parallel to be heated and evaporated; after settling and being pulped, saline-alkali pulp discharged by evaporator with each effect through a pipeline is subjected to centrifugal dewatering to obtain saline-alkali slags; centrifugal mother liquid is settled to obtain clear liquid returned to a hydrazine hydrate coarse solution storage tank; the saline-alkali slags are pulped by saturated liquid and are respectively made into salt pulp and alkali pulp by multiple gravity fractionations; and the salt pulp and alkali pulp are respectively subjected to centrifugal dewatering to obtain salt slags and alkali slags. According to the invention, the process is unique and the ADC foaming agent production wastewater only contains a mass of ammonium sulfate, so that the aim of treating the wastewater pollution of an ADC foaming agent is fulfilled.
Owner:NINGXIA RISHNEG HIGH NEW IND CO LTD
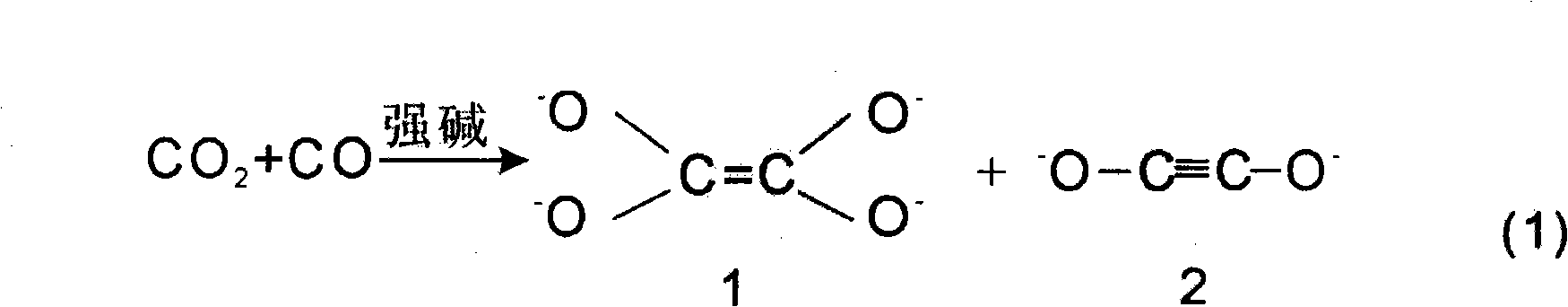
Method for preparing acetylene, ethylene, ethanol and ethylene glycol and coproducing hydrazine hydrate, benzene and derivatives of hydrazine hydrate and benzene by using CO or CO2
InactiveCN103664463AHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesOrganic compound preparationHydrazine compoundDeoxygenation
The invention relates to a new technical route or technical approach for synthesizing acetylene, ethylene, ethanol and ethylene glycol and coproducing hydrazine hydrate, benzene and derivatives of hydrazine hydrate and benzene by using CO or CO2 according to a reaction which is derived from the rule of a synthetic reaction discovered recently: a tandem substitution rearrangement reaction (TSRE reaction for short) of elementary chemistry, namely the deoxygenation homocoupling reaction (TSRE coupling for short) of CO2 and CO; the technical route or technical approach can be used for directly synthesizing the products such as acetylene, ethylene, ethanol, ethylene glycol, hydrazine hydrate, benzene and so on with the CO or CO2 as the raw material; compared with the traditional technical route or technical approach for preparing the products, the technical route or technical approach provided by the invention does not require petroleum resources, and is mild in synthesis conditions, and is generally implemented under the conditions of low pressure and normal temperature; as a result, the preparation cost is reduced by more than 40% to 80%; no three wastes are generated in the preparation process; and therefore, the new technical route or technical approach is completely up to the standards of the clean production process and more suitable for the development of large-scale industrial and commercial techniques.
Owner:李坚
Popular searches
Decorative surface effects Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Liquid chemical processes Liquid-liquid reaction processes Hydrogen peroxide Phosphorus oxides Gaseous chemical processes Electric discharge tubes Nitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compounds Liquid-gas reaction of thin-film type
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com