Patents
Literature
89 results about "Hofmann rearrangement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
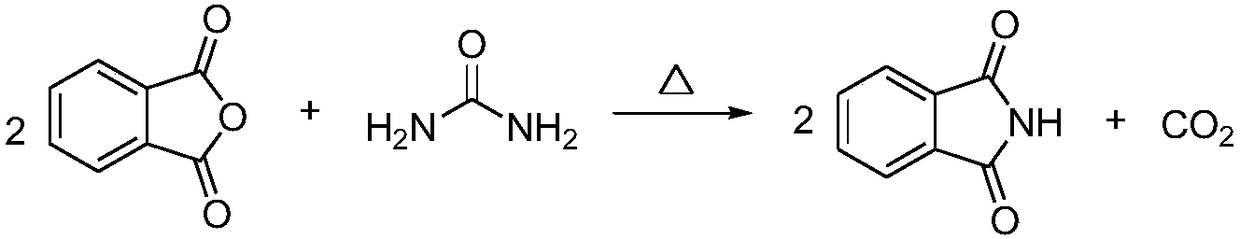
The Hofmann rearrangement is the organic reaction of a primary amide to a primary amine with one fewer carbon atom. The reaction is named after its discoverer – August Wilhelm von Hofmann. This reaction is also sometimes called the Hofmann degradation, and should not be confused with the Hofmann elimination.
Method for producing optically active 3-aminopiperidine or salt thereof
InactiveUS20100105917A1Inexpensive and readily availableEasy to produceFermentationOptically-active compound separationEnzymeStereoselectivity
The present invention relates to a method for producing an optically active 3-aminopiperidine or salt thereof. In the method, a racemic nipecotamide is stereoselectively hydrolyzed to obtain an optically active nipecotamide and an optically active nipecotic acid in the presence of an enzyme source derived from an organism, and then the optically active nipecotamide is derived into an optically active aminopiperidine or salt thereof by aroylation, Hofmann rearrangement, deprotection of the amino group and further deprotection; or the optically active nipecotamide is derived into an optically active aminopiperidine or salt thereof by selective protection with BOC, Hofmann rearrangement and further deprotection. It is possible by the present invention to produce an optically active 3-aminopiperidine or salt thereof useful as a pharmaceutical intermediate from an inexpensive and easily available starting material by easy method applicable to industrial manufacturing.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
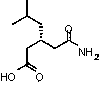
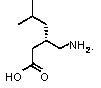
Preparation method of pregabalin
InactiveCN104140375AHigh purityEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationPregabalinDissociation reaction
The invention provides a preparation method of pregabalin. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing chiral separation reaction, dissociation reaction and Hofmann degradation reaction with 3-(carbamoyl methyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid serving as raw material to prepare pregabalin, wherein a pregabalin chiral isomer generated in the process reacts under the action of an alkali reagent so as to obtain a hydrolysis product, and the hydrolysis product is hydrolyzed further and recycled to obtain the raw material 3-(carbamoyl methyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method is convenient to carry out; the prepared pregabalin is high in purity; the used raw material can be recycled, so that the production cost is greatly reduced; the preparation method is favorable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:NANTONG CHANGYOO PHARMATECH CO LTD
Preparation method of amino pyridine bromide compound
InactiveCN101704781ASimple processLow equipment requirementsOrganic chemistryOrganic synthesisSodium hydroxide
The invention discloses a preparation method of an amino pyridine bromide compound, relating to the field of organic synthesis. The amino pyridine bromide compound takes pyridine bromide formamide as raw material, and is prepared according to the following formula of Hofmann degradation reaction which comprising the following steps of: (1) dropping liquid bromine into alkali liquid with the concentration of 2.0-4.0 mol / L at -5-0 DEG C, reacting for 1.0 hour to obtain sodium hypobromite or potassium hypobromite, wherein the alkali is sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide or sodium methoxide; (2) adding the pyridine bromide formamide with the general foumula I to the hypobromite solution at room temperature for dissolving, raising temperature to 50-80 DEG C, reacting for 0.5-2 hours, decreasing temperature to 0 DEG C for separating out solids, and filtrating to obtain crude products; extracting the filtrate with an organic solvent, removing the solvent, and merging the crude products; re-crystallizing by using petroleum ether, and drying to obtain amino pyridine bromide. Wherein, the mole ratio of the general formula I to the alkali is 1:4-8, the mole ratio of the general formula I to water is 1:80-160, and the mole ratio of the general formula I to the liquid bromine is 1:1-2; and the organic solvent is dichloromethane, chloroform or normal hexane. The invention has the advantages of one-step reaction, simple process, low requirement on equipment, and high product purity, and the yield coefficient is around 50 percent.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Synthetic method of 1, 3-two substituted ureas and carbamate
InactiveCN102503860AEasy to separateExperiment operation is simpleUrea derivatives preparationCarbamic acid derivatives preparationCarbamateAlcohol
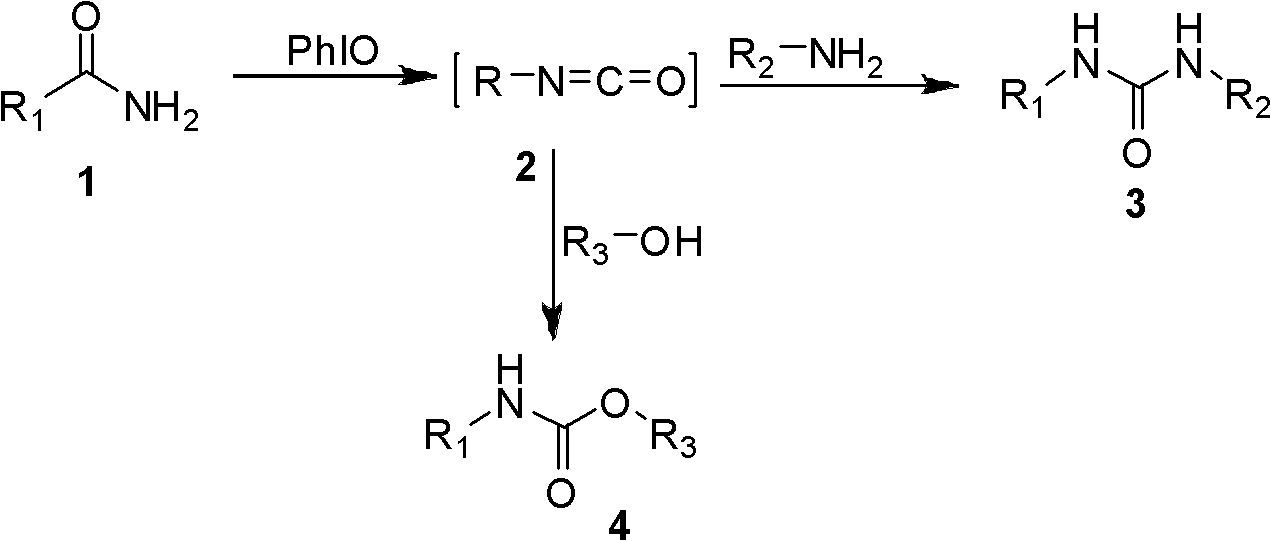
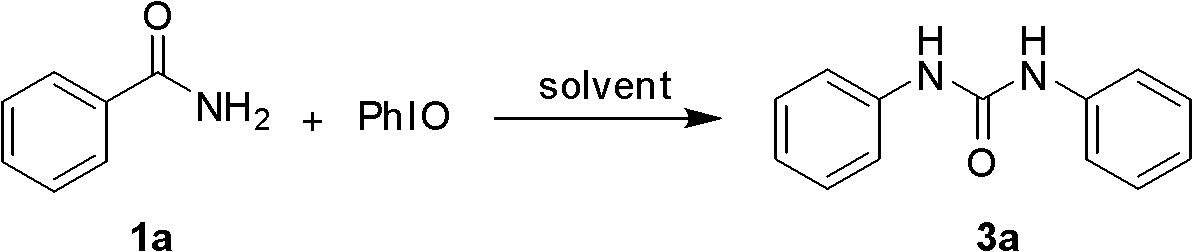
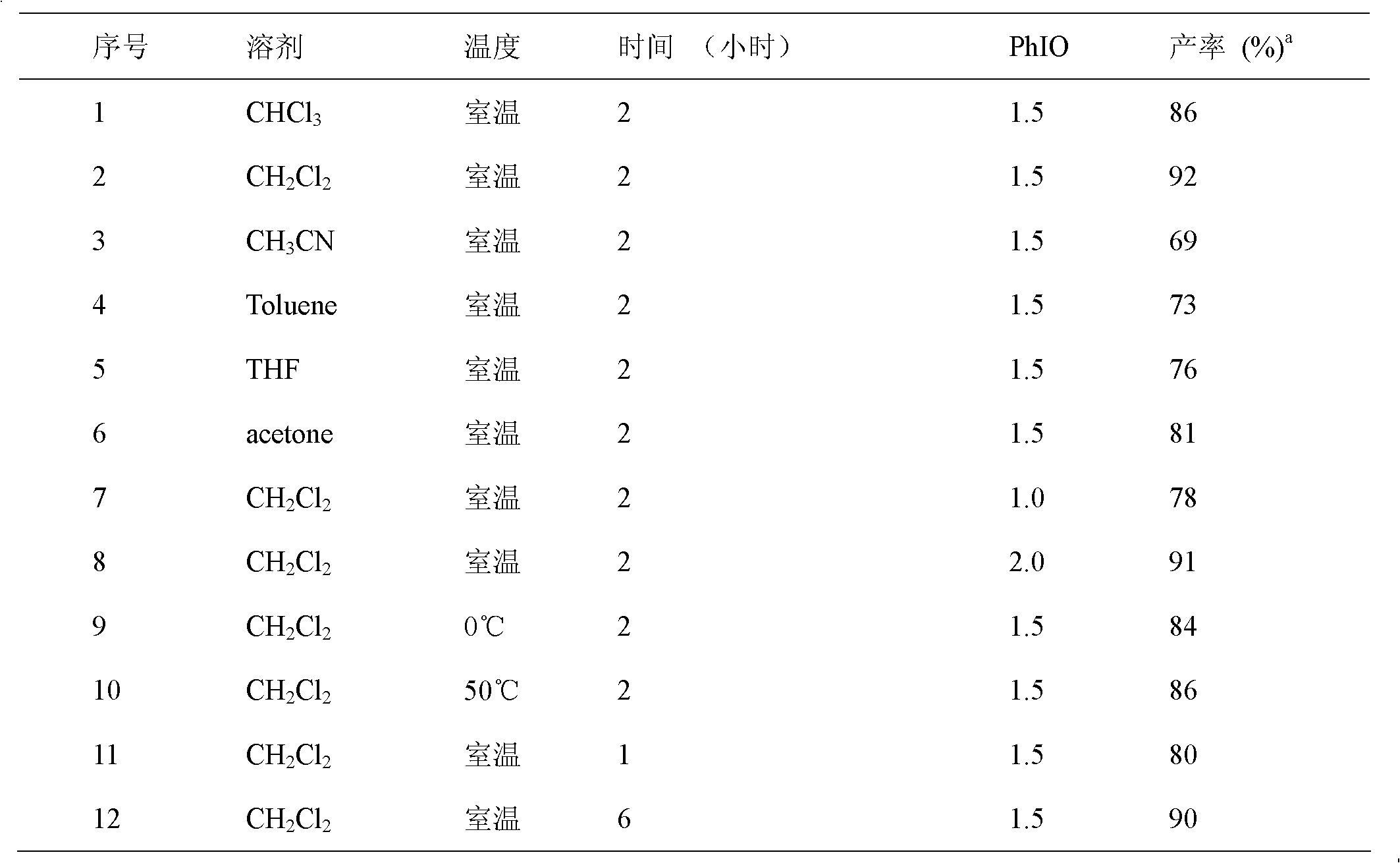
The invention relates to a simple and efficient preparation method of 1, 3-two substituted ureas and carbamate. The method comprises the steps as follows: amide is taken as substrate, and the 1, 3-two substituted ureas and carbamate are prepared by using Hofmann rearrangement reaction induced by hypervalent iodine. Only acid amide and oxidization iodobenzene are added into the reaction system, stirring is performed for 2 hours in methylene dichloride at a room temperature, and symmetrical 1, 3-two substituted ureas can be obtained with high yield. When acid amide, oxidization iodobenzene and nucleophilic agent amine are in reaction, and stirring is performed for 2 hours in methylene dichloride at a room temperature, unsymmetrical 1, 3- two substituted ureas can be obtained. When acid amide, oxidization iodobenzene and nucleophilic agent alcohol are in reaction, and stirring is performed for 2 hours in alcoholic solution at a room temperature, carbamate can be prepared. The method is simple to operate, the product selectivity is strong, and the application is wide.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
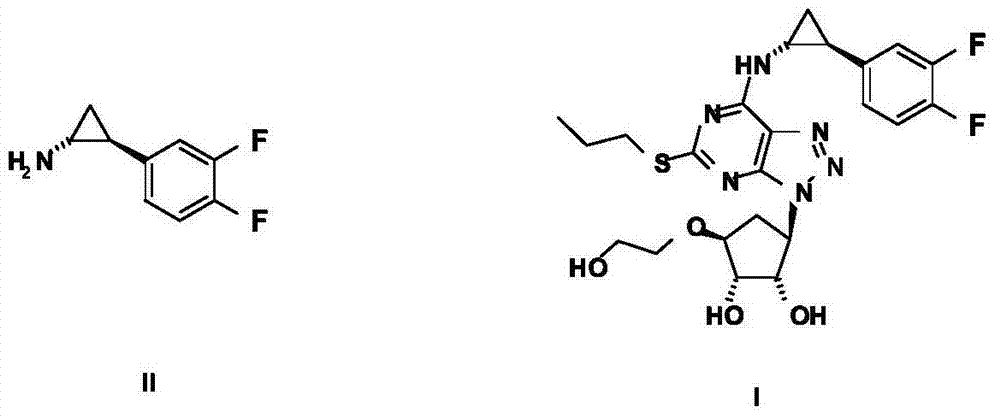
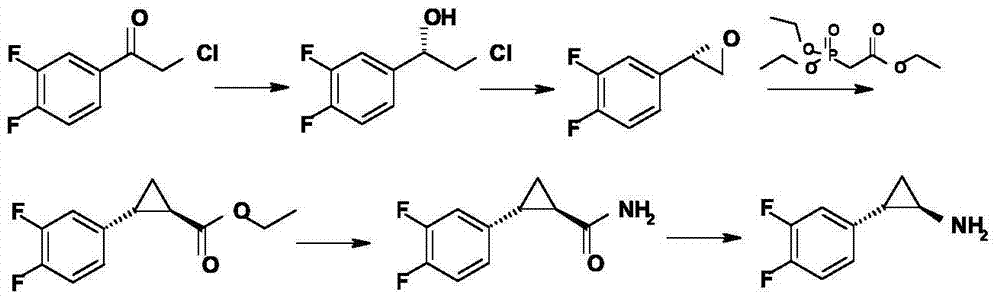
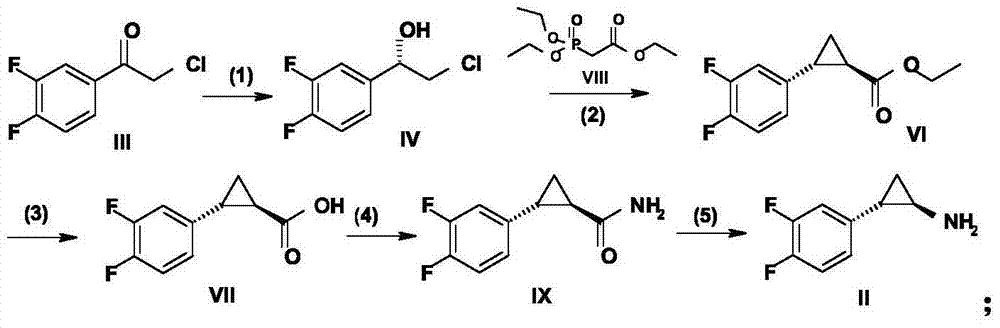
Method for preparing (1R, 2R)-2-(3, 4-difluoro phenyl)cyclopropylamine
ActiveCN105712889AReduce usageEasy to operateGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationHydrolysisRaw material
Owner:DAILY FAME TRADING LTD +1
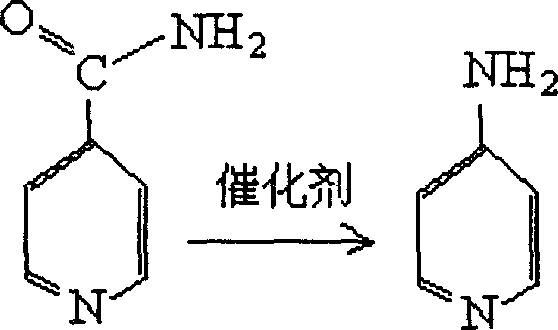
4-aminopyridine preparation method
The invention relates to a Method for preparation of 4-aminopyridine. This invention is based on the Hofmann degradation rezction of iosniacinamide to prepare 4-aminopyridine, making catalyzer by low-cost iodine or alkali metal iodide, sodium hydroxide orporassium hudroxide and bromine according to certain proportion and condition. The productivity of Hofmann degradation rezction of iosniacinamide is improved above 90%, the purity of 4-aminopyridine is higher than 99%. This can not only improve the productivity of 4-aminopyridine which is made by isonicotinic acid, but also reduce the cost of catalyzer greatly. It has important application-value to prepare 4-aminopyridine which is made by isonicotinic acid.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for preparing flocculation aid for pretreating blue algae biogas slurry
ActiveCN102432090AReduce usageSolve the problem of small flocsWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationFlocculationPentaerythritol
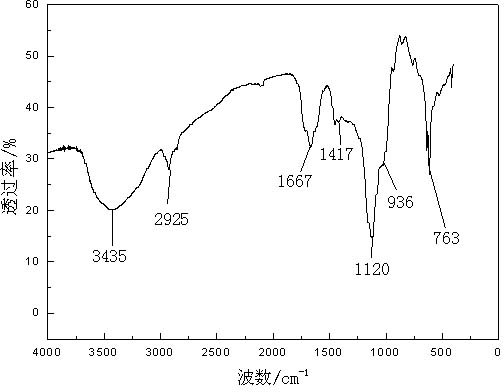
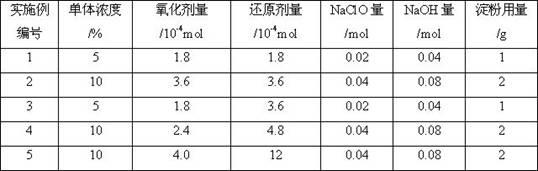
The invention relates to a method for preparing a flocculation aid for pretreating blue algae biogas slurry, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The method comprises the following steps of: initiating free radical polymerization of an acrylamide (AM) monomer by using high-valence cerium salt and pentaerythritol as an oxidation reduction system to prepare star polyacrylamide (SPAM), performing chloramination reaction on the SPAM and NaClO, performing Hofmann rearrangement to convert part of amide group into an active isocyanate group, and reacting with .OH in starch to prepare starch-grafted-SPAM (ST-g-SPAM). A rigid and flexible reticular macromolecular structure is formed by grafting the polyacrylamide with a flexible star structure onto a rigid chain serving as aframework of the starch and has a more expanded conformation, so a better flocculation effect can be achieved compared with that of the common linear polymeric flocculant; and the flocculation aid has the characteristics of small using amount, wide adaptable pH range and the like, is convenient to operate and use, and is safe and non-toxic.
Owner:溧阳常大技术转移中心有限公司
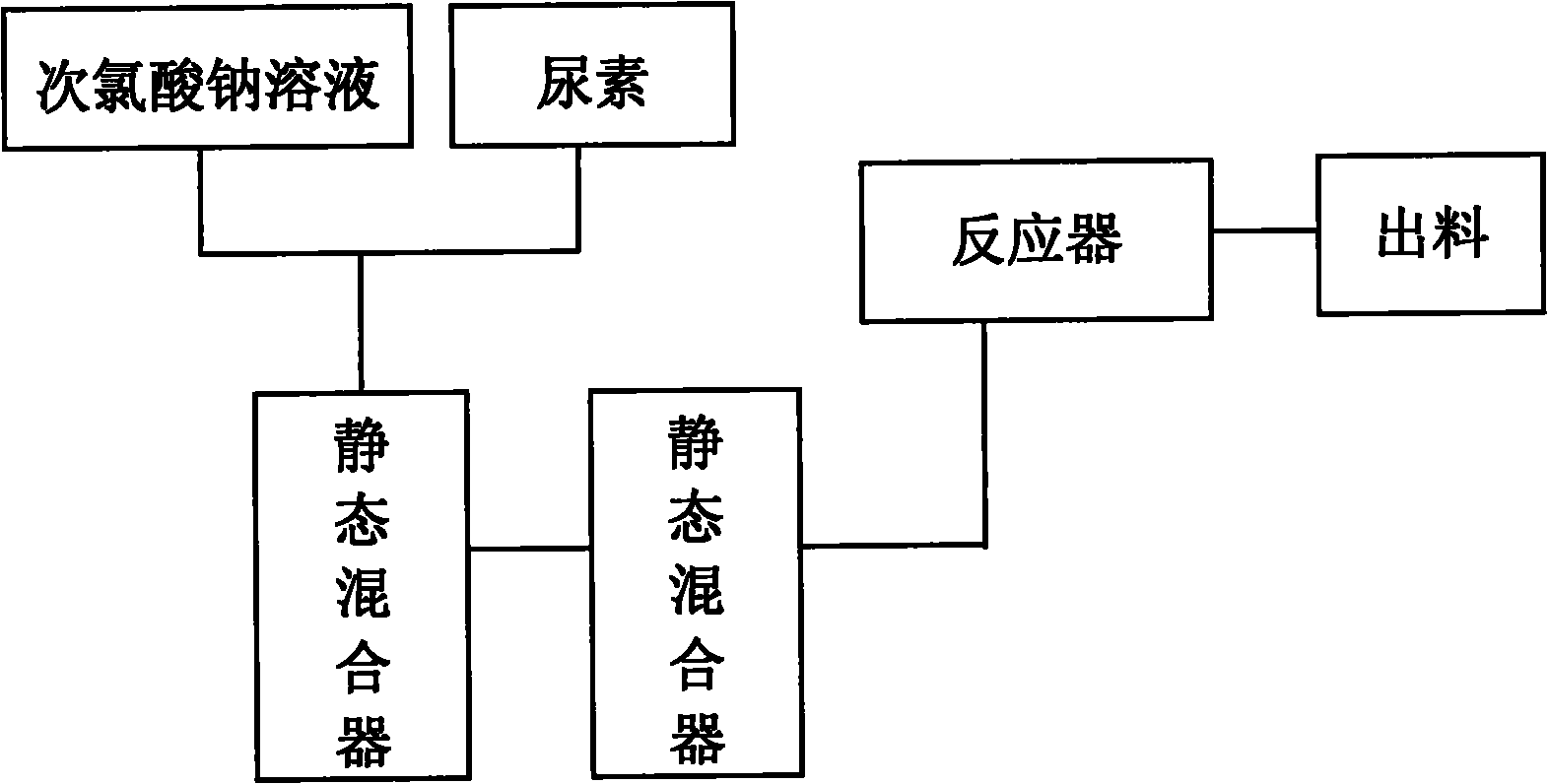
Technology for continuously producing hydrazine hydrate
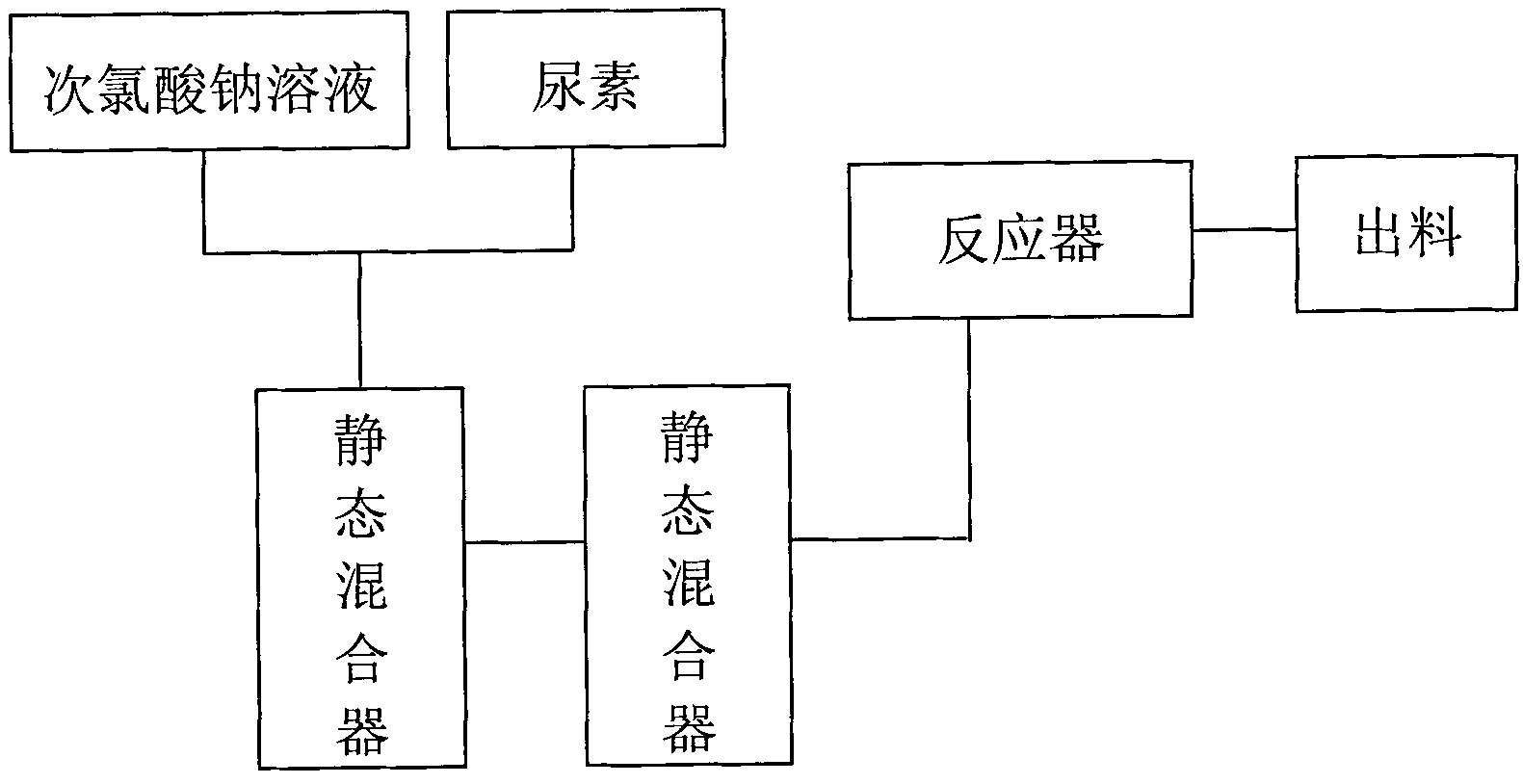
The invention relates to a technology for continuously producing hydrazine hydrate. A two-step method is adopted for reaction in the technology and the two steps is as follows: firstly, urea and sodium hypochlorite are subjected to full oxidization reaction in low temperature, concretely, two or more than two static mixers with freezing brine jackets are adopted for fully mixing materials to ensure the full performance of the oxidization reaction; and secondly, the product of the first step reacts rapidly in high temperature under the action of sodium hydroxide and is subjected to Hofmann rearrangement so as to generate the hydrazine hydrate. The benefits are as follows: the method is simple in technology and can realize continuous production; only the quantity of the static mixers needs to be increased, so that the investment is little; and the content of the obtained hydrazine hydrate is over 85%.
Owner:HANGZHOU HI TECH FINE CHEM
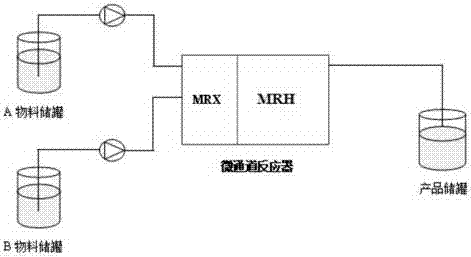
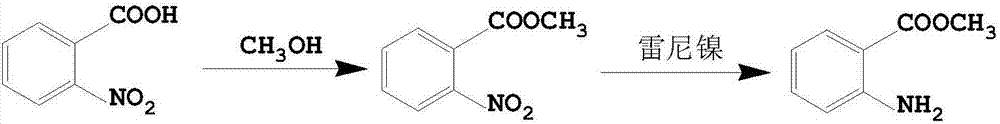
Preparation method of methyl orthoaminobenzoate by means of microchannel reactor
InactiveCN106905172AIncrease choice flexibilityImprove securityOrganic compound preparationChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsSodium hypochlorite solutionMethyl anthranilate
The invention relates to a method of preparing methyl orthoaminobenzoate by means of a microchannel reactor. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: pumping a phthalimide source liquid and a sodium hypochlorite solution into a mixing module MRX of the microchannel reactor; and after mixed reaction, feeding the mixture into a reaction module MRH of the microchannel reactor again for Hofmann degradation reaction to obtain methyl orthoaminobenzoate, wherein the volume ratio of the phthalimide source liquid to the sodium hypochlorite solution is 1: (1.0-2.2). The method provided by the invention is short in reaction time, the prepared methyl orthoaminobenzoate product is high in purity and high in yield, the production cost is greatly lowered, and the production efficiency is increased.
Owner:田振民 +1
Preparation method of ticagrelor intermediate
ActiveCN104744266AReduce pollutionReduced Possibility of ContaminationOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationPotassium borohydrideTicagrelor
The inventiondiscloses a preparation method of ticagrelor. The method comprises the following steps: (1) reducing a compound shown in a formula III in the presence of a proton source provided by sodium borohydride or potassium borohydride and diethyl aniline hydrochloride to obtain a compound shown in a formula IV; (2) reacting the compound IV in the presence of alkali to generate a compound VI; (3) hydrolyzing the compound VI without purification to generate a compound VII; (4) reacting the compound VII to generate acyl chloride, reacting the acyl chloride to generate formamide, thus obtaining a compound shown in a formula IX; and (5) carrying out Hofmann rearrangement on the compound IX to obtain a compound shown in a formula II. Regents used in the method are nontoxic, harmless, environmentally friendly and low in price; the used key reagents can be recycled. Therefore, the method is applicable to industrial production.
Owner:SHANGYU JINGXIN PHARMA +1
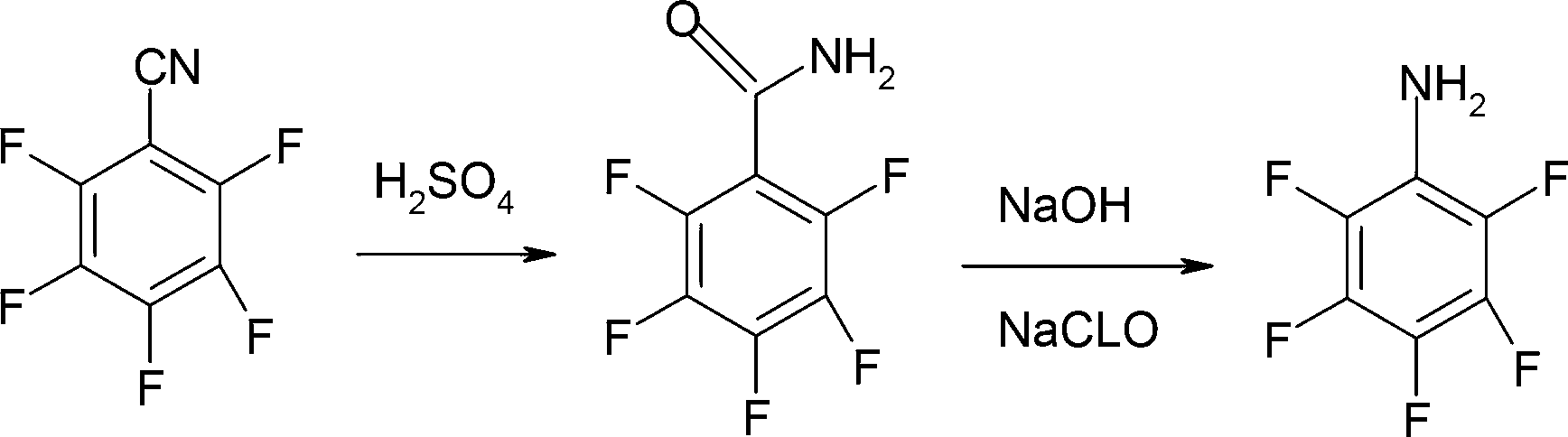
Preparation method of pentafluoroaniline
ActiveCN103012162AOvercoming not easy to getOvercome high pricesPreparation by rearrangement reactionsPentafluoroanilineSteam distillation
The invention provides a preparation method of pentafluoroaniline. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) adding pentafluorobenzonitrile into sulfuric acid with the concentration of 70-98% for hydrolysis, controlling the hydrolysis temperature to be 70-120 DEG C and the reaction time to be 3-5 hours, and then adding the product into water to separate out, and filtering to obtain pentafluorobenzamide; and (2) mixing the pentafluorobenzamide prepared by step (1) with alkali solution and halogen or hypohalite, preserving the heat for 4-6 hours at -10 to 20 DEG C and then heating up to 70-110 DEG C to carry out Hoffman degradation, controlling the reaction time to be 0.5-3 hours, and then performing steam distillation to obtain the pentafluoroaniline. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the raw materials are easily available, the process is simple, the operation is convenient, the product purity is high (99% or higher), the yield is high (as high as over 80%), the cost is low, and the method is safe and efficient with energy conservation, consumption reduction and little discharge of three wastes, so the method provided by the invention is suitable for industrial production on a large scale.
Owner:FUXIN RUIGUANG FLUORINE CHEM
Method for preparing 2-aminopyridine and alkyl derivative
A process for preparing 2-amino pyridine and its alkyl derivative from 2-cyanopyridine or its alkyl derivative includes incomplete hydrolysis and Hofmann degradation. Its advantage is high output rate (80%) and purity up to 99% or more.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing phenylaniline
ActiveCN102070465AGuaranteed catalytic efficiencyLow costPreparation by rearrangement reactionsNickel catalystHydrogen
The invention provides a method for preparing phenylaniline, which comprises the following steps: mixing cyanophenyl shown in the formula II, first alkaline compounds, nickel catalysts and borophenylic acid shown in the formula III or borophenylic esters shown in the formula VI to carry out suzuki coupling reaction for obtaining cyanobiphenyl shown in the formula IV; mixing the cyanobiphenyl, second alkaline compounds and oxyful, and hydrolyzing the cyanobiphenyl to obtain amido biphenyl shown in the formula V; and mixing the amido biphenyl, third alkaline compounds and sodium hypohalite to generate Hofmann degradation reaction for obtaining phenylaniline shown in the formula I, wherein R1 is chlorine, bromine, iodine, sulphonic acid ester radicals, carbonic ether radicals or alkyl ester radicals; R2 is alkyl, alkoxy, cyano, amido or hydrogen; R3 is chlorine, bromine or iodine; and R4 is alkyl, alkoxy, cyano, amido or hydrogen. The preparing method provided by the invention has the advantages of mild condition, low cost, cleanness and environment protection.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
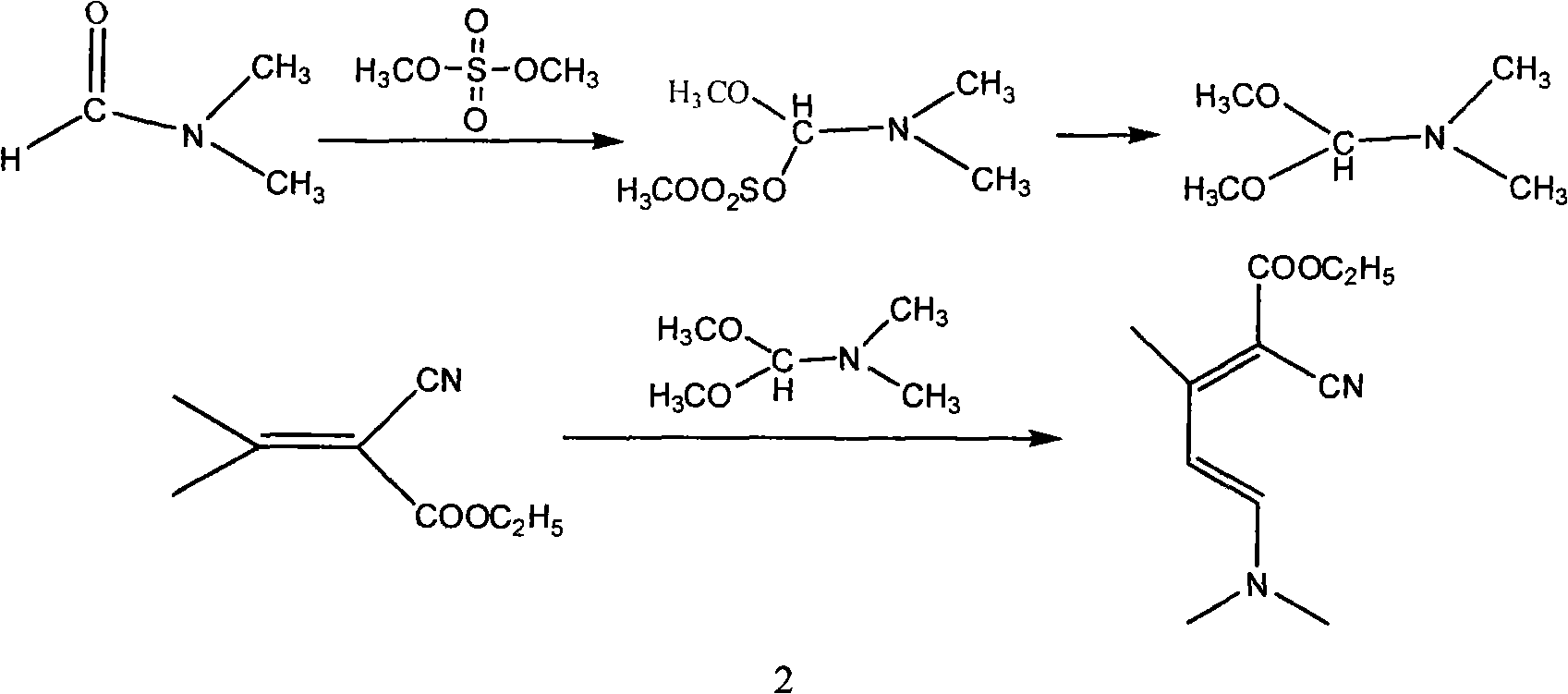
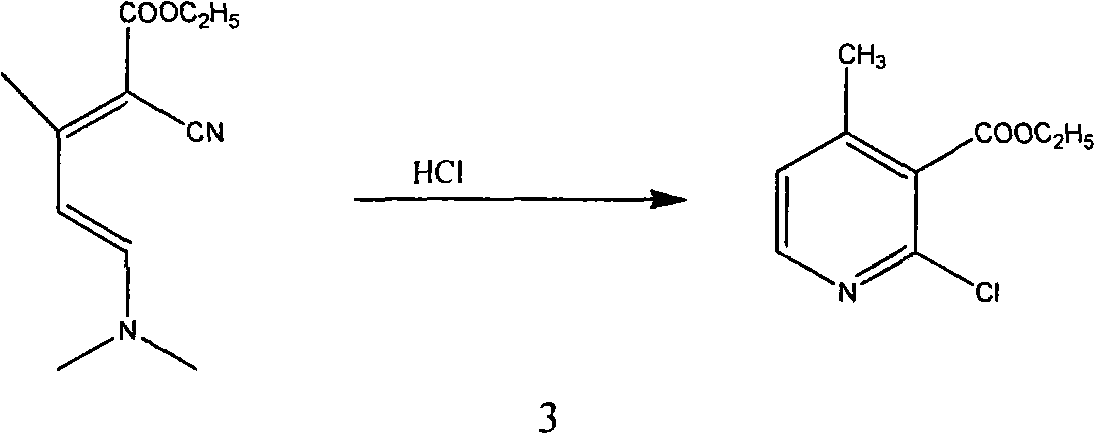
Method for synthesizing 2-chloro-3-amino-4-methylpyridine by ethyl cyanoacetate and acetone
InactiveCN101565399AComplicated operationFew stepsOrganic chemistrySodium methoxideOrganic synthesis
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing an important intermediate 2-chloro-3-amino-4-methylpyridine for an anti-AIDS medicament Nevirapine, and belongs to the technical field of organic synthesis. The method comprises the following process steps that: ethyl cyanoacetate and acetone are dehydrated and condensed to generate a condensation compound I under the action of a catalyst; dimethyl formamide, dimethyl sulfate and sodium methoxide solution react to generate N,N-dimethylformamiade dimethyl acetal (N,N-dimethyl formamide A), and then the N,N-dimethylformamiade dimethyl acetal reacts with the condensation compound I to generate conjugated enamine, namely a condensation compound II; the condensation compound II is cyclized by hydrochloric acid and ethanol to form a cyclic compound 2-chloro-4-methyl-ethyl nicotinate; the 2-chloro-4-methyl-ethyl nicotinate is ammonolyzed by ammonia gas to form 2-chloro-4-methyl-niacinamide; and the 2-chloro-4-methyl-niacinamide is subjected to Hofmann degradation reaction to form the 2-chloro-3-amino-4-methylpyridine. Compared with the prior synthesizing method, the method of the invention has the remarkable characteristic of reducing the reaction steps, and is suitable for large-scale industrialized production; the molar total yield of the five-step reaction is improved to 27 percent from the prior 24 percent; and the purity of the product reaches over 99 percent.
Owner:江苏鼎昊医药科技有限公司
Process For Manufacturing Paper And Board Having Improved Retention And Drainage Properties
ActiveUS20130139986A1Improve performanceDosage controlNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperCardboardFiber
A method for manufacturing a sheet of paper and / or board having improved retention and drainage properties is provided, according to which, before the formation of the sheet and / or board, at least two retention aids are added to the fibrous suspension. These two retention aids are a main retention aid corresponding to a (co)polymer having a cationic charge density above 2 meq / g, obtained by the Hofmann degradation reaction, and a secondary retention aid corresponding to a water-soluble or water-swellable polymer having an anionic charge density above 0.1 meq / g. The main retention aid is introduced into the fibrous suspension in a proportion of 100 to 800 g / t of dry pulp, and the secondary retention aid is introduced into the fibrous suspension in a proportion of 50 to 800 g / t of dry pulp and has an intrinsic viscosity IV above 3 dl / g.
Owner:S P C M SA
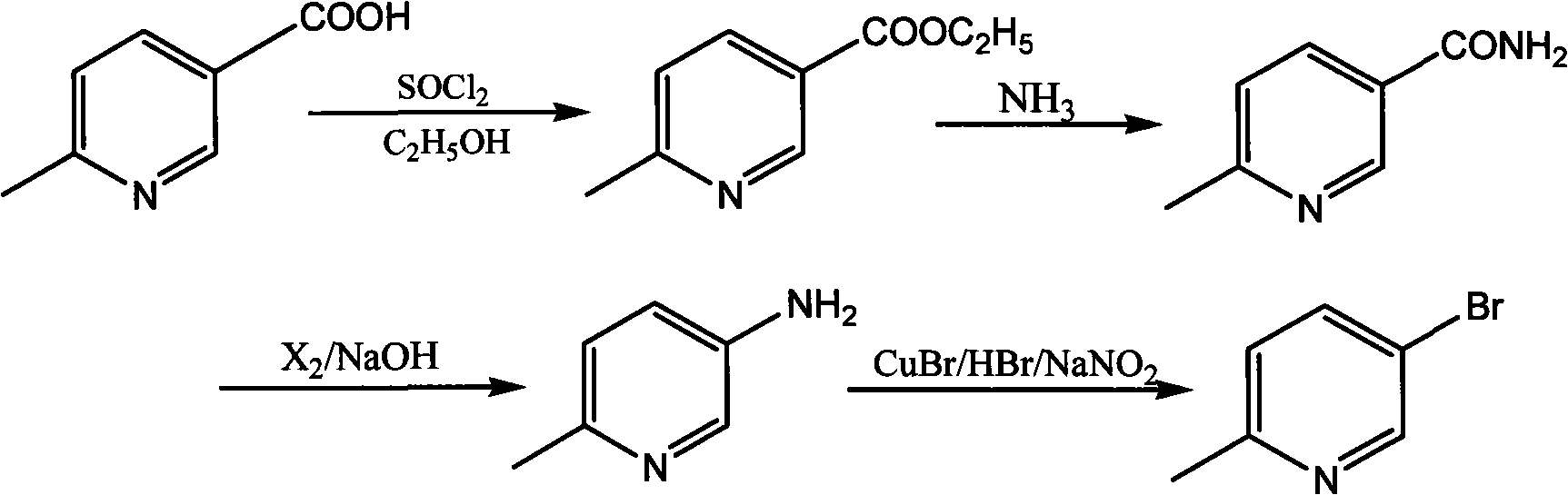
Synthetic method for 5-bromine-2-methylpyridine
InactiveCN101514184AReduce wasteMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryPhotochemistryPicolinic acid
The invention discloses a synthetic method for 5-bromine-2-methylpyridine: using 6-methyl-3-picolinic acid as the raw material to react with ethyl alcohol to generate 6-methyl-3-picolinic acid ethyl ester; carrying out ammonolysis reaction by aqueous ammonia on the 6-methyl-3-picolinic acid ethyl ester to generate 6-methyl-3-pyridine carboxamide; carrying out Hofmann degradation reaction to obtain 6-methyl-3-aminopyridine; and finally reacting the 6-methyl-3-aminopyridine with a bromizing reagent to generate 5-bromine-2-methylpyridine. In the method, the process reaction condition is mild, the yield is high, the raw material is available, the cost is lower, and no 3-subsidary products are generated in the whole process, the load of post separation is eliminated and the prospect of industrialization is good.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Acrylamide-derived cationic copolymers, and uses thereof
Cationic or amphoteric (co)polymer obtained by Hofmann degradation reaction, in aqueous solution, in the presence of an alkaline-earth and / or alkali metal hydroxide and of an alkaline-earth and / or alkali metal hypohalide, on a base (co)polymer comprising at least one nonionic monomer chosen from the group comprising acrylamide (and / or methacrylamide) and N,N-dimethylacrylamide, is characterized in that the base (co)polymer is modified beforehand with at least one polyfunctional compound containing at least 3 heteroatoms chosen from N, S, O and P and each having at least one mobile hydrogen. Use as a flocculation, retention and / or drainage aid, and dry strength aid is contemplated.
Owner:S P C M SA
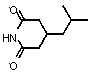
Synthesis method of gabapentin hydrochloride
InactiveCN102093237AOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationGabapentinSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a synthesis method of gabapentin hydrochloride. The method comprises the following steps of: with 1,1-cyclohexyldiacid monoacyl amine as a starting material, carrying out a Hoffman degradation reaction; dewatering and condensing; carrying out product phase transfer; and hydrolyzing. The method artfully integrates relevant processes in the prior art and realizes the preparation of the gabapentin hydrochloride through the generation and the phase transfer of 3,3-pentylidene butyrolactam in a reaction process; the reaction does not relate to an acidification process, avoids the consumption of a large quantity of inorganic acids and the generation of inorganic salts and thoroughly solves the problem of difficult separation of the gabapentin hydrochloride in the original process; and in the reaction process, an organic solvent is directly cycled and mechanically applied and closed in the reaction process all the time, which is hopeful to realize the zero organic solvent discharge of the process. The method has the advantages of reasonable process design, simpleness and convenience of operation, high raw material conversion rate and high yield.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
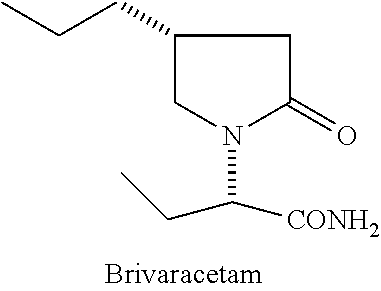
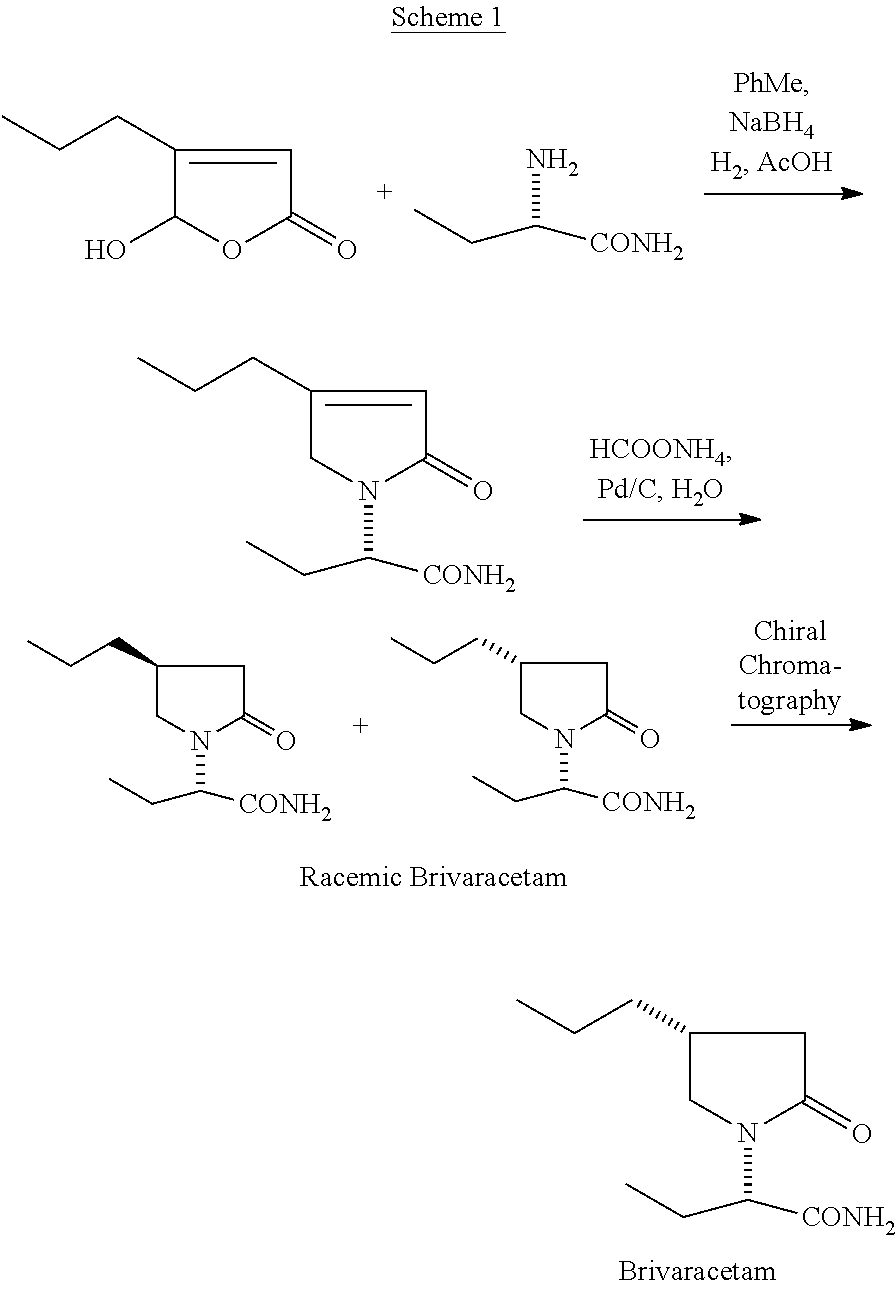
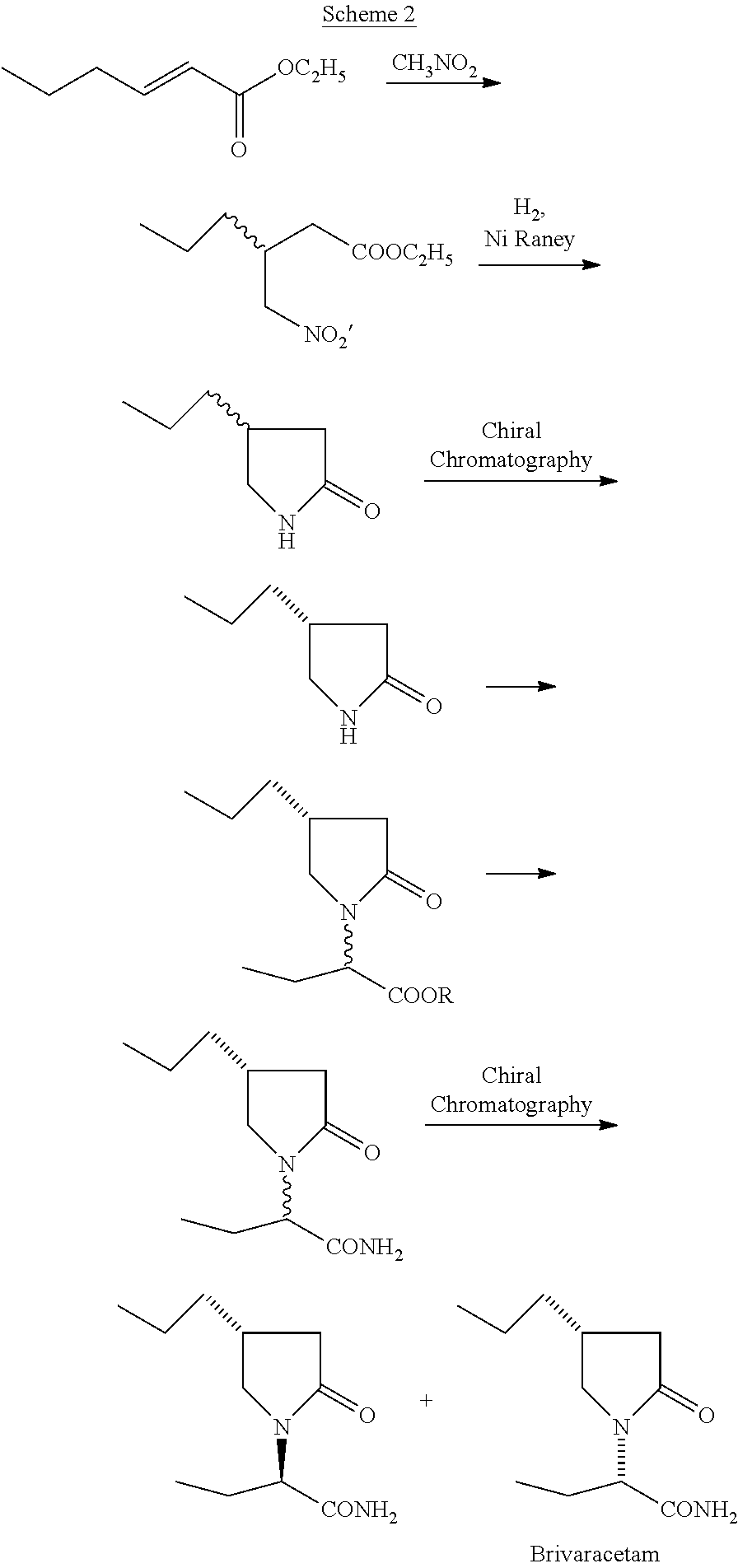
Process for preparing Brivaracetam
A process for the preparation of Brivaracetam, an anti-convulsion drug, is provided comprising Hofmann rearrangement of (S)-3-(2-(chloroamino)-2-oxoethyl) hexanoic acid, followed by cyclization resulting in (R)-4-propyl-pyrrolidin-2-one which on condensation with bromo butyric acid or ester followed by reaction with ammonia results in Brivaracetam.
Owner:DIVI S LAB LTD
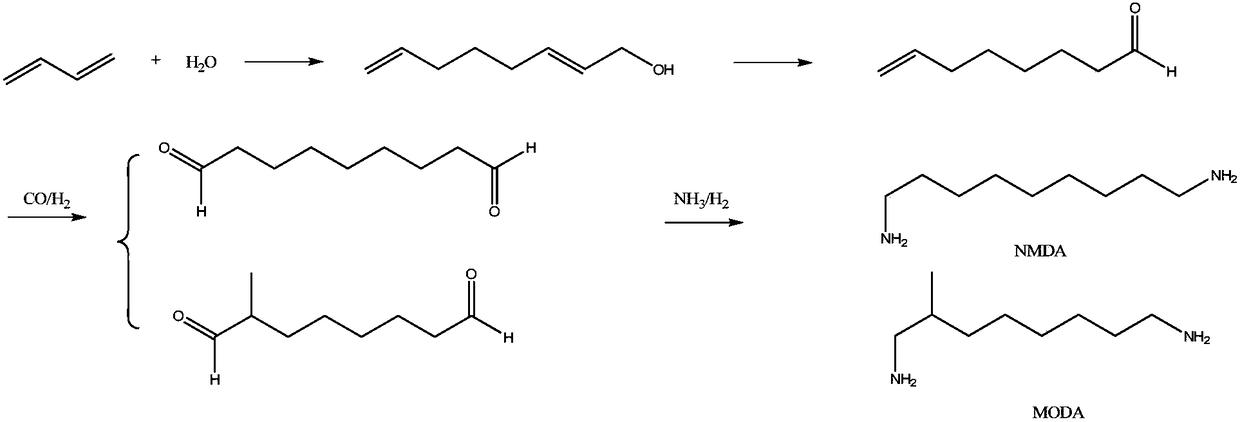
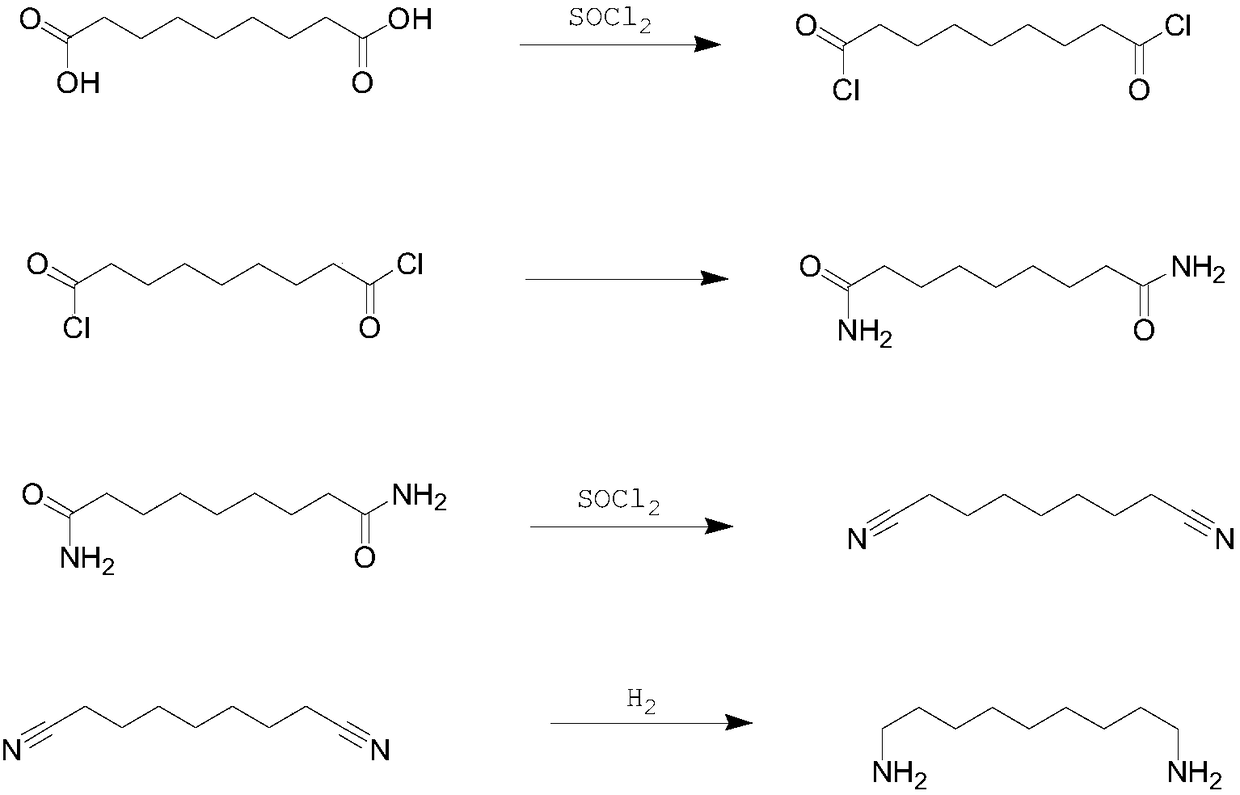
Synthetic method of 1,9-diaminononane
ActiveCN108727200AHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationHydrogenation reactionHigh pressure
The invention provides a synthetic method of 1,9-diaminononane. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out condensation reaction on undecanoic acid and transforming the undecanoicacid into a derivative of the undecanoic acid; then carrying out ammoniation to generate undecendiamide, and then carrying out Hofmann rearrangement reaction to generate a target product 1,9-diaminononane. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that raw materials are inexpensive and easily obtained and have a sufficient supply, and high-temperature and high-pressure reaction conditions are not involved, and a production process has more security. Compared with an abroad production technology, the synthetic method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of less side reaction, high purity of the product, less reaction steps and low requirement on equipment. Compared with a production process reported by domestic companies, the synthetic method has the advantages of less three wastes, and meanwhile, hydrogenation reaction is not involved, and the synthetic method has higher reaction security.
Owner:BEIJING RISUN TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol
ActiveCN107129435ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getThe reaction process is simpleOrganic compound preparationPreparation by cyanide reactionPropionitrileSodium cyanide
The invention relates to a method for preparing 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol. The method comprises the following steps: 1) enabling 2-chloropropane and sodium cyanide to react to generate 2-methyl propionitrile; 2) performing aldol condensation reaction on the 2-methyl propionitrile and formaldehyde so as to generate 2,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxy propionitrile; 3) performing hydrolysis reaction on 2,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxy propionitrile so as to generate 2,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxy propanamide; and 4) performing Hofmann degradation on the 2,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxy propanamide, thereby obtaining 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol. The method is cheap and easy in obtaining of raw materials of different steps, simple in reaction process, free of hash reaction condition, remarkable in cost advantage, high in yield, low in pollution and easy in product purification.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
Preparation method of pregabalin
ActiveCN103922950AReduce usageHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationN-ChlorosuccinimidePregabalin
The invention discloses a preparation method of pregabalin. According to the preparation method, (R)-(-)-3-(carbamyl methyl)-5-methylhexanol has a Hofmann degradation reaction under the action of N-chlorosuccinimide in the presence of an alkali to produce pregabalin. By adopting N-chlorosuccinimide as a reagent of Hofmann degradation reaction, the use of bromine is avoided, the reaction yield is improved and the content of impurities in the product is reduced, so that the reaction is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MENOVO PHARMA
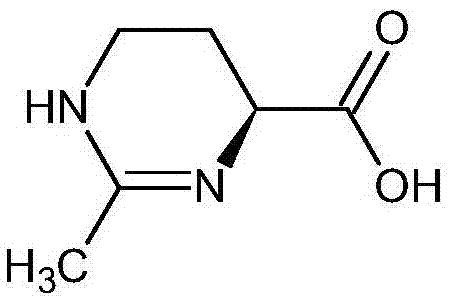
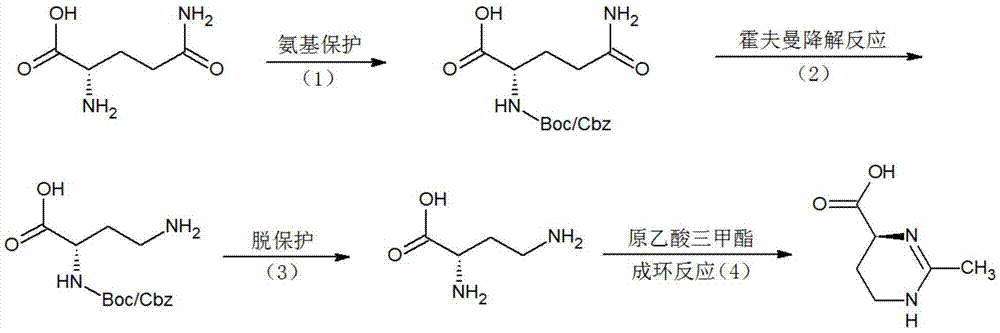
(S)-2-methyl-1,4,5,6-tetrahydromethylpyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid synthesis method
InactiveCN106916111ALow yieldThe synthesis method is simpleOrganic chemistry methodsBulk chemical productionChemical synthesisAcetic acid
The present invention relates to a (S)-2-methyl-1,4,5,6-tetrahydromethylpyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid synthesis method. According to the method, L-glutamine is used as a raw material, the alpha-amino of the L-glutamine is protected with a protection group, a decarbonylating agent is added, a Hofmann degradation reaction is performed to remove the carbonyl group attached to the remaining amino, the protection group is removed to obtain L-2,4-diaminobutyric acid, and finally the prepared L-2,4-diaminobutyric acid and trimethyl orthoacetate are subjected to a ring forming reaction to obtain the (S)-2-methyl-1,4,5,6-tetrahydromethylpyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid. Compared to the method in the prior art, the method of the present invention has the following characteristics that the chemical synthesis route is provided, the steps of the synthesis process are simple, the raw materials are easy to obtain, the product purity is high, and the method is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:上海予利生物科技股份有限公司
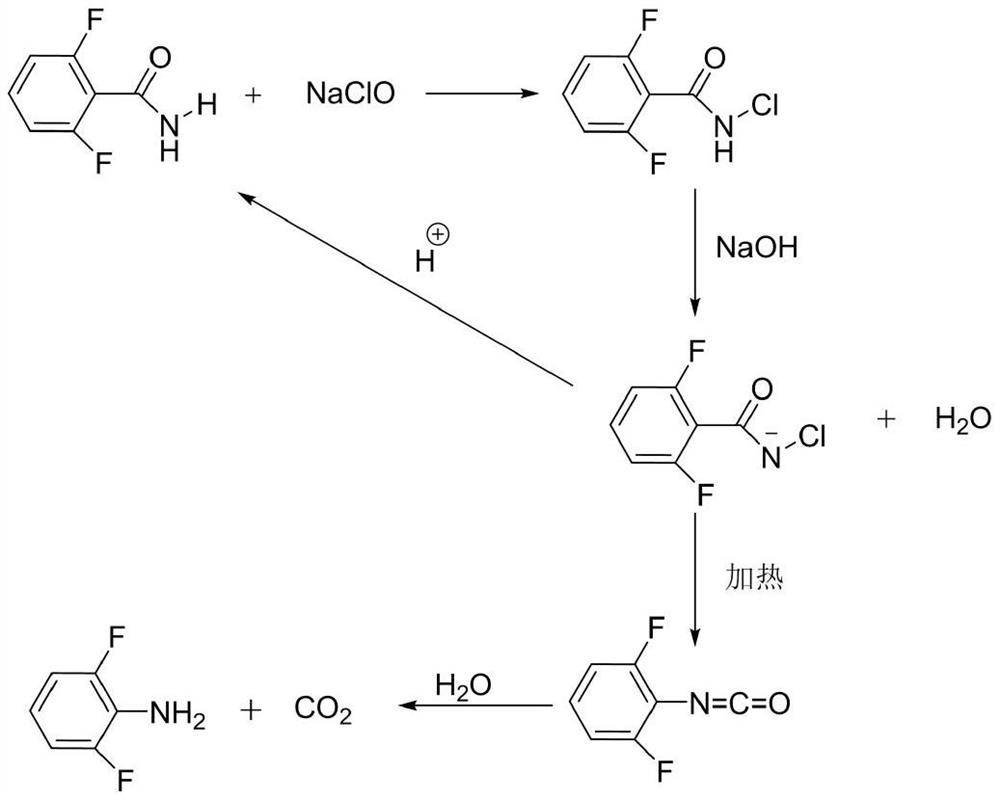
Safe and green production method of high-quality 2, 6-difluoroaniline
InactiveCN111777515ASolve the problem of excessive degradation of wastewaterReduce productionAmino compound purification/separationOrganic compound preparationPotassium hydroxideWastewater
The invention discloses a safe and green production method of high-quality 2, 6-difluoroaniline, and belongs to the field of fine chemical engineering. 2, 6-difluoroaniline, sodium hypochlorite, water / recycled water and sodium hydroxide / potassium hydroxide are used as raw materials for reaction; the violent heating process of the Hofmann degradation reaction is avoided in a manner of steaming outthe product while feeding, and meanwhile, the product is rapidly separated from a high-temperature system through steam distillation, so that the generation amount of impurities is reduced, and the high-purity 2, 6-difluoroaniline is obtained. The purity of the obtained 2, 6-difluoroaniline is greater than 99.9%, the maximum single impurity content is less than 0.10%, and the water content is lessthan 0.10%. According to the method, the water phase separated from the water vapor distillate is directly reused, so that the wastewater discharge is greatly reduced, the green production of the 2,6-difluoroaniline is realized, the pollution in the whole operation process is small, and the production process is safe and reliable.
Owner:恒劲生物技术(大连)有限公司
Synthesis method of tertiary aliphatic amine
ActiveCN103965053AOrganic compound preparationPreparation by reductive alkylationSynthesis methodsAliphatic amine
The invention provides a synthesis method of tertiary aliphatic amine. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, fatty acid amide is taken as a raw material, and the tertiary aliphatic amine is synthesized by Hofmann degradation and reaction for reducing methylation. The synthesis method has the advantages of simple synthesis process, mild reaction conditions, complete reaction, few side reactions, low energy consumption and high yield.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of boscalid
ActiveCN113831280ALow costLow equipment requirementsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationChlorobenzeneFluorenone
The invention relates to a preparation method of boscalid, and correspondingly relates to a preparation method of intermediates 4 '-chloro-2-biphenylformamide and 4'-chloro-2-aminobiphenyl. The method comprises the following steps: taking 9-fluorenone as a raw material, carrying out ring opening, acyl chloride substitution, amidation, chlorination and Hofmann rearrangement degradation to obtain 2-(4 '-chlorophenyl) aniline, and condensing the 2-(4'-chlorophenyl) aniline and 2-chloronicotinamide to obtain the product boscalid. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the target product can be obtained at high yield and high purity, and the harm to the environment can be reduced while the cost is reduced.
Owner:上海埃农生物科技有限公司 +1
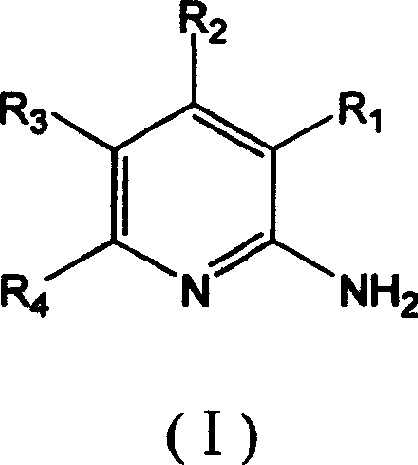
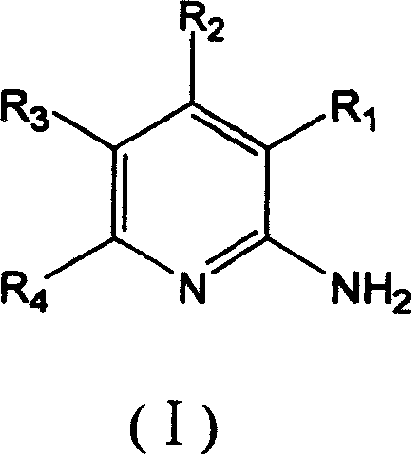
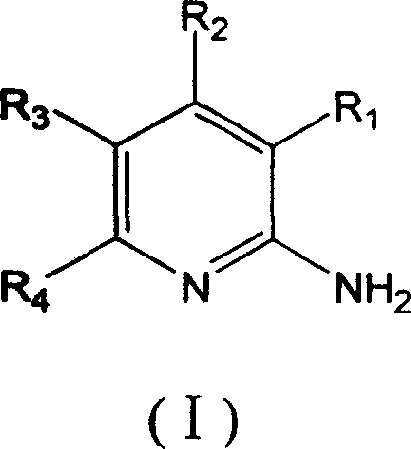
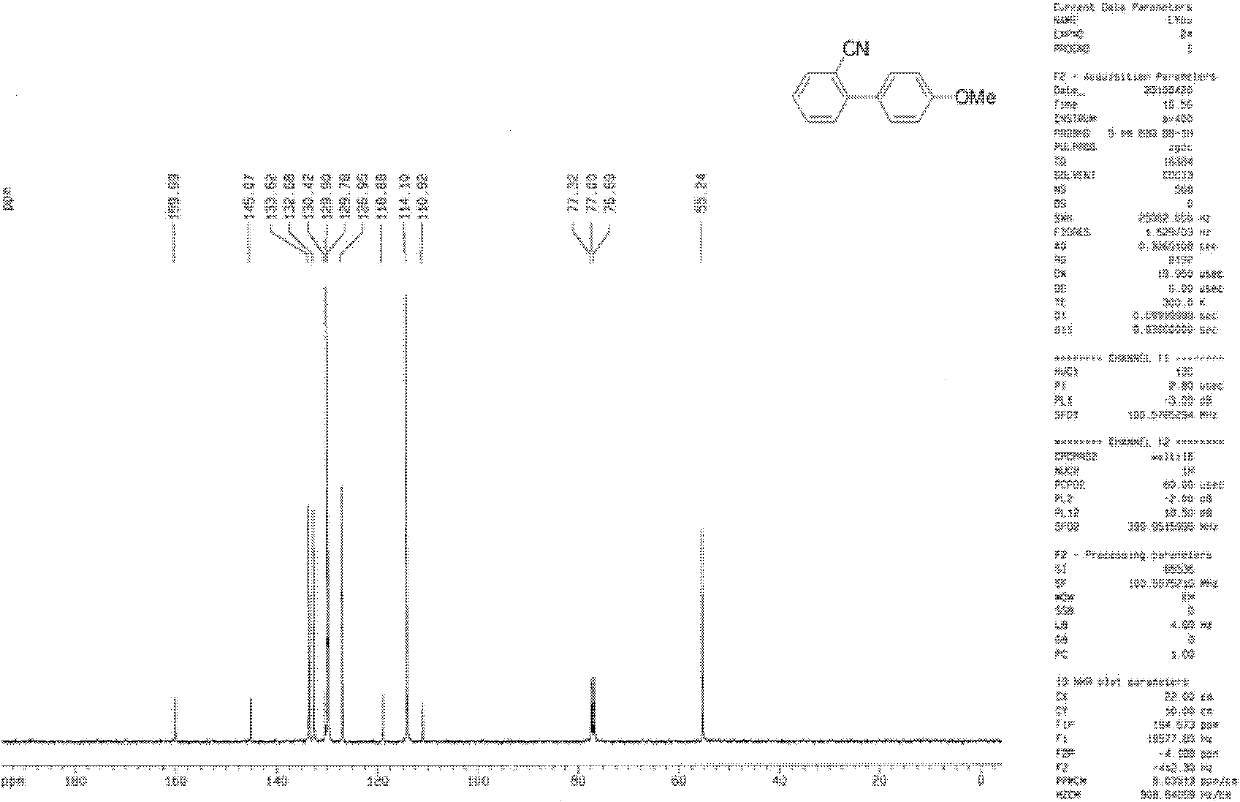
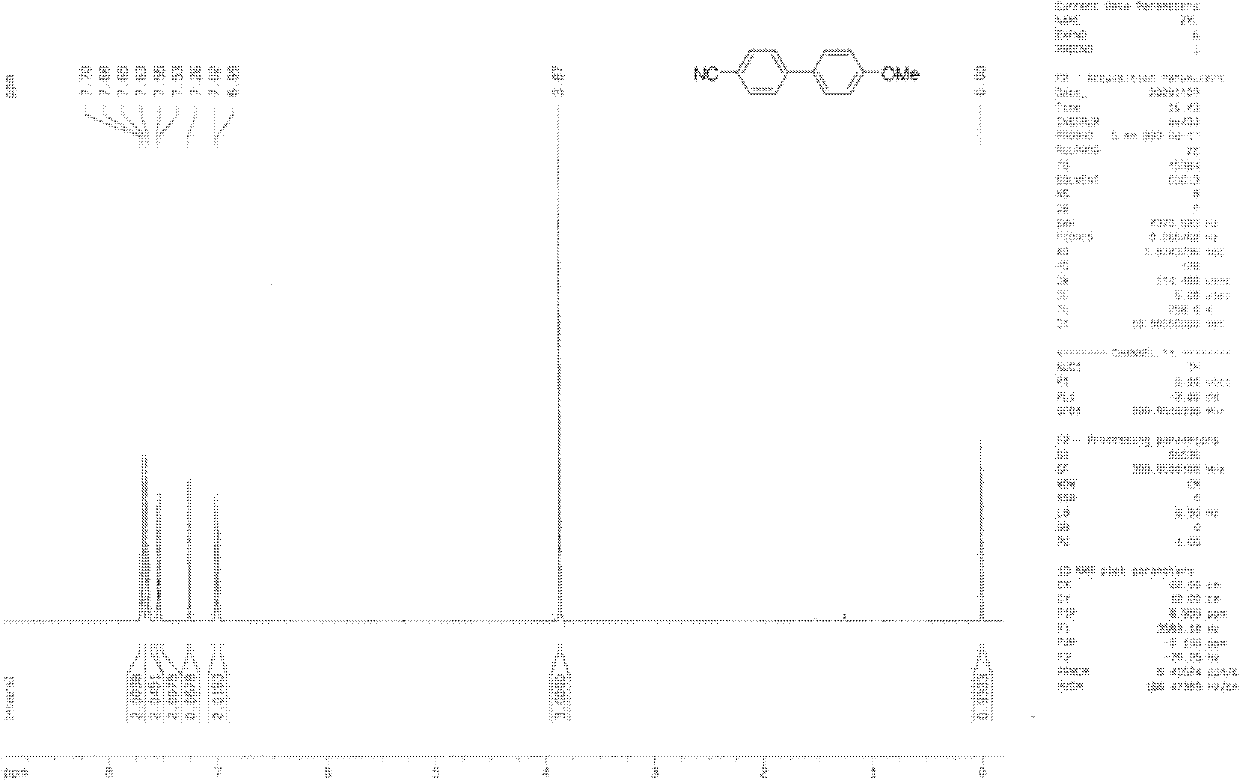
Synthesis method of 2,6-dichloropyridine [3,4-B] pyrazine
InactiveCN106831768AAvoid dangerous reactionsReduce manufacturing costOrganic chemistryBulk chemical productionSocial benefitsPyrazine
The invention discloses a synthesis method of 2,6-dichloropyridine [3,4-B] pyrazine. A target compound is obtained from 3-amino-4-picolinic acid as a main starting material through esterification, chloro, aminolysis, BOC protection, hofmann rearrangement and cyclization. The route of the synthesis method is two steps longer than that of an existing route, but basically comprises amino protection and deprotection; the whole route is unit reaction basically, the operation is simple and the conditions are mild; and the target compound can be obtained through simple treatment; and the whole route is relatively high in yield. Great economic benefits and social benefits are brought for production by employing the route. In a word, the synthesis method has the characteristics of being mild in reaction condition, simple in technological operation, environment-friendly, low in cost and high in yield.
Owner:JIANGSU YUXIANG CHEM
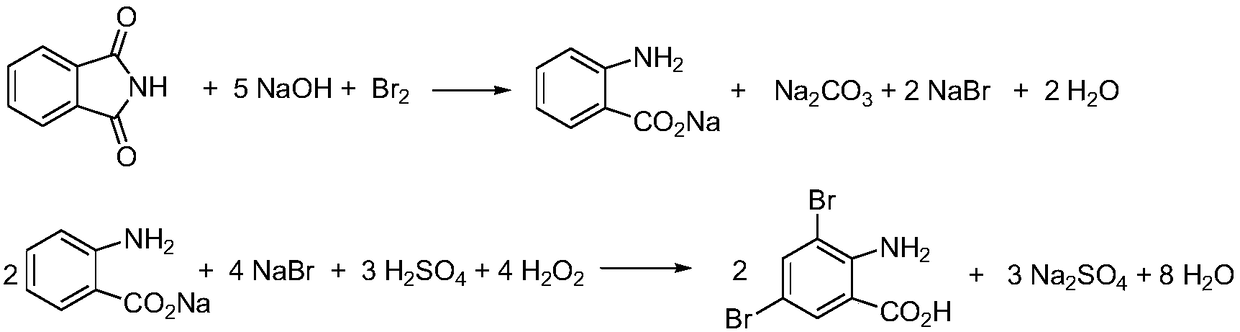
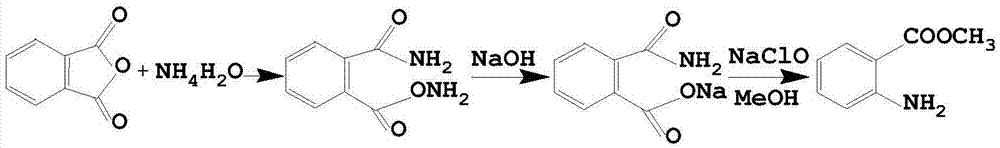
Preparation method for ambroxol hydrochloride intermediate 3,5-dibromo-2-aminobenzoic acid
InactiveCN109096135ALow toxicityLow priceOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationBromineTwo step
The invention discloses a preparation method for an ambroxol hydrochloride intermediate 3,5-dibromo-2-aminobenzoic acid. The method enables the ambroxol hydrochloride intermediate 3,5-dibromo-2-aminobenzoic acid to be obtained through the following two-step reaction: (1) under the action of alkali and bromine, phthalimide undergoes the Hofmann degradation reaction to obtain 2-amino-benzoate and bromine anion; (2) under acidic conditions, the bromine anion is oxidized in situ to be bromine by hydrogen peroxide, and the bromine further undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction on an aromaticring with 2-aminobenzoic acid to obtain the 3,5-dibromo-2-aminobenzoic acid. The method takes phthalic acid imine as an initiating raw material, the raw material is cheap and easy to obtain, and a production process for the raw material is also more environmentally friendly and saves more energy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
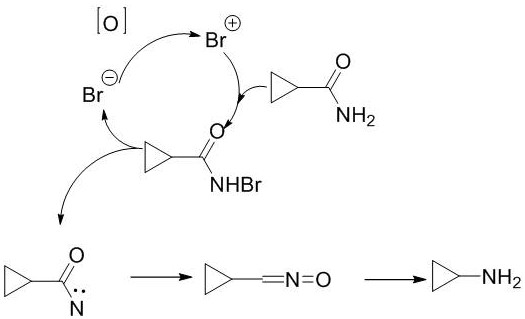
Method for preparing cyclopropylamine through Hofmann rearrangement by using hydrogen peroxide
PendingCN114702391AMolecular sieve catalystsPreparation by rearrangement reactionsPtru catalystPropylamine
The invention discloses a method for preparing cyclopropylamine through Hofmann rearrangement by using hydrogen peroxide, sodium bromide and cyclopropanamide as raw materials. The preparation method comprises the following specific steps: dissolving cyclopropanamide and sodium bromide in water in a low-temperature environment, adding a catalyst, hydrogen peroxide and liquid caustic soda for reaction, then heating for decarboxylation, and distilling to obtain the product. The problem of use of chlorine, liquid bromine and other reagents harmful to the environment in the prior art is solved, mother liquor can be recycled and reused, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Process for manufacturing paper and board having improved retention and drainage properties
ActiveUS8999112B2Heavy equipmentSimple in-line or tangential dilutionNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperFiberCardboard
Owner:S P C M SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
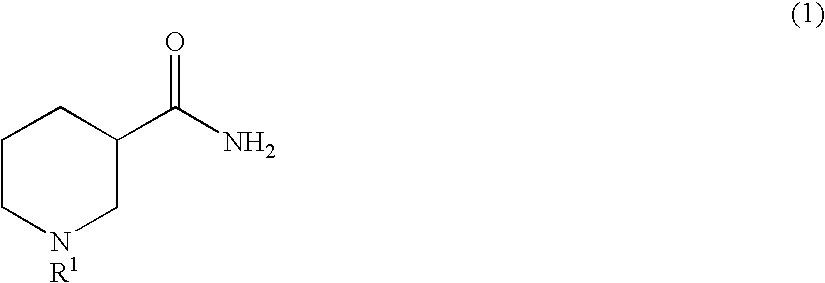
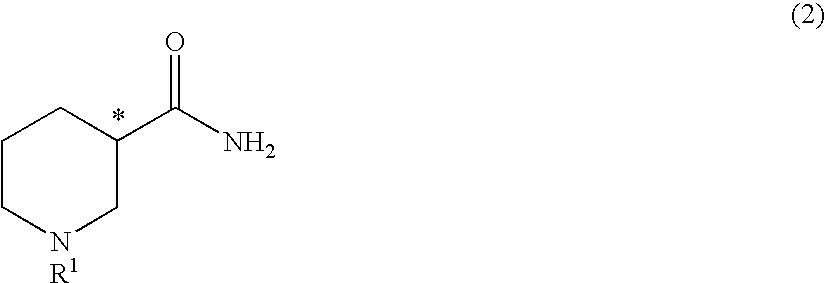




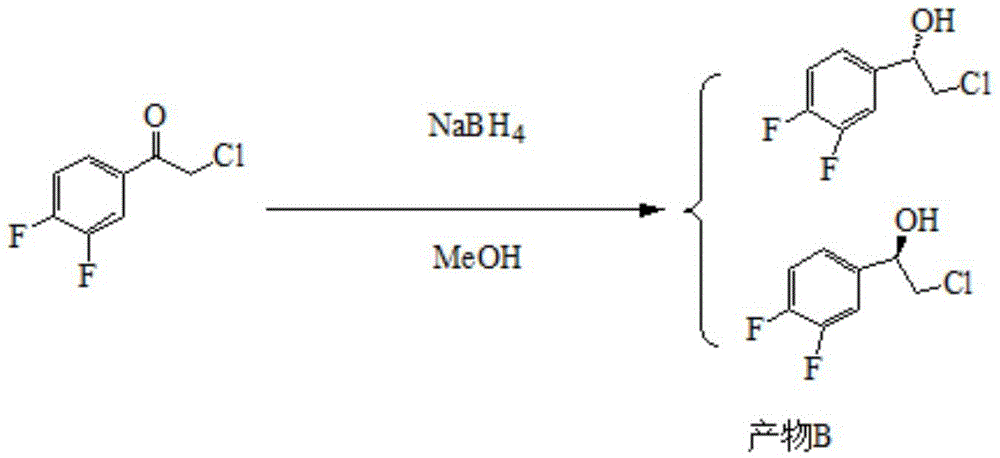
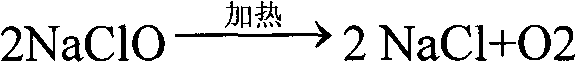

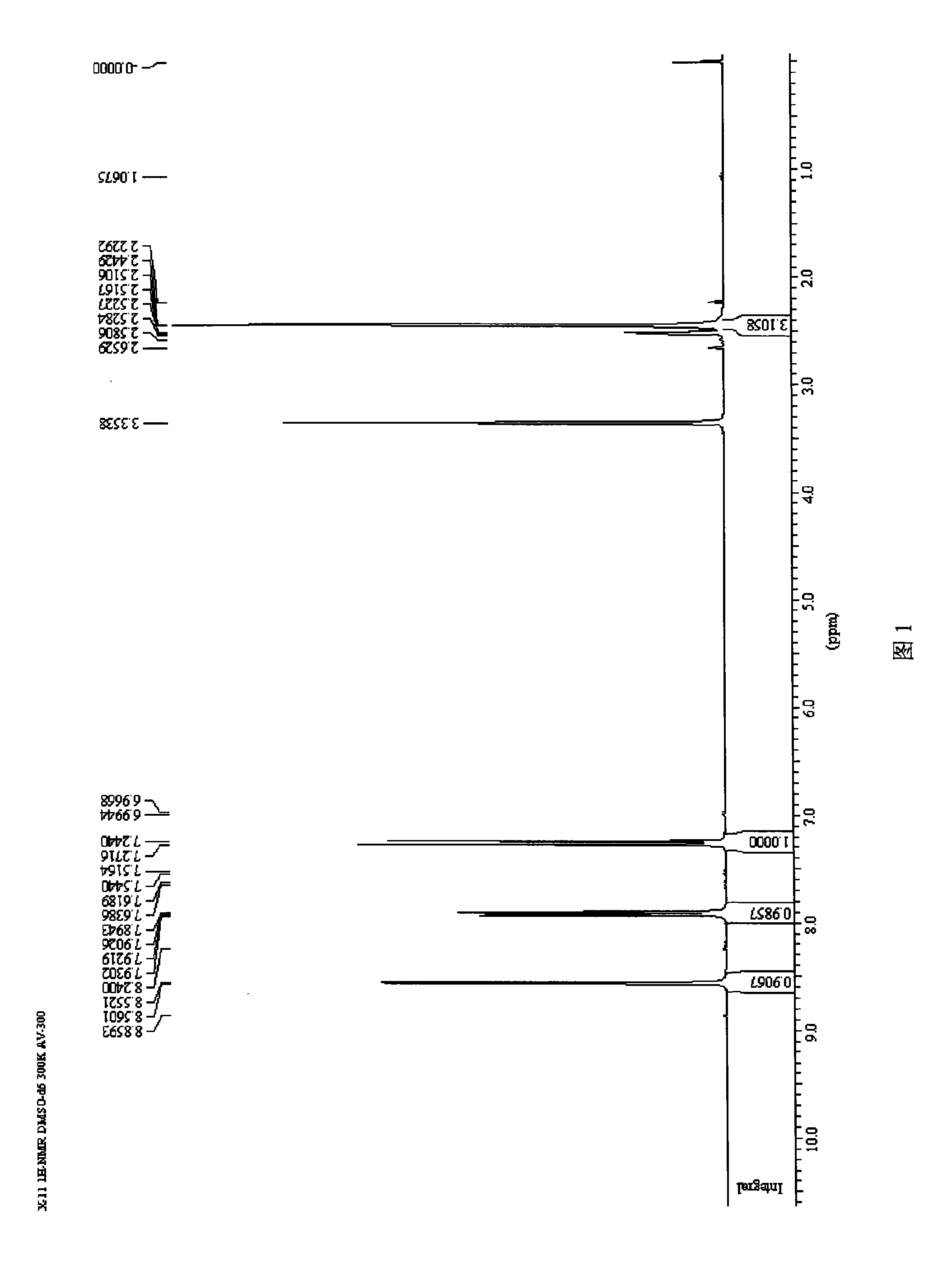
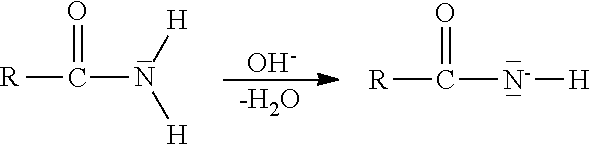
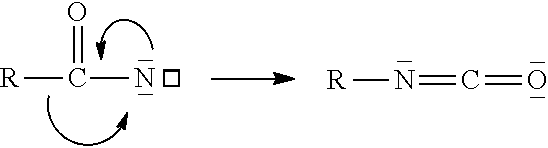
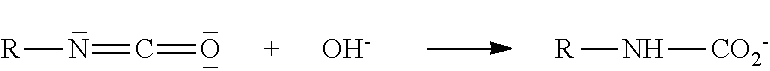


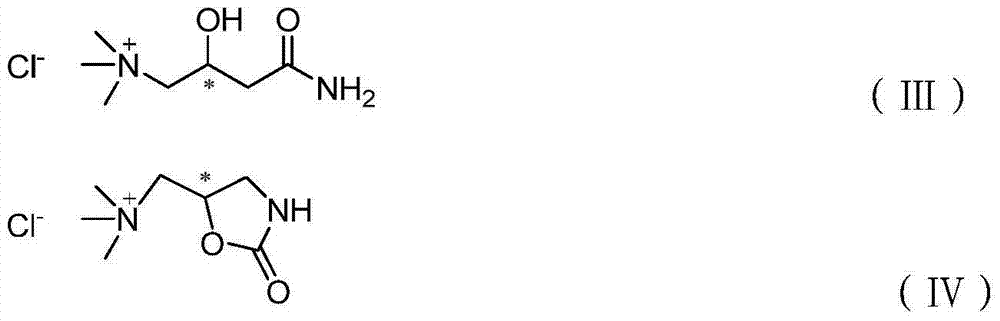
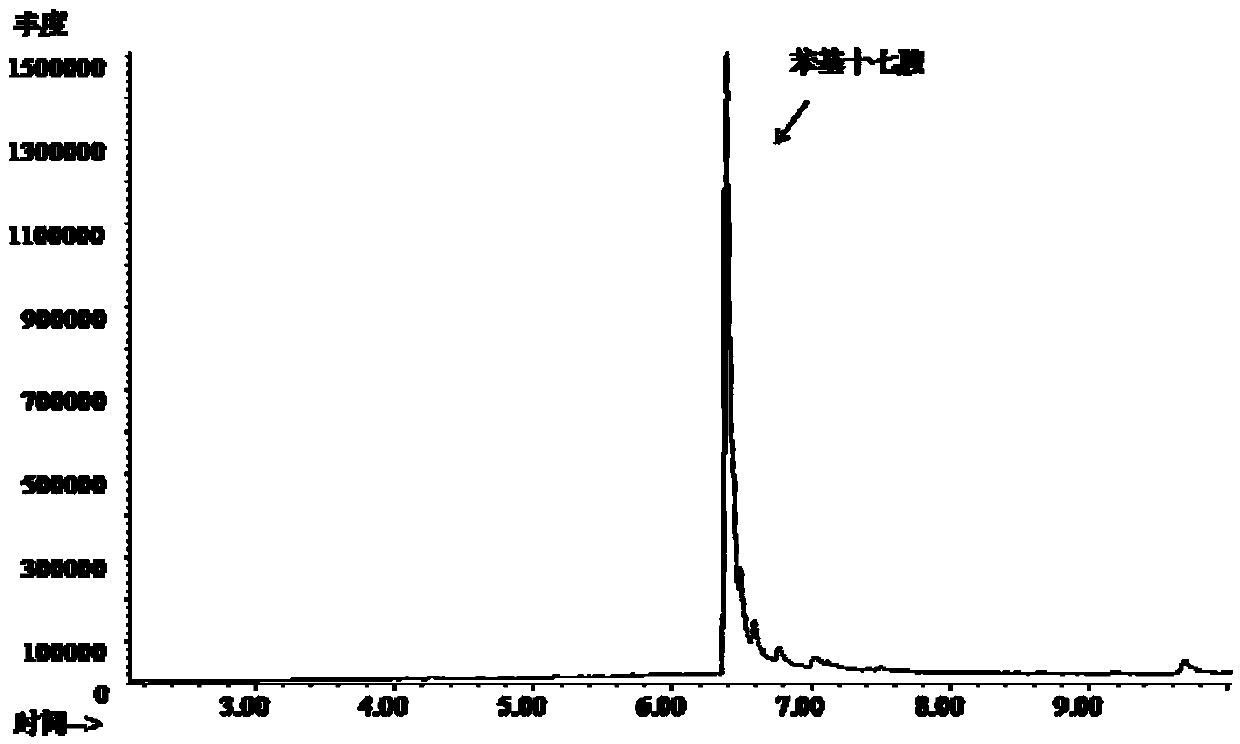
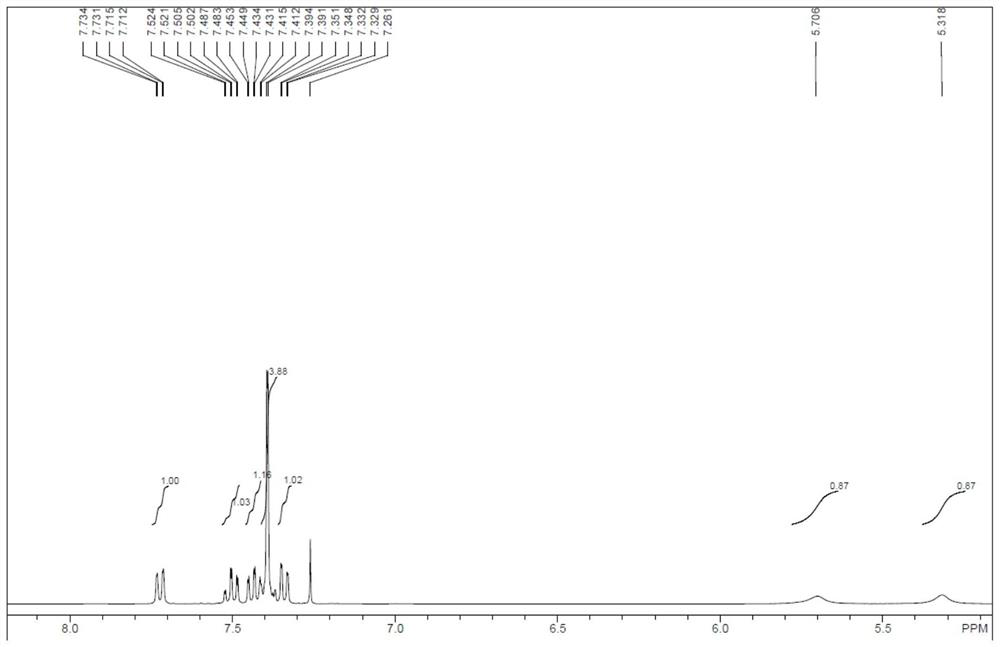
![Synthesis method of 2,6-dichloropyridine [3,4-B] pyrazine Synthesis method of 2,6-dichloropyridine [3,4-B] pyrazine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a9e4465f-0c0d-4e76-8974-46c7a530b682/BDA0001204298250000011.png)
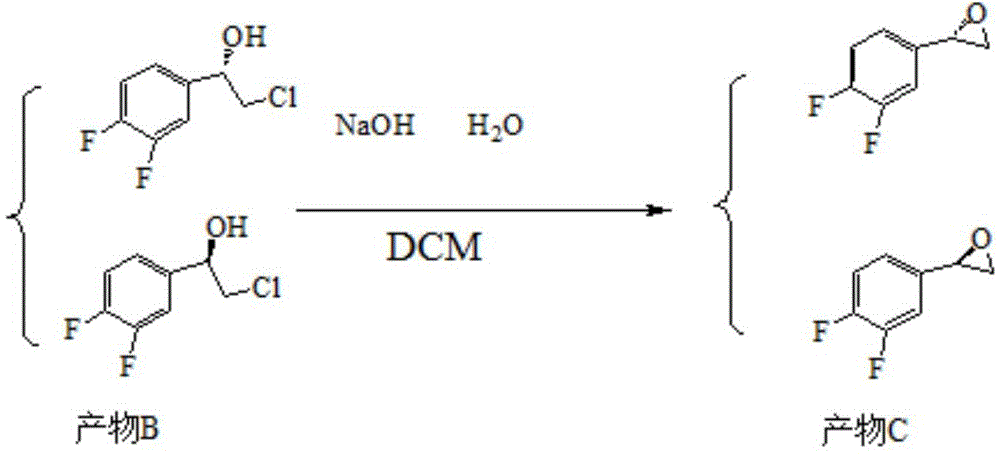
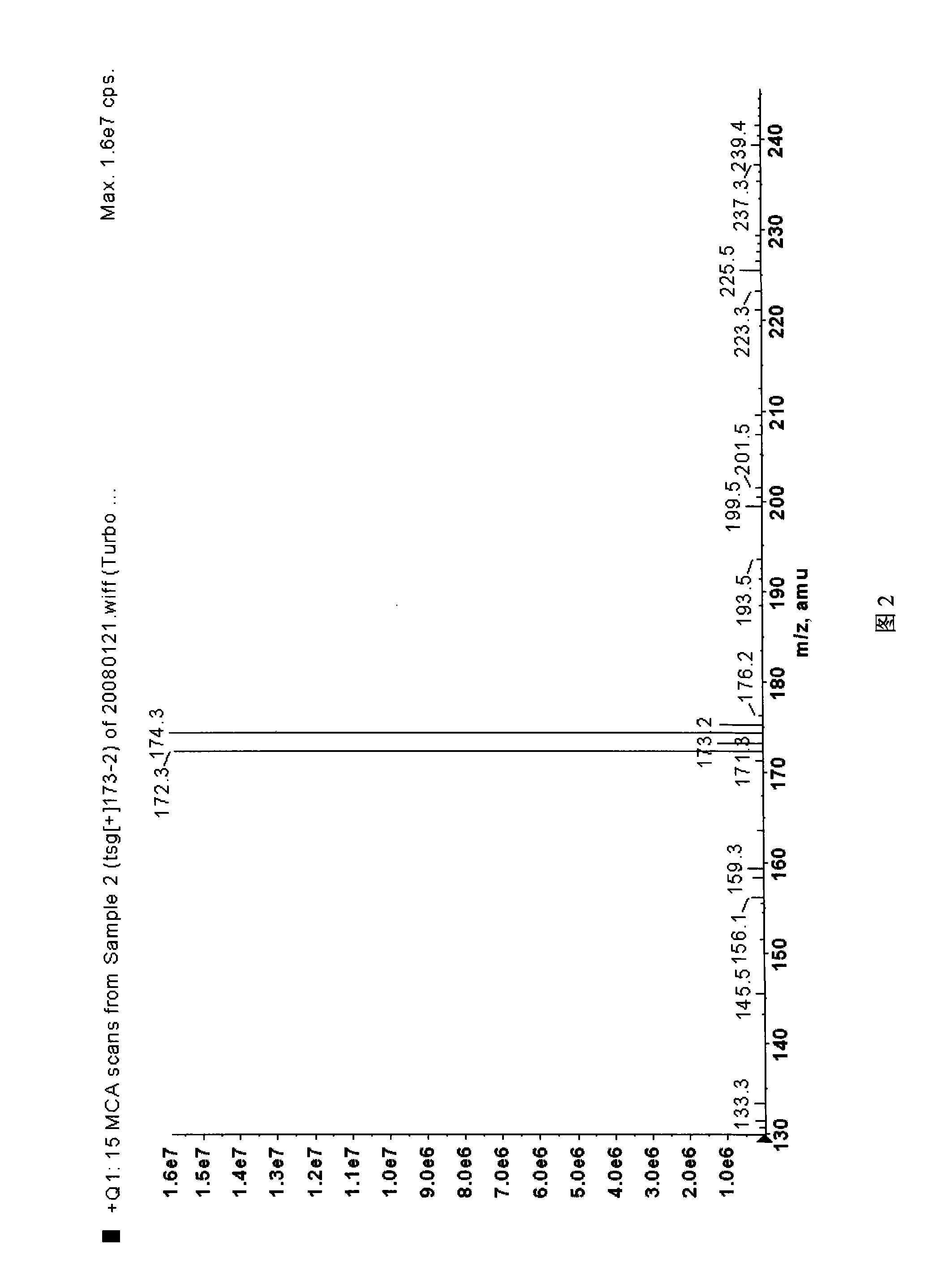
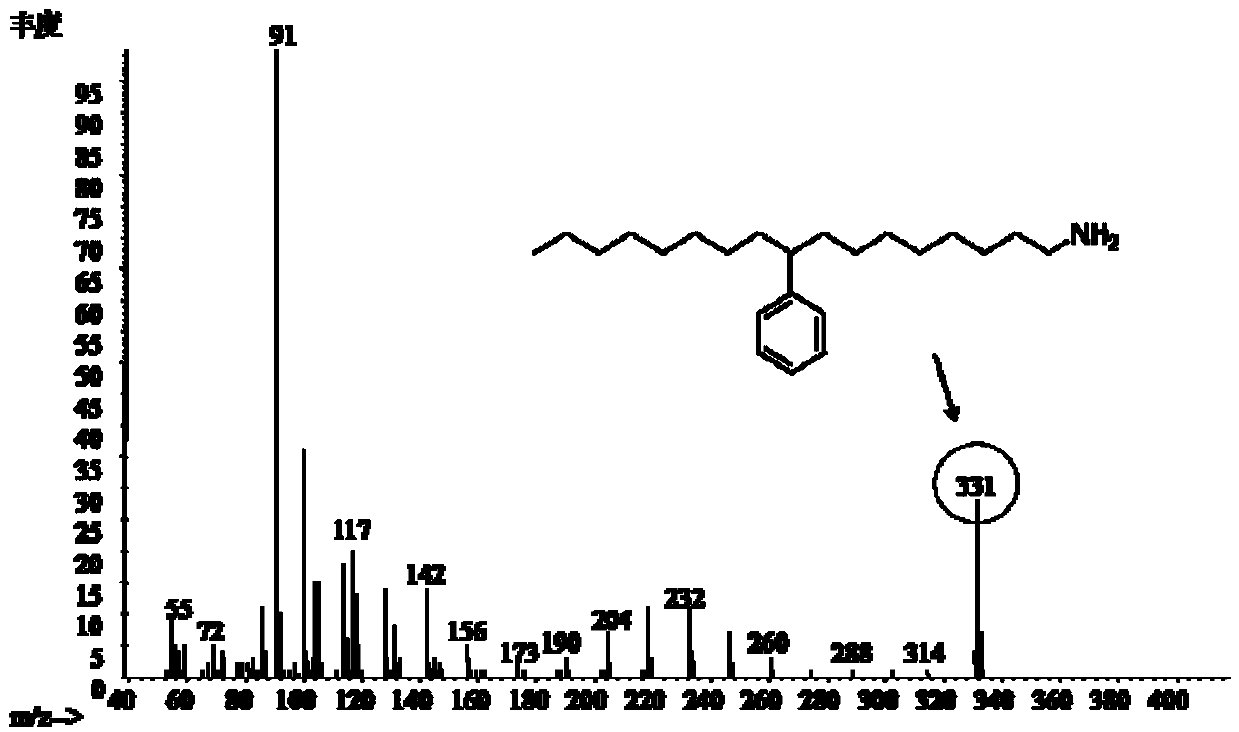
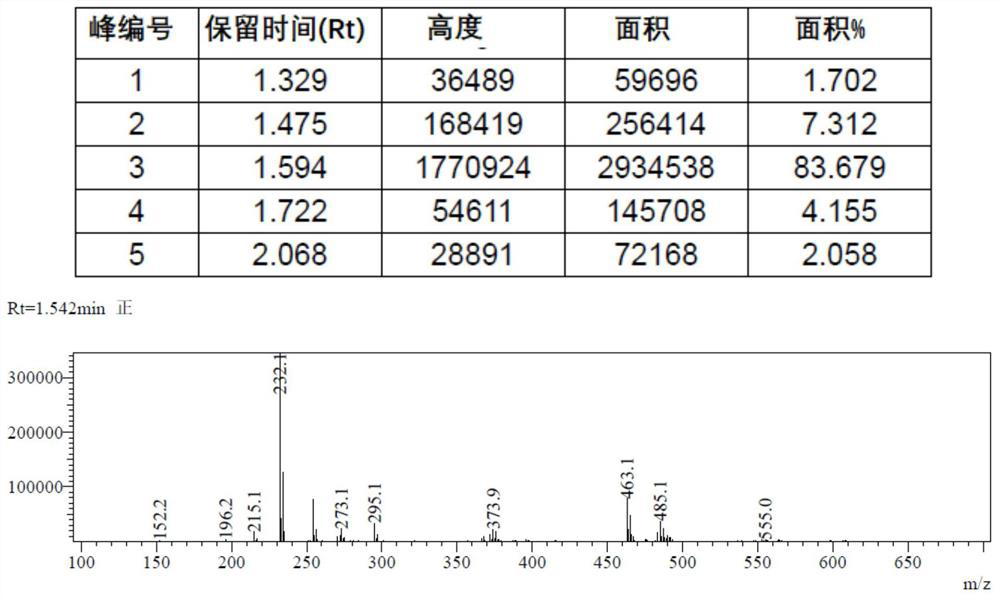
![Synthesis method of 2,6-dichloropyridine [3,4-B] pyrazine Synthesis method of 2,6-dichloropyridine [3,4-B] pyrazine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a9e4465f-0c0d-4e76-8974-46c7a530b682/BDA0001204298250000012.png)
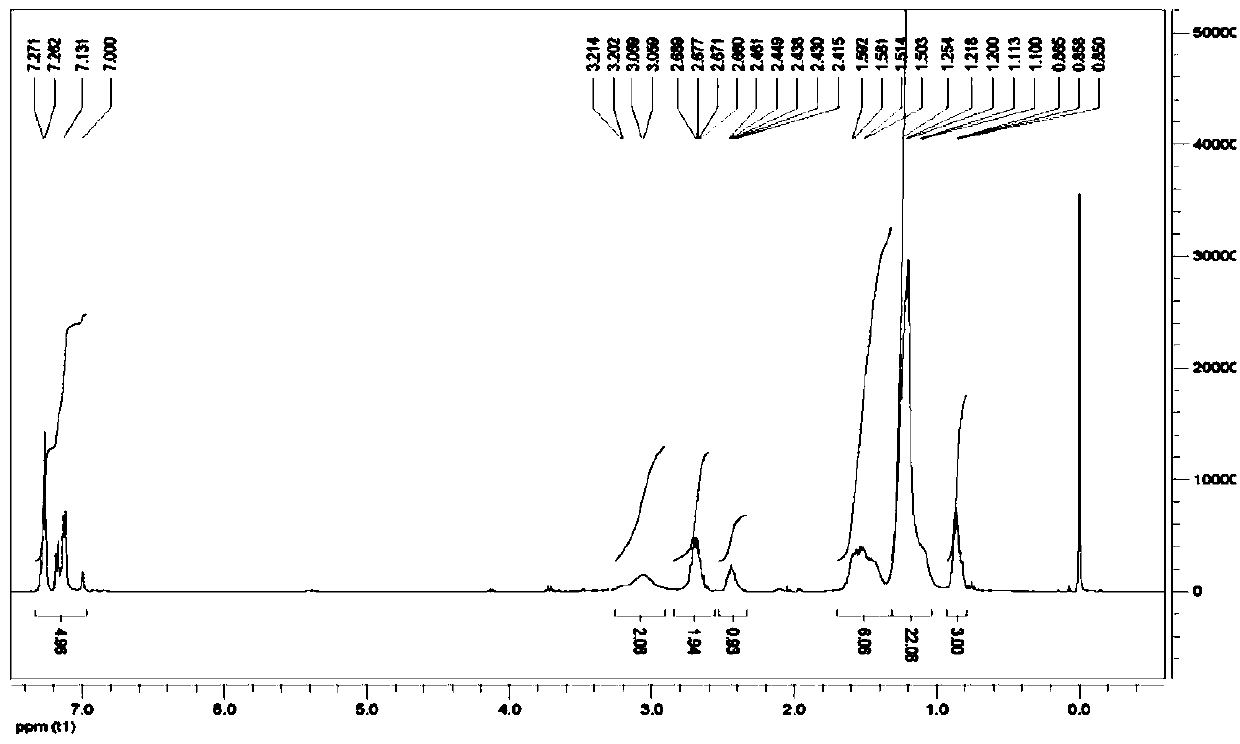
![Synthesis method of 2,6-dichloropyridine [3,4-B] pyrazine Synthesis method of 2,6-dichloropyridine [3,4-B] pyrazine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a9e4465f-0c0d-4e76-8974-46c7a530b682/BDA0001204298250000021.png)